Thoroughly analyzing TS 10th Class Social Model Papers Set 2 with Solutions helps students identify their strengths and weaknesses.
TS 10th Class Social Model Paper Set 2 with Solutions
Time:3.00 hrs
Max. Marks: 80
Instructions:
- Read the questions carefully, understand them, and answer.
- Write the answers for the questions in Part – A in the answer sheet.
- Attach the Map to Part- A answer sheet.
- Attach Part – B to Part A answer sheet.
- Part – A consists of, II and III Sections.
- Write the answers clearly duly following the instructions given for each section.
Part – A (Marks 60)
Section-I (6 x 2 = 12 M)
1. Answer all questions.
2. Answer each question in 3 -4 sentences.
3. Each question carries 2 marks.
Question 1.
Write about the first five-year plan.
Answer:
The first five-year plan focussed on agriculture and stressed on the need for increasing food production, development of transportation and communications and provision of social services.
Question 2.
What are the advantages of dams?
Answer:
The advantages of dams are:
- Providing irrigation,
- Generating hydroelectricity,
- Controlling floods,
- Conservation of soil fertility,
- Promoting tourism.
Question 3.
What is the significance of the year 1946?
Answer:
The year 1946 was a year of strikes and work stoppages in factories and mills in many parts of the country. CPI and the Socialist parties were active in these movements. The countryside was also on the boil.
![]()
Question 4.
Write about
a) Life expectancy at birth
b) Mean ‘ears of schooling
Answer:
a) Life expectancy at birth: Denotes the average expected length of life of a person at the time of birth.
b) Mean years of schooling: Average number of completed years of education of a country’s population aged 25 years and older, excluding years spent repeating individual grades.
Question 5.
Observe the following pictures and describe them.
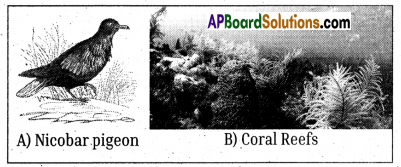
Answer:
A) Nicobar pigeons live in Nicobar Islands.
B)
- They are called coral reefs.
- Coral is often used in jewelry
- They also help marine creatures.
Question 6.
How is land distributed in Rampur?
Answer:
In Rampur, about /3rd i.e., 150 families are landless. There are 60 families are medium and large farmers, who cultivate 2 hectares of land. 240 Families cultivate small plots of land less than 2 hectares in size.
Section-II
6 x 3 = 18 M
1. Answer all questions.
2. Answer each question in 5 – 6 sentences.
3. Each question carries 3 marks.
Question 7.
Read the following information and answer the questions.
Total Cropped Area – in million hectares
| Region | 1955-56 | 2006-07 | Growth % |
| Andhra Region | 4.2 | 5.3 | 20 |
| Telangana Region | 4.8 | 5 | 5 |
Net irrigated area in lakh hectares
| Region | 1955-56 | 2006-07 | Growth % |
| Andhra Region | 17 | 23 | 135 |
| Telangana Region | 7 | 19 | 257 |
Net irrigated area in lakh hectares 2007
| Region | Wells | Canals | Tanks | Others |
| Andhra Region | 5 | 13 | 2.5 | 2.5 |
| Telangana Region | 14 | 2.5 | 2 | 0.5 |
i) What is the main irrigation method of Telangana region?
Answer:
In Telangana, wells are dug and used as main irrigation method in 14 lakh hectares.
ii) Which region showed a less net irrigated area?
Answer:
Telangana showed a less net irrigated area of 19 lakh hectares when compared with Andhra’s net irrigated area of 23 lakh hectares.
iii) What type of irrigation is followed mainly in Andhra?
Answer:
Canal irrigation is followed mainly in Andhra. Canal irrigation is carried out in 13 lakh hectares.
iv) What percentage of’ increase was the total cropped area recorded in both the regions?
Answer:
Andhra region recorded an increase of 20% in total cropped area. And Telangana region recorded an increase of only 5%.
v) Which region showed a higher growth rate of net irrigated area? And how much?
Answer:
Telangana region recorded higher growth rate in net irrigated area. And the growth rate was 257%. Net irrigated area rose from 7 lakh hectares to 18 lakh hectares.
![]()
Question 8.
Read the following paragraph and answer the question that follows.
We read earlier that the liberalisation of foreign trade and investment in India was supported by some very powerful international organizations. These organizations believe that barriers to foreign trade and investment are harmful. Trade between countries should be ‘free’ without any barriers. World Trade Organisation (WTO) is one such organisation whose aim is to liberalise international trade. Started at the initiative of the developed countries, WTO establishes rules regarding international trade and sees that these rules are obeyed. Nearly 164 countries of the world are currently members of the WTO.
Q) What is the WTO?
