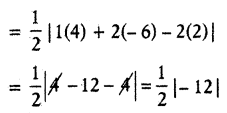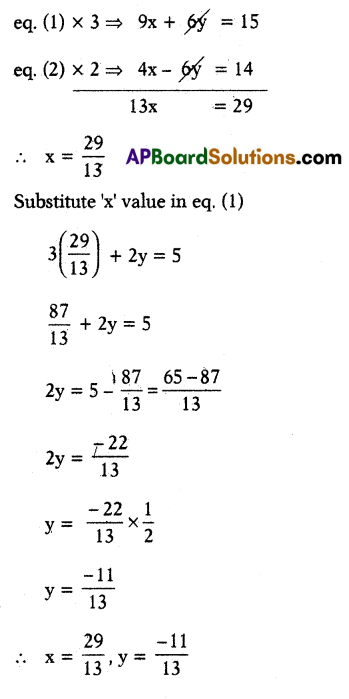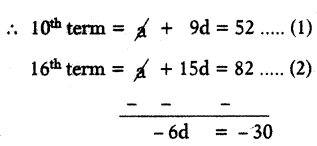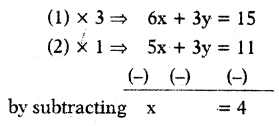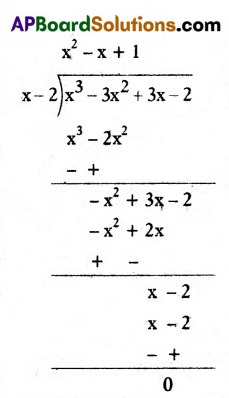The strategic use of TS 10th Class Maths Model Papers Set 1 can significantly enhance a student’s problem-solving skills.
TS SSC Maths Model Paper Set 1 with Solutions
Time: 3 Hours
Maximum Marks: 80
General Instructions:
- Answer all the questions under Part-A on a separate answer book.
- Write the answers to the questions under Part – B on the question paper itself and attach it to the answer book of Part – A.
Part – A (60 Marks)
Section – I (6 × 2 = 12 Marks)
Note :
- Answer ALL the following questions.
- Each question carries 2 marks.
Question 1.
Ramu says, “If log10 x = 0, value of x = 0″. Do you agree with him ? Give reason.
Solution:
log10x = 0 [∵ logaN = x ⇒ ax = N]
100 = x
x = 1 & x ≠ 0
∴ I don’t agree with Ramu.
Question 2.
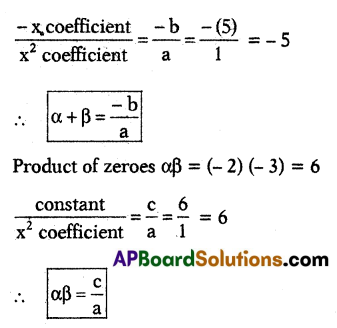
-3, 0 and 2 are the zeroes of the polynomial p(x) = x3 + (a – 1)x2 + bx + c, find a and c.
Solution:
Given solution compare with
ax3 + bx2 + cx + d
Given equation p(x) = x3 + (a – 1) x2 + bx + c.
Given roots -3, 0, 2
Sum of the roots ⇒ α + β + γ = \(\frac{-b}{a}\)
-3 + 0 + 2 = \(\frac{-(a-1)}{1}\)
– 1 = – a + 1 ⇒ – 1 – 1 = -a
∴ a = 2
product of the roots αβγ = \(\frac{-d}{a}\)
(-3)(0)(2) = \(\frac{-c}{1}\) ⇒ c = 0
∴ a = 2 and c = 0

Question 3.
\(\frac{1}{4}\), \(\frac{1}{16}\), \(\frac{1}{64}\), \(\frac{1}{256}\), …………….
are in G.P. justify
Solution:
To justify \(\frac{1}{4}\), \(\frac{1}{16}\), \(\frac{1}{64}\), \(\frac{1}{256}\), ……………. is a G.P
We need to show the ratio of any two successive terms is equal.
Now the common ratio = r1 = \(\frac{1}{16}\) + \(\frac{1}{4}\) + \(\frac{1}{4}\)
r2 = \(\frac{1}{64}\) + \(\frac{1}{16}\) + \(\frac{1}{4}\) ⇒ r1 = r2
Hence it is a G.E
Question 4.
What can you say about
cot 0° = \(\frac{1}{\tan 0^{\circ}}\). Is it defined ? Why ?
Solution:
tan 0° = 0
cot 0° = \(\frac{1}{\tan 0^{\circ}}\) = \(\frac{1}{0}\) = undefined,
Reason:
Division by ‘0’ is not allowed, hence \(\frac{1}{0}\) is indeterminate.
Question 5.
Write two examples for equally likely events.
Answer:
Example 1 : Tossing a coin
Head and tails have equal chances.
Example 2 : Rolling a dice.
All faces have equal chances.
