The strategic use of TS 10th Class Social Model Papers and TS 10th Class Social Question Paper April 2023 can significantly enhance a student’s problem-solving skills.
TS 10th Class Social Question Paper April 2023
Time:3 hours.
Max. Marks: 80
Introduction
- Read the questions carefully and understand them.
- Write the answers for the questions in Part – A in the answer sheet.
- Attach the Map to the Part – A answer sheet.
- Attach Part B to Part A answer sheet.
- Part A consists of I, II, and III Sections.
- Write the answers clearly duly following the instructions given for each section.
Part – A (Marks: 60)
Section – I (6 x 2 = 12 M)
Instructions:
- Answer all questions.
- Answer each question in 3 – 4 sentences.
- Each question carries 2 marks.
Question 1.
What are the factors that affect the density of the population in India?
Answer:
Factors that affect the density of population in India include:
- Topography and geography: Physical features influence habitable areas. ‘
- Economic opportunities: Urban centers attract higher population density.
- Infrastructure and amenities: Availability of resources affects settlement patterns.
Question 2.
What are the main objectives of the National Food Security Act?
Answer:
The main objectives of the National Food Security Act in India are to provide food and nutritional security by ensuring access to adequate food at affordable prices for all eligible beneficiaries.
Question 3.
Which quality of Dr. B.R. Ambedkar do you like the most? Give reasons.
Answer:
The quality of Dr. B. R. Ambedkar that I admire the most is his relentless pursuit of social justice and equal rights for marginalized communities. His commitment to empowering the oppressed through education, advocacy, and constitutional reforms is commendable and has left a lasting impact on India’s social fabric.
Question 4.
What are the consequences of frequent violation of election code of conduct by political parties at present?
Answer:
Frequent violations of the election code of conduct by political parties can lead to an erosion of democratic values, electoral integrity, and fair representation, potentially resulting in electoral malpractices and public distrust in the electoral process.
![]()
Question 5.
Draw the outline map of Telangana.
Answer:

Question 6.
Observe the following table and answer the questions A & B.
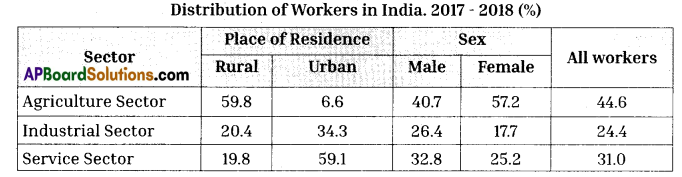
A) What does the above table show?
B) Why the share of employment in the agriculture sector has not decreased?
Answer:
A) The above table shows the Distribution of Workers in India.
B) The share of employment in the agricultural sector has not decreased significantly due to a lack of alternative employment opportunities in other sectors and the continued reliance on traditional farming practices in many regions.
Section – II
(6 x 4 = 24 M)
‘Instructions:
- Answer all questions.
- Answer each question in 5 – 6 sentences.
- Each question carries 4 marks.
Question 7.
What are the basic concepts that contribute to an area becoming a Settlement? Explain them.
Answer:
The basic concepts that contribute to an area becoming a settlement are:
1. Availability of Resources: Settlements form where essential resources such as water, fertile land, and natural resources are available for šustenance and economic activities.
2. Accessibility: Proximity to transportation routes, trade networks, and communication facilities enhances connectivity and fosters settlement growth.
3. Social Factors: Cultural, religious, and historical factors can influence the establishment of settlements as centers of community Life.
4. Economic Opportunities: The presence of job opportunities, markets, and economic activities attracts people to settle in a particular area.
5. Defense and Security: Strategic locations with natural barriers or defensive advantages often lead to the development of settlements for protection.
6. Government Policies: Supportive policies and infrastructure development by authorities can encourage settlement growth in certain regions.
7. Topography: Favorable terrain and climate contribute to the suitability and desirability of an area for settlement.
Question 8.
What changes occurred in Indian democracy between 1975-85?
Answer:
Between 1975 and 1985, India witnessed significant changes in its democracy, including:
1. Emergency (1975-1977): A period of suspended civil liberties, censorship, and political repression declared by then Prime Minister Indira Gandhi.
2. Return to Democracy: The end of the Emergency in 1977 led to free and fair elections, with the Janata Party forming the government.
3. Political Shifts: The Janata Party government’s collapse in 1979 and the re-emergence of the Congress Party under Indira Gandhi in 1980.
