Telangana SCERT 10th Class Biology Study Material Telangana 3rd Lesson Transportation Textbook Questions and Answers.
TS 10th Class Biology 3rd Lesson Questions and Answers Telangana – Respiration
Question 1.
What is transport system? How does this help the organism?
Answer:
1. To lead a normal daily life, we need several items such as food grains, vegetables, fruits, clothes, medicines, fuel, electricity, etc. Most of these are produced at some other place and are transported to the place, where we live.
2. We might have observed goods being transported daily by road, rail and some times ships and aeroplanes. If the transport of these items is stopped, our routine life becomes disturbed and we will have to face many difficulties.
3. A lot of waste material is produced in our homes, in shops and in industries. These should be collected and transported to a far off place for disposal. If the transport system fails, our surroundings become dirty, un-hygienic and our life becomes miserable. Transport system has become an essential part of our life.
4. Similarly transport systems are present in the bodies of all the organisms and they are essential to keep the cells alive and healthy. Failure of these transport systems would result in a disease.
5. The system which transports the materials from where they are produced and to the place where they are needed is called transport system.
6. Cells of our body require various substances to live, grow and carry out their activities. So they should be supplied with food and substances such as amino acids, fatty acids, vitamins and minerals. Cells also require water. All the substances are derived from the food we eat and water we drink. To supply all these materials, we need a transport system.
7. At the same time undigested materials should be removed from the digestive system.
8. Oxygen is required for the food to be oxidised. Oxygen is taken into the lungs and from here it should be transported to every cell in the body. Carbon dioxide produced during oxidation process should be collected and transported to the lungs for elimination.
9. Several waste materials produced in the cells are to be collected and are transported to various sites in the body for disposal.
10. Hormones are the chemicals which control and co-ordinate the functions in the body. They are produced by endocrine glands present at different locations in the body and work at different places. Therefore hormones are to be transported.
![]()
Question 2.
What is the relationship between blood and plasma?
Answer:
- Blood is a red coloured liquid which circulates in our body. Blood is red due to the presence of red pigment haemoglobin in its red cells.
- Blood is fluid connective tissue which consists of plasma, red blood cells, white blood cells and blood platelets.
- The liquid part of the blood is called plasma. Plasma is a colourless liquid which consists mainly of water with many substances dissolved in it.
- Plasma contains about 90 percent of water.
- Plasma also contains dissolved substances such as proteins, digested food, hormones, salts, waste products, etc.
- Plasma carries all these dissolved substances from one part to another part in the body.
- Red blood cells, white blood cells and platelets are immersed in the liquid plasma of blood.
Question 3.
Which type of blood vessels carry blood away from the heart?
Answer:
The rigid vessels are called arteries which originate from the heart and supply blood to various organs in the body,
- Arteries, which starts from heart and supply oxygenated blood to various organs in the body. The biggest artery is the aorta
- Pulmonary artery carries blood to lungs
- Coronary artery supply blood to muscles of heart.
Question 4.
What are the three main types of blood vessels in the body?
Answer:
The three main types of blood vessels in the human body are ;
- Arteries
- Veins and
- Capillaries
Question 5.
Which is the largest artery in the body? Why is it the largest ?
Answer:
- The Aorta is the biggest artery in the human body.
- The Aorta is big in size because it has to supply oxygenated blood to all the body parts except lungs.
Question 6.
Which blood vessel carries blood for oxidation?
Answer:
Pulmonary artery carries blood to lungs for oxygenation.
Question 7.
Name the structures which are present in veins and lymph ducts and absent in arteries.
Answer:
Valves are present in veins and lymphatic ducts whereas they are absent in arteries.
![]()
Question 8.
What is the use of platelets?
Answer:
- Blood platelets play an important role in blood clotting.
- When the blood vessel is injured, the platelets collect at the site of the injury and form a plug.
- This reduces the loss of blood to some extent.
- They also release several factors into the blood which help in blood clotting and in the repair and healing of blood vessels.
Question 9.
