Telangana SCERT 10th Class Biology Study Material Telangana 2nd Lesson Respiration Textbook Questions and Answers.
TS 10th Class Biology 2nd Lesson Questions and Answers Telangana – Respiration
Question 1.
Distinguish between
a. inspiration and expiration
b. aerobic and anaerobic respiration
c. respiration and combustion
d. photosynthesis and respiration
Answer:
a.
| Inspiration | Expiration |
| 1. it is an active process. | 1. It is a passive process. |
| 2. Contraction of external intercostal muscles and relaxation of internal intercostal muscles occur. | 2. Relaxation of external intercostal muscles (muscles present between ribs) and contraction of internal intercostal muscles occur. |
| 3. Rib cages move forward and out – ward. | 3. Rib cages move downward and inward. |
| 4. Diaphragm contracts and becomes flattened. | 4. Diaphragm relaxes and becomes original dome-shaped. |
| 5. Increase in volume of thoracic cavity. | 5. Decrease in volume of thoracic cavity. |
| 6. Air pressure in lungs is less than atmospheric pressure. | 6. Air pressure in lungs is greater than atmospheric pressure. |
| 7. Intake of air into lungs. | 7. Expulsion of air from the lungs. |
b.
| Aerobic respiration | Anaerobic respiration |
| 1. It takes place in the presence of oxygen. | 1. it takes place in the absence of oxygen. |
| 2. In aerobic respiration, complete oxidation of glucose takes place. | 2. In anaerobic respiration, the glucose molecule is incompletely oxidised. |
| 3. End products are CO2 and water. | 3. End products are either ethyl alcohol or lactic acid and CO2. |
| 4. Lot of energy is liberated (38 ATP). | 4. Relatively small energy is liberated (2 ATP). |
| 5. It occurs in plants’ and animals’ cells. | 5. Occurs in many anaerobic bacteria and human muscle cells. |
| 6. C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6 CO2 + 6H2O + 686 K.cal | 6. C6H12O6 → 2C2HrOH + 2CO2 + 56 K.cal |
c.
| Respiration | Combustion |
| 1. It occurs in living cells. | 1. It is non-cellular. |
| 2. Oxidation of food materials especially glucose to carbon dioxide and water is called respiration. | 2. When sugar burns CO2 and water are produced and energy is released as heat. This process is called combustion. |
| 3. Oxidation of sugar molecules occurs at the body temperature of an organism. | 3. Heat is to be applied for the sugar molecule to burn. |
| 4. The energy is released in several stages. | 4. The energy is released at once as heat. |
| 5. Several intermediates are formed. | 5. No intermediates are formed. |
| 6. Enzymes are required for oxidation. | 6. Enzymes are not required for combustion. |
| 7. Respiration occurs in the presence of water. | 7. Combustion occurs in the absence of water. |
| 8. It is a controlled process. | 8. It is an uncontrolled process. |
| 9. Energy is stored in ATP in the body. | 9. Energy is not stored and is released into the atmosphere. |
d.
| Photosynthesis | Respiration |
| 1. Occurs only in plants and some photosynthetic bacteria. | 1. Occurs in all living organisms. |
| 2. Takes place in the presence of sunlight. | 2. Takes place throughout the day. |
| 3. It occurs in chloroplast and is dependent on light. | 3. Aerobic respiration occurs in cytoplasm and mitochondria and is independent of light. |
| 4. Raw materials are CO2 and water. | 4. Uses carbohydrates or organic substances and oxygen. |
| 5. In this process light energy is fixed in the form of chemical energy and stored in carbohydrates. | 5. In this process chemical energy stored in the carbohydrates burns to release energy. |
| 6. Oxygen is liberated in this process and carbon dioxide is utilized. | 6. Oxygen is utilized and carbon dioxide is released. |
| 7. Produces ATP by use of light energy. | 7. Produces ATP by oxidation of glucose. |
| 8. ATP and NADPH2 are mainly used for synthesis of organic compounds. | 8. NADPH2 and ATP are made available for cellular respiration. |
| 9. It is an anabolic process. | 9. It is a catabolic process. |
| \begin{aligned} & 6 \mathrm{CO}_2+12 \mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O} \underset{\text { Lhight energy }}{\stackrel{\text { Chlorophyll }}{\longrightarrow}} \\ & \mathrm{C}_6 \mathrm{H}_{12} \mathrm{O}_6+6 \mathrm{O}_2+6 \mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O} \\ & \end{aligned} |
10. CgH12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O + Energy |
Question 2.
State two similarities between aerobic and anaerobic respiration.
Answer:
- Both aerobic and anaerobic respiration release energy by breaking down glucose molecule.
- The energy produced by these two processes will be used to carryout various functions of the body.
- Both aerobic and anaerobic respirations take place in a cell.
![]()
Question 3.
Food sometimes enters the wind pipe and causes choking. How does it happen?
Answer:
- The trachea is commonly called the wind pipe.
- It is covered by the epiglottis so when a person swallows food, it does not go into the trachea.
- If food enters the trachea, it can block it completely and cause a person to choke to death.