4. Economic Reforms: Economic liberalization measures were introduced in the 1980s to boost the economy and attract foreign investment.
5. Punjab Conflict: The rise of Sikh separatist movement in Punjab, leading to escalating violence and the Operation Blue Star in 1984.
6. Assassination of Indira Gandhi: Prime Minister Indira Gandhi was assassinated in 1984 by her Sikh bodyguards, resulting in anti-Sikh riots.
7. Rajiv Gandhi’s Leadership: Rajiv Gandhi took over as Prime Minister after his. mother’s assassination, bringing in a new era of leadership.
8. Assam Agitation: The movement against illegal immigrants in Assam demanding the updation of the National Register of Citizens. These changes had a profound impact on India’s political landscape and shaped the course of its democracy during the given period.
Question 9.
Prepare a pamphlet explaining the need for organic farming.
Answer:
Pamphlet on Needt of Organic Farming:
Need of Organic Farming
Nowadays many people consume the food grains grown by using chemical fertilizers. There is no usage of organic food. Governments and Non-governmental agencies are concentrating various awareness programmes but there is no concentration on farming and. consuming Organic Food grains.
Due to chemicals, there are many diseases and people suffer a lot with health problems. Whenever the farmers sprinkle some chemical spray in plants, the remains of chemicals join with water when there is a rain and the remains mix with water and reach any tank. The fish consume the water and the chemical enters the fish. When the humans consume the fish it affects them. Sometimes it leads to cancer.
My appeal to the farmers and government is that everyone should give priority to Organic Food which has no side effects; It is healthy food. Natural manure like animal dung, dry leaves and grass, humus, etc., are to be used in farming. Government should encourage cow-based agriculture instead of chemical farming Including maintaining grain banks for next season so that the side effects will not be there. Healthy society can be seen.
No. of copies: 3000
Published by: Welfare Society
![]()
Question 10.
Read the given paragraph and interpret it.
Most small farmers have to borrow money to arrange for the working capital. They borrow from large farmers or the village moneylenders or the traders who supply various inputs for cultivation. The rate of interest on such loans is very high.
Answer:
The paragraph suggests that small farmers often need to borrow money for their farming operations. They typically borrow from large farmers, village money lenders, or input suppliers. The interest rates on these loans are exorbitantly high.
Question 11.
Locate the following on the outline map of the World.
1. Washington
2. Japan
3. Congo
4. Italy.
Answer:
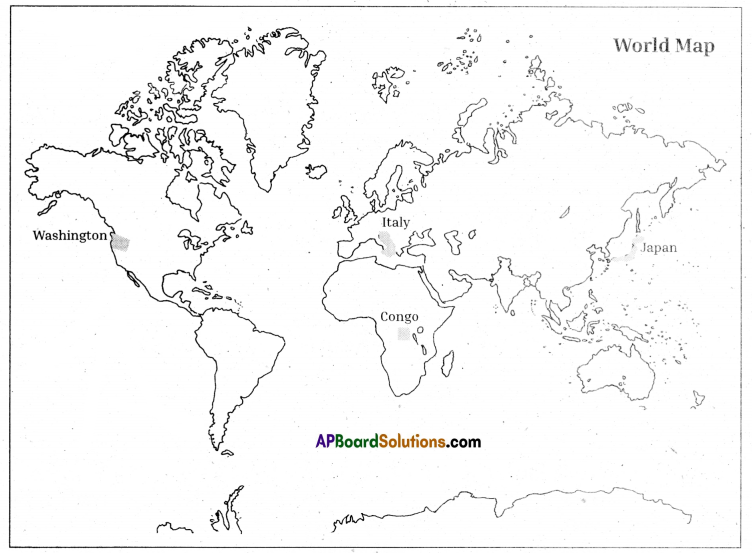
Question 12.
Observe the given table and analyse it.
Net Irrigated_area in lakh hectares
| Region | 1955-56 | 2006-07 | Growth % |
| Andhra Region | 17 | 23 | 135 |
| Telangana Region | 7 | 19 | 257 |
Answer:
The table provides data on population growth in two regions of India: the Andhra Region and Telangana Region, over a period of 51 years from 1955-56 to 2006-07.