Write differences between
a. systole – diastole
b. veins – arteries
c. xylem – phloem
Answer:
a.
| Systole | Diastole |
| 1) It is the contraction phase of the heart. | 1) It is the relaxation phase of the heart. |
| 2) During systole blood circulated through heart. | 2) During diastole blood flows in to all the body parts. |
| 3) Systolic pressure is higher and occurs during ventricular contraction. | 3) Diastolic pressure is lower and occurs during ventricular expansion. |
b.
| Veins | Arteries |
| 1) Moves towards the heart. | 1) Moves away from the heart. |
| 2) Collects blood from body organs. | 2) Distributes blood to the body organs. |
| 3) Blood pressure in veins is low. | 3) Blood pressure is high in arteries. |
| 4) Valves are present. | 4) Valves are absent. |
| 5) Carry deoxygenated blood, except pulmonary vein. | 5) Carry oxygenated blood except pulmonary artery. |
| 6) Veins start in blood capillaries. | 6) Arteries end in capillaries. |
| 7) They can be seen subcutaneously. | 7) They are deep-seated. |
c.
| Xylem | Phloem |
| 1) It transports water and minerals from roots to the apical parts of the plant. | 1) It transports food material from the leaves to growing parts of the plant. |
| 2) Xylem consists of tracheids, vessels, xylem fibres and xylem parenchyma. | 2) Phloem consists of sieve tubes, sieve cells, companion cells, phloem fibres and phloem parenchyma. |
| 3) Only xylem parenchyma is living. | 3) Sieve tubes, sieve cells, companion cells and phloem parenchyma are living. |
| 4) Tracheids, vessels, xylem fibres are dead tissues. | 4) Phloem fibres are dead tissues. |
| 5) Xylem gives mechanical strength to the plant. | 5) Phloem does not give mechanical strength to the plant. |
| 6) Conduction of water by xylem is unidirectional i.e., from roots to apical parts of the plant. | 6) Food material conduction is bidirectional i.e., from leaves to storage organs or growing parts or from storage organs to growing parts of plants. |
| 7) Xylem is star-shaped. | 7) Phloem is not in star-shaped. |
| 8) Xylem occupies the center of the vascular bundle. | 8) Phloem occurs on outer side of the vascular bundle. |
| 9) Tubular with hard walled cells. | 9) Tubular with soft walled cells. |
Question 10.
Explain the way how the plants absorb water from soil ?
Answer:
- Root hair plays an important role in absorption of water by osmosis.
- Root hairs grow out into the spaces between the soil particles and that the hairs are surrounded by moisture.
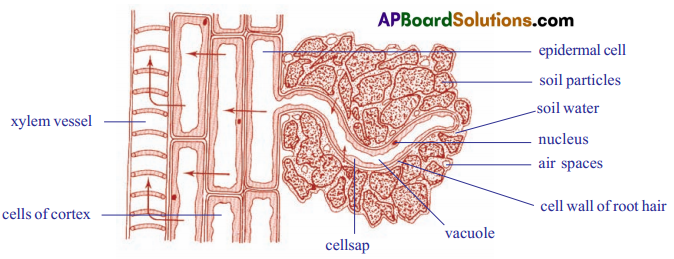
- The soil water is more dilute than that of the cell sap in the root hair, therefore water will pass into the vacuole of the root hair by osmosis.
- The entry of water dilutes the contents of the root hair vacuole so that it becomes weaker than its neighbour.
- Therefore water passes into the neighbouring cell which in turn becomes diluted, finally water enters the xylem vessels.
- As there are vast number of root hairs and root cells involved, a pressure in the xylem vessels develops which forces the water upwards.
- This total pressure is known as root pressure.
- Root pressure is not the main cause of movement of water in xylem but it is certainly one factor.
![]()
Question 11.
What is root pressure? How it is useful to the plant?
Answer:
- Root pressure is osmotic pressure within the cells of a root system that causes sap to rise through a plant stem to the leaves.
- Root pressure develops due to the absorption of water by roots and pushes the water upwards by few meters and is enough to supply water to leaves in small plants and small trees.
Question 12.
Phloem is a food source for some animals. How can you justify this statement?
Answer:
- Certain mammals scratch the bark of trees to get at the food stored in the phloem, especially during hard winters when food is scarce.
