Telangana SCERT 10th Class Biology Study Material Telangana 4th Lesson Excretion Textbook Questions and Answers.
TS 10th Class Biology 4th Lesson Questions and Answers Telangana – Excretion
Question 1.
What is meant by excretion? Explain the process of formation of urine.
Answer:
Due to metabolism several harmful excretory products are formed, the process of removing toxic waste from the body is called excretion.
Formation of urine involves four stages:
1) Glomerular filtration
2) Tubular reabsorption,
3) Tubular secretion and
4) Formation of concentrated urine.
1) Glomerular filtration:
- The which blood flows into glomerulus, it is filtered under high pressure.
- As a result waste materials along with sorne water and useful substances are filtered out.
- They enter into the Bowman’s capsule. This is called glomerular filtration.
- This filterate is also called as ‘primary urine’.
2) Tubular Reabsorption:
- Primary urine which is in glomerulus is almost equal to blood in chemical composition except the presence of blood cells.
- Peritubular capillaries present around the Henle’s loop reabsorb essential substances and excess water present in the primary urine.
3) Tubular secretion:
- After reabsorption of essential substances and water urine travels through the loop of Henle.
- From peritubular capillaries, present around the loop of Renie, waste materials left unfiltered in the blood during glomerulus filteration are secreted into the loop of Henle.
4) Formation of concentrated Urine:
- Urine that reaches into the collecting tubule, from the loop of Renie is further concentrated in the presence of hormone vasopressin.
- Deficiency of vasopressin causes excessive dilute urination called diabetes insipidus’.
![]()
Question 2.
How are waste products excreted in amoeba?
Answer:
- Special excretory organs are absent in unicellular organisms like amoeba.
- Amoeba possess osmoregulatory organelle called contractile vacuole.
- It collects water and wastes from the body. swells up, reaches the surface and bursts to release its content to outside.
- The main excretion takes place through body surface by simple diffusion.
- The waste material carbon dioxide is removed by diffusion through the cell membrane.
Question 3.
Name different excretory organs in human body and excretory material generated by them?
Answer:
| Excretory organs. | Excretory material generated |
| 1. Kidney | Filters blood and eliminates nitrogenous wastes and other harmful things. Filters urea from the blood. |
| 2. Lungs | They remove carbon dioxide and water in respiration. |
| 3. Skin | Sweat and metabolic wastes. Sebaceous glands in skin eliminates sebum which contains waxes,sterols, hydrocarbons and fatty acids. |
| 4. Liver | Bile patients bilirubin, biliverdin and ur(home are metabolic wastes of hemoglobin of dead red blood cells. Urochrorne is eliminated through urine. Liver also eliminates cholesterol and derivatives of steroid hormones, extra drug, vitamins and alkaline salts. Urea is also formed in liver. |
| 5. Intestine | Excess salts of calcium, magnesium, undigested food material and iron are excreted by epithelial cells of the colon for elimination along with feces. |
| 6. Endocrine glands | These allow excess water to leave the body. They are present mainly on the forehead, the bottom of the feet and the palms. |
| 7. Salivary glands and Lacrimal glands |
Small amount of nitrogenous wastes are also eliminated through saliva and tears. |
Question 4.
Deepak said that Nephrons are functional and structural units of kidneys’ how will you support him?
Answer:
I support Deepak’s statement that nephrons are functional units of kidneys because
- Nephron’s chief function is to regulate the concentration of water and soluble substances like sodium salts by filtering the blood, reabsorbing what is needed and excreting the rest as urine.
- Nephron eliminates wastes from the body, regulates blood volume and blood pressure, controls level of electrolytes and metabolites and regulates blood pH.
- Its functions are vertical level and are regulated by the endocrine system.
- Proper function of nephon mean proper function of kidneys.
- Hence, nephrons are the functional units of kidneys.
![]()
Question 5.
How plants manage the waste materials?