1. Andhra Region:
- Population in 1955-56:17 million
- Population in 2006-07: 23 million
- Growth %: 135% Growth %: 257%
2. Telangana Region:
- Population in 1955-56: 7 million
- Population in 2016-07: 19 million
Analysis:
- Both regions experienced significant population growth over the 51-year period.
- Telangana Region had a higher rate of population growth (257%) compared to Andhra Region (135%).
- The higher growth rate in Telangana may indicate factors such as better economic opportunities, infrastructure development, or natural population increase.
- However, it’s important to note that this data alone may not provide a complete understanding of the underlying factors contributing to the population growth in each region.
Section – III
(4 x 6 = 24 M)
Instructions:
- Answer any 4 questions.
- Answer each question in 8 – 10 sentences.
- Each question carries 6 marks.
Question 13.
Classify the Himalayas and explain.
Answer:
The Himalayas can be classified based on their geographical features and their location within the mountain range. They are categorized into three main subdivisions:
1. Greater Himalayas (Himadri):
- This is the northernmost and highest subdivision of the Himalayas.
- It consists of some of the world’s highest peaks, including Mount Everest and K2.
- The Greater Himalayas are primarily composed of snow-capped peaks and glaciers.
2. Middle Himalayas (Himachal or Lesser Himalayas):
- The Middle Himalayas lie south of the Greater Himalayas and run parallel to them,
- This region is characterized by densely forested hills and valleys.
- The elevation of the Middle Himalayas is lower than the Greater Himalayas.
3. outer Himalayas (Shiwalik or Sub-Himalayas):
- The Outer Himalayas are the southernmost and outermost subdivision of the Himalayas.
- They are composed of relatively lower hills and foothills, known as the Shiwalik Range.
- The Outer Himalayas act as the transition zone between the mountains and the plains.
Explanation: The Himalayas are a vast and formidable mountain range in South Asia, stretching across several countries, including India, Nepal, Bhutan, China, and Pakistan. They are the result of the collision between the Indian tectonic plate and the Eurasian plate, which began around 50 million years ago and continues to this day.
The Greater Himalayas form the majestic northern barrier, with towering peaks that are snow-clad throughout the year. These peaks are a testament to the immense forces of nature and attract mountaineers and trekkers from around the world.
The Middle Himalayas, Lying south of the Greater Himalayas, are characterized by lush green valleys and are home to a variety of flora and fauna. The hill stations of Shimla, Mussoorie, and Nainital are part of the Middle Himalaýas, making this region a popular tourist destination.
The Outer Himalayas, the southernmost subdivision, mark the transition between the mountainous terrain and the plains below. These foothills provide a natural buffer and help in regulating water flow into the river systems that sustain the vast population living in the Indo-Gangetic plains.
The Himalayas are not only a spectacular geographical feature but also hold immense cultural, religious, ahd ecological significance for the people living in the region. They act as a crucial water source, supply essential resources, and influence weather patterns, making them an indispensable part of life in South Asia.
Question 14.
Explain the relations between India and China.
Answer:
India and China, being two major Asian powers with ancient civilizations, have a complex relationship that has evolved over centuries and continues to be a significant factor ¡n regional and global geopolitics. Here is a brief overview of the key aspects of their relations:
1. Historical ties: India and China have historical ties dating back thousands of years, with interactions in trade, culture, and religious exchanges. However, there have also been periods of conflict and territorial disputes.
2. Border Disputes: The most significant point of contention between India and China is their unresolved border dispute, which led to a war in 1962. The border issues continue to be a sensitive and contentious topic.
3. Geopolitical Rivalry: India and China are both emerging as major economic and geopolitical powers in the 21st century. As a result, there is an element of competition for regional influence and resources, leading to occasional tensions.
4. Economic Relations: Despite political differences, India and China have substantial economic ties. They are significant trade partners, with bilateral trade volumes reaching billions of dollars. However, there is a trade imbalance in China’s favor, which is a matter of concern for India.
5. Strategic Cooperation and Rivalry: Both countries are part of various regional and international forums and organizations. They cooperate on issues like climate change and multilateral platforms. However, they also have competing interests in areas like the Indian Ocean region and the Belt and Road Initiative (BRI).
6. Diplomatic Engagements: India and China engage in high-level diplomatic dialogues, including bilateral summits and meetings between their leaders. These interactions aim to manage and address differences and find common ground on various issues.
7. Security Concerns: Both countries share concerns over terrorism, regional stability, and maintaining peace along their borders. They sometimes collaborate on security issues while remaining vigilant about each other’s military activities.