- Voles do this to young saplings at ground level and rabbits can do much damage to older ones.
- Aphids absorb so much sugar from the phloem that they cannot assimilate all of it and it passes out of the anus as a sticky syrup called honeydew.
Question 13.
Read the given para and name the parts of the heart.
We have observed that the heart is divided into four chambers by muscular structure. Any structure that divides two chambers is known as septum. Now let us try to name the septa present in the heart.
a. The septum that divides the two atria can be named as ………………………
Answer:
inter-atrial septum
b. The septum that divides the two ventricles can be named as ……………………….
Answer:
Inter-ventricular septum.
c. The septum that divides the atrium and ventricle can be named as ………………………
The holes that connect two chambers are called apertures. Let us try to name the apertures which connect the atria and ventricles.
Answer:
Inter-atrioventricular septum.
d. The aperture that connects the right atrium and right ventricle can be named as ……………………….
Answer:
Right atrioventricular aperture.
e. The aperture that connects the left atrium and left ventricle can be named ……………………….
Any structure that closes an aperture, and allows one way movement of materials is called as valve. Now let us name the valves that are present in the chambers of the heart.
Answer:
Left atrioventricular aperture.
f. The valve that is present between left atrium and left ventricle can be named as ……………………….
Answer:
Left atrioventricular valve (Bicuspid or Mitral valve).
g. The valve that is present between right atrium and right ventricle can be named as ……………………….
Answer:
Right atrioventricular valve (Trricuspid valve)
Question 14.
If the valves in veins of the legs fail to stop the flow of blood what could be the consequences of this failure?
Answer:
- Normally the blood that comes out from a wound clots in 3 – 6 minutes. But in some people due to vitamin K deficiency it takes more time to clot.
- Due to genetic defect blood may not coagulate. This type of defect is called Haemophilia.
- Haemophilia is a common disorder in the children who have born from the marriages between very close relatives.
Question 15.
What would happen if transpiration doesn’t take place in plants?
Answer:
If the process of transpiration stops in the plants, then the excess water inside the plants will not be able to come out. Hence the plants will burst due to the presence of excess of water inside them.
Question 16.
John made a stethoscope using a paper cup and plastic tube. Write down the procedure he followed.
Answer:
Preparation of stethoscope with paper cups, paper plate and plastic tube :
- Take paper cups and decorate with marker and allow them to dry before piercing a hole in the bottom.
- Thread a piece of plastic tube through the hole and tie a knot so that the cup hangs from the end.
- Cut the centre out of a flexible paper plate so you are left with a ring shape.
- Cut one side of the ring so you can open it and later place it around the child’s neck.
- Make a hole in the side of the ring opposite from the cut.
- Thread the unknotted end of the plastic tube from the cup through the hole in the paper plate ring and knot it so that the cup hangs.
- Place the stethoscope around one’s neck and allow him to try using it like a real doctor would.
Question 17.
How did scientists prove that the food is transported through the phloem?
Answer:
- Biologists studied about food transportation in plants with the help of Aphids. (Green fly)
- To obtain this juice an aphid pierces the plant tissue with it’s long needle like organ ‘proboscis’.
- When a feeding aphid is killed and the stem carefully sectioned, the proboscis only penetrates upto phloem sieve tube.
- The experiment can be done when an aphid is killed while in the act of feeding and the body is then carefully cut away, leaving the hollow proboscis still inserted into phloem.
- From the cut end of proboscis a fluid is found which contain sugars and amino acids.
![]()
Question 18.
What is your inference about experiments with aphids’?
Answer:
- Biologists studied about food transportation in plants with the help of aphids,
- Aphids feed on the plant juices of young stems.
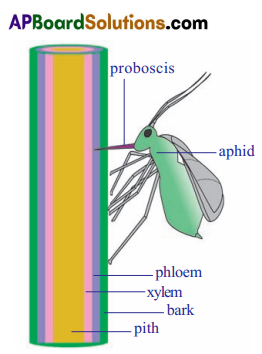
- Aphid uses its long needle-like organ “proboscis” to extract plant juices from phloem tissue.
