The strategic use of TS 10th Class Maths Model Papers Set 4 can significantly enhance a student’s problem-solving skills.
TS SSC Maths Model Paper Set 4 with Solutions
Time: 3 Hours
Maximum Marks: 80
General Instructions:
- Answer all the questions under Part – A on a separate answer book.
- Write the answers to the questions under Part – B on the question paper itself and attach it to the Part – A
Part – A (60 Marks)
Section – I (6 × 2 = 12 Marks)
Note :
- Answer ALL the following questions.
- Each question carries 2 marks.
Question 1.
If A = {x : x ∈ N, x < 5} and B = {x : x ∈ N, 2 < x < 7}, then draw Venn diagram for A∪B.
Solution:
A = {1, 2, 3, 4}
B = {3, 4, 5, 6}
A∪B Venn diagram
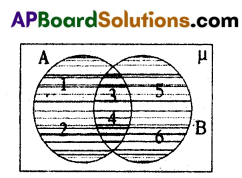
A∪B {1, 2, 3, 4, 5 , 6}
Question 2.
Check whether the given pair of linear equations x + 2y – 4 = 0 and 2x + 4y – 12 = 0 is intersecting lines or parallel lines.
Solution:
Given pair of linear equations
x + 2y – 4 = 0
a1 = 1, b1 = 2, c1 = -4
2x + 4y – 12 = 0
a2 = 2, b2 = -4, c2 -12
\(\frac{a_1}{a_2}\) = \(\frac{1}{2}\), \(\frac{b_1}{b_2}\) = \(\frac{2}{4}\) = \(\frac{1}{2}\), \(\frac{c_1}{c_2}\) = \(\frac{-4}{-12}\) = \(\frac{1}{3}\)
\(\frac{a_1}{a_2}\) = \(\frac{b_1}{b_2}\) ≠ \(\frac{c_1}{c_2}\)
∴ Given lines are parallel lines.
![]()
Question 3.
Give one example each for an Arithmetic progression and a Geometric progression.
Solution:
Examples for an Arithmetic progression and Geometric progression
A.P. : 3, 5, 7, 9, 11, ……………
G.P. : 3, 6, 12, 24, 48, ………….
Question 4.
Find the probability of getting a ‘vowel’ if a letter is chosen randomly from English alphabet.
Solution:
Total number of alphabets in English n(S) = 26
Number of Vowel in English alphabets n(V) = 5
∴ P(V) = \(\frac{\mathrm{n}(\mathrm{V})}{\mathrm{n}(\mathrm{S})}\) = \(\frac{5}{26}\)
Question 5.
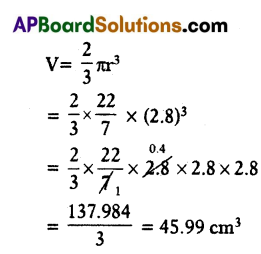
Find the volume of a hemispherical bowl whose radius is 2.8 cm.
Solution:
Radius of hemispherical bowl r = 2.8 cm
Volume of the hemispherical bowl
Question 6.
In ΔABC, DE||BC. If AO : DB = 2 : 3, AE = 3x + 1 and EC = 5x, then find the value of ‘x’.
Solution:
Given in ΔABC, DE||BC, AD : DB = 2 : 3, AE = 3x + 1, EC = 5x
∴ \(\frac{\mathrm{AD}}{\mathrm{DB}}\) = \(\frac{\mathrm{AE}}{\mathrm{EC}}\)(BPT)
\(\frac{2}{3}\) = \(\frac{3 x+1}{5 x}\)
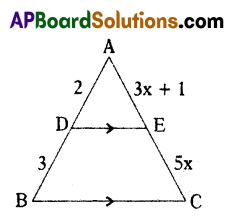
10x = 3(3x + 1)
10x = 9x + 3
10x – 9x = 3
∴ x = 3
![]()
Section – II (6 × 3 = 18 Marks)
Note :
- Answer ALL the following questions.
- Each question carries 3 marks.
Question 7.
If log (1 + tan θ + sec θ) + log (1 + cot θ – cosec θ) = log k (0°< θ < 90°), then find the value of k.