- If the food goes down the trachea, it can lodge in the main pipe and cause suffocation.
- If the food enters the trachea, it generally causes a person to cough forcefully enough to remove the food.
Question 4.
Why does the rate of breathing increase while walking uphill at a normal pace in the mountains? Give two reasons
Answer:
The rate of breathing increases while walking uphill at a normal pace in the mountains.
- It is because as we go up the hill above sea level the concentration of oxygen is greatly reduced. So we have to breathe more to get required amount of oxygen.
- While walking uphill a lot of oxygen is used by our body to release energy from glucose.
- This leads to lack of oxygen in the cells.
- We take in oxygen when we breathe.
- Hence to increase the amount of oxygen intake there is an increase in breathing rate during walking uphill.
Question 5.
Air leaves the tiny sacs in the lungs to pass into capillaries. What modification is needed in the statement?
Answer:
The modification needed in this statement :
It is not the air that leaves the tiny sacs in the lungs to pass into capillaries but it is the oxygen that leaves the tiny sacs in the lungs to pass into capillaries.
Question 6.
Plants photosynthesize during the day time and respire during the night. Do you agree to this statement? Why? Why not’?
Answer:
- Yes, I do agree partially with this statement. Plants photosynthesize during day time only. Dark reaction takes place during night time and respire during the day time as well as night time also.
- During day time when photosynthesis occurs, oxygen is produced. The leaves use some of this oxygen for respiration and the rest diffuses into air.
- During day time CO2 produced by respiration is all used up in photosynthesis by leaves but rate of respiration is slow.
- At night time no photosynthesis occurs and oxygen diffuses into leaves to carryout respiration and during night dark reaction takes place O2 releases. But rate of photosynthesis is slow during night.
![]()
Question 7.
Why does a deep sea diver and mountain air cany oxygen cylinder on her back?
Answer:
- Oxygen is present in dissolved state in water.
- Human beings do not have gills like the fish which can extract dissolved oxygen from water and utilise it for breathing.
- Moreover as we go deep down in water, the oxygen level starts decreasing.
- So a deep sea diver or mountaineer carries an oxygen gas cylinder for breathing when he/she goes deep under the sea water.
Question 8.
How are alveoli designed to maximize the exchange of gases?
Answer:
The human lungs have been designed to maximise the exchange of gases as follows.
- There are millions of alveoli in the lungs.
- The presence of millions of alveoli in the lungs provide a very large area for the exchange of gases.
- Availability of large surface area maximises the exchange of gases.
Question 9.
Where will the release of energy from glucose in respiration take place? Mala writes lungs while Raziya writes muscles. Who is correct and why?
Answer:
- Respiration is the process of releasing energy from the breakdown of glucose.
- Respiration takes place in every living cell, all of the time and all cells need to respire in order to produce the energy that they require.
- The release of energy from the glucose in respiration takes place in muscles but not in lungs.
- So Rajiya is correct. The energy is released from the muscle cells during respiration. Only gaseous exchange takes place in lungs.
Question 10.
What is the role of the epiglottis and diaphragm in respiration?
Answer:
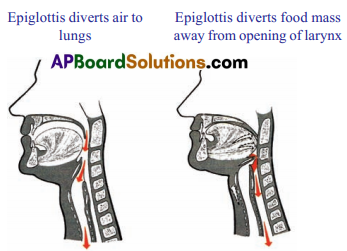
Epiglottis:
- Epiglottis, a flap-like muscular valve controls movement of air and food towards their respective passages.
- The epiglottis serves as protection to our wind pipe. It stops food and liquid from going down into air way.
- Epiglottis allows air pass through the larynx and the respiratory system.
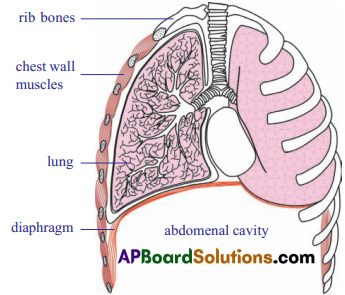
Diaphragm :
- The diaphragm in the respiratory system is the dome-shaped sheet of muscle that separates the chest from the abdomen.
- During inhalation, the diaphragm contracts and moves in the inferior direction, thus enlarging the volume of the thoracic cavity.
- This reduces the pressure in the lungs and air enters into lungs.
- During exhalation, the diaphragm relaxes and assumes its dome shape. This change increases the pressure on the lungs and squeezes the air out through the nose to the external atmosphere.
Question 11.
How does gaseous exchange takes place at blood level (or) cellular level?
Answer:
- Lungs are made up of several thousands of small chambers called alveoli.
- Within the alveoli, exchange of gases takes place between the gases inside the alveoli and blood.
- Blood arriving in the alveoli has a higher CO2 concentration which is produced during respiration by the body’s cells.
- At the same time air in the alveoli has a much lower concentration of CO2, and this allows the diffusion of CO2, out of the blood and to alveolar air.
- Similarly blood arriving in the alveoli has a lower oxygen concentration while air in the alveoli has a higher oxygen concentration.