Question 6.
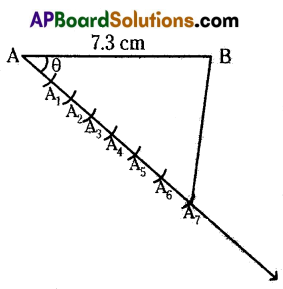
Draw a line segment of length 7.3 cm and divide in the ratio 3 : 4
Answer:

Section – II (6 × 3 = 18 Marks)
Note :
- Answer ALL the following questions.
- Each question carries 3 marks.
Question 7.
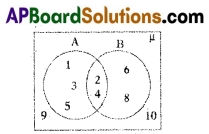
If A = {x : x is a factor of 12} and
B = {x : x is a factor of 6}, then find A∪B and A∩B.
Solution:
Given A = {x : x is a factor of 12}
= {1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 12}
B = {x : x is a factor of 6}
= {1, 2, 3, 6}
A∪B = {1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 12} ∪ {1, 2, 3, 6}
= {1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 12} ;
A∩B = {1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 12} ∩ {1, 2, 3, 6} = {1, 2, 3, 6}
Question 8.
For what value of’m1 in the following, mx + 4y = 10 and 9x + 12y = 30 system of equations will have no solution ? Why ?
Solution:
Given equations have no solutions. They have no solution mean they are parallel.
Given equations compare with
a1x + b1y + c1 = 0 and a2x + b2y + c2 = 0 are parallel
If \(\frac{a_1}{a_2}=\frac{b_1}{b_2} \neq \frac{c_1}{c_2}\) here given
a1 = m, b1 = 4, c1 = -10
a2 = 9, b2 = 12, c2 = -30
\(\frac{\mathrm{a}_1}{\mathrm{a}_2}=\frac{\mathrm{b}_1}{\mathrm{~b}_2}\)
⇒ \(\frac{\mathrm{m}}{9}=\frac{4}{12}\)⇒ m = 3
∴ If m = 3 then the above system will have no solution.
Question 9.
In a flower garden, there are 23 plants in the first row, 21 plants in the sec¬ond row, 19 plants in the third row and so on. If there are 10 rows in that flower garden, then find the total num- her of plants in the last row with the help of the formula
tn = a + (n – 1)d.
Solution:
Number of plants in the 1st row = 23
Number of plants in the 2nd row = 21
Number of plants in the 3rd row = 19 and so on.
The progression is 23, 21, 19, ………….. .
Here common difference is same so the series is an A.P
Here a = 23, d = 21 – 23 = -2. n = 10
nthterm of an A.P in tn = a + (n – 1)d
t10 = 23 + (10 – 1) (-2)
= 23 + 9(-2)
= 23 – 18 = 5 .
Number of plants in the last row is 5.
Question 10.
A box contains 4 red balls, 5 green balls and P white halls. If the probability of randomly picked ball from the box to be a red ball is \(\frac{1}{3}\), then find the number of white balls.
Solution:
P(E) = \(\frac{\text { No. of outcomes }}{\text { Sample Space }}\)
\(\frac{1}{3}\) = \(\frac{4}{4+5+P}\)
4 + 5 + P= 12
⇒ P = 3
∴ Number of white balls = 3

Question 11.
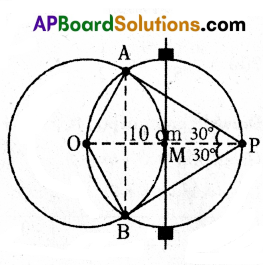
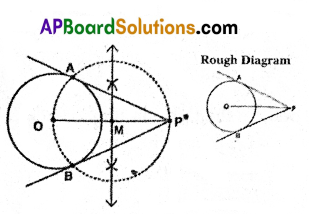
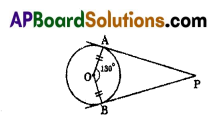
In the given figure AB, AC and PQ are tangents to a circle and AB = 6 cm. Find the perimeter of ΔAPQ.
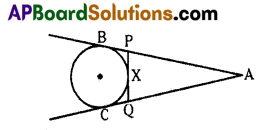
Solution:
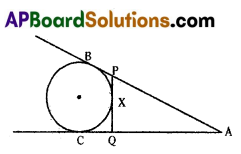
We know that tangents drawn from an external point to a circle are equal in length.
∴ AB = AC
AP + PB = AQ + QC
AP + PX = AQ + QX (∵ PX = BP and QX = QC)
AP + PX = AQ + QX = 6 cm
Now, Perimeter of
ΔAPQ = AP + PQ + AQ
= (AP + PX) + (QX + AQ)
= 6 + 6
= 12 cm
∴ Perimeter of ΔAPQ = 12 cm
Question 12.
If the ratio of areas of two equilateral triangles is 25 : 36, then find the ratio of heights of the triangles.