Solution:
Given
log (1 + tan θ + sec θ) + log (1 + cot θ – cosec θ) = log k
= log (1 + tan θ + sec θ) log (1 + cot θ – cosec θ) = log k (∵ log x + log y = log xy)
∴ (1 + tan θ + sec θ) (1 + cot θ – cosec θ) = k
Now
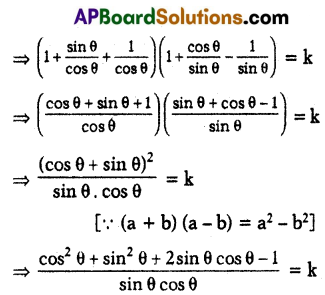
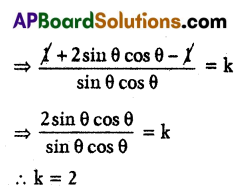
Question 8.
Write the formula for mode of a grouped data and explain each term of it.
Solution:
Mode = l + \(\left[\frac{\mathrm{f}_1-\mathrm{f}_0}{2 \mathrm{f}_1-\mathrm{f}_0-\mathrm{f}_2}\right]\) × h
l = lower boundary of mode class
f1 = frequency of mode class
f0 = frequency of preceding class to the mode class
f2 = frequency of succeeding class to the mode class
h = size of class
Question 9.
Prove that 2 + 3√5 is an irrational number.
Solution:
Let us assume that 2 + 3√5 is a rotational number.
∴ 2 + 3√5 = \(\frac{a}{b}\), (b ≠ 0) and a, b are co-primes.
3√5 = \(\frac{a}{b}\) – 2 = \(\frac{a-2 b}{b}\)
∴ √5 = \(\frac{a-2 b}{3 b}\)
Since a, b are integers \(\frac{a-2 b}{3 b}\) is rational number. So √5 is rational number.
This contradicts the fact that √5 is an irrational number.
Hence 2 + 3√5 is an irrational number.
Question 10.
Prove that x2 + 2x + 1 divides x4 – 2x3 – 4x2 + 2x + 3 exactly.
Solution:
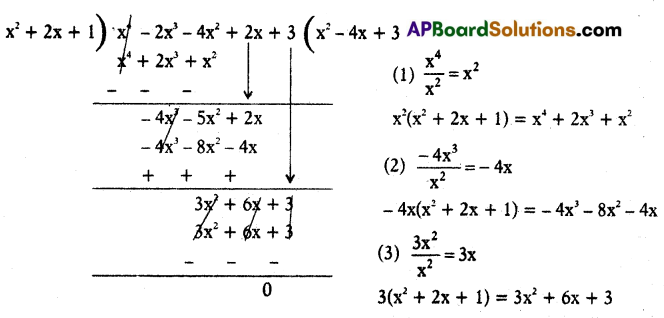
Remainder (x) = 0
∴ x2 + 2x + 1 divides x4 – 2x3 – 4x2 + 2x + 3.
Question 11.
In a circle of radius 3.5cm, a chord subtends a right angle at the centre. Find the area of the corresponding
major segment. (Take π = \(\frac{22}{7}\))
Solution:
Radius of the circle r = 3.5 cm
Sector angle at centre x° = 90°
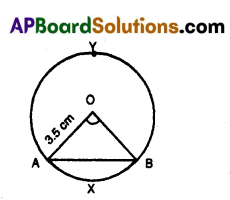
Area of minor segment AXB = Area of Sector AOBXA – Area of ΔAOB
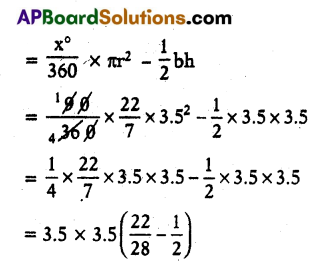
= 12.25 × \(\frac{22-14}{28}\)
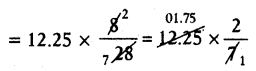
= 3.5 cm2
∴ Area of major segment AYB = Area of circle – Area of minor segment
= \(\frac{22}{7}\) × (3.5)2 – 3.5 [Area of Circle = πr2]
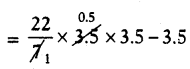
= 38.5 – 3.5 = 35cm2
Another Method:
Area of Major segment = Area of Major sector AYBOA + Area of ΔAOB
= \(\frac{270^{\circ}}{360}\) × πr2 + \(\frac{1}{2}\)bh
= \(\frac{3}{4}\) × \(\frac{22}{7}\) × 3.5 × 3.5 + \(\frac{1}{2}\) × 3.5 × 3.5
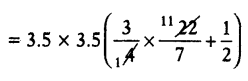
= 3.5 × 3.5 × (\(\frac{33}{7}\) + \(\frac{1}{2}\))
= 3.5 × 3.5 × \(\frac{33+7}{14}\)
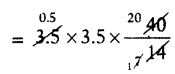
= 35 cm2
∴ Area of major segment = 35 cm2
![]()
Question 12.