- The proboscis of the Aphid only penetrates up to a phloem sieve tube.
- The juices extracted by aphid contains sugars and amino acids.
- Aphids absorb so much sugar from the phloem but cannot assimilate all of it and passes out of the body as a sticky syrup called honey dew.
Question 19.
Collect information about blood pressure of your school teachers or neighbours. Prepare a report on their health problems due to changes in blood pressure.
Answer:
| Name of the person | Blood pressure | Health condition |
| 1. Mr. Vijay | 120/80 | Normal |
| 2. Mrs. Kamala | 125/85 | Irritation, worried |
| 3. Mr. Raju | 140/90 | Fear, easily getting anger, high irritation, tiredness. |
| 4. Mrs. Chandu | 110/70 | Weakness, dizziness, fainting |
| 5. Mr. Rama Rao | 140/100 | Dizziness, fainting |
Question 20.
Draw a schematic diagram to explain single and double circulation. Write differences between them.
Answer:
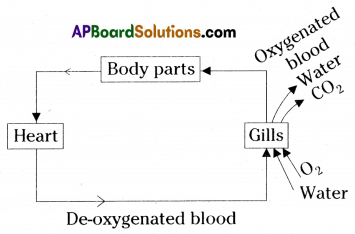
A. Single circulation:
Eg: Fish
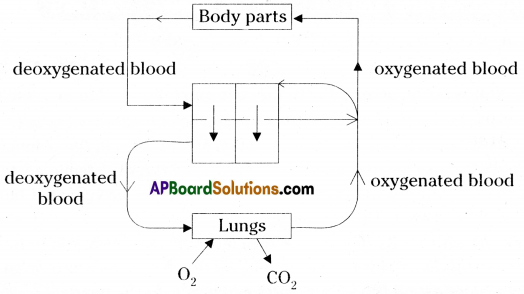
B. Double circulation:
| Single circulation | Double circulation |
| 1) Blood flows through heart only once for completing one circulation. It is called single circulation. Eg : Fishes |
1) If the blood flows through heart two times for completion of one circulation. It is called double circulation. Eg : Mammals, birds. |
Question 21.
Prepare a block diagram showing water absorption by roots to transpiration by leaves.
Answer:
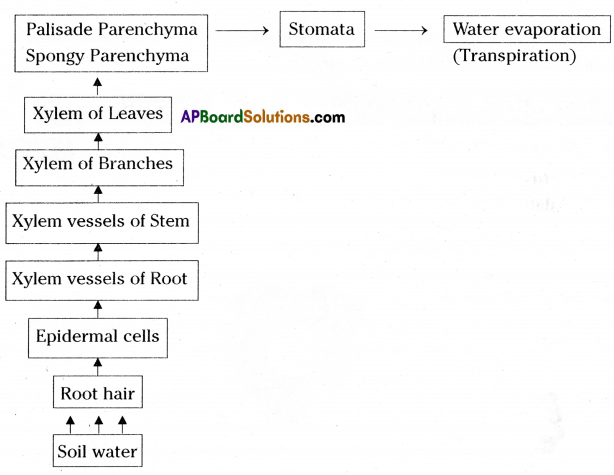
Question 22.
What can circulatory system in man be compared with?
Answer:
1. Transportation of blood in blood vessels can be compared with the (conduction of. transportation of water and food by xylem and phloem in the plants.
2. Heart pumps oxygenated blood into the large artery systemic aorta. This artery divides into arteries and arterioles and distributes oxygenated blood to all the body parts and ends with capillaries.
3. Veins start with capillaries. These form into venules, these join to form into veins. All these veins join to form superior and inferior venacava. These large veins collect deoxygenated blood from body parts and brings to the heart.
4. Heart pumps deoxygenated blood to lungs by pulmonary artery. For oxygenation and this oxygenated blood is sent to heart by pulmonary veins to heart. The circulation repeats.
5. This transportation is compared to transportation in plants. Root hairs absorb water and mineral salts from soil by osmosis. This water enters into xylem and transport to the stem and leaves by root pressure.
