Telangana SCERT 10th Class Biology Study Material Telangana 6th Lesson Reproduction Textbook Questions and Answers.
TS 10th Class Biology 6th Lesson Questions and Answers Telangana – Reproduction
Question 1.
Why do fish and frog produce a huge number of eggs each year?
Answer:
- External fertilisation occurs in frog and fish.
- The females lays a vast number of eggs in water and males release some millions of sperms on to them in water.
- As the chance of fertilisation is controlled by nature, which occurs externally hence it is inevitable to give rise to vast number of eggs by fish and frog.
![]()
Question 2.
Give examples and explain what is meant by external fertilisation?
Answer:
- If the fusion of sperms and ova occurs outside the body of the animal, it is called external fertilisation.
- External fertilisation is seen in fish, frog and earthworm.
Question 3.
Write differences between.
a. Grafting – Layering
b. stamen-carple
Answer:
a.
| Grafting | Layering |
| 1. Grafting is a technique of inserting a part of one plant into another plant in such a way that the two will unite and continue their growth. | 1. Stems that form roots while still attached to the parent plants are called layers. Propagating the plants in this method is known as layering. |
| 2. Two plants of the same species are required for grafting. | 2. Only one plant is required for layering. |
| 3. Grafting helps to pressure and perpetuate varieties that cannot reproduce by vegetative method. | 3. In layering we can propagate the plant varieties which are required by us. |
| 4. Grafting is used to obtain a plant with desirable characters. | 4. In layering the plant already has desirable characters is propagated. |
| 5. The two plants stock arid scion and joined together in such a way that two stems join and grow as a single plant. | 5. The common practice in layering is to injure the portion to be layered by notching, cutting, girdling. |
b.
| Stamen | Carpel |
| 1. Male reproductive organ of flowering plant. | 1. Female reproductive organ of flowering plant. |
| 2. It has two parts-anther and filament. | 2. It has three parts – style, stigma and ovary. |
| 3. Stamen produces pollen grains. | 3. Carpel produces ovule. |
| 4. Pollen grain contains the maleamete. | 4. Ovule contains the female gamete ovum or egg. |
Question 4.
Explain the process of fertilisation in plants
Answer:
- Fertilisation is the process of fusion of male and female gametes.
- For the fusion of male and female gametes pollengrains have to reach the surface of the stigma. This Is called pollination.
- Pollen grains received by the stigma, germinate and give rise to pollen tubes. Only one pollen tube finally reaches the embryosac.
- This tube will have two male nuclei, which migrate to the tip of the pollen tube at the time of fertilization.
- Usually the pollen tube enters the ovule through micropyle and discharges the two niale gametes into its embryosac.
- One male nucleus (gamete) approaches the egg and tuses with it to form a diplohi (2n) zygote. This is first fertilisation.
- The other male nucleus (gamete) reaches the secondary nucleus (2n) and fuses with it to form endosperin nucleus which will be triploid. This is second fertilization in the embryosac.
- Thus double fertilisation occuts in embryosac which is unique in flowering plants.
![]()
Question 5.
What are the different modes of asexual reproduction? Cite them with examples.
Answer:
Asexual reproduction takes place by six different methods. They are:
- Fission
- Budding
- Spore formation
- Regeneration
- Fragmentation and
- Vegetative propagation.
1. Fission: Single-celled organisms split into two equal offsprings or more offsprings.
Ex: Pararnoecium, bacteria.
2. Budding: A growth on the body as a bud grows to form identical copy of parent.
Ex: Yeast
3. Spore formation : Spores are produced in sporangium.
Ex: Rhizopus, mucor, bacteria, ferms and mosses.
4. Regeneration : Ability of organisms to give rise to new individual organisms.
Ex : Hydra, flatworm, tapeworm.
5. Fragmentation: New individual growth from a separate piece of parent organism.
Ex: Flatworms. moulds, lichens. spirogyra.
6. Vegetative propagation:
a. Natural propagation:
Leaves : Eg: Bryophyllum
ii. Stems:
Eg: Stolon – Vallisneria, Strawberry
Bulbs – Onion
Corms – Colacasia
Tuber – Potato
b. Artificial propagation:
- Layering: Eg: Neriurn, guava. orange. rose.
- Cutting: Eg: Rose, Hibiscus, Sugarcane.
- Grafting: Eg: Sapota, Guava, Mango.
![]()
Question 6.
In what ways does sexual reproduction differs from asexual one? State at least three reasons.
Answer:
Sexual reproduction differs from asexual reproduction in the following ways:
1. Number of organisms involved in reproduction : Sexual reproduction required two parents to mate whereas asexual reproduction requires only one parent.
2. Cell division : In sexual reproduction, cell divides by meiosis whereas iii asexual reproduction only mitotic division occur.
3. Involvement of sex cells: Formation and fusion of gametes takes place in sexual reproduction. In asexual reproduction no formation and fusion of gametes takes place.
4. Unit of reproduction : Gamete is the unit of sexual reproduction whereas In asexual reproduction it may be whole parent. body or a bud or a fragment or a single somatic cell.
5. Thne period : Sexual reproduction need more time to complete and it is less time in asexual reproduction.
6. Evolution: Sexual reproduction leads to genetic variation in new generation of offspring. This is fun(Iamental in evolution. In asexual reproduction, there is little chance of genetic variations. Only mutation in DNA can change the genetic
Question 7.
How are sperm cells adapted for their function?
Answer:
- Sperm cell is adapted to its function by carrying genetic information to an egg
- It has a stream lined body that allows it to move quickly.
- They also contain large number of mitochondria in the mid region, so it is able to produce a Jot of energy in order to operate tail.
- Special structure in the head called acrosome helps in penetrating the ovum.
- The head of the sperms also contains enzymes to break down and digest the ZOflou the egg through which it penetrates and can fertilise it.
Question 8.