Find the area of the triangle whose vertices are (5, 2) (3, -5) and (-3, -4).
Solution:
Let A (5, 2), B(3, -5) and C(-3, – 4)
Area of ΔABC
= \(\frac{1}{2}\)|x1(y2 – y3) + x2(y3 – y1) + x3(y1 – y2)|
= \(\frac{1}{2}\)|5[- 5 – (- 4)] + 3[- 4 – 2] + (- 3) [2 – (- 5)]
= \(\frac{1}{2}\)|5(- 1) + 3(- 6) – 3(7)|
= \(\frac{1}{2}\)|- 5 – 18 – 21 | = \(\frac{1}{2}\)|- 44|
= \(\frac{1}{2}\) × 44 = 22
∴ Area of ΔABC = 22 sq. units.
Section – III (6 × 5 = 30 Marks)
Note :
- Answer all the following questions.
- In this section, every question has internal choice. Answer any one alternative.
- Each question carries 5 marks.
Question 13.
A) Find mean for the following data.

Solution:
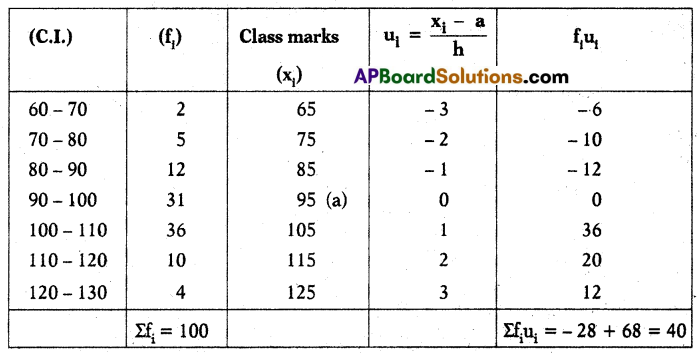
a = 95, Σfi = 100, Σfiui = 40
Mean \(\overline{\mathrm{x}}\) = a + \(\frac{\Sigma f_i u_i}{\Sigma f_i}\) × h
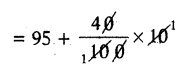
= 95 + 4 = 99
Mean \(\overline{\mathrm{x}}\) = 99
(OR)
B) The angle of elevation of the top of a building from the foot of the tower is 30° and the angle of elevation of the top of the tower from the foot of the building is 60°. If the tower is 100m high, then find the height of the building.
Solution:
AB = Height of the tower = 100 m
CD = Height of the building
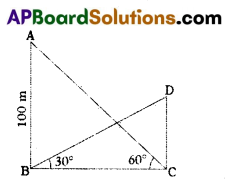
In ΔABC,
tan 60° = \(\frac{\mathrm{AB}}{\mathrm{BC}}\)
√3 = \(\frac{100}{B C}\) ⇒ BC = \(\frac{100}{\sqrt{3}}\) ……….. (1)
In ΔDCB,
tan 30° = \(\frac{\mathrm{CD}}{\mathrm{BC}}\)
\(\frac{1}{\sqrt{3}}\) = \(\frac{\mathrm{CD}}{\mathrm{BC}}\) ⇒ √3 CD = BC
√3 CD = \(\frac{100}{\sqrt{3}}\) [From (1))]
CD = \(\frac{100}{\sqrt{3} \times \sqrt{3}}=\frac{100}{3}\)
∴ Height of the building CD = \(\frac{100}{3}\)m = 33\(\frac{1}{3}\)m
Question 14.