6. From leaves excess water is sent outside through stomata by transpiration as water vapour. This water vapour cools down and forms as rain. This is absorbed by roots and the cycle continues.
7. Transpiration helps in the formation of clouds and occurrence of rains. We can appreciate nature’s wonderful activities where it cannot be reached to the human brain.
![]()
Question 23.
What is Haemophilia?
Answer:
- Normally the blood that comes out from a wound clots in 3 – 6 minutes. But in some people due to vitamin K deficiency it takes more time to clot.
- Due to genetic defect blood may not coagulate. This type of defect is called Haemophilia.
- Haemophilia is a common disorder in the children who have born from the marriages between very close relatives.
Question 24.
Prepare a cartoon on heart beating?
Answer:
Heart: How am I beating?
Stethoscope: It is lubb dubh, Iubb duhh.

Question 25.
After reading this lesson what precautions would you suggest to your elders about edima.
Answer:
Edema is formally known as dropsy or hydroxy. This is abnormal accumulation of fluid in the interstitium, which is located beneath the skin or one or more cavities of the body. It is clinically shown as swelling.
Generally this occurs by inactivity and is clearer in elders, the lower part of the legs will be swollen.
Simple methods recommended by health care professionals are as follows :
1. Compression stocking : It reduces the fluid build up and improves circulation.
2. Movements : Sitting and standing for too long promotes the fluid flow into the legs and feet. Getting up and stretching the legs once in a while avoid fluids build up, specially travelling long in bus and train.
Leg exercise increases circulation while preventing fluid retention in the legs and feet moving and using the leg muscles helps pump excess fluids back to the heart People with swollen feet or legs, can keep the legs elevated above the level of heart for 30 minutes a day or 3 or 4 times a day.
3. Massage the effected areas with firm pressure towards the heart which helps to move the excess fluid away from swelling.
4. Low salt diet: Practising low salt diet can prevent or reduce swelling. Reducing the amount of salt including table salt in the diet may prevent swelling problems from reoccurring.
5. Avoid temperature changes : Temperature changes to very hot or cold can make edema worse. This can happen when going from hot doors into an air conditioner building or vice versa. Avoid hot baths, hot showers when swelling occurs.
6. Diuretics, medications help increase urine output, excrete water and sodium.
7. Reducing swelling symptoms : Diuretics can be used carefully because much use of medication can remove excess fluid too rapidly and lead to lower blood pressure or kidney impairment.
![]()
8. Homeopathetic treatment: It has not been proved effective by scientific research. People should discuss them with doctor before going by journey.
Choose the correct answer
Question 1.
The term cardiac refers to which organ in the body ?
A. Heart
B. Vein
C. Lymph
D. Capillary
Answer:
A. Heart
Question 2.
In which chamber of the human heart the blood is low in oxygen ?
A. Right atrium
B. Right ventricle
C. Left atrium
D. A and B
Answer:
D. A and B
Question 3.
Which structures of the heart control the flow of the blood ?
A. Arteries
B. Veins
C. Valves
D. Capillaries
Answer:
C. Valves
Question 4.
Which of the following statement is wrong ?
A. Serum is the liquid portion formed after blood clotting.
B. Lymph is the link between blood and tissues.
C. The xylem and phloem transport water and food in plants.
D. In insects closed type of circulatory system is seen.
Answer:
D. In insects closed type of circulatory system is seen.
Question 5.
An aphid pierces its proboscis into the ………… to get plant juices.
A. Xylem
B. Phloem
C. Cambium
D. Vascular bundle
Answer:
B. Phloem
TS 10th Class Biology 3rd Lesson Transportation Intext Questions
1 Mark Question and Answers :
Question 1.
Why do blood vessels (just below our skin) bulge on the side away from the heart
when the hand Is tied ? What do you understand from It?
Answer:
When the hand is tied the blood which is passing away from heart is stopped. So the blood vessels bulge. When a tie is knot on a hand there will be no flow of deoxygenated to the heart and the hand bulges on the side of below the knot…. which is away from the heart.
Question 2.
Discuss the differences between pulmonary artery and pulmonary vein.