Solution:
For similar triangles
Ratio of area = Ratio of sides
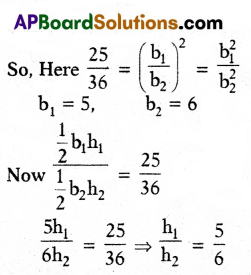
∴ h1 : h2 = 5 : 6
∴ The ratio of heights of the triangles = 5 : 6
Section – III (6 × 5 = 30 Marks)
Question 13.
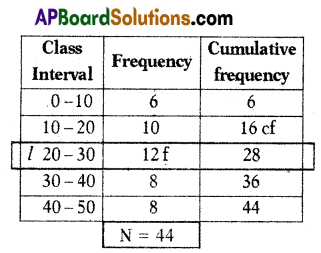
A) If the mean of the following frequency distribution is 50, then find the value of k.

Solution:
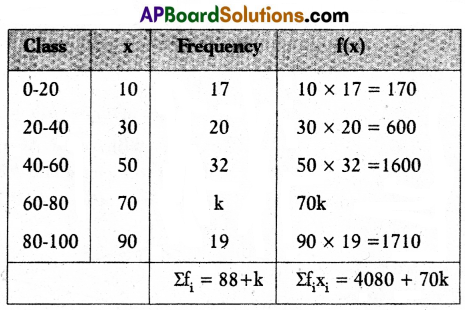
Mean = \(\frac{\Sigma \mathrm{f}_{\mathrm{i}} \mathrm{x}_{\mathrm{i}}}{\Sigma \mathrm{f}_{\mathrm{i}}}\)
50 = \(\frac{4080+70 \mathrm{k}}{88+\mathrm{k}}\)
50(88 + k) =4080 + 70k
4400 + 50k = 4080 + 70k
4400 – 4080 = 70k – 50k
320 = 20k
\(\frac{320}{20}\) = k ⇒ k = 16
(OR)
B) Find the area of the segment shaded in the figure in which PQ =12 cm, PR = 5 cm and QR is the diameter of the circle with centre ‘O’. (Take π = \(\frac{22}{7}[latex] )
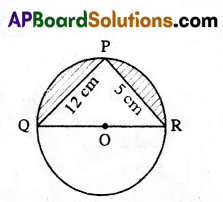
Solution:
To find the area of the segment shaded in the given figure.
Here ‘PQ’ = 12 cm; ‘PR’ = 5 cm; ‘QR’ is diameter
Now PQOR is a semicircle
then angle in a semicircle is 90°
then ∠QPR = 90°
∴ ΔPQR is a right angled triangle
∴ Area of ΔPQR = [latex]\frac{1}{2}\)bh
= \(\frac{1}{2}\) × PQ × PR
= \(\frac{1}{2}\) × 12 × 5 =30 cm2 ………….. (1)
Now the area of shaded part = area of semicircle – area of ΔPQR
= \(\frac{1}{2}\) πr2 – 30 cm2 ……………. (2)
In ΔPQR, QR2 = PQ2 + PR2 (from Pythagoras theorem)
QR2 = 122 + 52
= 144 + 25
= 169 = 132
∴ QR = 13 then
Radius of the circle (r) = QO = \(\frac{\mathrm{QR}}{2}\) = \(\frac{13}{2}\) = 6.5 cm
then area of semicircle
\(\frac{1}{2}\) πr2
= \(\frac{1}{2}\) × \(\frac{22}{7}\) × \(\frac{13}{2}\) × \(\frac{13}{2}\) \(\frac{1}{2}\)
= 66.39 cm2 – (3)
Now putting the values of (1) and (3) in (2) we get
Area of shaded part = (66.39 – 30) = 36.39 cm2.

Question 14.
A) Use division algorithm to show that the square of any positive integer is of the form 5m or 5m + 1 or 5m + 4, where ‘m’ is a whole number.
Solution:
a = bq + r, 0 ≤ r < b
b = 5 so r = 0, 1, 2, 3, 4
Then ‘a’ can be of the forms
5q + 0, 5q + 1, 5q + 2, 5q + 3, 5q + 4
Case (i) When a = 5q
a2 = (5q)2 = 5 (5q2) = 5m
where m = 5q2 ∈ W.
Case (ii) When a = 5q + 1
a2 = (5q + 1)2
= 25q2 + 10q + 1
= 5 (5q2 + 2q) + 1
= 5m + 1 where m = 5q2 + 2q ∈ W Similarly,
Case (iii) a2 = (5q + 2)2 = 5m + 4
Case (iv) a2 = (5q + 3)2 = 5m + 4
Case (v) a2 = (5q + 4)2= 5m + 1
So the square of any positive integer is of the form 5m or 5m + 1 or 5m + 4 where n e W.