Answer:
- Plants can get rid of excess water by a process like transpiration and guttation.
- Waste products may be stored in leaves, bark and fruits.
- When these dead leaves, bark and ripe fruits fall off from the tree then waste products in them are get rid of.
- Some of the plants waste gets stored in the fruits in the form of solid bodies called Raphides. e.g : Yam.
- Several plants prepare chemicals and store them in roots, leaves, seeds, etc., for protection against herbivores.
- The plants excrete carbon dioxide produced as a waste during respiration only at night time.
- The plants excrete oxygen as a waste only during the daytime.
- The plants get rid of wastes by secreting them in the form of gums and resins.
- Plants also excrete some waste substances into the soil around them.
Question 6.
Why do some people need to use a dialysis machine? Explain the principle involved in it.
Answer:
Dialysis machine is used to filter the blood of a person when two kidneys are damaged. The process is called ‘haemodialysis’.
Principles involved in haemodialysis:
- In this process blood is taken out from the main artery, mixed with an anticoagulant such as heparin and then pumped into the apparatus called dialyzer.
- In this apparatus blood flows through channels or tubes. These tubes are embedded in the dialyzing fluid.
- The membrane separates the blood flowing inside the tube and dialyzing fluid, which
has the same composition as that of plasma, except the nitrogenous wastes. - The patient’s blood ¡s passed through the tubes, during this passage the waste products from the blood pass into dialysing fluid by diffusion.
- This process is called dialysis.
- The purified blood is pumped back into the patient through a vein. This is similar to the function of kidney but it is different since there is no reabsorption involved.
- Each dialysis session lasts for 3 to 6 hours. This method has been using for thousands of uremic/kidney failure patients all over the world.
Question 7.
What is meant by osmoregulation? How is it maintained in human body?
Answer:
- Osmoregulation is the process of maintaining salt and water balance across membranes within the body.
- The kidneys are the main osmoregulatory organs in human body.
- They function to filter blood and maintain the dissolved ion concentrations of body fluids.
- The nephron is the functional unit of the kidney, which actively filters blood and generates urine.
- Hormones like antidiuretic hormone vasopressin and aldosterone used in the body to help to increase the permeability of the collecting ducts found in the kidney.
- This further allows diffusing to occur easily, it also allows the kidneys to be able to absorb water and prevent it from being excreted.
- Humans are also able to regulate by controlling the total amount of water that is passed out of the body through the urine or sweat.
- Absence of vasopressin hormone produces dilute urine. Hormone action maintains osmotic concentration of body fluids.
- Deficiency of vasopressin causes excessive, repeated, dilute urination.
![]()
Question 8.
Do you find any relationship between circulatory system and excretory system? What are they?
Answer:
- Circulatory system delivers oxygen, nutrients, water, hormones and other essential materials to each cell of the body.
- And it also transports aB the carbon dioxide and other waste products of the cells to the lungs to be expired or to the kidneys to be excreted.
- The excretory system is closely related to the circulatory system by virtue of the process of cleaning the blood of waste, removing excess fluids and generally keeping other fluids in balance.
- An excretory system releases hormones to elevate blood pressure and accelerate red blood cells production
- Kidney stimulates the red blood cell production by erythropoiesis and regulates blood pressure with the secretion of renin.
Question 9.
Give reasons
a. Always vasopressin is not secreted.
b. When urine is discharged, in beginning it is acidic in nature later it become alkaline.
c. Diameter of afferent arteriole is bigger than efferent arteriole.
d. Urine is slightly thicker in summer than in winter’?
Answer:
a. Reason :
- Absence of vasopressin hormone produces dilute urine.