Answer:
Pulmonary artery: Pulmonary artery carries deoxygenated blood from heart to lungs.
Valves are absent.
Pulmonary vein : Pulmonary vein carries oxygenated blood from lungs to heart. Valves are present.
Question 3.
How many times did your pointer touch body parts:’
Answer:
Onetime.
![]()
Question 4.
How many times did your pointer touch the heart?
Answer:
- One time
- Two times
Question 5.
How many times did the pointer touch respiratory organs?
Answer:
One time.
Question 6.
What is the mechanism behind this?
Answer:
Root absorb water due to Root Pressure and transpiration.
Question 7.
Are roots directly in contact with water?
Answer:
Yes. The root hairs are directly contact with water.
Question 8.
How is water absorbed?
Answer:
Water is absorbed due to Osmosis.
Question 9.
Is there any increase in the water level?
Answer:
Yes.
Question 10.
What is the role of xylem ?
Answer:
Water absorbed by roots is transported to all the parts of the plant by Xylem.
2 Mark Question and Answers :
Question 1.
Why do our legs swell?
Answer:
After overnight journey, in sitting position without moving, we feel that our feet (the lower part of the legs) swollen. This is called edema. Because the blood circulation becomes slow ¡n the lower portion and causes swelling.
Question 2.
Is there anything like that in plants which corresponds to circulatory system?
Answer:
Yes.
Vascular bundles are present in the plant parts which have xylem and phloem. These are responsible for the transportation of materials in plats.
Xylem transports water from roots to the leaves. Phloem transports food prepared by leaves to all the parts of the plant.
Question 3.
Artery walls are very strong and elastic. Why ?
Answer:
The walls of the arteries are strong and elastic. When the blood enters with a pressure
into arteries the walls will stretch and this enables the arteries to withstand the increase in the pressure, without bursting.
![]()
Question 4.
Why do we compare arteries like tree which divides into smaller and smaller branches ?
Answer:
Arteries carry oxygenated blood to the tissues. The largest aorta after comes outside of the heart, it divides into small branches called arteries and these still divide into small arterioles and supply oxygenated blood to the tissues which are present throughout the body. It looks like a tree with smaller and smaller branches and is compared to a tree.
Question 5.
The lumen size is bigger in vein when compared with artery. Why ?
Answer:
Veins are generally large in diameter, carry more blood volume and have thinner wall in proportion
4 Mark Question and Answers :
Question 1.
After reading the experiments by Harvey fill in the following table. Use the clues/options given in the first column.
| Structure / Function of blood vessel | Artery | Vein |
| 1. Thickness of walls (thick / thin) | ||
| 2. Valves (present / absent) | ||
| 3. Capacity to retain shape when blood is absent (can retain / can’t retain) | ||
| 4. Direction of blood flow (heart to organs / body organs to heart) |
||
| 5. Pressure in the vessel (low / high) | ||
| 6. Type of blood transported |
Answer:
| Strurcture / Function of blood vessel | Artery | Vein |
| 1. Thickness of walls (thick / thin) | Thick | Thin |
| 2. Valves (present / absent) | Absent | Present |
| 3. Capacity to retain shape when blood is absent (can retain / can’t retain) | Can retain | Can retain |
| 4. Direction of blood flow (heart to organs / body organs to heart) |
Heart to organs | Body organs to heart |
| 5. Pressure in the vessel (low / high) | High | Low |
| 6. Type of blood transported (oxygenated / de-oxygenated) | Oxygenated (except pulmonary artery) |
De-oxygenated (except pulmonary veins) |
TS 10th Class Biology 3rd Lesson Transportation Activities
Question 1.
How can you find out your pulse rate?
Answer:
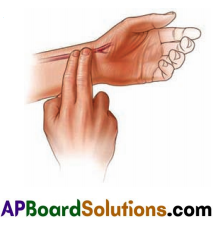
- Keep your index and middle fingers oil your wrist below the thumb as shown in the figure.
- You feel something pushing your fingers rhythmically UI) and down.
- Count the rhythm also called the pulse rate per minute.
