Students must rely on TS 10th Class Biology Model Papers Set 9 to gauge their understanding of exam patterns.
TS 10th Class Biology Model Paper Set 9 with Solutions
Time: 1 Hour 30 minutes
Maximum Marks: 40
General Instructions:
- Read the question paper carefully and understand.
- Answer the questions under Part – A in the answer sheet provided.
- Part – A contains three sections : section – I, II and III.
- There is an internal choice to the questions under section – III.
- Part – B Answers should be written in the given brackets and attach to the Part – A answer sheet.
- Write the answers following the instructions given in each section.
Part – A (30 Marks)
Section – I (3 × 2 = 6M)
Instructions :
- This section contains 3 very short answer questions. .
- Answer ALL the questions.
- Write answer to each question in 3 to 4 sentences.
- Each question carries 2 marks.
Question 1.
Write the reasons and symptoms of Kwashiorkor disease.
Answer:
- The reason for kwashiorkor disease is deficiency of proteins in diet.
- Very poor muscle development, swollen legs, fluffy face, difficult to eat, diarrhoea, dry skin are the symptoms of kwashiorkor disease.
Question 2.
Which form a continuous network all over the plant ?
Answer:
The stomatal openings lead to a series of spaces between the cells inside the plants which form a continuous network all over the plant.
Question 3.
What is Hypertension ? (Or) What is high blood pressure ?
Answer:
In some people high blood pressure more than the normal blood pressure of 120/80 is present during rest period. Such condition is called Hypertension usually called high B.P.
Section – II (3 × 3 = 9M)
Instructions :
- This section contains 3 short answer questions.
- Answer ALL the questions.
- Write answer to each question in 5 to 6 sentences.
- Each question carries 3 marks.
![]()
Question 4.
What are ganglia ?
Answer:
- Ganglia or neural ganglia are the structures located outside the central nervous system made of concentration of neuron bodies.
- Examples of neural ganglia are the ganglia that concentrate cell bodies of sensory neurons in the dorsal roots of the spinal cord and the ganglia of the myenteric plexus responsible for the peristaltic movements of the digestive tube.
- In the central nervous system the concentrations of neuron bodies called nuclei not ganglia.
Question 5.
If a trait ‘A’ exists in 10% of a population of an asexually reproducing species and a trait ‘B’ exists in 60% of the same population, which trait is likely to have arisen earlier ?
Answer:
- Trait B.
- In asexual reproduction the traits which are present in previous generation are carried over to meet generation with minor variations.
- Therefore the traits present in high percentage have higher chances of persisting earlier.
Question 6.
Write few slogans on increase of regular cycling and walking.
Answer:
- Save energy – Ride on bicycle
- Believe in walk – Increase health
- The one who walks is a lover of environment – Not a vehicle.
- Bicycle is the close friend to environment.
- Use cycle from today for future.
Section – III (3 × 5 = 15M)
Instructions :
- This section contains 3 essay type questions.
- Answer ALL the questions.
- There is an internal choice for each question.
- Write answer to each question in 8 to 10 sentences.
- Each question carries 5 marks.
Question 7.
Write the different steps in the process of nutrition in animals.
(OR)
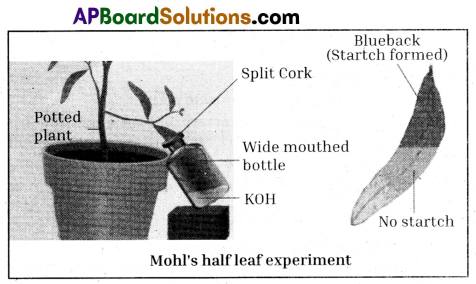
Explain the way how plants get water by osmosis through root hair.
Answer:
There are five steps in the process of nutrition in animals.
They are :
1) Ingestion
2) Digestion
3) Absorption
4) Assimilation and
5) Egestion
1) Ingestion : The process of taking food into the body is called ingestion.
2) Digestion : The process in which the food containing large insoluble molecules is broken down into small, water soluble molecules which can be absorbed by the body is called digestion.
3) Absorption : The process in which the digested food passes through intestinal wall into blood stream is called absorption.
4) Assimilation : The process in which the absorbed food is taken in by body cells and used for energy growth and repair is called assimilation.
5) Egestion : The process in which the undigested food is eliminated from the body is called egestion.