(OR)
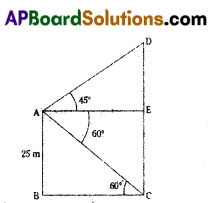
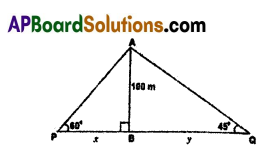
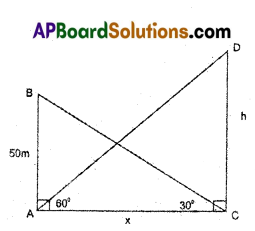
B) Two poles of equal heights are standing opposite to each other on either side of the road which is 80 m wide. From a point between them on the road, the angles of elevation of top of the poles are 60° and 30°. Find the height of poles.
Solution:
As shown in the figure
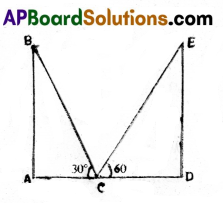
AD = width of road = 80 cm.
AB, DE are two poles
AB = DE (∵ they have equal heights)
‘C’ is a point on road.
∠ACB = 30°, ∠DCE = 60°
Then in ΔACB
tan C = \(\frac{\mathrm{AB}}{\mathrm{AC}}\)
⇒ tan 30 = \(\frac{\mathrm{AB}}{\mathrm{AC}}\)
⇒ \(\frac{1}{\sqrt{3}}=\frac{A B}{A C}\) ⇒ AC = AB√3 ……… (1)
In ΔCDE
tan C = \(\frac{\mathrm{DE}}{\mathrm{CD}}\) ⇒ tan 60 = \(\frac{\mathrm{DE}}{\mathrm{CD}}\)
√3 = \(\frac{\mathrm{DE}}{\mathrm{CD}}\)
⇒ CD = \(\frac{\mathrm{DE}}{\sqrt{3}}\) ………… (2)
but AC + CD = AD
AB√3 + \(\frac{\mathrm{DE}}{\sqrt{3}}\) = 80
But DE = AB
⇒ AB√3 + \(\frac{\mathrm{AB}}{\sqrt{3}}\) = 80
⇒ \(\frac{3 \mathrm{AB}+\mathrm{AB}}{\sqrt{3}}\) = 80
⇒ 4AB = 80√3
⇒ AB = \(\frac{80 \sqrt{3}}{4}\) = 20√3
So height of the pole = 20√3 m.
Question 15.
A) On dividing x3 – 3x2 + x + 2 by a polynomial g(x), the quotient and remainder were x – 2 and – 2x + 4, respectively. Findg(x).
Solution:
Given, p(x) = x3 – 3x2 + x + 2
q(x) = x – 2 and
r(x) = – 2x + 4
By division algorithm, we know that Dividend = Divisor × Quotient + Remainder
p(x) = q(x) × g(x) + r(x)
Therefore,
x3 – 3x2 + x + 2
= (x – 2) x g(x) + (- 2x + 4)
⇒ x3 – 3x2 + x + 2 + 2x – 4
= (x – 2) × g(x)
⇒ g(x) = \(\frac{x^3-3 x^2+3 x-2}{x-2}\)
On dividing x3 – 3x2 + 3x – 2 by x – 2, we get
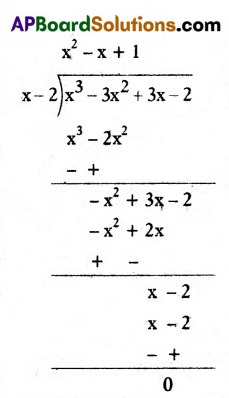
First term of g(x) = \(\frac{x^3}{x}\) = x2
Second term of g(x) = \(\frac{-x^2}{x}\) = -x
Third term of g(x) = \(\frac{x}{x}\) = 1
Hence, g(x) = x2 – x +1.
(OR)
B) From a pack of 52 playing cards, Jacks, Queens, Kings and Aces of red colour are removed. From the remaining, a card is drawn at random. Find the probability that the card drawn is (i) a black queen, (ii) a red card. :
Solution:
Probability of black queen = \(\frac{1}{26}\)
Probability of red card = \(\frac{1}{2}\)
n(S) = 52
i) Probability of black queen n(a) = 2
p(a) = \(\frac{\mathrm{n}(\mathrm{a})}{\mathrm{n}(\mathrm{S})}\) = \(\frac{2}{52}\) = \(\frac{1}{26}\)
ii) Probability of a red card n(b) = 26
P(b) = \(\frac{\mathrm{n}(\mathrm{b})}{\mathrm{n}(\mathrm{S})}\) = \(\frac{26}{52}\) = \(\frac{1}{2}\)

Question 16.
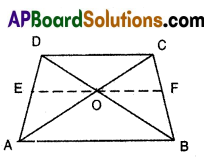
A) ABCD is a trapezium in which AB||DC and its diagonals intersect each other at point ‘O’. Show that
\(\frac{A O}{B O}=\frac{C O}{D O}\).
Solution:
Given: In trapezium ABCD, AB// CD.