- Therefore oxygen moves into the blood by diffusion.
![]()
Question 12.
Explain the mechanism of gaseous exchange at bronchiole level.
Answer:
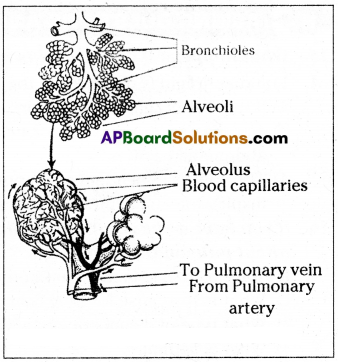
- Each bronchus divides in the lungs to form a large number of still smaller tubes called bronchioles.
- Each bronchus divides in the lungs to form a large number of still smaller tubes called bronchioles.
- The smallest’ bronchioles have tiny air sacs at their ends.
- The pouch – like air sacs at the ends of the smallest bronchioles are called alveoli.
- The walls of the alveoli are very thin and they are surrounded by very thin blood capillaries.
- Since the concentration of the gases in the blood and the alveoli are not equal, there is a concentration gradient which causes the diffusion of carbon dioxide from the blood to the alveolar air and of oxygen from the alveolar air into blood.
Question 13.
After a vigorous excercise or work we feel pain in muscles. What is the relationship between pain and respiration?
Answer:
- We obtain energy by aerobic respiration.
- But anaerobic respiration can sometimes take place in our muscles.
- During vigorous exercise oxygen gets used up faster in the muscle cells that can be supplied by the blood.
- When anaerobic respiration takes place in human muscles, glucose is converted into lactic acid with the release of a small amount of energy.
- The anaerobic respiration by muscles bring about partial breakdown of glucose to form lactic acid.
- The accumulation of lactic acid in the muscles causes muscular pains or cramps.
Question 14.
Raju said stems also respire along with leaves in plants. Can you support this statement? Give your reasons.
Answer:
Yes. I support the statement of Raju that stems also respire along with leaves in plants. The reasons are :
- The stems of herbaceous plants have stomata.
- So the exchange of respiratory gases in the stems of herbaceous plants takes place through stomata.
- The oxygen from air diffuses into the stem through stomata and reaches all the cells for respiration.
- The carbon dioxide released due to respiration diffuses out into the air through the stomata.
- In woody stems the bark has lenticels for gaseous exchange. Through lenticels oxygen diffuses in and carbon dioxide diffuses out into the air.
![]()
Question 15.
What happen if diaphragm is not there in the body?
Answer:
- If diaphragm is not there in the body, we would not be able to breathe.
- If the diaphragm is absent, breathing movements will stop.
- The diaphragm is the major muscle of respiration and separates the thoracic and abdominal cavities.
- The body is dependent on diaphragm for normal respiratory function, in its absence inspiration and expiration process may not take place properly.
Question 16.
If you have a chance to meet pulmonologist what questions are you going to ask about pulmonory respiration
Answer:
If I have a chance to meet pulmonologist, I would like to ask the following questions :
- What is the cause for lung cancer ?
- What type of diagnostic tests will be performed to assess the function of lungs ?
- What is asthma ?
- How can asthma be cured ?
- What is chronic obstructive pulmonary disease ?
- What is pneumonia ? How is it caused ?
- What is tuberculosis ? Can it be cured permanently ?
- What is pulmonary edema ? How does it occur ?
- What is the organism that causes acute bronchitis ?
- Can all the diseases of lungs be cured permanently ?
- How can we protect from lung diseases ?
- What are the reasons for different kinds of lung diseases ?
Question 17.
What procedure do you follow to understand anaerobic respiration in your school laboratory’?
Answer:
Aim : To prove that CO2, is released during anaerobic respiration.
Apparatus: Thermos flask, splitted corks, thermometer, wash bottle, glass tubes, liquid paraffin, glucose solution, yeast cells, bicarbonate solution, Janus Green B solution.
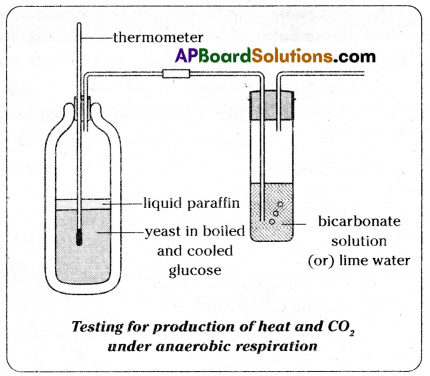
Procedure:
- Heat the glucose solution in a beaker, pour it in a thermos flask.
- To remove dissolved oxygen from glucose solution by boiling it in thermos flask for a minute and then cooling it without shaking.
- Now add some yeast to the glucose solution and fix two- holed rubber stopper to the flask.
- The supply of oxygen from the air can be cut off by pouring a lcm layer of liquid paraffin on the mixture (Thermos is heat resistant can’t be used for boiling).
- Insert one end of the thermometer into the thermos flask. See the end of thermometer kept inside the solution.
- Another bottle containing bicarbonate/indicator solution (or lime water) is attached as in the Figure.