The menstrual cycle prepares the uterus for a fertilised egg. How long is an average menstrual cycle from start to finish?
Answer:
- The cycle of changes that occur in the female reproductive system is called menstrual cycle.
- The average menstrual cycle from start to finish is 28 days long.
Question 9.
When the foetus is growing inside the uterus it needs nutrients. What provides these nutrients?
Answer:
Placenta supplies nutrients to the foetus which is growing inside the uterus
Question 10.
Which type of substances are obsorbed by foetus from the mother ?
Answer:
The digested food from the mother travel through the mother’s blood stream and exchange to the blood stream of the foetus through the placenta. In addition to ingested food the mother’s body continuously breakes down muscles, fat and bones. Releasing proteins, fat and calcium to the mother’s blood that can be absorbed through the placenta to provide nutrients to the foetus.
![]()
Question 11.
What is the job of the amniotic sac?
Answer:
- The amniotic sac is a bag of fluid inside a woman’s womb (uterus) where the unborn baby develops and grows.
- The cavity within the amnion becomes filled with fluid called amniotic fluid.
- The embryo or unborn baby floats and moves in the amniotic fluid.
- Amniotic sac and amniotic fluid give protection against minor mechanical injury.
Question 12.
What are the advantages of sexual reproduction?
Answer:
- Sexual reproduction promotes diversity of characters in the offsprings by providing genetic variation.
- Sexual reproduction plays an important role in the origin of new species having different characteristics.
- This genetic variation leads to the continuous evolution 01 various species to form better and still better organisms. All this is not possible in case of asexual reproduction.
- Diversity of characters in the new generation give a better chance to adjust or adopt to changing environmental conditions to tolerate diseases, to spread to new areas and increase their population.
Question 13.
How does reproduction help in providing stability to population of species?
Answer:
- The reproduction is directly linked to the stability of the population of species because it helps in replacing the lost section of population with the new population and thus ensures the survival of the species.
- In the absence of reproduction one particular species will disappear with time.
Question 14.
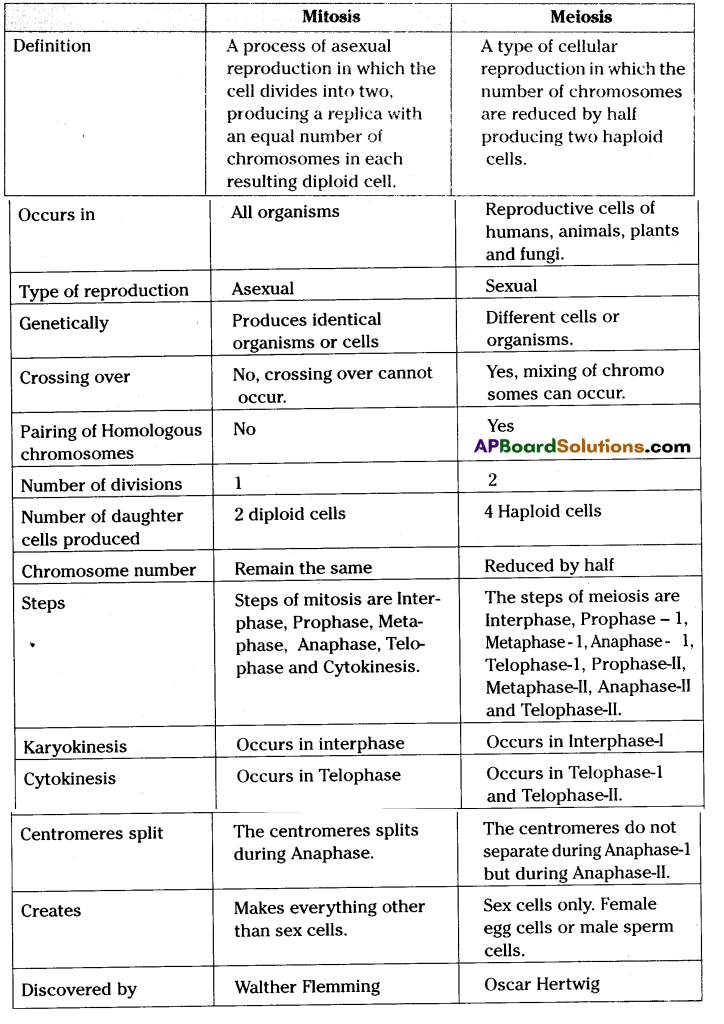
Write the differences between mitosis and meiosis.
Answer:
Question 15.
What happens to the wall of the uterus during menstruation?
Answer:
- During early stage of menstruation the cells in the wall of uterus increase in number by repeated mitotic divisions.
- The inner lining of uterus becomes thick and soft with lot of blood capillaries in it.
- These changes in the uterus are necessary because the ovum released by the ovary gets fertilised by the sperm, then the uterus has to keep this fertilised ovum for further development and supply it with food and oxygen, etc.
Question 16.
“All unicellular organisms undergo only mitotic cell division during favourable conditions”- Do you support this statement? Why?
Answer:
- Yes, I support this statement. Because it is the simple way of increasing ones own population.
- During favourable conditions, organisms give rise to more of its kind from a single parent by simply splitting into two daughter organisms.
- The time required for the completion of mitotic cell division is also very less.
![]()
Question 17.
Vicky’s father wants to grow a single plant having two desirable characters colourful flowers and big fruits What method will you suggest him and why?
Answer:
Aim : To observe the different stages of mitosis in onion root tip.
Apparatus: Slide, microscope, cover slip, dilute HCl, spirit lamp, glass rod, needle,brush, fresh onion roots.
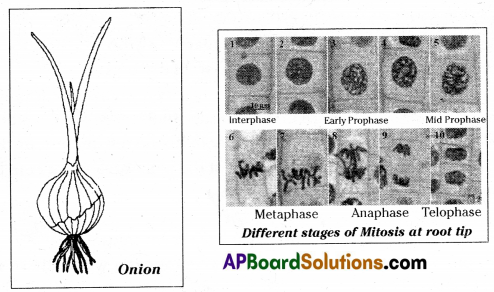
Procedure:
- Collect freshly grown onion root tips cut off the last 5mm of it and place them in a test tube.