Diagonals AC, BD intersect at 0.
R.T.P : \(\frac{A O}{B O}=\frac{C O}{D O}\)
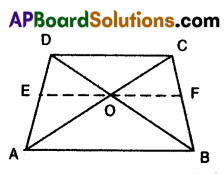
Construction: Draw a line EF passing through the point ‘O’ and parallel to CD and AB.
Proof: In ΔACD.E0//CD
∴ \(\frac{A O}{C O}=\frac{A E}{D E}\) ……….. (1)
[∵ line drawn parallel to one side of a triangle divides other two sides in the same ratio by Basic proportionality theorem] ,
In ΔABD, EO//AB
Hence, \(\frac{D E}{A E}=\frac{D O}{B O}\)
[∵ Basic proportionality theorem]
\(\frac{B O}{D O}=\frac{A E}{E D}\) ………… (2) [∵ Invertendo]
From (1) and (2)
\(\frac{A O}{C O}=\frac{B O}{D O}\)
\(\frac{A O}{B O}=\frac{C O}{D O}\) [∵ Alternendo]
(OR)
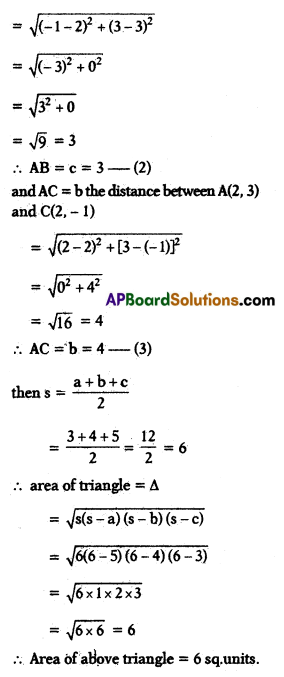
B) Find the area of the triangle formed by the points (2, 3), (-1, 3)and (2, -1) using Heron’s formula.
Solution:
To find the area of the triangle formed by (2, 3) (- 1, 3) and (2, – 1) using Heron’s formula.
Let the co-ordinates of A = (2, 3) ; B ='(- 1, 3); C = (2, – 1) then the sides of ΔABC are represented by as follows
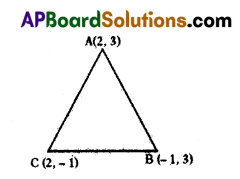
AB = c, BC = a, CA = b
then the formula of the triangle usingHeron’s formula
= \(\sqrt{s(s-a)(s-b)(s-c)}\)
where s = \(\frac{a+b+c}{2}\)
Now, we find the sides of ΔABC, using the formula \(\sqrt{\left(x_2-x_1\right)^2+\left(y_2-y_1\right)^2}\)
∴ CB = a = distance between the points, (2, – 1) and (- 1, 3)
= \(\sqrt{(2-(-1))^2+(-1-3)^2}\)
= \(\sqrt{3^2+(-4)^2}\)
= \(\sqrt{3^2+4^2}\)
= \(\sqrt{9+16}\)
= \(\sqrt{25}\)
⇒ CB = a = 5 …….. (1)
Question 17.
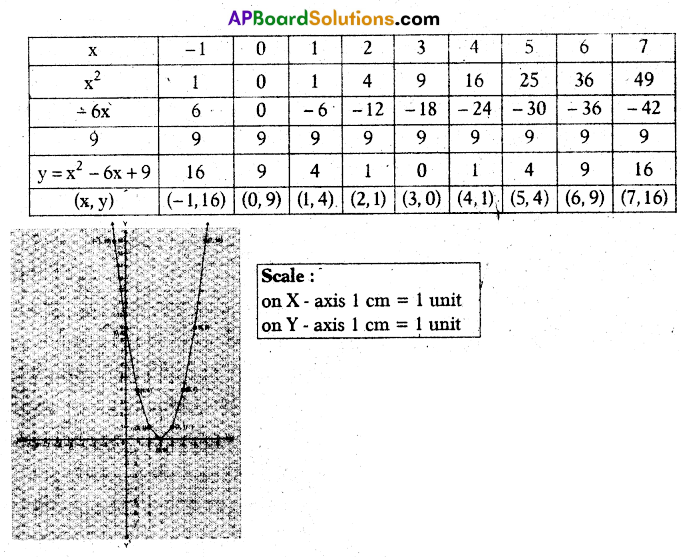
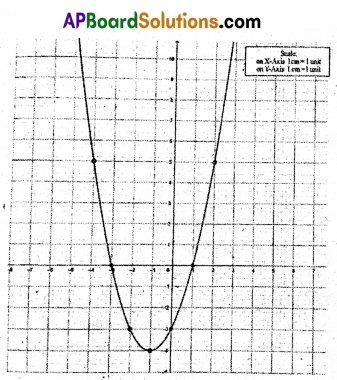
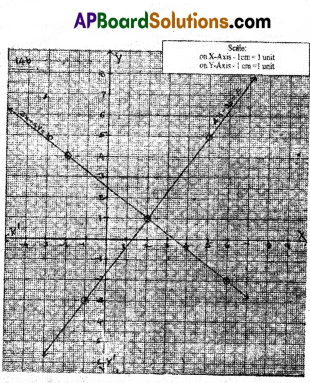
A) Draw the graph of p(x) = x2 – 2x – 8 and find the zeroes/of the polynomial from it.