Answer:
The WTO is the only global international organisation dealing with the rules of trade between nations. The goal of WTO is to help producers of goods and services, exporters and importers conduct their business. Nearly 164 countries of the world are currently members of the WTO (As on 29-7-2016).
Question 9.
Write about the military alliances.
Answer:
Both the USA and the USSR were in the possession of nuclear weapons but knew very well neither would be the winner in a nuclear war. Yet, they formed military and strategic alliances – the West formalised its alliances in an organisation known as North Atlantic Treaty Organisation (NATO) in 1949. To counter this, Communist nations made similar alliances and signed the Warsaw Pact. In addition to this, the US established regional military and strategic alliances like South East Asian Treaty Organisation (SEATO) and Central Treaty Organization (CENTO).
Question 10.
What was meant by liberalisation?
Answer:
- Liberalisation means a lot of things put together like drastic reduction of government expenditure, reducing restrictions and taxes on imports, etc.
- It proved for reducing restrictions on foreign investments in India and allowed foreign countries to set up companies in India.
- It is required to the opening of many sectors of the economy to private investors.
- It brought in foreign goods and Indian businessmen were forced to compete with them.
- It had many positive and negative impacts on India.
Question 11.
Describe the categories of working population.
Answer:
The Census of India groups the working population into four categories. Cultivators are farmers, who farm or supervise the land that they own or take on rent. Agricultural labourers are those who work on another’s farm for wages in cash or kind. Workers in household industries would be those who are manufacturing or repairing some product at home such as dehusking of paddy, bidi workers, potters, weavers, repair of footwear, manufacture of toys, matches, etc. Other workers would be those who are employed ¡n factories, trading, casual labour and all other occupations.
Question 12.
explain the land and water relationship.
Answer:
The amount of sunlight that is first absorbed and then radiated back or directly reflected depends on the nature of the surface. Darker areas, such as heavily vegetated regions, tend to be good absorbers; lighter areas such as snow and ice-covered regions tend to be good reflectors. The ocean absorbs and loses heat more slowly than land. This affects climate in many ways.
![]()
Section – III
6 x 5 = 30 M
1. Answer alt questions.
2. There is an internal choice for each question.
3. Answer each question in 8-10 sentences.
4. Each question carries 5 marks.
Question 13.
What are the salient features of food security bill?
(OR)
‘Denial of equal rights was the root cause of many social movements”. Elucidate.
Answer:
- The Indian government came out with a new law in 2013 called the ‘National Food Security Act’ to legalise people’s Right to Food.
- Every person of low-income family is entitled to 5 kgs of foodgrains per month at subsidised rates.
- The poorest families are entitled to 35 kgs of food grains.
- For a few years, the central government supply rice, wheat and millets for ‘ ₹ 3 ₹ 2, and ₹ 1 respectively.
- If government is not able to arrange food grains, it will give cash for the people to buy food grains.
- Providing free cooked meals for pregnant women, lactating mothers, children aged 1-6 coming to Anganwadis and mid-day meals for children aged 6 -14 years in schools are also the features of the bill.
(OR)
- Many social movements have fought for equal rights for the deprived classes.
- Black Americans suffered from segregation in schools, buses and in public places.
- They were also discriminated in appointments housing and even voting rights.
- Many Eastern European countries did not allow free multiparty elections, free uncensored press, freedom of expression, movement of ordinary people.
- Many movements for equal treatment of women, equal rights, wages, and opportunities, justice are also organised.
- Thus, we can say that denial of equal rights was the root cause of many social movements.
Question 14.
Read the para and answer the given questions. Rajeshwari is working as a construction worker. She goes for work at 7 a.m. and returns home at 7 p.m. She travels about 8 to 10 kilometers daily for work by bus. Construction workers get one hour lunch break between 1 pm and 2 p.m. She gets, work only for 10 to 12 days a month. In the remaining days, she has no work, and she does not get any wage. She gets 150 per day as wages. Mostly, she is paid the wages on the spot in the evening. When she works for three or four days at the same day, she is paid after the work is completed.
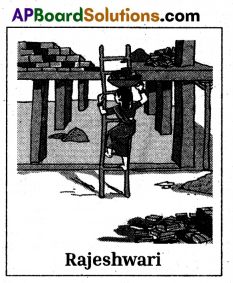
She gets more work from February to June. July to January is unseasonal. Rajeshwari is a member of a Self Help Group
in her locality. The government will pay some compensation in case of death or major injury while she is at work. There is no help from the government for the treatment in accidents while working. She is also a part of a group that works under a mason. There are 6 to 10 workers under each mason.
i) Where is Rajeshwari working?
ii) What are the working hours of Rajeshwari?
iii) How much money does she earn every day?
iv) Which months does Rajeshwari get more work?
v) In which group Rajeshwari is a member?