A) Prove that \(\frac{\tan \theta+\sec \theta-1}{\tan \theta-\sec \theta+1}=\frac{1+\sin \theta}{\cos \theta}\)
Solution:
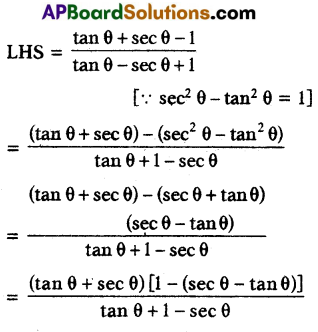
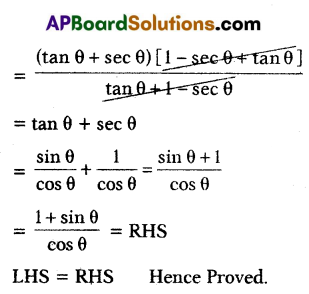
(OR)
B) Show that the quadrilateral obtained by joining the points (-2, 4) (-6, -2) (-2, -8) and (2, -2) is a Rhombus.
Solution:
Let A(-2, 4), B(-6, -2), C(-2, -8) and D(2, -2)
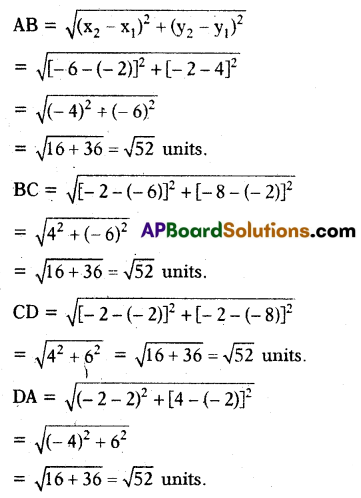
∴ AB = BC = CD = DA
ABCD is a Rhombus.
![]()
Question 15.
A) Solve \(\frac{2}{x-1}+\frac{3}{y+1}\) = 2 and \(\frac{3}{x-1}+\frac{2}{y+1}\frac{3}{x-1}+\frac{2}{y+1}\) = \(\frac{13}{6}\) where x ≠ 1, y ≠ 1.
Solution:
Given
\(\frac{2}{x-1}+\frac{3}{y+1}\) = 2 and \(\frac{3}{x-1}+\frac{2}{y+1}\frac{3}{x-1}+\frac{2}{y+1}\) = \(\frac{13}{6}\)
Let \(\frac{1}{x-1}\) = a and \(\frac{1}{y+1}\) = b then the given equations
2a + 3 b = 2 …………… (1)
3a + 2b = \(\frac{13}{6}\) = 18a + 12b = 13 …………. (2)
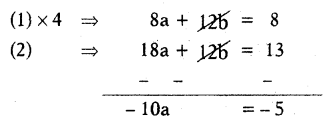
10 a = 5
a = \(\frac{5}{10}\) = \(\frac{1}{2}\)
a = \(\frac{1}{2}\) substitute in (1)
2(\(\frac{1}{2}\)) + 3b = 2
1 + 3b = 2
3b = 1
∴ b = \(\frac{1}{3}\)
But a = \(\frac{1}{x-1}\) = \(\frac{1}{2}\),
∴ x – 1 = 2
x = 3
b = \(\frac{1}{y+1}\) = \(\frac{1}{3}\)
∴ y + 1 = 3
y = 3 – 1
y = 2
∴ Solutions x = 3, y = 2
(OR)
B) Cards marked with numbers 2 to 101 are placed in a box. They are mixed thoroughly and one card is selected randomly from the box. Find the probability that the number on the selected card is
(i) an even number
(ii) a number less than 14
(iii) a number which is a perfect square
(iv) a prime number less than 20
Solution:
Total number of cards in a box = 100
∴ Number of total outcomes n(S) = 100
i) Number of even number marked cards = 50
∴ Number of favourable outcomes to select an even number n(E) = 50
∴ The probability to select an even number card P(E) = \(\frac{\mathrm{n}(\mathrm{E})}{\mathrm{n}(\mathrm{S})}\) = \(\frac{50}{100}\) = \(\frac{1}{2}\)
ii) Number of favourable outcomes to select a number less than 14
n(F) = 12
F = (2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13}
∴ The probability to select a number less than P(F) = \(\frac{\mathrm{n}(\mathrm{F})}{\mathrm{n}(\mathrm{S})}\) = \(\frac{12}{100}\) = \(\frac{3}{25}\)
iii) Number of favourable outcomes to select a number which is a perfect square n(G) = 9
G = {4, 9, 16, 25, 36, 49, 64, 81, 100}
∴ The probability to select a perfect square number P(G) = \(\frac{\mathrm{n}(\mathrm{G})}{\mathrm{n}(\mathrm{S})}\) = \(\frac{9}{100}\)
iv) Number of favourable outcomes to select a prime number less than 20
n(H) = 8
H = (2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, 17, 19}
∴ The probability to select a prime number less than 20
P(G) = \(\frac{\mathrm{n}(\mathrm{H})}{\mathrm{n}(\mathrm{S})}\) = \(\frac{8}{100}\) = \(\frac{2}{25}\)
![]()
Question 16.