Solution:
p(x) = x2 – 2x – 8
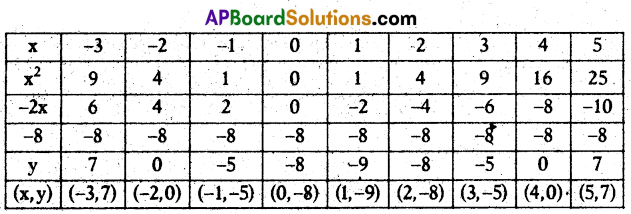
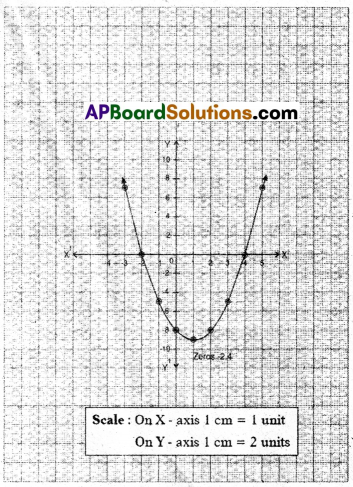
Zeroes of the given polynomial are -2, 4.
(OR)
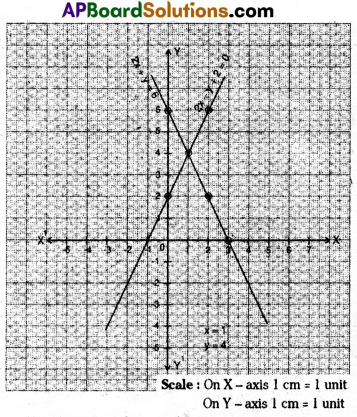
B) Show that the following pair of equations are consistent and solve them graphically,
x + 3y = 6,
2x – 3y = 12
Solution:
x + 3y = 6
| x |
0 |
6 |
3 |
| y |
2 |
0 |
1 |
| (x, y) |
(0, 2) |
(6, 0) |
(3, 1) |
2x – 3y = 12
| x |
0 |
6 |
3 |
| y |
-4 |
0 |
-2 |
| (x, y) |
(0, -4) |
(6, 0) |
(3, -2) |
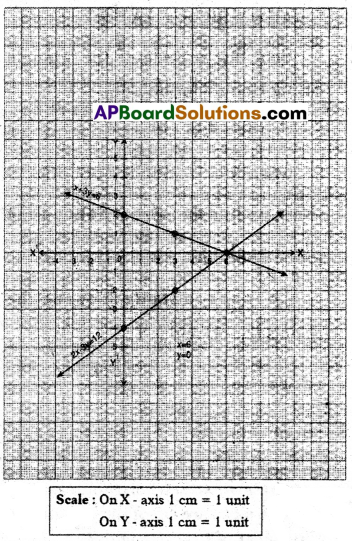
Point of intersection is (6, 0)
Since the two lines are intersecting at one point, we can say that they are Consistent.
∴ x = 6, y = 0

Question 18.
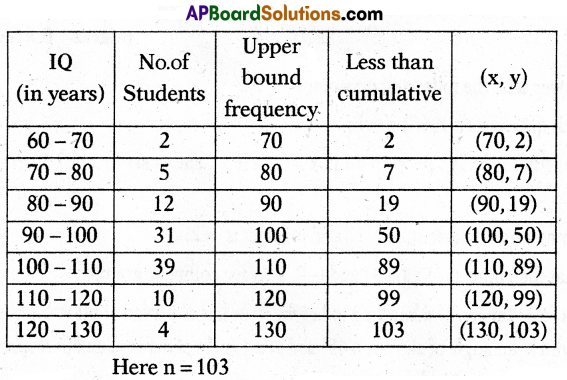
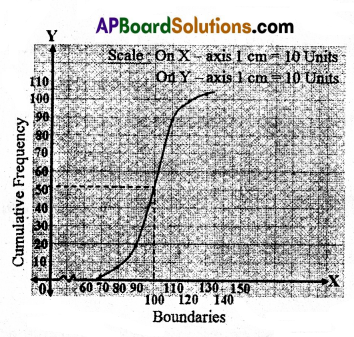
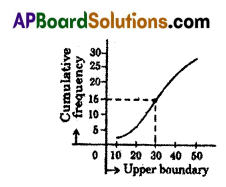
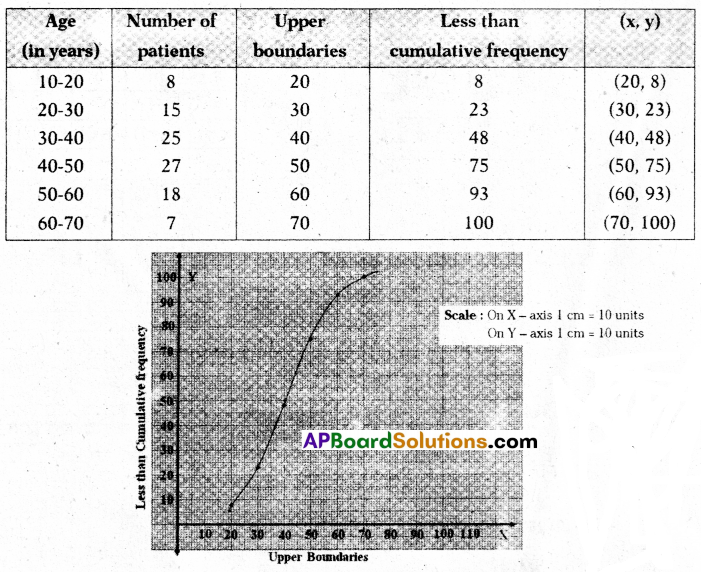
A)The following table shows that ages of the patients admitted in a hospital during a year.