8. Cultural Exchanges: Cultural exchanges and people-to-people interactions between India and China help build understanding and goodwill between the two nations.
9. International Relations: India and China’s stances on global issues often differ, but they also cooperate on certain international platforms, such as BRICS (Brazil, Russia, India, China, and South Africa) and the Shanghai Cooperation Organization (SCO).
Overall, India-China relations are characterized by a mix of cooperation, competition, and occasional tensions. Managing their differences and finding common ground is crucial for regional stability and prosperity.Both nations recognize the importance of engaging with each other constructively while safeguarding their respective national interests.
![]()
Question 15.
Why are the working conditions of workers in unorganised sector not improving even today? Suggest suitable measures.
Answer:
The working conditions of workers in the unorganized sector often do not improve due to various reasons:
I. Lack of Regulation: The unorganized sector operates outside formal labor regulations, making it challenging to enforce labor standards and ensure better working conditions.
2. Informal Nature: Many unorganized sector jobs lack formal contracts and social security benefits, leaving workers vulnerable to exploitation and, uncertain employment.
3. Limited Skill Development: Workers in the unorganized sector often have, limited access to skill development and training programs, hindering their ability to seek higher-paying and safer jobs.
4. Inadequate Awareness: Many workers in the unorganized sector are unaware of their rights and labor laws, making them susceptible to unfair treatment and low wages.
5. Market Pressures: The informal nature of the unorganized sector makes it susceptible to market fluctuations, affecting wages and job stability.
6. Lack of Collective Bargaining Power: Individual workers in the unorganized sector often lack the bargaining power to demand better working conditions and wages.
Suggested Measures to Improve Working Conditions:
1. Legal Reforms: Strengthen labor laws and regulations to cover workers in the unorganized sector, ensuring minimum wages, social security, and safe working conditions.
2. Skill Development: Invest in skill development programs to enhance the employability of unorganized sector workers and provide opportunities for better-paying jobs.
3. Social Security Nets: Introduce social ‘security schemes tailored for unorganized sector workers to provide them with health benefits, insurance coverage, and old-age pensions.
4. Awareness Campaigns: Conduct awareness campaigns to educate unorganized sector workers about their rights and entitlements.
5. Worker Organizations: Facilitate the formation of worker cooperatives and associations to enhance collective bargaining power and negotiate for better working conditions.
6. Microfinance and Access to Credit: Promote microfinance initiatives and improve access to credit for workers in the unorganized sector to help them start and expand their own enterprises.
7. Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR): Encourage private companies to engage in CSR activities that support the welfare and skill development of unorganized sector workers.
8. Monitoring and Enforcement: Strengthen enforcement mechanisms to ensure compliance with labor laws and penalize violators.
9. Government Schemes: Extend government welfare schemes to cover unorganized sector workers and ensure their inclusivity.
Improving the working conditions of workers in the unorganized sector requires a multi-faceted approach involving legal reforms, social policies, and public-private partnerships. It demands a collective effort from the government, employers, workers, and civil society to create a more equitable and sustainable work environment for all.
Question 16.
Read the following paragraph and write your opinion.
Land reforms were however implemented in a halfhearted manner across India. While the Zamindari system was abolished, redistribution of land to the landless did not take place. The rich and powerful in the rural areas continued to control most of the land.
Answer:
Opinion: The paragraph highlights a significant issue With land reforms in India. While the abolishment of the Zamindari system was a positive step, the failure to effectively redistribute land to the landless population is concerning. This lack of proper implementation allowed the rich and powerful in rural areas to retain control over the majority of the land. Land reforms are essential to address historical íncqualities empower marginalized communities and promote equitable development. Without meaningful and comprehensive land redistribution, the benefits of land reforms may not reach those who need it the most. It is crucial for policymakers to prioritize effective implementation and ensure that land reforms are carried out in a more equitable and impactful manner to create a fairer and more inclusive society.
Question 17.
Locate the following on the outline map of India.
1) Maiwa plateau
2) River Godavari
3) Circar coast
4) The state with the lowest density of population
5) Chandigarh
6) Bihar.