- Add dil. HCl and heat it on spirit lamp for 5 min. to soften the root tissue.
- Decant the liquid carefully, wash the root tip on a watch glass containing water to remove acid.
- Remove the excess water with help of filter paper.
- Place the tip on the slide and add one drop of methylene blue.
- Now gently tap the root with end of the glass rod until it is completely hr ken.
- Place a cover slip on tip and warm gently for a few seconds over very low flame. Take care that it must not boil.
- Put a piece of filter paper over the preparation and press the cover slip with your thumb avoiding any side way movements.
- Observe under microscope and draw what you have observed, in your notebook.
Question 18.
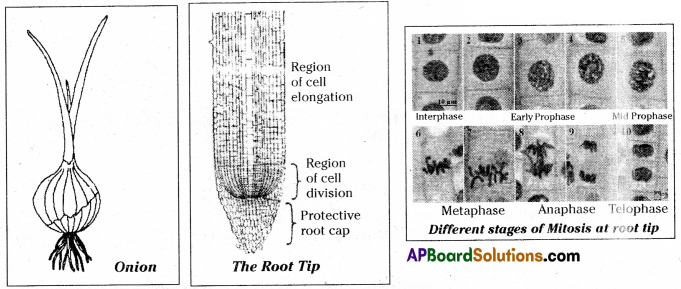
Uproot an onion plant and take a thin section of its root tip. Stain it and observe under microscope. Draw as you see and identify the stages of the cell division
Answer:
Question 19.
Visit a nearby village and collect information how farmers grow sugarcane, flowering plants like chrysanthemum, primerose and vegetables like stem tubers, plump gourd (dondakaya) etc. Make a report and present in class.
Answer:
I visited a nearby village and collected the following information about growing of different plants from farmers.
1. Sugarcane:
- Farmers use stem cuttings for growing sugarcane crop.
- They select healthy sugarcane plants for stem cuttings.
- Farmers chop off upper leaves and split sugarcane stems into foot long pieces.
- Using a spade or hoe they dig a furrow about 6 inches deep and water the furrow.
- They place the stem cuttings horizontally in the furrow but not upright.
- Shorts will start to grow from the nodes of the stem breaking through the soil to form individual sugarcane stalks.
2. Chrysanthemum:
- It is grown from its seeds and also by means of cuttings.
- Farmers place seeds and cuttings of chrysanthemums where there is an ample amount of sun.
- The well-draining soil is required when planting.
- Enough water should be given at intervals.
3. Prime – rose:
- Primeroses that are healthy in appearence preferably with unopened buds are utilised for growing.
- Primeroses can also be grown from seeds with an equal mixture of soil, sand peatmoss.
- Generally seeds are sown indoors during winter.
- Once seedings have obtained their second or third leaves they can be transplanted in the garden.
- Cuttings can also be taken from some varieties during summer to grow prime-roses.
4. Stem tubers (Potato):
- They are mainly propagated by vegetative methods (cloning).
- Potato tubers have nodes or eyes from which new growth begins.
- Vegetative seed can be either a whole tuber or cut tuber.
- Most potato cultivating farmers produce tubers. Each tuber contain several eyes, tuber with eye cut and sow in soil.
5. Plumpgourd (Dondakaya):
- Farmers usually sow seeds of plump gourd to grow a new crop.
- Stem cuttings are also being used by the farmers to grow plump gourd crop.
- First they dig the soil to make burrows. Moist the furrow before planting the stem cutting upright.
- After 35 to 45 days lateral buds begin to grow from the nodes of stem cuttings.
![]()
Question 20.
Collect information from school library or using internet what vegetative methods are followed in your district as well as in your state to propagate various plants of economic importance. Represent it in a graph.
Answer:
Vegetative methods followed in our district as well as in our state to propagate various plants of economic importance.
1. Natural vegetative propagation: In this method of vegetative propagation, a part of the plant which may be stem, root-leaf or flower gets detached from the body of the mother plant.
- Vegetative propagation : Roots of raddish, carrot, dahlia develop adventious buds which grow into leaf ly shoots.
- Vegetative propagation by stems : Stolons – Vallisiieria, offsets – Eichhornia,
Rhizome – Banana, Ginger Bulbs – Aiiuincepa (Onion); Corn – Colacasia; Tuber Potato. - Vegetative propagation by leaves: Bryophylluni.
- Vegetative propagation by modified flowers (Bulbils) : Agave.
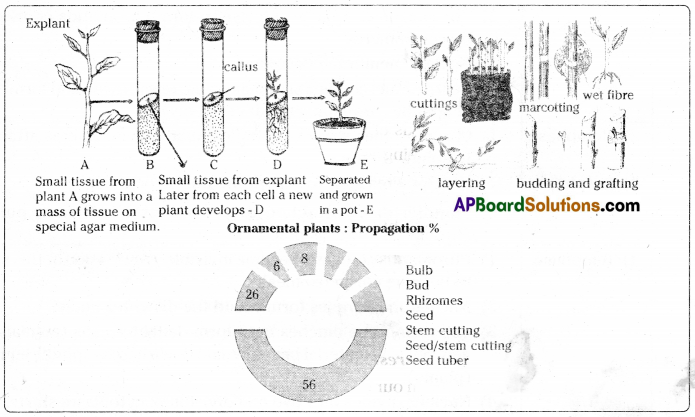
2. Artificial vegetative propagation : Certain flowering plants have the capacity to develop a part of their somatic body into a new independent plant. In artificial vegetative propagation such plants are identified and special techniques are applied to obtain new independent plant.
- Cutting Stems : Sugarcane, Roses, Hibiscus, Citrus plants.