- When amount of water in body is low and concentrated urine is to be passed. Then only vasopressin secretes.
b. Reason : It is acidic In the beginning but becomes alkaline on standing due to decomposition of urea to form ammonia.
c. Reason : The afferent arteriole in a nephron has a larger diameter than the outgoing efferent arteriole and this rise the blood pressure in the glomeruhis capillaries lead to the ultrafiltration of the blood in the Bowman’s capsule.
d. Reason : In summer sweating takes place and water losses from our body. So to maintain the water balance in the body only harmful nitrogenous wastes are removed from the body. Water is reabsorbed considerable into body. That is why urine is thicker in summer.
Question 10.
Write differences
A. Functions of PCT and DCT
B. Kidney and artificial kidney
C. Excretion and secretion
D. Primary metabolites and secondary metabolites
Answer:
a. Functions of PCT and DCT:
Functions of PCT:
- Reabsorbs glucose, amino acids, phosphates, potassium, urea and other organic solutes from the filtrate into the peritubular network.
- The PCT regulates the pi-l of the filtrates by exchanging hydrogen ions in the interstitium for bicarbonate ions in the filtrate.
- It is also responsible for secreting organic acids such as creatinine and other bases into the filtrate.
- Proximal convoluted tubule regulate the pH of the filtrate in the kidneys.
Functions of DCT:
- It maintains a proper concentration and pH of the urine.
- Extra salts, ions of K, Na, CT and W secretes from peritubular capillaries into DCT.
- It secretes ammonium ions and hydrogen ions.
- It is relatively impermeable to water but in the pressure of Antidiuretic hormone (ADH) its permeability to water Increases making urine concentrated.
![]()
b.
| Kidney | Artificial kidney |
| 1. It is a natural excretory organ in human beings to filter blood and forms urine. | 1. It is a device to remove nitrogenous waste products from the blood through dialysis. |
| 2. Kidney is used to filter blood in healthy persons. | 2. It is used in persons in which both kidneys are spoiled. |
| 3. Blood that passes through kidney contains nitrogenous wastes. | 3. Dialysing fluid used in dialysis machine do not contain nitrogenous wastes. |
| 4. Person’s blood passes through Malphigian body and renal tubule during filtration. | 4. Patient’s blood is passed through number of tubes with semi-permeable lining suspended in a tank filled with dialysing fluid. |
| 5. Reabsorption of materials takes place in proximal convoluted tubule and distal convoluted tubule of renal tubule. | 5. No absorption of material takes place in artificial kidney. |
c. Excretion and secretion:
| Excretion | Secretion |
| 1) It is the removal of materials from a living being. | 1) It is movement of material from one point to other point. |
| 2) Excretion is passive in nature. | 2) Secretion is active in nature. |
| 3) Humans excrete materials such as tears, urine, carbon dioxide and sweat. | 3) Humans secretions includes enzymes, hormones and saliva. |
| 4) Excretion is mostly body waste. | 4) Secretion is important materials that can be metabolized and used by our body. |
| 5) Plants excrete through roots into its surroundings and falling off leaves and bark. | 5) Secretions occur in the plant body in the form of latex, resins, gums etc. |
d. Primary metabolites and secondary metabolites:
| Primary metabolites | Secondary metabolites |
| 1) They are involved in normal growth, development and reproduction. | 1) They are not directly involved in the normal growth, development and reproduction. |
| 2) Examples for primary metabolites are carbohydrates, fats and proteins. | 2) Examples for secondary metabolites are alkaloids, tannins, resins, gums and latex etc. |
| 3) They are not poisonous. | 3) Some of these compounds are poisonous. |
Question 11.
There is a pair of bean-shaped organs ‘P’ in the human body towards the back.,just above the waist. A waste product ‘Q’ formed by the decomposition of unused proteins in liver is brought into organ ‘P’ through blood by an artery ‘R’. The numerous tiny filters ‘S’ present in organ ‘p’ clean the dirty blood goes into circulation through a vein ‘T’. The waste substance ‘Q’ and other waste salts and excess water form a yellowish liquid ‘U’ which goes from organ ‘P’ into a bag like structure ‘V’ through two tubes ‘W’. This liquid is then thrown out of the body through a tube ‘X’.
a. What is
i. organ P and
ii. waste substance Q.