Draw a less than Ogive curve for the above data.
Solution:
OR
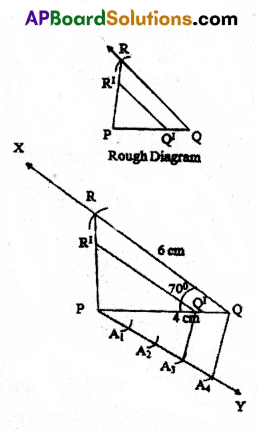
B) Construct a triangle ABC in which AB = 5 cm, BC = 7 cm and ∠ABC = 50°, then construct a triangle similar to it, whose sides are 4/5 of the corresponding sides of first triangle.
Solution:
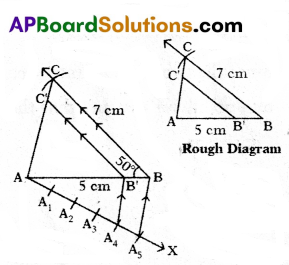
Steps of Construction:
- Draw a triangle ABC with AB = 5 cm, BC = 7 cm and ∠ABC = 50°.
- Draw a ray \(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{AX}}\) such that ∠BAX is an acute angle.
- Draw A1, A2, A3, A4, A5 arcs on \(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{AX}}\) such that AA1 = A1A2 = A4A5.
- Join A5 and B.
- Draw a parallel line to A5 B through A4 to meet AB at B!.
- Draw a parallel line to BC through B’ to meet AC at C’.
- ΔAB’C’ is required similar triangle.

Part – B (20 Marks)
Note :
- Answer all the questions.
- Each question carries 1 mark.
- Answers are to be written in the Question paper only.
- Marks will not be awarded in any case of over writing, rewriting or erased answers.
Note : Write the capital letters (A, B, C, D) showing the correct answer for die following questions in the brackets provided against them. (Marks: 20 × 1 = 20)
Question 1.
If a, b, care in A.P., then b =
A) \(\frac{a+c}{2}\)
B) a + c
C) \(\sqrt{\mathrm{ac}}\)
D) ac
Answer:
A) \(\frac{a+c}{2}\)
Question 2.
If the number of subsets of a given set is 32, then the number of elements in the set will be
A) 2
B) 4
C) 5
D) 3
Answer:
C) 5
Question 3.
The distance of (3, 4) from origin is
A) 3
B) 4
C) 5
D) 7
Answer:
C) 5
Question 4.
The sum of the roots of 6x2 = 1 is
A) 0
B) \(\frac{1}{6}\)
C) –\(\frac{1}{6}\)
D) 6
Answer:
A) 0
Question 5.
If the polynomial p(x) = x4 – 2x3 + x2 – 1 is divided by (x +1), then the degree of quotient polynomial.
A) 1
B) 3
C) 4
D) 2
Answer:
B) 3
Question 6.
The sum of a number and reciprocal is \(\frac{17}{4}\), then the number is
A) 3
B) 4
C) 5
D) 17
Answer:
B) 4

Question 7.
If log102 = 0.3010, then log1032 is
A) 5.3010
B) 2.3010
C) 015050
D) 0.3010
Answer:
C) 015050
Question 8.
The point (-2, -2) is in the quadrant.
A) Q1
B) Q2
C) Q3
D) Q4
Answer:
C) Q3
Question 9.
In a G.P., the 5th term is 32 and 7th term is 128, then the common ratio of G.P.
A) 2
B) 5
C) 7
D) 3
Answer:
A) 2
Question 10.