- Cutting (Root): Lemon, Tamarind.
- Layering : Jasmine, Strawberry, gooseberry.
- Grafting: Rubber, apple, pear, citrus, mango, Guava.
- Propagation by tissue culture technique Lily, Rose, Magnolia. Fern, Banana for micro propagation, a small amount of tissue from a suitable part of the parent plant is excised and grown on a nutrient medium under aseptic conditions.
![]()
Question 21.
Make a flow chart to show the cell cycle and explain cell division describing different stages of mitosis.
Answer:
Different stages of cell division in mitosis are prophase, rnetaphise, anapliase and telophase.
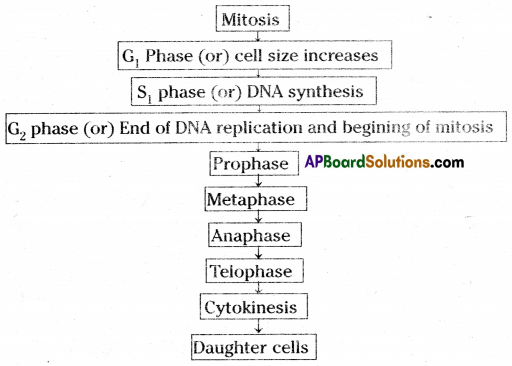
During cytokinesis a new membrane (and a cell wall in plants) is formed at the equitorital plate dividing the cell into two daughter cells.
| Stages | Description |
| 1. Prophase | 1. Chromosomes condense and get coiled. They become visible even in light microscope and nucleoli become smaller (material to chromosomes). 2. Chromosomes split lengthwise to form chroniatids concected by centromeres. 3. Nuclear membrane disappears. 4. Centrosome. containing rod-like centrioles, divide and form ends of spindle (probably animal cells only) |
| 2. Metaphase | 1. Chromosomes move to spindle equator, centromeres attached to spindle fibers. |
| 3. Anaphase | 1. Centromeres split to separating the chromatids. 2. Spindle fibres attached to centroincres contract, pulling chromatids towards poles. |
| 4. Telophase | 1. Chromatids elongate, become invisible. (replication at this stage to become chromosomes). 2. Nuclear membranes form round the daughter micle 3. Cell membrane pinches into form (laughter cells (animals) or new cell wall material becomes laid down across spindle equator (plants) 4. Nucleus divides into two and division of cytoplasm starts. |
Question 22.
Draw neat labelled diagrams of male and female reproductive system of the plant.
Answer:
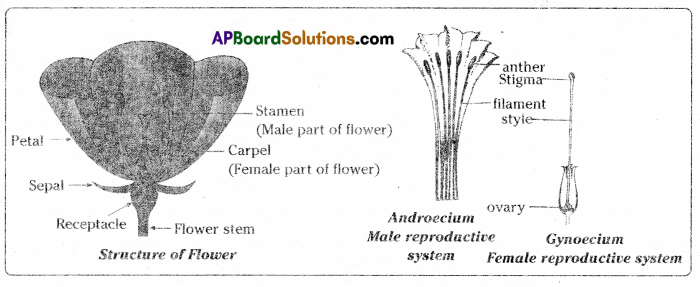
Question 23.
Observe the following part of a flowering plant prepare a note.
Answer:
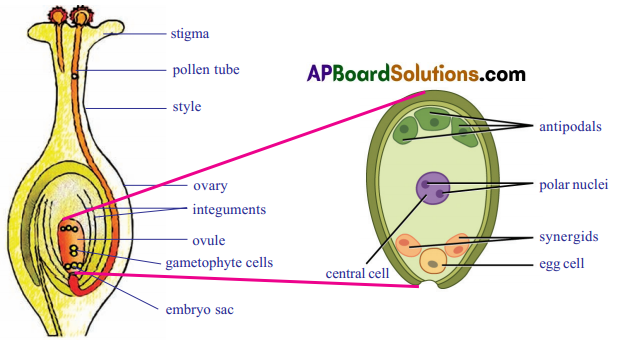
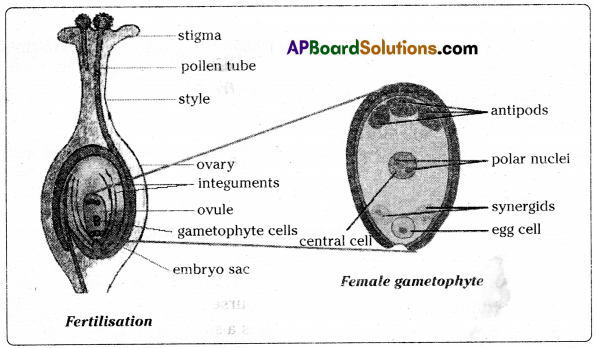
The given diagram is the structure ot ovule which is present in the ovary (carpel) of plant
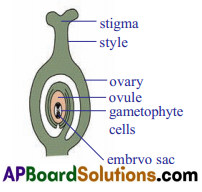
- An ovule is an egg shaped structure attached by a stalk (Funicle) to the inner side of the ovary.
- Depending Upon the species of plant involved, an ovary may have one, two, several or even hundreds of ovules.
- At the center of each ovule there is a microscopic embryo sac filled with food and water.
- The embryo sac is Composed of gametophyte cells.
- The majority of flowering plants have an embryo sac consisting of seven cells and eight nuclei.
- They are une egg (female gamete), two synergids. one central cell (secondary nucleus) and three antipodals.
- Central cell contains two nuclei, they are called polar nuclei.
Question 24.
Prepare a flow chart to explain the process of sexual reproduction in plants.