- Add a few drops of diazine green (Janus Green B) solution to the yeast suspension before you pour liquid paraffin over it.
- The blue diazine green solution turns pink when oxygen is in short supply around it.
- Warm the apparatus to about 37° F in order to speed up the test. (If you do experiment in test tube).
Keep the apparatus undisturbed for one or two days.
Observations:
- After two days it can be observed that lime water of the wash bottle turns into milky white precipitate.
- Increase in temperature noted on yeast cells respire and release energy.
- Alcohol smell given off from the flask.
Result: These observations indicate that yeast cells respire anaerobically converting glucose solution into CO2, ethyl alcohol and releasing heat energy.
![]()
Question 18.
What are your observations in combustion of sugar activity?
Answer:
Observations in combustion of sugar :
- When sugar is heated first it chars and later burns producing flames.
- When sugar combusted carbon dioxide and water are produced.
- Energy is also released in the form of heat and it released at once.
- We cannot control the combustion of sugar and also intermediate products are not formed.
- We can combust sugar in the absence of water and also enzymes are not required.
- Due to combustion of sugar heat energy is released into the atmosphere and we cannot store it for further use.
Question 19.
Collect information about cutaneous respiration in frog. Prepare a note and display them in your classroom.
Answer:

- Respiration through skin is called cutaneous respiration.
- This type of respiration is seen in some invertebrates and vertebrates.
- In frog, skin is an additional or secondary or accessory respiratory organ. (Similarly Earthworm also respires through skin only. It lives in moist places only.)
- Frog is an amphibious animal that lives in water and on land.
- Skin is a very important respiratory organ in both on land and water.
- One-third of the total oxygen taken up by frog is through the skin.
- Frog keeps their skin moist. Skin has a large number of mucous glands which secrete mucous onto the surface of the skin.
- The mucous layer retains water and reduces evaporation of water from body.
- To keep the skin wet and moist frogs jumps into water very frequently.
- Frog skin is supplied with a large number of blood vessels which help in absorbing oxygen from the water.
- The carbon dioxide produced due to respiration diffuses out into the water through the blood vessels present in the skin of the frog.
- During winter sleep or hibernation frogs respire through the skin.
Question 20.
Collect information about respiratory diseases (because of pollution, tobacco) and discuss with your classmates.
Answer:
Respiratory diseases because of pollution :
1. Irritation of eyes, nose, mouth and throat.
2. Headaches, nausea and dizziness.
3. Respiratory symptoms such as coughing and running nose.
4. Respiratory and lung diseases including
- Asthma attacks
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)
- Reduced lung function
- Pulmonary cancer caused by a series of carcinogen chemicals that through inhalation
- Mesothelioma : A particular type of lung cancer, usually associated with exposure to asbestos (it usually occurs 20 – 30 years after the initial exposure)
- Pneumonia : Infection of lungs caused by bacteria.
- Bronchitis : It is inflammation or swelling of bronchial tubes.
- Emphysema : It is a lung condition in which tiny air sacs in lungs alveoli fill up with water.
Respiratory diseases due to tobacco :
- Chronic bronchitis : A long term inflammation of the bronchi is characterized by coughing.
- Lung cancer : An abnormal continual multiplying of cells that can result in tumors can begin in the lining of the bronchi.
- Emphysema : A chronic lung condition that affects the air sacs in the lungs characterized by shortness of breath, coughing, fatigue, sleep and heart problems.
![]()
Question 21.
What is the pathway taken by air in the respiratory system? Illustrate with a labelled diagram.
Answer:
The pathway taken by air in the respiratory system :
Nostrils → Nasal cavity → Pharynx → Larynx → Trachea → Bronchus → Bronchioles → Alveolus → Blood.
- Air enters the body through the nostrils.
- Air is filtered in the nasal cavity and its temperature is also brought close to that of the body.
- Pharynx is the junction of respiratory and digestive system. Epiglottis – a flap-like muscular valve controls movement of air and food towards their respective passages.
- Larynx is also called sound box. It contains vocal cords. When air passes out of the lungs and over the vocal cords, it causes them to vibrate. This produces sounds on the basis of our speech, song, etc.
- Trachea is also called wind pipe. It channels air to lungs.
- Trachea at its lower end divides into two bronchi one leading to each lung.
- The bronchi further divided into smaller and smaller branches called bronchioles.
- Bronchioles finally terminate in clusters of air sacs called alveoli in the lungs which are very small and numerous.
- Gaseous exchange takes place here as blood capillaries take up oxygen and expel carbon dioxide here.
- Blood carries oxygen to each and every cell of the body and collects CO2, from them. The whole passage from nostrils to alveoli is moist and warm.
Question 22.