- Now stand up and jog for one minute standing at the same place. Note the pulse for a minute.
|
S.No. |
Name of the person | Pulse rate per minute | |
| at rest |
after jogging |
||
| 1. | Goutham | ||
| 2. | Naganeeraj | ||
| 3. | Nagamani | ||
| 4. | Swathi | ||
| 5. | Subba Rao | ||
a) What did you observe ? Is the pulse rate same in both conditions ?
Answer:
There is increase in pulse rate after jogging for one minute.
![]()
Activity 2.
How do you observe the pulse rate of classmates ?
Answer:
- Pulse rate varies from person to person and situation to situation.
- When we are afraid or excited the pulse rate goes up.
- There is a relationship between the pulse rate and the beat of our heart.
- Try to observe pulse rhythm after climbing stairs, running etc.
- For this you have to make your own pulse indicator.
- Take an injection bottle lid/shirt button.
- Insert a match stick as shown in figure.
- Place it on your wrist.
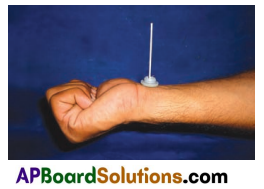
Observation :
- Observe movements in matchstick.
- Put your other hand on your chest and feel the beat of your heart. Does the pulse rate indicator move with the beat of your heart ? Yes, the pulse rate indicator move with the beat of my heart.
Activity 3.
(i) How do you measure the heart beat and pulse rate at rest ?
OR
What activities you will do to find relation between heart beat and pulse rate ?
Answer:
- Make a paper tube 10 inch long and one inch in diameter.
- Keep one end of it at your ear and the other end on the chest of your friend, so that your friend’s hearbeat is audible to you.
- Listen carefully and count the beats for a minute.
- Also count down your friend’s pulse rate. Note observations of at least 10 students of your class in the following tabular form.
- Repeat this experiment after jogging note down values in table and compare.
| Sl.No. | Name of the student | Heart beat at rest/min | Pulse rate at rest |
| 1. | Eswar | ||
| 2. | Venkateswara Rao | ||
| 3. | Gopinath | ||
| 4. | Yashwanth | ||
| 5. | Srisailam | ||
| 6. | Manga | ||
| 7. | Kamala | ||
| 8. | Lakshmi | ||
| 9. | Kavitha | ||
| 10. | Latha |
Q. What is the relationship between the heart beat and the pulse rate ?
Answer:
The rate of pulse will be equal to the number of heart beats,
(ii) How do you observe the mammalian heart ?
OR
How do you observe internal &external features of mammalian heart ?
Answer:
Aim : Observation of the internal structure of the mammalian heart.
Material required : Freshly collected specimen of heart of sheep or goat from the butcher. Soda straws, used pen refils, sharp and long blade or scalpel, tray, a jug of water, Dissection scissors, forceps. Since the structure of all the mammalian hearts are similar, we take the sheep’s or goat’s heart for our observation.
For this we need the following materials :
Freshly collected specimen of heart of sheep/goat from the butcher, soda straws, used pen refils, sharp and long blade or scalpel, tray and a jug of water, dissection scissors and forceps.
Procedure :
Before conducting the activity wash the heart thoroughly so that, blood is completely drained from the chambers.
Take the soda straws and insert them into the stumps of the blood vessels.
Note your observations as you proceed.
i. What is the shape of the heart ?
Answer:
Heart is a pear shaped structure, triangle in outline, wider at the anterior end and narrower at the posterior end.
ii. How many layers are covering the heart ?
Answer:
Two thin, transparent layers are covering the heart.
iii. How many large blood vessel stumps are attached to the heart ?
Answer:
There are six blood vessels attached to the heart.
![]()
iv. Which end of the heart is broader and which end is narrow ?
Answer:
The anterior end of the heart is broader and the posterior end is narrow,
Observe the internal structure of the heart – observe the wall of the heart.
v. Is the thickness of the wall of the heart uniform throughout ?
Answer:
No, the thickness of the wall of the heart is not uniform throughout. Atria are thin and ventricles are thick.
vi. How many chambers are there in the heart ?
Answer:
There are four chambers (2 atria, 2 ventricles) in the heart
vii. Are all the chambers of the same size ?