Answer:
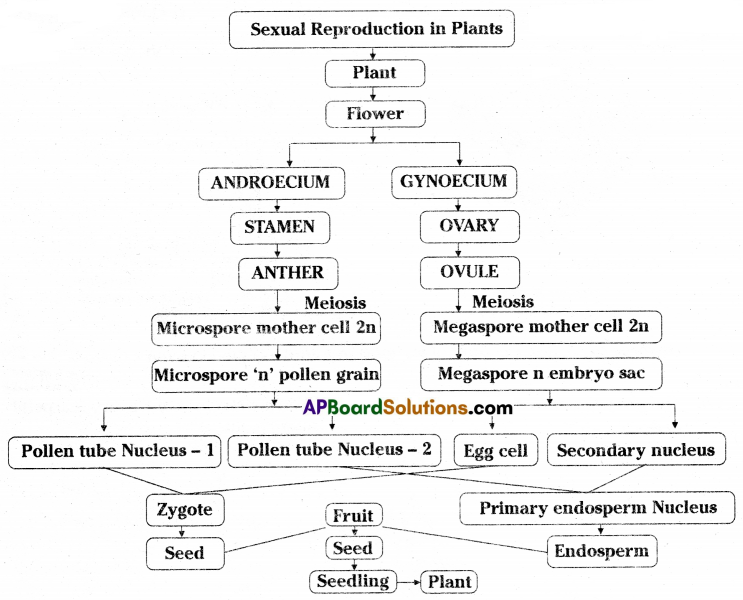
Question 25.
Draw a neatly labled diagram to explain plant fertilisation. Write few cells points on pollen grain.
Answer:
![]()
Pollen grains:
- Pollen grains develop in anther.
- Anther consists of spore forming. tissue. Some of the cells in the spore forming tissue develop as pollen mother cells.
- Each pollen mother cell undergoes meiosis to form four daughter cells which develop into pollen grains.
- Pollen grains are haploid (‘n’) and are otherwise known as microspores or male gametes.
- They contain only one set of chromosomes (‘n’).
- The study of pollen grain is called palynology.
- During pollination pollen grains are dispersed by wind and insects.
- Pollen grains are formed in large numbers. They are light in weight and are easily carried by wind currents.
Question 26.
What would be the consequences if there is no meiosis in organisms that reproduce sexually?
Answer:
- If meiosis did not occur, fusion of gametes would result in a doubling of the chromosomes for each successive reproduced generation.
- For example in case of man egg cells and sperm cells like other cells must contain 46 chromosomes.
- But If this were so then the union of egg nucleus and sperm nucleus, which takes place during fertilisation would produce a total of 92 chromosomes in zygote.
- If it continues this would be 184, 368 and so on.
- This results in formation of abnormalities in each generation.
- If meiosis did not occur, there is no genetic variation in the offsprings produced by random fusion of the gametes.
- Without meiosis the number of chromosomes are varied ¡n every generation. Hence no species holds it’s characters and continues it or species is disordered.
Question 27.
How will you appreciate cell division that helps in perpetuation of life?
Answer:
- Cell division is necessary for maintainance and perpetuation of life as it helps in increasing cell size, surface area, as well as the cell volume.
- Cell division (mitosis) helps in the replacement of the cells in the skin and in the digestive system as they are peeled off every day.
- Mitosis also helps in replacing the red blood cells after their life span of 120 days.
The red blood cells are produced in the bone marrow. Without their production there is no carrier for oxygen to the tissues in the body. - Cell division also helps in wound healing cells present at the margins of the wound divide repeatedly by mitosis and the resulting daughter cells fill the wound.
- Meiotic division is important for the reproduction and propagation of the species.
- Crossing over of chromosomes occurs during melotic division is important for the exchange of genetic information between individuals of species and evolution of species.
Question 28.
What precautions will you take to keep away from various sexually transmitted diseases?
Answer:
Precautions to be taken to keep away from various sexually transmitted diseases:
- Avoid sex with any one who has genital sores, a rash, discharge or other symptoms.
- The only time unprotected sex is a safe if the partners have sex only with each other.
- I use latex condoms every time I participate in sex. I use it for the entire sex act.
- I will follow Abstinence, Becareful and correct lifestyle, which is known as ABC for being healthy.
- I wash genital organ before and after intercourse.
- I will get a vaccination for hepatitis B. This is a series of three shots.
- I will get tested for HIV for every six months.
- I will not be drunk or on drugs. Under these conditions I may fail to have sale sex.
- I consider that not having sex is the only way, sure way to prevent sexually transmitted diseases.
- Sexual act is supposed to be an act between husband and wife. Hence I will not participate in sex before marriage.
- When I grow up and get married, I will be upright and faithful to the life partner and will not behave immorally.
- Hence as a student I will concentrate on studies and create activities to achieve success in life.
Question 29.
Conduct a seminar on child marriages and foeticide.
Answer:
Child marriage is a type of violation of girl’s human rights. Child marriage has become serious in some countries such as Africa, Indonesia, India, Bangladesh, Nigeria, Afghanistan, etc. Child marriage is a type of marriage that involves either one or both partners who are under age and this type of marriage carried out illegally. Child marriages can also be defined as “any marriage carried out under the age of 18 years and involves the girl who is physically, psychologically, mentally and physiologically immature”.
Child marriages always take place under pressure and either one of the partners is not willing to marry. We could recognize that child marriage has brought lot of adverse consequences for young girl and also became a hindrance to the development of the country. Child marriage can be caused by various factors. For instance poverty, tradition, religion, lack of education and job opportunities, etc. How ever the main reason for this problem to occur is poverty.
In many undeveloped countries economy is low. The citizens of these countries do not have enough job opportunities. This caused some poor families to marry off their young daughters to reduce their burdens. The question that arises is what can be done to stop this crime? Apart from measures taken by the Government, it is essential for colleges and other institutions to make certain moves.
It is advisable to approach such villages and districts and educate the jarents about the ill effects of child marriage. Short films, live plays can be shown to them and the moral behind these plays should obviously show the pathetic future of kids who are forced to get married.