Solution to \(\frac{a^2}{x}-\frac{b^2}{y}\) = 0; \(\frac{\mathbf{a}^2 \mathbf{b}}{x}+\frac{b^2 a}{y}\) = a + b, x ≠ 0, y ≠ 0 is ……………….
A) (-a2, -b2)
B) (a, b2)
C) (a, -b)
D) (a2, b2)
Answer:
D) (a2, b2)
Question 11.
The probability of sure event is
A) 0
B) \(\frac{1}{2}\)
C) 1
D) Undefined
Answer:
C) 1
Question 12.
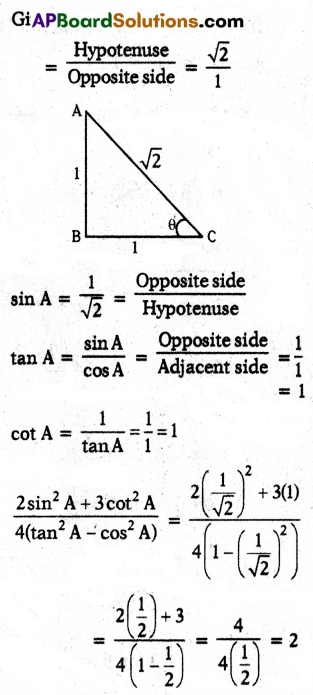
\(\sqrt{1+\sin A} \cdot \sqrt{1-\sin A}\) =
A) sin A
B) 1 – sin2A
C) cos A
D) 1
Answer:
C) cos A

Question 13.
Side of a cube and diameter of a sphere are equal, then the ratio of their volume will be
A) 4 : π
B) 6 : π
C) 3 : π
D) 2 : π
Answer:
B) 6 : π
Question 14.
A dice is thrown once. The probability of getting a prime number is [ ]
A) \(\frac{1}{3}\)
B) \(\frac{1}{2}\)
C) \(\frac{2}{3}\)
D) \(\frac{1}{6}\)
Answer:
B) \(\frac{1}{2}\)
Question 15.
Volumes of two spheres are in the ratio of 8 : 27, the ratio of their surface areas is ……………….
A) 2 : 3
B) 4 : 3
C) 2 : 9
D) 4 : 9
Answer:
D) 4 : 9
Question 16.
Mean of certain number of observations is \(\). If each observation is divided by m(m ≠ 0) and then increased by n, then the mean of new observation is
A) \(\frac{\bar{x}}{n}\) + m
B) \(\overline{\mathbf{x}}+\frac{\mathbf{n}}{\mathrm{m}}\)
C) \(\overline{\mathbf{x}}+\frac{\mathbf{m}}{\mathrm{n}}\)
D) \(\frac{\bar{x}}{m}\) + n
Answer:
D) \(\frac{\bar{x}}{m}\) + n
Question 17.
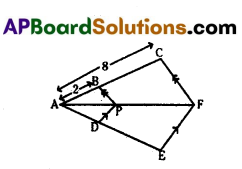
A) \(\frac{1}{3}\)
B) \(\frac{3}{4}\)
C) \(\frac{1}{4}\)
D) \(\frac{2}{3}\)
Answer:
A) \(\frac{1}{3}\)

Question 18.
A ladder 15m long just reaches the top of vertical wall. If the ladder makes an angle of 60° with the wall. Then the height of the wall is
A) 15√3 m
B) \(\frac{15 \sqrt{3}}{2}\) m
C) 7.5 m
D) 15 m
Answer:
B) \(\frac{15 \sqrt{3}}{2}\) m
Question 19.
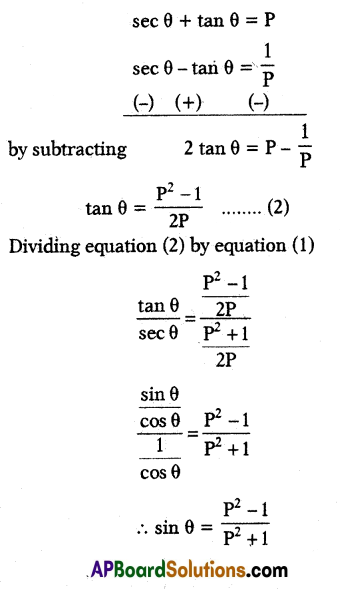
If sec θ + tan θ = x, then sec θ =
A) \(\frac{x^2+1}{x}\)
B) \(\frac{x^2+1}{2 x}\)
C) \(\frac{x^2-1}{2 x}\)
D) \(\frac{x^2-1}{x}\)
Answer:
B) \(\frac{x^2+1}{2 x}\)
Question 20.
At point ’P’ on a circle, PQ is a tangent and ‘O’ is the centre of the circle. If ΔOPQ is an isosceles triangle, then ∠OQP is equal to
A) 90°
B) 30°
C) 45°
D) 60°
Answer:
C) 45°