(OR)
- Roots have small hair like structures called root hairs originating from the cells of a single layered epidermis.
- Root hairs grow out into the space between soil particles and the hairs are surrounded by moisture.
- Every living cell acts as an osmotic system. The cytoplasm lining of the cell wall acts as the semipermeable membrane.
- The soil water is a dilute solution of salts, water molecular concentration is more dilute than of the cell sap in the root hair.
- Therefore water will pass into the vacuole of the root hair by osmosis.
- The entry of water dilutes the content of the root hair vacuole so that it becomes more dilute than its neighbouring cell.
- The water passes into the neighbouring cell which in turn becomes diluted. Finally water enters the xylem system.
- A pressure in the xylem vessels develops which forces the water upwards. This total pressure is known as ’Root pressure’.
Question 8.
Describe different artificial vegetative methods to produce large scale production plants.
(OR)
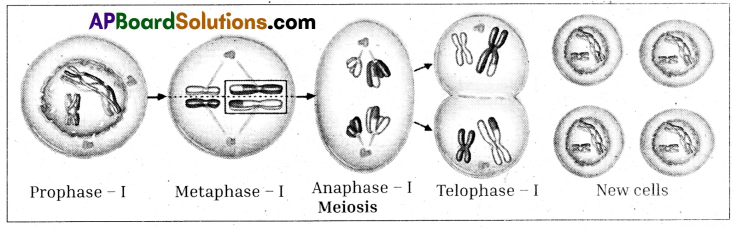
What are the consequences if meiosis not happen in the body cells of the organism ?
Answer:
- Different artificial vegetative propagation methods are cutting, layering, grafting and tissue culture methods.
- Cutting : Some plants grow individually when a piece of parent plant having bud is cut from the existing plant. After burying in the soil the cut parts having buds grow as an individual plant after developing roots. E.g.: Rose.
- Layering : A branch of the plant with at least one node is bent towards the ground and part of it is covered with moist soil. After some time, new roots develop from the part of the branch hurried in the soil. The branch is then cut off from the parent plant. E.g.: Nerium.
- Grafting : Two plants are joined together in such a way that two stems join and grow as a single plant. This technique is very useful in propagating improved varieties of various flower and fruits. Grafting is used to-obtain a plant with desirable character. E.g.: Mango, citrus, apple, rose.
- Tissue culture : In this method, few plant cells or plant tissues are placed in a growth medium with plant hormones in it and it grows into new plants. Thousands of plants can be grown in very short interval of time.
(OR)
- Each organism has a fixed number of chromosomes.
- This number has to be maintained in its offspring.
- Any sudden change in the number of chromosomes will be harmful to the offspring. Assume parent has 10 chromosomes.
- In the absence of meiosis during sexual reproduction gametes will also have the same number of chromosomes as parent i.e., 10 chromosomes.
- Union of female and male gametes occur forming zygote during sexual reproduction. The zygote will have the double number of chromosomes as compared with the parent organism paren i. e., the number of chromosomes in zygote will have 10 + 10 chromosomes.
- In the next generation, the off spring will have forty chromosomes. If this continues cells in the offsprings will have thousands of chromosomes within few generations.
- This results in formation of abnormalities in each generation. Hence by way of meiotic division, the chromosome number is maintained constant from generation to generation.
![]()
Question 9.
To understand the activity of saliva what test is to be conducted on carbohydrates ? Write about the precautions to be followed while doing activity. (Or) Explain the experiment which you have conducted in your school laboratory to know the affect of saliva on the starch by drawing a diagram.
(OR)
Do pesticides cause Bioaccumulation and Biomagnification ? Support your answer.
Answer:
Aim : To understand the action of saliva oh flour.
Apparatus :
- Test tube
- Water
- Ata flour
- Watch glass
- Iodine solution
- Saliva
Procedure:
- Take a test tube, half filled with water and add a pinch of flour to it. Shake the test tube well till the flour gets mixed.
- Take a few drops of this in a watch glass and test for the presence of starch by putting a drop of diluted tincture iodine in it.
- A blue black colour formed, confirms the presence of starch.
- Now divide the mixture into two equal halves by transferring it to another test tube.
- Note that both test tubes have equal amounts.
- Add a teaspoon of saliva to one of the test tubes and mark it.
- Do not add anything in another test tube.
- After sometime add a drop of diluted tincture Iodine solution to test tubes containing the solution.