Schools should be set up in such villages as a result of, which people will sooner of later get this children admitted. Such people should also he informed about the punishments give by the law and order of the Jountry. In India though the Government has taken strict actions and child marriage has been declared as a big crime, the practice is still prevelent till today.
![]()
Foetlcide : Foeticide is the illegal practice of killing a foetus. Female foeticide is prevalent in our country as a major social evil.
Choose the correct answer:
Question 1.
The part of the female reproductive system produces the eggs ……..
A. Ovary
B. Epididymis
C. Cervix
D. Fallopian tube
Answer:
A. Ovary
Question 2.
The term that we use to describe a sperm cell fusing with an egg cell …….
A) Fragmentation
B) Fermentation
C) Fertilisation
D) Fusion
Answer:
C) Fertilisation
Question 3.
Which part of the male reproductive system produces (human) the sperm cells?
A. Vasdeference
B. Epididymis
C. Seminiferous tubules
D. Scrotum
Answer:
D. Scrotum
Question 4.
How does the sperm break through the egg cell membrane? Choose the option you think is right.
A.Tears a hole in the membrane
B. Dissolves the membrane with chemicals
C. Bites through the membrane with teeth
D. Squeezes through gaps in the membrane
Answer:
B. Dissolves the membrane with chemicals
Question 5.
Why are egg cells larger than sperm cells? Choose the option you think is right.
A. Egg cells have more cells in them
B. Have food store to help growth after fertilisation
C. Have thicker cell membranes
D. Have larger nuclei
Answer:
B. Have food store to help growth after fertilisation
Question 6.
Which of these things will affect the way a foetus grows? Choose the option you think is right.
A. Chemicals in cigarette smoke
B. Alcohol
C. Drugs
D. All of the above
Answer:
D. All of the above
Question 7.
Which of the following is the correct sequence of steps in the human life cycle? Choose the right option.
A. Babyhood, childhood, adolescence, adulthood
B. Childhood, babyhood, adulthood, adolescence
C. Adolescence, babyhood, adulthood, childhood
D. None of these
Answer:
A. Babyhood, childhood, adolescence, adulthood
TS 10th Class Biology 6th Lesson Reproduction Intext Questions
1 Mark Question and Answers :
Question 1.
How do you think bacteria were dividing to form curd?
Answer:
Curdling indicates that the increase in number of bacteria by fission.
Question 2.
Which type of fission would produce larger colonies in less period of time? Why?
Answer:
Multiple fission would produce larger colonies in less period of time because more number of (logfile.- cells are formed by multiple fission.
Question 3.
What mode of propagation would help you to produce the plants with desirable characters?
Answer:
Mode of propagation that would help me to produce the plants with selected characters is grafting.
Question 4.
Do you find any similarities between rhizopus and fern spores and sporangia?
Answer:
- Both rhizopus and fern reproduce asexually through spores.
- In both the spores are microscopic, unicellular bodies produced in the sporangia.
Question 5.
Think why testes are located outside the abdominal cavity.
Answer:
The testes are located outside the abdominal cavity because the temperature required for proper functioning of spermatic genesis is generally 2 to 3 degrees less than the body temperature.
![]()
Question 6.
What function do you think is served by petals and sepals?
Answer:
- Calyx consists of sepals give protection to the flower particularly in bud condition.
- Corolla consists of bright coloured petals and are useful in attracting insects for pollination.
Question 7.
How many nuclei are present in the pollen grain?
Answer:
Pollen gram has two nuclei. One is called a tube cell and the another is generative cell.
Question 8.
Which floral part may be seen In a fruit?
Answer:
Sometimes calyx may remain with fruit.
Question 9.
How would it affect the progeny formed by sexual reproduction?
Answer:
If the progeny have thousands of chromosomes in them, it results in formation of abnormalities in each generation.
Question 10.
What is the virus which causes AIDS?
Answer:
The virus which causes AIDS is Human Immuno Virus HIV.
2 Mark Question and Answers :
Question 1.
Regeneration is a type of fragmentation. Do you agree ? Why? Why not?
Answer:
- Yes. I agree that regeneration can be also known as a type of fragmentation. Because in both cases pieces and parts from the body of the organism can develop into a new individual.
- Fragmentation and regeneration occur ¡n multicellular animals.
- Fragmentation occurs in organisms with relatively simple body organisation.
- Whereas regeneration occurs in organisms with fully differentiated body organisation.
Question 2.
Will budding, fission and fragmentation lead to organisms that are exact copies of their parents? Why/ Why not?
Answer:
- The organisms reproduced by budding or fission or fragmentation are exact copies of their parents.
- Because budding or fission or fragments are not the methods of sexual reproduction.
- No gametes were formed or fused in these methods.
- Exchange of chromosomes or crossing over do not take place. Hence the offsprings produced are similar to their parents.
Question 3.
What about mushrooms, how do they grow ? Discuss in your class.
Answer:
Fungi grow from the fragmentation of hypae. They also form buds which are bulged forms out the side of cells which detaches after division of the nucleus. A special reproductive sac called sporangium produces asexual spores which are released out side. Fungal sexual reproduction includes plasmogamy, Karyogamy and gametangiAnswer:
Question 4.
How does the male reproductive cell reach the female reproductive cell in flowers of such plants (pea plants)?
Answer:
- In self pollinated plants anthers are usually present above the stigma.
- Pollen from the anthers drop on the stigma a process that takes place as the flowers close for the night and that sometimes occurs before they are completely developed and ready to open.
- At the time of pollination slightest movement of the flower’s petals to stimulate the stamen to dislodge its pollen and transfer it to the near by stigma is pea plant.
- Pollination usually occurs before the flower is fully open.
Question 5.
What would happen if the gametes do not have half the chromosome number as to their parental cell?
Answer:
- Daughter cells formed in meiosis are gametes.
- These gametes have half of the chromosomes number as the parent.
- When male and female gametes fuse together during fertilisation zygote is formed which have the saine number of chromosomes as the parent.