Answer:
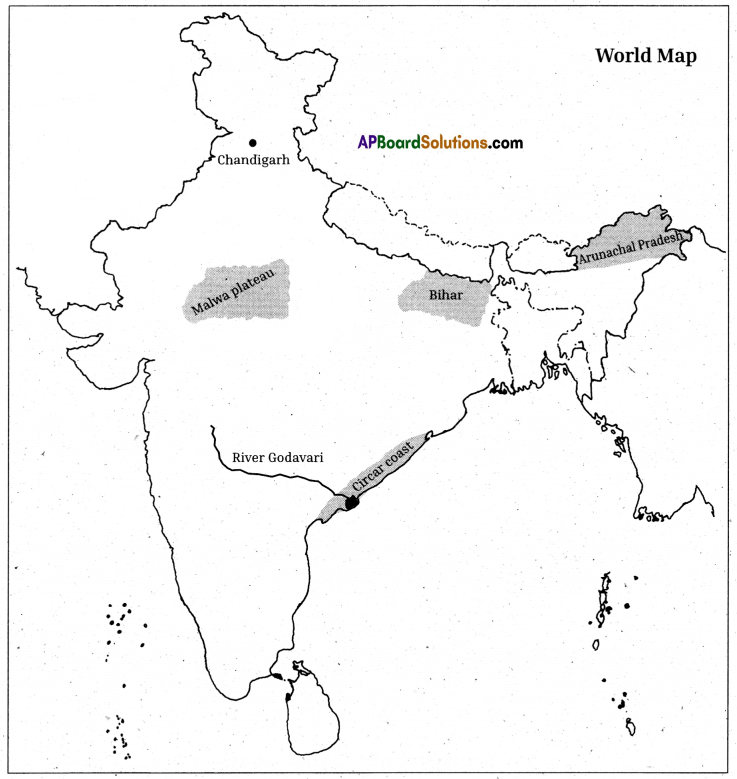
Question 18.
Observe the following graph and analyse it.
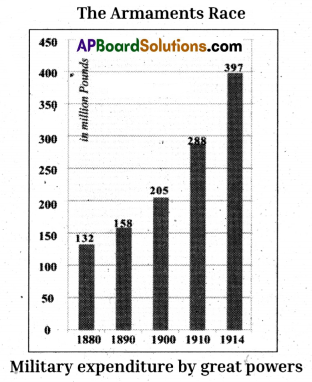
(Germany, Austria-Hungary, Great Britain, Russia, Italy and France 1880 – 1914)
(Source: The Times Atlas of World History, London 1978)
Answer:
- The graph shows that the military expenditure of the great countries has been increasing since 1880.
- During 1914, the weapons were prepared in large scale.
- Military expenditure increases for every 10 years because of armament race.
- Countries like Germany, Great Britain, Russia, Italy, and France are some countries that spend more money on weapons.
- Money spent on military expenditure in 1914 was 397 million pounds.
Part – B (20 Marks)
Instructions:
- Answer all questions.
- Each question carries 1 mark.
- Write the answers in the question paper itself.
- Marks are not given to corrected, dismissed, or erased answers.
Choose the correct option from the given four options and write the letter (A, B, C, and D) in CAPITAL LETTER in the brackets.
Question 1.
Match the following. ( )
| 1) Loo winds | A) Temperate zone |
| 2) North-East monsoons | B) Heavy rainfall to Coromandel coast |
| 3) The region to the north of the Tropic of Cancer | C) Hot winds blow in the northern plains |
| 4) South-West monsoons | D) Heavy rainfall along the West coast. |
A) 1 – A, 2-B, 3-C, 4-D
B) 1 – D, 2 C, 3-B, 4-A
C) 1-C, 2-B, 3-A, 4-D
D) 1-C, 2-B, 3-D, 4-C
Answer:
C) 1-C, 2-B, 3-A, 4-D
Question 2.
This is not an environmental movement. ( )
A) Chipko Movement
B) Greenpeace Movement
C) Meira Paibi Movement
D) Silent Valley Movement
Answer:
C) Meira Paibi Movement
Question 3.
There is a dispute between these two countries regarding the distribution of Ganga river waters. ( )
A) India – Pakistan
B) India – Bangladesh
C) India – Sri Lanka
D) India – Myanmar
Answer:
B) India – Bangladesh
Question 4.
Liberalization leads to ………….. . ( )
A) Trade barriers
B) Free Trade
C) Trade restrictions
D) More taxes
Answer:
B) Free Trade
Question 5.
The main allegation made by Punjab during the Punjab agitation was ………………… . ( )
A) Ignoring the role of the state in the development of the country.