Draw a block diagram showing events in respiration. Write what you understood about cellular respiration
Answer:
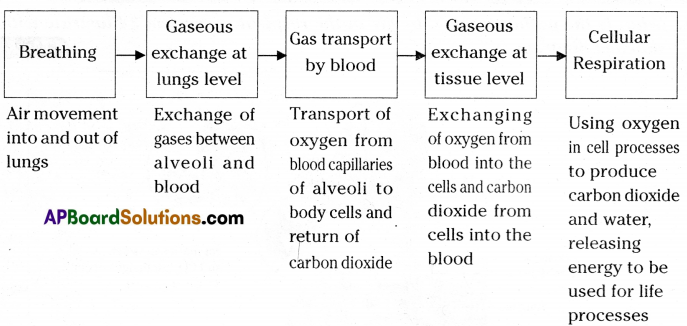
Cellular respiration :
- All living cells must carry out cellular respiration.
- During respiration, energy is produced when the glucose or fatty acids are oxidised in the cells. As this process occurs in the cells this is called cellular respiration.
- It can be in the presence of oxygen which is aerobic respiration or in its absence that is anaerobic respiration (fermentation).
- Cellular respiration in prokaryotic cells like that of bacteria occurs within the cytoplasm.
- In Eukaryotic cells cytoplasm and mitochondria are the site of cellular respiration.
- The complete breakdown of a sugar molecule with the release of all its available energy involves a series of different chemical reactions.
- The energy released in cellular respiration is stored in a special compound called ATP.
- ATP is utilised for carrying out other functions in the cell.
Question 23.
How you appreciate the mechanism of respiration in our body?
Answer:
1. Respiration is essential for life because it provides energy for carrying out all the life processes which are necessary to keep the organism alive.
2. The energy that is obtained from respiration is used to build the organism through cell growth and reproduction as well as cell repair.
3. All systems in a living thing needs energy to survive. Energy is defined as the ability to do work. So without respiration we would not have any energy to perform necessary day-to-day functions.
4. Respiration helps to expel out the toxic carbon dioxide out of the cells. This CO2 will be utilised by the plants to produce food materials through the process of photosynthesis.
5. The respiratory system goes into operation from the movement of our birth and works without ever stopping. As long as we live our breath continues.
6. During exhalation the vocal cards in the larynx vibrate to produce sounds and speaking as we like.
Question 24.
Prepare an article on anaerobic respiration to present school symposium
Answer:
Anaerobic respiration : Many prokaryotes, bacteria as well as archaea, can obtain energy for growth in the absence of oxygen by anaerobic respiration. It is called anaerobic respiration because it takes place in absence of oxygen. The microscopic organisms like yeast and some bacteria obtain energy by anaerobic respiration called fermentation.
In anaerobic respiration, the microorganisms like yeast breakdown glucose into ethanol and carbon dioxide and release energy. This energy is then used by the micro organisms. Anaerobic respiration produces much less energy which gets stored in the ATP molecules.
During anaerobic respiration 1 molecule of glucose produces only 2 energy rich ATP molecules. All the cells do not use oxygen to produce energy. Energy can be produced in cells even without oxygen.
In the first phase of respiration, glucose molecule is oxidised to a three carbon compound called pyruvate. This process yields very little amount of energy. In the absence of oxygen pyruvate will be converted to either lactic acid or ethanol.
Anaerobic respiration has an important impact on the cycle of matter in nature, including processes such as denitrification, dissimilatory sulfate reduction with the formation of sulfide, the formation of methane and acetate from carbon dioxide and different processes in the biogeochemical cycles of metals.
![]()
Anaerobic respiration has important economic implications both favourable (e.g : conversion of bound nitrogen to nitrogen gas in water purification plants) and unfavourable (e.g : loss of available nitrogen in agricultural soils, corrosion of steel pipes mediated by sulphate reducing bacteria.)
Question 25.
Prepare a cartoon on discussion between haemoglobin and chlorophyll about respiration
Answer:

Haemoglobln : Hello good morning Chlorophyll. How are you?
Chlorophyll : Very good morning Haemoglobin. I am fine.
Haemoglobin : I am also doing well. Tell me Chlorophyll, who are you?
Chlorophyll : I am a green coloured pigment present in leaves of plants.
Haemoglobin : How many different types of chlorophylls are there?
Chlorophyll : We are four types i.e., Chlorophyll a, Chlorophyll b. Chlorophyll e and Chlorophyll d.
Flaemoglobin : May I know your job in leaves?
Chlorophyll : Yes. Why not ? I am an essential factor required for the process of photosynthesis in plants.
Haemoglobin : Oh ! You are participating in the process of preparing food materials in green plants.
Chlorophyll : Now tell me about your presence.
Haemoglobin : I am present only in animal cells. That too in the red blood cells of the blood. The red colour of the blood is due to my presence.
Chlorophyll : Then tell me about your function in respiration?
Haemoglobin : During respiration, I carry oxygen to the cells in the body parts.
Chlorophyll : How are you able to do this?
Haemoglobin : I have an oxygen binding element iron. It binds oxygen on four corners of it. I form oxy-haemoglobin with oxygen in the lungs.
Chlorophyll : What happens to the digested food in the cells?
Haemoglobin : In cells, oxygen breakdown the glucose molecule into CO2 and H2O releasing large amount of energy. Around 38 ATP molecules are produced.
Chlorophyll : What is the use of this energy?