- lithe gametes do not have half of the chromosome number as the parent, when they fuse, they form zygote with double the number of chromosomes when compared to parent cell.
- If it continues, cells in the offspring will have thousands of chromosomes within few generations.
- If the chromosome number increases in a species it leads to the formation of abnormalities.
Question 6.
Why did the government of india fix the legal marriage age of boys (21 years) and girls (18 years)?
Answer:
- Government of India fixed legal marriage age of boys as 21 years, and girls as 18 years.
- This is because teenage mothers are not prepared mentally or physically for motherhood.
- Early marriage and motherhood cause health problems for the mother and child.
- It may also cause mental agony, as a teenage mother is not ready for responsibilities of motherhood.
Question 7.
Do you feel that It is a social responsibility to control birth after having one or two children?
Answer:
- Yes, it is a social responsibility of every individual to control birth after having one or two children.
- If we don’t control birth after having one or two children, population will grow an anonymously.
- If the population increases we can’t able to provide all the facilities such as education, medicine, employment, etc. to all the people.
- It shows impact on the economic conditions of the family and the society.
- The quality of life will decrease.
Question 8.
What do you understand by the term ‘Healthy Society’?
Answer:
- If all the people in a society are in the state of complete physical, mental and social well being, then the society is said to be healthy society.
- To be in a healthy society, every one in the society should take care of their own personal hygine, cleanliness of the surroundings.
- Avoiding child marriages, unprotected sex, creating awareness among the people regarding adverse effects of these are very essential to form a healthy society.
Question 9.
Will you encouvage child manluge? Why?
Answer:
- No. I never encourage pre-mature sex or child marriage.
- This is because, the sexual act always has potential to lead to pregnancy.
- Pregnancy will make major demands on the body and the mind of the woman, and if she is not ready for it, her health will be adversely affected.
- In case of pre-mature sex or child marriage, the age of girls is less than 18 years and so they are not prepared mentally or physically for motherhood.
- If they got pregnancy the health of them and their children will be affected.
![]()
Question 10.
Why doctors are prohibited to do sex determination through ultrasound scanning for pregnant women?
Answer:
Knowing the sex of foetus inside mother’s womb is a severe crime as per the act made by government. Ultrasound tests are meant to know the growing condition of the foetus and also to see whether is suffering with severe ailments. By knowing the sex of the foetus, if it is female, people are ready for aborting it. This leads to reduction in male, female ratio in the country. That’s why doctors are prohibited to do sex determination through ultrasound scanning for pregnant women.
4 Mark Question and Answers :
Question 1.
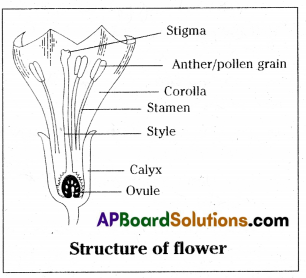
label parts of flower given in figure.
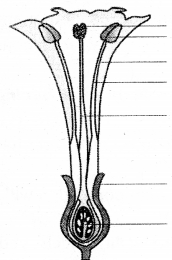
Answer:
Question 2.
Draw the diagram of the flower that you collect and label the parts shown and write their functions.
Answer:

- alyx – Consists of sepals – protects flower in bud conditions.
- orolla – Consists of coloured petals – helps in pollination.
- Androecluin – Consists of stamens – produce male gametes pollen grains.
- Gynoeclum – Female reproductive part – produce ovules inside the ovary. Stigma receives pollen grain.
Question 3.
What differences do you find in mitosis and meiosis ? Write in a tabular form.
Answer:
| Mitosis | Meiosis |
| 1. It occurs in somatic cells. | 1. It occurs in germ cells. |
| 2. Nucleus divides only once. | 2. Nucleus divides twice. |
| 3. Two daughter cells are formed. | 3. Four daughter cells are formed. |
| 4. Daughter cells are diploid. | 4. Daughter cells are haploid. |
| 5. It occurs more frequently. | 5. It occurs less frequently. |
| 6. Daughter cells form somatic organs. | 6. Daughter cells form gametes. |
| 7. There is only one prophase, one metaphase one anaphase and one telophase. | 7. There are two of each phase and five sub-phases in prophase -1. |
| 8. Number of chromosomes are not changed in the daughter cells. | 8. Number of chromosomes are reduced to half. |
| 9. Chromosome number doubles at the beginning of each cell division. | 9. Chromosome number is not doubled. It doubles after the end of first meiotic division. |
| 10. No crossing over in chromosomes. | 10. Crossing over occurs chromosomes. |
| 11. Equation division. | 11. Reduction division. |
Question 4.
Social discrimination against AIDS patient is also a social evil. Can you support this ? Why ?
Answer:
- Yes, I will support this statement.
- The persons suffering from HIV/AIDS are shown lot of social discrimination in the society.
- This happens even with their own family members.
- This is due to lack of awarness among public about spreading of disease, and illiteracy misconception about AIDS.
- If everyone knows how it will not spread they will treat HIV +ves with love and effection.
- HIV +ves are patients, it will spread through sexual contact, blood transfusion, mother to child and not with other modes.
- Hence they can live with us without any discrimination they need our love and family support.
- If anybody shows discrimination, it is definitely a social evil.
TS 10th Class Biology 6th Lesson Reproduction Activities
Activity – 1
How do you observe formation of bacterial colony in milk?
Answer:
- Take a tea spoonful of curd and mix it throughly with around 60 tea spoon full of (half of the glass) luke warm milk in a bowl.
- Take another tea spoonful of curd and mix it with 60 tea spoonful of cold milk in another bowl.
- Cover both the bowls and note the initial time.
- Keep observing every hour to see whether curd has formed.
- Curdling indicates that the increase in number of bacteria.
- Note the time taken for formation of curd in both the bowls.