B) Declaring Chandigarh as a Union Territory.
C) Claiming less water from Bhakranangal dam.
D) Recruiting fewer Sikhs into the army.
Answer:
A) Ignoring the role of the state in the development of the country.
![]()
Question 6.
Match the following. ( )
| 1) Hamlets | A) A group of houses within the revenue village. |
| 2) Class – 1 cities | B) Villages with defined borders. |
| 3) Metropolitan cities | C) Urban areas having population between 1 lakh and one million. |
| 4) Revenue villages | D) Cities having population between one million and 10 million. |
A) 1-ii. 2-i, 3-iii, 4-iv
B) 1-iii, 2-ii, 3-iv, 4-i
C) 1-i, 2-iv, 3-ii, 4-iii
D) 1-i, 2-iii, 3-iv, 4-ii
Answer:
D) 1-i, 2-iii, 3-iv, 4-ii
Question 7.
This is not the cause for reducing fertility of the soil. ( )
A) Unscientific use of chemical fertilisers
B) Excessive use of fertilisers and pesticides
C) Improper utilisation of natural resources
D) Use of organic fertilisers
Answer:
D) Use of organic fertilisers
Question 8.
The northern edge of Deccan plateau is ( )
A) Nilgiri mountains
B) Satpura mountains
C) Himalayan mountains
D) Western Ghats
Answer:
B) Satpura mountains
Question 9.
The Election Code of Conduct will come into force ……………… . ( )
A) After the announcement of election result.
B) At the time of commencement of election schedule.
C) After the submission of nominations.
D) On the day of polling.
Answer:
B) At the time of commencement of election schedule.
Question 10.
In China, the Communist Party of China worked for land reforms and …………………… . ( )
A) Encouraging the rich.
B) To participate landlords in the politics.
C) Discouraging the poor peasants.
D) Spreading literacy.
Answer:
D) Spreading literacy.
Question 11.
The first Five Year Plan gave priority to ………………. . ( )
A) Agriculture
B) Industries
C) Railways
D) Aviation
Answer:
A) Agriculture
12. The following is not the working capital. ( ).
A) Seeds
B) Pesticides
C) Machines
D) Chimicals fertilisers
Answer:
C) Machines
Question 13.
The Commission formed to study the developments in Andhra Pradesh and submit the report to the Centre is ……………….. . ( )
A) Justice Sri Krishna Commission
B) Dr. Fazal Mi Commission
C) Mandai Commission
D) Kothari Commission.
Answer:
A) Justice Sri Krishna Commission
Question 14.
Find Out the odd one regarding services. ( )
A) Brokers
B)’ Saving accounts
C) Banks
D) Handicrafts
Answer:
D) Handicrafts
Question 15.
This is a tributary of river Ganga. ( )
A) Dihang
B) Beas
C) Tapati
D) Chambal
Answer:
D) Chambal
Question 16.
As per 2011 Census, the male literacy is …………………. . ( )
A) 82%
B) 65%
C) 74%
D) 12%
Answer:
A) 82%
Question 17.
Match the following.
| 1) Announcement of partition of country | A) M.S. Khan |
| 2) A Naval Central Strike Committee | B) Mahammed Iqbal |
| 3) Need for North-West Muslim State | C) Jawaharlal Nehru |
| 4) A resolution on the rights of minorities | D) Lord Mount Batten |
A) 1-D, 2-A, 3-B, 4-C
B) 1-C, 2-A, 3-B, 4-D
C) 1-D,2-A,3-C,4-B
D) 1-B,2-D,3-A,4-C
Answer:
A) 1-D, 2-A, 3-B, 4-C
Question 18.
Imposing taxes on imported goods leads to ……………….. . ( )
1) Imported goods are cheaper.
2) Beneficial to domestic producers.
3) Prices of imported goods rise.
A) 1 and 2
B) 2 and 3
C) 1 and 3
D) 1,2 and 3
Answer:
B) 2 and 3
Question 19.
The present President of India is …………………. . ( )
A) Ramnath Kovind
B) Droupadi Murmu
C) Venkaiah Naidu
D) Chandra Shekhar Rao
Answer:
B) Droupadi Murmu
![]()
Question 20.
The present Secretary General of UNO is ……………… . ( )
A) Kofi Annan
B) U Thant
C) Ban Ki-Moon
D) Antonio Guterres
Answer:
D) Antonio Guterres