Haemoglobin : This energy is utilised by the cell to carry other functions.
Chlorophyll : What happens if you do not carry oxygen and supply it to cells?
Haemoglobin : The food mterials are not oxidised and the energy will not be released.
Chlorophyll : Then what happens to the cell ? What does it do?
Haemoglobin : In the; absence of oxygen the cells adopt anaerobic respiration during which very little amount of energy is released. i.e., 2ATP molecules are formed.
Chlorophyll : Where do we find this type of anaerobic respiration?
Haemoglobin : Anaerobic respiration occurs in some bacteria, yeast cell and muscle cells. Respiration occurs in the cytoplasm and mitochondria of the cell.
Chlorophyll : Is all the energy released during respiration utilized by the cell?
Haenioglobin : No. Some amount of energy will be stored in the form of a compound called Adenosine tri phosphate (ATP).
Chlorophyll : Thank YOU Haemoglobin. You have taught me everything about respiration. In our next meeting we will discuss another topic.
Haemoglobin : Thank you Chlorophyll for your patience.
Fill in the blanks:
1. Exhaled air contains ……………… and ……………….
2. A flap like muscular valve controls movement of air and food is ………………
3. Energy currency of the cell is called ………………
4. Lenticels are the respiratory organs that exist in ……………… part of the plant.
5. Mangrove trees respire with their ………………
Answer:
1. carbon dioxide, water vapour
2. Epiglottis
3. ATP (Adenosine Tri Phosphate)
4. wet places or marshes
5. aerial roots
![]()
Choose the correct answer :
Question 1.
We will find vocal cords in …………..
A. Larynx
B. Pharynx
C. Nasal cavity
D. Trachea
Answer:
A. Larynx
Question 2.
Cluster of air sacs in lungs are called ………….
A. Alveoli
B. Bronchi
C. Bronchioles
D. Air spaces
Answer:
A. Alveoli
Question 3.
Which of the following is correct?
i. The diaphragnì contracts – volume of chest cavity increased
ii. The diaphragm contracts – volume of chest cavity decreased
iii. The diaphragm relax – volume of chest cavity increased
iv. The diaphragm relax – volume of chest cavity decreased
A. i
B. i and ii
C. ii and iii
D. iv
Answer:
i. The diaphragnì contracts – volume of chest cavity increased
Question 4.
Respiration is a catabolic process because of …………….
A. Breakdown of complex food molecules
B. Conversion of light energy
C. Synthesis of chemical energy
D. Energy storage
Answer:
A. Breakdown of complex food molecules
Question 5.
Energy is stored in …………….
A. Nucleus
B. Mitochondria
C. Ribosomes
D. Cell wall
Answer:
B. Mitochondria
TS 10th Class Biology 2nd Lesson Respiration Intext Questions
1 Mark Question and Answers :
Question 1.
What gas was produced by combustion according to Lavoisier ?
Answer:
The gas produced by combustion is carbon dioxide.
Question 2.
What did Lavoisier find out about air from his experiments ?
Answer:
A fixed air carbondioxide and a respirable air oxygen which helped in burning were liberated during his experiments.
![]()
Question 3.
What conclusion can be drawn from Lavoisier’s experiments ?
Answer:
Oxygen and carbondioxide are the composition of air.
Question 4.
Which gas do you think is Lavoisier talking about when he says fixed air ?
Answer:
Carbondioxide.
Question 5.
Which gas according to Lavoisier is respirable air ?
Answer:
Oxygen.
Question 6.
It is a common observation that our breath is warmer than the air around us; does respiration have anything to do with this ?
Answer:
Our breathe is warmer than the air around us because heat is liberated during respiration.
Question 7.
What does this experiment indicate ?
Answer:
This experiment indicates that carbondioxide is liberated during respiration.
Question 8.
Which gas turns lime water milky ?
Answer:
Carbondioxide.
Question 9.
Which gas do you think might be present in greater quantities ?
Answer:
Nitrogen (78%) is present in greater quantities in the air.
Question 10.
We are also aware of the fact that water vapour deposits on a mirror if we breathe out on it; where does this water vapour come from in Exhaled air ?
Answer:
Water vapour is liberated during respiration.
Question 11.
Why are we advised not to talk while eating food ?
Answer:
We are advised so because while eating, some food particles might enter the wind pipe which can lead to choking.
Question 12.
What can be concluded from this ?
Answer:
All movements of breathing is controlled by nerves leading from the brain.
Question 13.
What happens during the process of breathing ?
Answer:
During the process of breathing, the patterns of breathing show a great range, for they are coordinated with moment by moment needs of the body for supply of oxygen and removal of carbon dioxide.
![]()
Question 14.
Which gas needs to be removed from our body during exhalation ? Where does the extra amount of gas come from ?
Answer:
Carbon dioxide needs to be removed during exhalation.
The extra amount of gas comes from breaking of glucose to release energy in the mitochondria. Carbon dioxide gas is released here.
Question 15.
What is the composition of inhaled air ?
Answer:
Oxygen 21%, Carbondioxide 0.03% Nitrogen 79%.