Q. Did it take the same time to form curd in both the bowls?
Answer:
No. Formation of curd in the bowl containing luke worm milk takes nearly 5-6 hours.
In the second bowl in which cold milk is present no curdling took place.
![]()
Q. What was the time taken to form 60 times the size of the bacterial colony? What did it indicate?
Answer:
Time taken to form nearly 60 times the size of the bacterial colony indicates how fast bacteria are growing.
Q. Examine Rhizopus or common mold under Microscope. Write your observation.
OR
Write the procedure which you follow to observe bread-mould Sporanglum in your laboratory. What precautions do you take during the activity?
OR
Write the materials required and the procedure followed by you to observe Rhizopus in the lab.
Answer:
Aim : To grow and examine rhizopus or common mold.
Materials required: Bread, plastic bag, plain glass slide, cover slip, water, eye dropper, disposable gloves, compound microscope.
Procedure to grow mold:
- Take a soft bread that is preservative free, and leave it in the open for about an hour so it is exposed to contaminants in the air.
- Place the bread in a plastic bag, sprinkle water over it, so it is damp and seal the bag living some air inside.
- Check the piece of bread regularly for every few days and add some water if it is drying.
- We can find whitish thread like growth with masses of black, gray and green fine dotted structures, the black dotted structure is that of bread mold.
- A good sample of mold may take up to two weeks to form.
- Using this mold make a slide and observe under the microscope.
![]()
OR
Aim : To prepare temporary slide of Rhizopus.
Material required: Mold sample, plain glass slide, cover slip, water, disposable gloves.
Procedure:
- Place a drop of water in the centre of the slide, using an eye dropper if you have one, or the tip of a clean finger.
- Using a tooth pick, scrape some of the mold off, and place it on the drop of water.
- Take the coverslip and set it at an angle to the slide so that one edge of it touches the water drop, then carefully lower it over the drop so that the covers lip covers the specimen without trapping air bubbles underneath.
- Use the corner of a tissue paper or blottìng paper to blot up any excess water at the edges of the coverslip.
- View the slide with a compound microscope, starting with a low objective.
Observation:
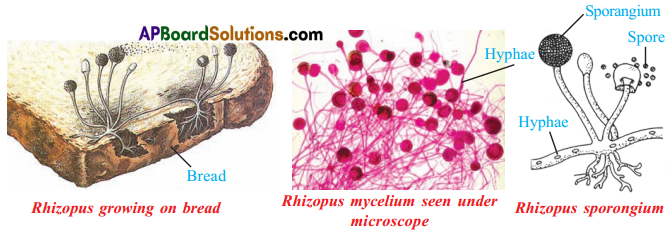
- The common bread mold l)laflt consists of fine thread like projections called hyphae and thin stems having knob-like structures called sporangia.
- Each sporangium contains hundreds of minute spores.
Precautions:
- This should not be done by those with allergies to mould or with severe asthma.
- Avoid opening the plastic bag as much as you can.
- If you touch the bread, be sure to thoroughly wash your hands afterwards.
![]()
Activity – 2.
How do you observe pollen grain under a microscope?
Answer:
Observation of pollen grain.
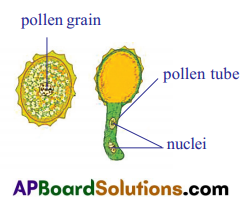
- Take a slide and put a few drops of water on it.
- Take any flower like hibiscus, tridax, marigold, etc, tap it over the drop of water.
- We will see small dot like structures in water. These are pollen grains.
- Observe the pollen grains under hand lens then under a compound microscope.
- Also see a permanent slide of pollen grain from your lab.
Activity – 3.
How do you observe the seed germination?
Answer:
Seed germination:
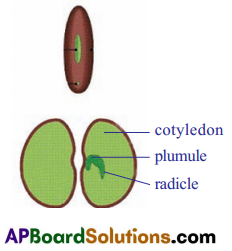
- Soak a few groundnut or bengal gram (chana) seeds overnight.
- Drain the excess water and cover the seeds with wet cloth.
- Leave them for a day.
- Keep sprinkling water at regular intervals so that they do not dry up.
- Open the seeds carefully and observe the parts, compare with figure to indentify the parts.
![]()
Activity – 4.
Observe different stages of mitotic cell division
OR
Observe the following figures and find the stages of cell division and explain.
Answer:
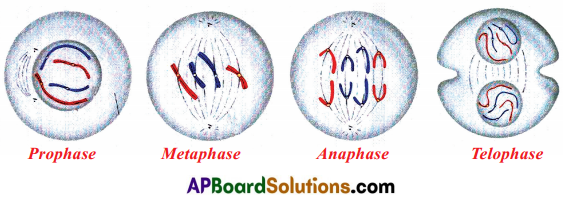
In the mitotic cell division, the division of nucleus (karyo kinesis) followed by the division of cytoplasm (cytokinesis). Finally brings about formation of two daughter cells. There are four stages in mitosis division. They are
- Prophase
- Metaphase
- Anaphase
- Telophase
| Prophase | 1. Chromosomes condense and get coiled. They become visible even in light microscope and nucleoli become smaller. 2. Chromosomes split lengthwise to form chromatids, connected by centronieres. 3. Nuclear membrane disappears. 4. Centrosome containing rod-like centrioles, divide and form ends of spindle (probably animal cells only) |
| Metaphase | 1. Centrosomes move to spindle equator, spindle fibres attached to centromeres. |
| Anaphase | 1. Centrorneres split, separating the chrornatids. 2. Spindle fibres attached, centrorneres contract, pulling chromatids towards pote. |
| Telophase | 1. Chromatids elongate, become invisible to become chromosomes. 2. Nuclear membrane form round daughter nuclei. 3. Nucleus divide into two and division of cytopLasm starts. Two cells are formed. 4. Cell membrane pinches to form daughter cells (animals) or new cell wall material becomes laid clown across spindle equator (plants) |