A) A metallic vessel is in the shape of a right circular cylinder mounted over a hemisphere. The common diameter is
56 cm and the height of the cylindrical part is 21cm. Find the capacity of the vessel. (Take π = \(\frac{22}{7}\))
Solution:
Common diameter of cylinder and hemisphere d = 56 cm
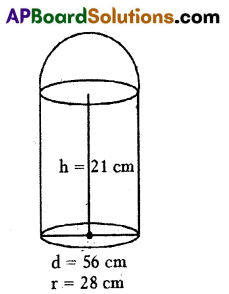
∴ Common radius r = 28 cm
Height of the cylinder h = 21 cm
∴ Volume the vessel = Volume of cylinder + Volume of hemisphere.
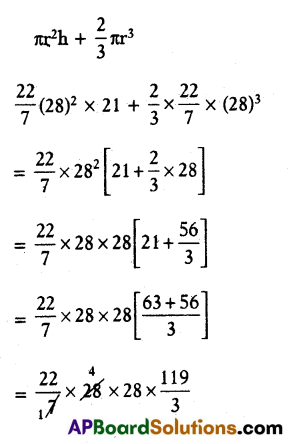
∴ Volume the vessel = \(\frac{293216}{3}\)
= 97738.66 cm2
(OR)
B) A motor boat travels a distance of 18 km upstream and travels back to reach the starting point. Fôr up and down
trip, It takes 12 hours. If the speed of the stream is 2 kmph, then find the speed of the boat in still water. (Assume that the motor boat maintains a constant speed)
Solution:
Let the speed of the boat in still water = x km/h
Speed of the stream = 2 km/h
Now the speed of the boat in upstream = x – 2 km/h
Speed of the boat in downstream = x + 3 km/h
Distance d = 18 km
By the problem total time for the trip = 12 hours
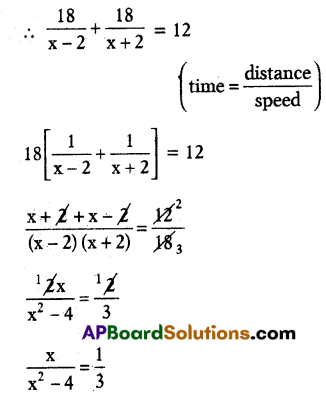
∴ x2 – 4 = 3x
x2 – 3x – 4 = 0
x2 – 4x + x – 4 = 0
x(x – 4) + 1(x – 4) = 0
(x – 4)(x + 1) = 0
∴ x – 4 = 0 (or) x + 1 = 0
x = 4 (or) x = -1
But x > 0
∴ x = 4
Speed of the boat in still water = 4 km/h
Question 17.
A) Draw the graph of the polynomial p(x) = x2 – x – 6 and then find its zeroes from the graph.
Solution:
Given that y = x2 – x – 6
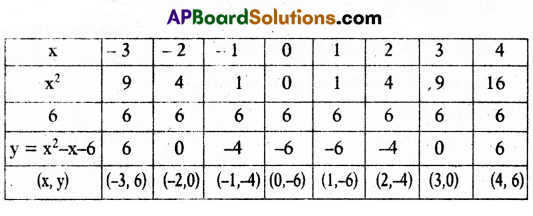
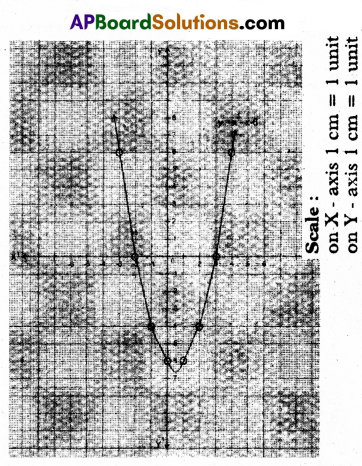
Result : From the graph we observe that 3 and -2 are the intersecting points of X – axis.
So, the zeroes of given quadratic polynomial are 3 and -2.