Question 16.
When exhaled air is compared with inhaled air, is there any difference in composition ?
Answer:
Exhaled air contains Oxygen 16%, CO2 4%, Nitrogen – 79%.
Difference is Oxygen – 5% less, CO2 – 3.46% more, Nitrogen – equal.
Question 17.
Why does the amount of oxygen vary between exhaled and inhaled air ?
Answer:
Because some amount of oxygen will be utilised during cellular respiration in the body. Hence the difference in amount of oxygen occurs.
Question 18.
What has raised the percentage of carbon dioxide in exhaled air ?
Answer:
CO2 is released from all the cells in the body in respiration and is added in the exhaled air.
Question 19.
After undergoing strenuous exercise we feel pain in muscles. Does adequate oxygen reach the muscles ?
Answer:
No. Adequate oxygen does not reach the muscles.
Question 20.
What is being formed in the muscles ?
Answer:
Lactic acid.
![]()
Question 21.
In which set does the colour change faster ? Why ?
Answer:
In the set which has germinating seeds the colour changes faster. Because CO2 is formed faster in aerobic respiration.
2 Mark Question and Answers :
Question 1.
Can it be said that Priestly’s experiment helped us to find out more about composition of air ? How ?
Answer:
Yes, Priestly’s experiments helped to find out the composition of air when burning of charcoal, carbondioxide is produced which is the one of the composition of air done by Lavoisier.
Another experiment with phosphorus done by Lavoisier was cleared that a gas which is the respirable air that is helped in burning was oxygen also a component of air.
Lavoisier proved experimentally that carbondioxide and oxygen were the components of air. Lavoisier confirmed the experiments of Priestly about the gases present in the air.
Question 2.
What steps in the process of respiration does Lavoisier mention as an inference of his experiments ?
Answer:
Regarding the process of respiration respirable air (oxygen) is changed in the lungs to chalky acid air (carbondioxide). Exchange of gases takes place. The first step in respiration is inspiration (oxygen enters the lungs) the second step is expiration (carbondioxide leaves the lungs to out side).
Question 3.
What is the role of diaphragm and ribs in respiration ? Are both active in men and women ?
Answer:
When the diaphragm flattens and the ribs moves forward, the volume of chest cavity is increased the air from outside rushes into the lungs which is called inspiration.
Then the diaphragm relaxes and assumes its dome shape and the lungs move back the air from inside enters outside which is called expiration.
Diaphragm and ribs are helpful in respiration. In woman ribs play major role in respiration whereas diaphragm plays major role in man.
![]()
Question 4.
Do cells of alveoli or lungs also require oxygen to carry out cellular respiration? Why / Why not ?
Answer:
Alveoli are made of squamous epithelium tissue which is very thin and elastic.
Alveoli are so thin that oxygen can pass from air filled alveoli to R.B.C inside the vessels. Simple squamous epithelial cells function as mediators of filtration and diffusion. As these cells are living tissue they also need oxygen this is done through exchange of gases in the alveoli.
Question 5.
Observe the following graph and answer the questions given below.
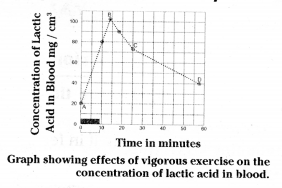
a. What was the concentration of lactic acid in the blood to start with ?
Answer:
It is 20 mg/cm3
b. What was the greatest concentration reached during the case study ?
Answer:
101 mg/cm
c. If the trend between points C and D were to continue at the same rate, how long might it take for the original lactic acid level to be reached once again ?
Answer:
55 minutes.
d. What does high level of lactic acid indicate about the condition of respiration?
Answer:
It indicates the accumulation of lactic acid in muscles through anaerobic respiration. The presence of lactic acid in the blood is the main cause of muscular pain and fatigue.
Question 6.
What will happen if the respiratory tract is not moist ?
Answer:
- If the respiratory tract is not moist the dirt particles in the inhaled air will not be removed from air in the nasal cavities and reaches lungs and create problems to lungs.
- The temperature of the inhaled air is brought close to that of the body for the smooth passage in the respiratory tract. If it is dry, it is not possible.
- If the surface dries out, gas exchange will happen at a very reduced rate since fast moving gaseous oxygen molecules do not efficiently cross the alveoli membrane.
- The reduced gas exchange is most likely not enough to support blood oxygenation for vital functions.
- Hence respiratory tract should be moist for smooth exchange of gases.
![]()
Question 7.
Are both lungs similar in size ?
Answer:
No. Right lung is slightly bigger than left lung.
Question 8.
Why are alveoli so small and uncountable in number ?
Answer:
- The pouch-like air sacs at the ends of the smallest bronchioles are called alveoli.
- The walls of the alveolus are very thin and they are surrounded by very thin blood capillaries.
- It is in the alveoli that gaseous exchange takes place.
- There are millions of alveoli in the lungs. The presence of millions of alveoli in the lungs provides a very large area for the exchange of gases.
- And the availability of large surface area maximises the exchange of gases.