Answer:
No. They are not of same size. Left atrium and ventricle are smaller when compared to that of right atrium and ventricle.
viii. What other differences could you observe between the chambers ?
Answer:
Left auricle and ventricle are smaller than right auricle and right ventricle.
ix. Do you find any specific observations in between the two chambers ?
Answer:
Yes. I can find some specific observations in between the two chambers.
x. Are all the chambers connected to each other ?
Answer:
No, only atria and ventricles are connected to each other.
xi. How are they connected to each other? How are they separated?
Answer:
Auricles are connected to ventricles by valves and are separated by septae (septum).
xii. How many blood vessels are attached to the heart?
Answer:
Five blood vessels are attached to the heart. They are
- Aorta
- Pulmonary artery
- Pulmonary vein
- Superior venacava
- Inferior venacava.
xiii. Are all the blood vessels rigid? How many of them are rigid?
Answer:
The rigid blood vessels are called arteries. They are
- The largest artery Aorta
- Pulmonary artery – which carries deoxygenated blood from heart to lungs.
xiv. Does the rigidity of blood vessel have anything to do with circulation?
Answer:
- The walls of the arteries are stiff/rigid.
- They are made up of muscle fibre and are elastic.
- When heart pumps blood into the arteries, the blood enters with a pressure into the arteries.
- Their walls will stretch and this enables the arteries to withstand the increase in the pressure without bursting.
Activity 4.
a) Aim : Observation of blood flow in arteries and veins.
Procedure:
- Sit on a table with one leg dangling and the other resting on it so that the back of one knee rests on the knee of the other.
- After sometime we feel the leg which is on top give a series of small movements with each heart beat.
- Repeat it for a long time.
Observation: The blood flow reduces to the leg and so develops “pins and needles”.
Conclusion : The blood flow from arteries to legs slowed down results pins and needles.
b) Swing the arm round several times to fill the veins with blood, hold the arm vertically downwards and gently press your finger along a prominent vein – stroking it in the reverse direction to the blood flow.
![]()
Observation : We can see the swellings.
Conclusion : Veins have to carry blood from body parts to the heart. When the arm is hold tightly blood is stopped in the veins there forms swelling.
Activity 5.
How is water absorbed into the roots ? Explain with an experiment.
OR
What experiment you will perform to observe root hairs? With the help of diagram explain the process of absorption water through root hairs, transmission to all parts of plant body by osmosis?
Answer:
Absorption of root hairs:

- Examine some mustard seedlings which have been grown on wet filter paper.
- Observe the mass of fine threads coming from the seed by hand lens.
- These are root hairs through which water enters the Plant.
- Gently squash a portion of the radicle between slide and coverslip in a drop of water and examine under a microscope.
- Note the thinness of the walls of the root hairs.
- Osmosis plays an important role in absorption of water by root hairs.
- Root hairs grow out into the space between the soil particles and the hairs are surrounded by moisture.
- The soil water is an extremely dilute solution of salts, more dilute than that of the cell sap in the root hair, therefore water will pass into the vacuole of the root hair by osmosis.
- The entry of water dilutes the contents of the root hair vacuole so that it becomes weaker than its neighbour.
![]()
Activity 6.
Describe an experiment to demonstrate root pressure in plants.
Answer:
Aim : To demonstrate root pressure in plants.
Apparatus : Potted plant with stem cut, rubber tube, glass tube, clamp.

Procedure:
- Take a regularly watered potted plant and cut the stem portion 1 cm above the ground level.
- Then connect a glass tube by means of a strong rubber tubing as shown in the figure.
- The size of glass tube should be equal to the size of the stem.
- Take care while joining tube and stem
- Now pour some water in the glass tube until water level can be seen above the rubber tube.
- Mark the level of water (M1) in tube.
- Keep your arrangement aside for 2 to 3 hours.
- Then observe and mark the water level (M2) in the tube.
- The difference between M2 and M1 indicates the level of water raised.
Observation : There is increase in the level of water raised in the stem.
Result: The raise in the water level is due to the root pressure created in the plant.