(OR)
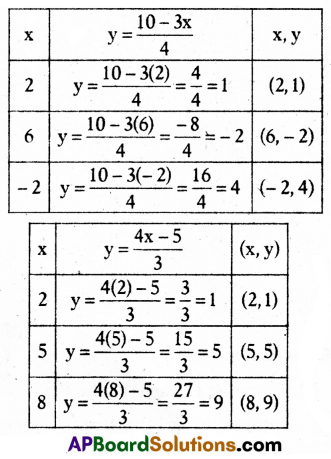
B) Solve the equations graphically
3x + 4y = 10 and 4x – 3y = 5.
Solution:
Given two equations 3x + 4y = 10 and 4x – 3y = 5
3x + 4y = 10
4y = 10 – 3x
y = \(\frac{10-3 x}{4}\)
4x – 3y = 5
– 3y = 5 – 4x
3y = 4x – 5
y = \(\frac{4 x-5}{3}\)
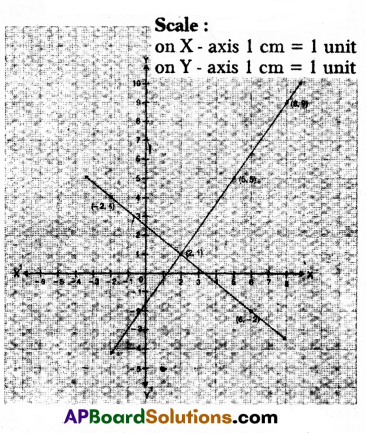
Given two lines intersect at (2, 1)
So the solution is x = 2, y = 1
![]()
Question 18.
A) Construct a triangle PQR, in which PQ = 4 cm, QR = 6 cm and ∠PQR = 60°. Construct another triangle similar to ΔPQR, with its sides equal to \(\frac{4}{3}\) times of the corresponding sides of the triangle PQR.
Solution:
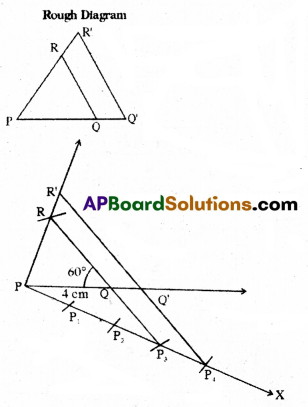
Construction Steps:
- Construct a triangle PQ R with the given measurements PQ = 4 cm, QR = 6 cm, ∠PQR = 60°
- Draw a ray \(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{PQ}}\) making an acute angle with PQ,
- Locate 4 points P1, P2, P3, P4 on PX. So that P1P2 = P2P3 = P3P4 = P4P1.
- Join P3 to Q, Draw a line form P4 parallel to QP3. It intersect PQ at Q’.
- Draw a line through Q’ parallel to QR intersect PR at R’
- ΔPQ’R’ is required triangle.
(OR)
B) Draw a circle of radius 5 cm. From a point 9 cm away from its centre, construct a pair of tangents to the circle.
Solution:
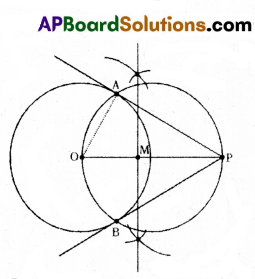
- Construct a circle with a radius of 5 cm.
- Trace the point ‘P’ in the exterior of the circle.
- Construct a perpendicular bisector to OP which meets at M.
- Draw a another circle with a radius of MP or MO and M as centre. It intersect previous circle at the points A and B.
- Join P, A and P B.
- PA, PB are the required tangents.
Part – B (20 Marks)
Note :
- Answer all the questions.
- Each question carries 1 mark.
- Answers are to be written in the Question paper only.
- Marks will not be awarded in any case of over writing, rewriting or erased answers.
Note : Write the capital letters (A, B, C, D) showing the correct answer for the following questions in the brackets provided against them. (Marks : 20 × 1 = 20)
Question 1.
The value of k for which the system of equations 4x + y = 3 and 8x + 2y = 5k has infinite solutions is
A) \(\frac{-5}{6}\)
B) \(\frac{-6}{65}\)
C) \(\frac{5}{6}\)
D) \(\frac{6}{5}\)
Answer:
D) \(\frac{6}{5}\)
![]()
Question 2.
Among the following, a statement that is NOT true is
A) sin θ = \(\sqrt{1-\cos ^2 \theta}\)
B) sec2 θ – tan2 θ = 1
C) cos θ. cosec θ = 1
D) tan θ. cot θ = 1
Answer:
C) cos θ. cosec θ = 1
Question 3.