(OR)
Write about peninsular rivers.
Answer:
i) Rajeshwari is working at a construction worker.
ii) She works from 7 a.m. to 7 p.m. every day.
iii) She earns ‘ ₹ 150 every day.
iv) She gets more work from February to June.
v) Rajeshwari is a member of Self Help Group in her locality.
(OR)
1. The Western Ghats are the water divide between the major peninsular rivers, discharging their water in the Bay of Bengal and as small rivulets joining the Arabian Sea.
2. Most of the major peninsular rivers except Narmada and Tapti flow from West to East.
3. The Chambal, Sind, Betwa, Ken, and Son originating in the northern part of the peninsular belongs to the Ganga river system.
4. The other major river systems of the peninsular drainàge are the Mahanadi, the Godavari, the Krishna, and the Cauveri.
5. Peninsular rivers are characterized by fixed course, absence of meanders, and largely perennial flow of water.
Question 15.
How far were secret alliances the cause for the World War — I ? (Or) “Secret alliances laid the first road map to world war – I”. Comment.
(OR)
Why does the oil spillage from oil wells have a major impact on the ecosystem?
Answer:
- After defeating France in 1870, Bismarck, the German Chancellor decided to isolate it.
- To achieve this end, he entered into secret alliances with Austria and Italy thus formed ‘Triple Alliance’ in 1882.
- The French broke their isolation by striking a mutual alliance with Russia.
- Again they resolved their irritants with Britain.
- Thus Russia, France, and Britain formed their Triple Entente in 1907.
- These European countries formed secret alliances to safeguard their freedom, economic and commercial interests.
- These secret alliances made European powers jealous and suspicious of one another.
- Instead of real peace, these alliances created an atmosphere of fear and armed peace in Europe.
- Thus we can say secret alliances were a justifiable cause for the World War I.
(OR)
- Oil spillage from oil wells has a major impact on the ecosystem.
- Large tracts of the mangrove forests, which are especially susceptible to oil (this is mainly because it is stored in the soil and re-released annually with inundation), have been destroyed.
- As estimated 5-10% of Nigerian mangrove ecosystems have been wiped out either by clearing or oil.
- Spills destroy crops and aquaculture through contamination of the groundwater and soils.
- Drinking water is also frequently contaminated and a sheen of oil is visible in many local water bodies.
- Offshore spills, which are usually much greater in scale, contaminate coastal environment and cause a decline in local fish production.
![]()
Question 16.
What makes an election democratic?
(OR)
Describe the features of Indian Federalism.
Answer:
Elections can be held in many ways. All the democratic countries held elections, but really some countries only conducted in fair manner.
Minimum conditions of a democratic election:
- Everyone should be able to choose.
- Everyone should have one vote one person and one value.
- Parties and candidates should be free contest elections and should offer some real choice to the voters.
- The choice should be offered at regular intervals.
- The candidate preferred by the people should get elected.
- Elections should be conducted in free and fair manner.
(OR)
The features of Indian Federalism:
- Supremacy of the Constitution: The suprçmacy of the Constitution means that both the Union and State governments shall operate within the limits set by the Constitution.
- Written constitution: The constitution of India is the largest and most elaborate one, which discusses on several issues.
- Division of powers: The Indian constitution clearly described administrative powers into three lists viz The Union List, The State List, and The Concurrent List.
- Supremacy of the Judiciary: As per the Constitution of India, Judiciary is Independent and supreme. It can declare a contrivances law as unconstitutional.
Question 17.
What are the problems of overpopulation?
(OR)
What is Organic fanning?
Answer:
The problems of overpopulation are:
- Resource crisis
- Water and Energy crisis
- Traffic problems
- Inflation
- Pollution problems
- Unemployment crisis
- Slum areas increases
- Dearth of housing
- Anti-social activities
- Rise of poverty levels
- Corruption, Mafia
- Violence extends etc.
(OR)
- Organic farming is to forego the use of chemical fertilizers and pesticides.
- It rely mainly on natural techniques such as crop rotation, natural compost, and biological pest control in farming.
- Farms can be bio-diverse.
- Farmers can produce a variety of crops.
- Organic farming use local resources like on-farm biological process.
- It protects the environment from pollution.
Question 18.