Observation :
- The solution of the test tube to which saliva is added shows no colour change as starch is converted to sugar.
- There is a colour change to black in the other test tube to which saliva is not added.
Precautions while doing the experiment :
- Do the procedure gently while adding the reagents.
- We should see that there must be equal division of flour and iodine mixture solution before testing with saliva.
(OR)
- Pesticides are the toxic chemicals used to destroy pests and insects which damage our crops and stored foods.
- These pesticides vary in their length of life as toxic materials.
- Some of the pesticides are degradable that can be broken down into harmless substances in a comparatively short time and others are non-degradable.
- Non-degradable pesticides accumulate in the bodies of animal and pass right through the food web.
- Thus the pesticides cause bioaccumulation.
- These accumulated pesticides concentrate as they move from one trophic level to the next, thus leads to biomagnification.
Part – B (20 Marks)
Instructions :
- Write the answers to the questions under Part – B on the question paper itself and attach it to the answer book of Part – A.
- Each question carries 1 mark.
- Marks will not be awarded in any case of overwriting, rewritten or erased answers.
- Write the capital letter (A / B / C / D) showing the correct answer for the following questions in the brackets provided against them.
Question 1.
Pelletier and Canventou obtained an extract of the green coloured Substance, What was it ?
A) Chlorophyll
B) Nucleus
C) Mitochondria
D) Stomata
Answer:
A) Chlorophyll
Question 2.
Consider the following statements.
a) Temperature of inhaled air is regulated to the body temperature in nasal cavities.
b) The inhaled air becomes moist.
A) Both a and b are true
B) a is true, b is false
C) a is false, b is true
D) Both a and b are false
Answer:
A) Both a and b are true
Question 3.
Breathing roots are present in
A) Aquatic plants
B) Mangrove plants
C) Terrestrial plants
D) Desert plants
Answer:
B) Mangrove plants
Question 4.
Xylem and phloem are examples of
A) Dermal Tissue
B) Simple Tissue
C) Complex Tissue
D) Transpiration
Answer:
C) Complex Tissue
Question 5.
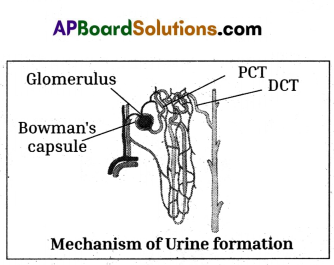
The order of excretory organs
A) i – Blood vessel, ii – Kidney, iii – Ureter, iv – Urinary bladder
B) i – Kidney, ii – Blood vessel, iii – Urinary bladder, iv – Ureter
C) i – Blood vessel, ii – Kidney, iii – Urinary bladder, iv – Ureter
D) i – Urinary bladder, ii – Ureter, iii – kidney, iv – Blood vessel
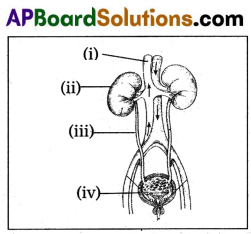
Answer:
A) i – Blood vessel, ii – Kidney, iii – Ureter, iv – Urinary bladder
![]()
Question 6.

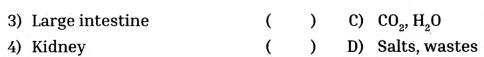
Identify the correctly matched pairs.
A) 1) a, 2) b, 3) c, 4) d
B) 1) b, 2) a, 3) c, 4) d
C) 1) c, 2) d, 3) a, 4) b
D) 1) a, 2) c, 3) d, 4) b
Answer:
C) 1) c, 2) d, 3) a, 4) b
Question 7.

Correct answer is :
A) Only 1 is correct
B) Only 2 is correct
C) 1 and 3 are correct
D) 2 and 3 are correct
Answer:
A) Only 1 is correct
Question 8.
Name the part to be labelled in the ’?’

A) Axon
B) Neuron
C) Dendrite
D) Cyton
Answer:
C) Dendrite
Question 9.
Find out the organisms that perform budding,
i) Amoeba
ii) Hydra
iii) Yeast
iv) Bacteria
A) i only
B) iii only
C) ii, iii
D) All
Answer:
C) ii, iii
Question 10.
Red ribbon club educates the people on …………….
A) Leprosy
B) Family planning
C) AIDS
D) Ebola disease
Answer:
C) AIDS