The logarithmic form of 7 = 3x is
A) log3x = 7
B) log73 = x
C) log7x = 3
D) log37 = x
Answer:
D) log37 = x
Question 4.
The decimal form of \(\frac{3}{8}\) is
A) 3.75
B) 0.365
C) 0.375
D) 0.0375
Answer:
C) 0.375
Question 5.
If 72, 63, 54,………… is an Arithmetic progression, then the terhithat becomes zero in it
is
A) 11th
B) 10th
C) 9th
D) 8th
Answer:
C) 9th
Question 6.
The equal set of A = {x : x is a letter of the word “FOLLOW”} is
A) {f, o, l, l, o, w}
B) {f, o, l, l, w)
C) {f, l, o, w}
D) (f, o, l, o, w}
Answer:
C) {f, l, o, w}
Question 7.
If n(A – B) = 5, n(B – A) = 7 and n(A∩B) = 3, then n(A ∪B) is
A) 9
B) 12
C) 10
D) 15
Answer:
D) 15
![]()
Question 8.
Among the following, the value which is not possible for the probability of an event is
A) \(\frac{1}{3}\)
B) 0.5
C) 25%
D) \(\frac{4}{3}\)
Answer:
D) \(\frac{4}{3}\)
Question 9.
Among the following, a linear polynomial is
A) 3x2 + 2x – 4
B) 2x + 3
C) 5
D) x3 – 3x2 + 7
Answer:
B) 2x + 3
Question 10.
IF p(x) = x2 – 2x + 2, then the value of p(0) is
A) 4
B) 0
C) 2
D) -2
Answer:
C) 2
Question 11.
The value of Discriminent of x2 + x + 1 = 0 is
A) 3
B) 4
C) -4
D) -3
Answer:
D) -3
Question 12.
A quadratic equation whose roots are -2 and -3 is
A) x2 – 5x – 6 = 0
B) x2 + 5x + 6 = 0
C) x2 + 5x – 6 = 0
D) x2 – 5x + 6 = 0
Answer:
B) x2 + 5x + 6 = 0
Question 13.
If the product of the first 5 terms of a Geometric progression is 243, then its third term is
A) 9
B) 27
C) 3
D) 1
Answer:
C) 3
![]()
Question 14.
LCM of numbers 27 × 34 × 7 and 23 × 34 × 11 is
A) 23 × 34
B) 27 × 34
C) 27 × 34 × 7 × 11
D) 23 × 34 × 7 × 11
Answer:
C) 27 × 34 × 7 × 11
Question 15.
In an Arithmetic progression nth term is an = a + (n – 1 )d. In this formula “d” represents
A) Number of terms
B) nth term
C) First term
D) Common difference
Answer:
D) Common difference
Question 16.
In ΔABC, if ∠C = 30°, AB = 1 unit, then AB : AC : BC is
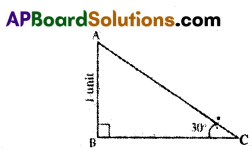
A) 1 : 2 : 3
B) 3 : 2 : 1
C) √3 : 2 : 1
D) 1 : 2 : √3
Answer:
D) 1 : 2 : √3
Question 17.
If the radius of a cylinder is doubled and its height is halved, then the volume of the new cylinder formed is
A) 4 times the volume of the first cylinder
B) 3 times the volume of the first cylinder
C) 2 times the volume of the first cylinder
D) Volume remains the same
Answer:
C) 2 times the volume of the first cylinder
Question 18.
E and \(\overline{\mathbf{E}}\) are two complementary events in a random Experiment. If P( \(\overline{\mathbf{E}}\)) = 0.07, then the value of P(E) is
A) 0.3
B) 0.93
C) 0.03
D) 0.83
Answer:
B) 0.93
![]()
Question 19.
The mean of 9 observations is 45. In doing so, if an observation was wrongly taken as 42 for 24, then the correct mean of the data is
A) 34
B) 43
C) 37
D) 45
Answer:
B) 43
Question 20.
Base radii and heights of a cylinder and a cone are equa}. If the volume of cone is 9 cubic units, then the volume of the cylinder is
A) 27 cubic-units
B) 18 cubic-units
C) 9 cubic-units
D) 36 cubic-units
Answer:
A) 27 cubic-units