Locate the following on the physical map of India on the raised relief Map:
1) Malwa Plateau
2) Bundelkhand
3) Bhagelkhand
4) Rajmahal Hills
5) Chotanagpur plateau
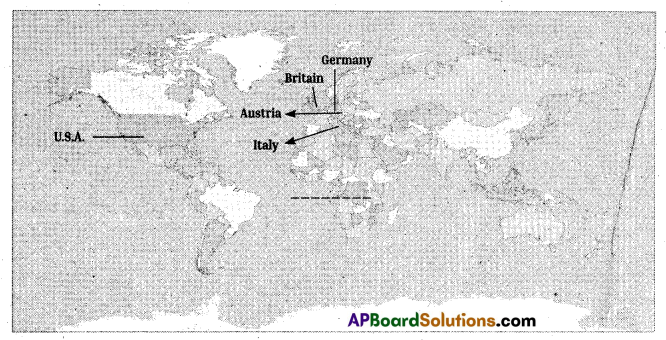
(OR)
Locate the following in the map of the world.
1) Germany
2) Italy
3) Austria
4) U.S.A
5) Britain
Answer:
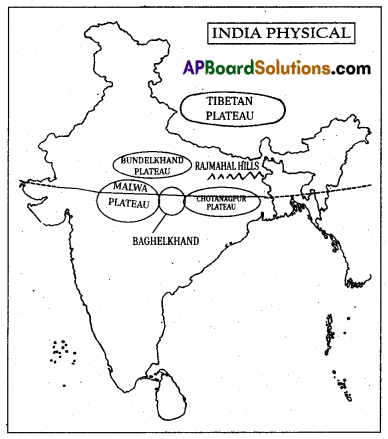
or
Part – B (Marks 20)
Instructions:
- Answer all questions.
- Choose the correct option from the given four Options and write the letter (A to B or C or D) in CAPITAL LETTER in the brackets.
- Each question carries 1 mark.
- Write the answers in the question paper itself.
- Marks are not given to corrected, dismissed or erased answers.
Question 1.
……………….. is the highest peak in South India. ( )
A) Dodabetta
B) Anaimudi
C) Everest
D) Annamalai Hills
Answer:
B) Anaimudi
Question 2.
All human efforts put In production is ( )
A) casual labour
B) manual labour
C) capital
D) labour
Answer:
D) labour
Question 3.
Nationalists from Coastal Andhra also supported this Telangana movement in ( )
A) 1960s
B) 1970s
C) 1940s
D) 1980s
Answer:
C) 1940s
![]()
Question 4.
This is playing vital role in deciding the value of a currency. ( )
A) Government
B) Reserve Bank of India
C) Market forces
D) People
Answer:
C) Market forces
Question 5.
World Health Organisation is located at ( )
A) Hague
B) New York
C) Geneva
D) Paris
Answer:
C) Geneva
Question 6.
This party led anti-Hindi agitation in South. ( )
A) AIADMK
B) DMK
C) TDP
D) TRS
Answer:
B) DMK
Question 7.
The idea of equality is also based on the ………………. . ( )
A) country
B) religion
C) region
D) people
Answer:
A) country
Question 8.
The least temperature and rainfall is recorded at ………………… . ( )
A) Leh
B) Delhi
C) Chennai
D) Jaipur
Answer:
A) Leh
Question 9.
Public Distribution System is associated with ( )
A) Ration shops
B) Co-operative stores
C) Super Bazaars
D) General stores
Answer:
A) Ration shops
Question 10.
Alcohol prohibition in Andhra Pradesh was imposed in ( )
A) 1991
B) 1992
C) 1993
D) 1995
Answer:
D) 1995
Question 11.
This is not an example for a final good. ( )
A) Car
B) Notebook
C) TV
D) Tyre
Answer:
D) Tyre
![]()
Question 12.
Second largest peninsular river is ( )
A) Krishna
B) Mahanadi
C) Godavari
D) Cauvery
Answer:
A) Krishna
Question 13.
Mussolini belonged to ‘( )
A) Italy
B) Germany
C) France
D) Russia
Answer:
A) Italy
Question 14.
Nigeria was the colony of this country. ( )
A) Britain
B) France
C) Germany
D) Spain
Answer:
A) Britain
Question 15.
In which part of the constitution Election Commission’s functions are mentioned ( )
A) 14
B) 16
C) 15
D) 20
Answer:
C) 15
Question 16.
The Constitution of India is ( )
A) Flexible
B) Only women
C) Partly flexible and Partly rigid
D) Discrimination on women
Answer:
C) Partly flexible and Partly rigid
Question 17.
The largest city in population is ( )
A) Chennai
B) Kolkata
C) Delhi
D) Mumbai
Answer:
D) Mumbai
Question 18.
“Chipko Andolan” started in ( )
A) Uttarakhand
B) Kerala
C) Tripura
D) U.P.
Answer:
A) Uttarakhand
19. The Second World War was started in ( )
A) 1944
B) 1938
C) 1937
D) 1939
Answer:
D) 1939
Question 20.
Gender bias. ( )
A) Men and women
B) Rigid
C) Only men
D) None of these
Answer:
D) None of these.