TS 10th Class Biology 2nd Lesson Respiration Activities
Activity – 1.
How do you test the working of epiglottis in human?
OR
Swallowing and breathing will not take place at once. How can you prove with simple activity ?
Answer:
- Keep your palm around an inch away from your nose.
- Feel you are breathing out.
- Do not remove your palm until you have finished the activity.
- Breathe steadily for 1 – 2 minutes.
- Now take a piece of any fruit.
- Chew and before swallowing it keep the fingers of the other palm on your neck, now swallow it, while swallowing, breathing stops for a while.
- Epiglottis help to swallow without deflecting food to the wind pipe.
![]()
Activity – 2.
Write an experiment to observe changes during the combustion of sugar.
Answer:
Aim : To observe changes during combustion of sugar.
Apparatus: Wooden stand, test tubes, rubber stopper, delivery tube, glucose or sucrose powder, lime water.
Procedure:
- Take a small amount of glucose in a small test tube. Fit with one holed rubber cork.
- Arrange a delivery tube such that one end dip into test tube containing lime water.
- Heat the test tube with glucose powder over a flame.
- Go on heating the test tube until the glucose catches fire.
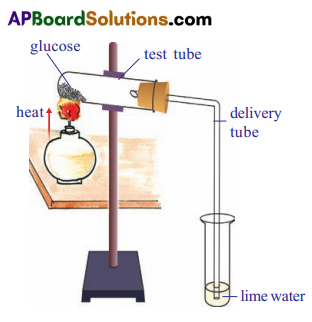
Observations:
- When glucose burns, carbon dioxide and water are produced and energy is released as heat.
- Glucose must be burnt at high temperature in the laboratory to liberate energy.
- Once the glucose starts burning we cannot stop the process easily.
- Here combustion of sugar can be stopped by adding water to the burning glucose powder.
- The CO2 released changes the lime water to milky white.
Conclusion :
- From this experiment, we can conclude that during combustion of glucose in the laboratory carbon dioxide, water and heat are produced.
- The carbon dioxide produced changes lime water to milky white in nature.
![]()
Activity – 3.
How can you prove that carbon dioxide is evolved during respiration ?
OR
How can you prove that sprouted seeds evolve CO2 during respiration ? Write experimental procedure.
Answer:
Aim : To prove that CO2 is released during aerobic respiration.
Apparatus : Two plastic or glass bottles, germinating seeds, dry seeds, two small injection bottles or beakers with lime water.

Procedure:
- Take a handful of moong or Bengalgram seeds.
- Soak the seeds in water a day before.
- Keep these soaked seeds in a cloth pouch and tie with a string tightly.
- Keep the cloth pouch in a corner of your classroom.
- Next day collect the sprouts/germinated seeds from the pouch, keep it in a glass bottle/plastic bottle around 200 ml capacity.
- Take a small beaker.
- Fill three-fourth of the beaker with lime water.
- Keep it in the beaker carefully.
- Close the plastic bottle tightly.
- Make a similar set with dry (unsprouted) seeds.
- Keep both the sets undisturbed for one or two days.
- During this time observe the colour of lime water in both the sets.
Observation :
After two days it can be observed that lime water of the injection bottle or beaker placed in the bottle containing the germinating seeds turns into milky white precipitate. Result: It indicates that germinating seeds are respired and liberated carbon dioxide which turns lime water into white precipitate.
Activity – 4.
How can we show that heat is liberated during respiration ?
Explain the procedure you have adopted in your school to prove that heat is liberated during respiration. What result we will get, if you perform this experiment with dry seeds.
OR
Write the procedure you have followed to observe “heat is evolved during respi¬ration” in your laboratory. What precautions did you take during the activity ?
Answer:
Aim : To prove that heat is liberated during respiration.
Apparatus : Thermos flasks, two thermometers, rubber corks, dry seeds, germinating seeds.
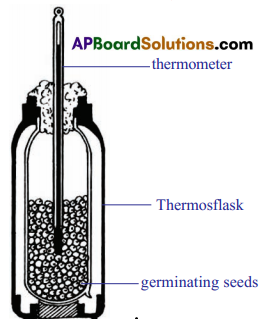
Procedure:
- Take a handful of moong or bazra seeds.
- Soak the seeds in water a day before experiment.
- Keep these soaked seeds in a cloth pouch and tie with a string tightly.
- Next day collect the sprouts / germinated seeds from the pouch in a thermos flask and take dry seeds in another thermos flask.
- Remove the lid and prepare a cork through which you can bore a hole to insert thermometers into two flasks in such a way that the bulb of the thermometer should dip in to the germinating and dry seeds.
- Close the thermos flasks with tight fitting rubber corks.
- Record the initial temperature in both the flasks and record it for every two hours for atleast 24 hours.
Observation: Constant increase in the temperature is observed in thermometer placed in the germinating seeds.
Result: Hence it is proved that germinated seeds respire and liberate heat which is responsible for increase in the temperature.
![]()
Precautions:
- Take the care that the bulb of the thermometer should dip in the sprouts.
- See that air should not enter in the flask.