Answer:
i) Organ P is, kidney and
ii) Waste substance Q is urea.
b. Name
i. artery R and
ii. vein T
Answer:
i) Artery R is Renal arteryand
ii) Vein T is Renal vein.
c. What are tiny filters S known as?
Answer:
Tiny filters S are Nephrons.
d. Name
i. liquid U
ii. structure V
iii. tubes W
iv. tube X.
Answer:
i. Liquid Ui urine.
ii. Structure V is urinary bladder.
iii. Tube W is ureters.
iv. Tube X is urethra.
![]()
Question 12.
The organ ‘A’ ofa person has been damaged completely due to a poisonous waste material B has started accumulation in his blood, making it dirty. In order to save this person’s life, the blood from an artery in the person’s arm is made to flow into long tubes made of substance ‘E’ which are kept in coiled form in a tank containing solution ‘F’. This solution contains three materials ‘G’, ‘H’ and ‘I’ similar proportions to those in normal blood. As the person ‘s blood passes through long tubes of substance ‘E’, most if the wastes present in it go into solution ‘F’. The clean blood is then put back into a vein in the person for circulation.
(a) What is organ A?
Answer:
Kidney
(b) Name the wastes substance B.
Answer:
Urea
(c) What are (i) E, and (ii) F?
Answer:
- Long tubes E are made of cellulose.
- Solution ‘F’ is dialysing fluid contains three materials like : water, glucose and salts.
(d) What are G, H and I?
Answer:
Waste molecules, nutrient molecules and water.
(e) What is the process described above known as?
Answer:
Dialysis.
Question 13.
Imagine what happens if waste materials are not sent out of the body from time to time?
Answer:
- If waste materials are not sent out of the body from time to time they get accumulates in the body.
- The accumulation of toxic wastes in the body harms an organism.
- For an organism to lead a normal life, the toxic wastes being produced in its body
must be removed from time to time. - If all the waste released is not sent out, the waste gets stagnated, produce toxins and poisons which pollute the body. They lead to death of the organism.
Question 14.
To keep your kidneys healthy for long period what questions will you ask a nephrologist/urologist?
Answer:
The questions iam going to ask a nephrologist/urologjst to keep my kidneys healthy for long period are
- How can prevent formation of stones in kidney?
- Does a renal failure hereditary?
- What are the dietary measures to be taken for normal functioning of kidney?
- How does diabetes harm kidneys?
- What shall I do to keep my kidneys healthy for a long time?
- What are the factors responsible for kidney failure?
- What is the normal functioning of kidney?
- Is there any relationship between blood pressure and kidney function?
- What are the kidney function tests?
- What kind of medications should I avoid?
- What are the symptoms of kidney failure?
- How frequently should my kidney function be checked?
- How can I prolong my kidney health?
- What causes chronic kidney disease?
- How much water should I drink per a day?
- Why is smoking bad for the kidneys?
- What are the different types of kidney disease’s?
- Who is most prone to kidney disease?
- What can I do to help fight kidney disease?
- If one kidney fails can we live on another kidney?
(You can add some more questions)
![]()
Question 15.
What are the gum-yielding trees in your surroundings? What procedure you should follow to collect gum from trees?
Answer:
- Gum yielding plants : Neem, Acacia, Eucalyptus, Sapota, etc.
- Though some gum will flow naturally from cracks in the bark of acacia and neem,we have to stimulate the flow by removing thin strips of bark an operation that requires some skill.
- Gum is collected about four weeks after stripping and can be repeated every few weeks thereafter several months.
- For collecting gum from trees we have to locate some mature gum trees.
- From the location we have to identify the best species of gum tree for collecting gum.
- Some tools are required for collecting gum.
- We have to choose a tree to make tap into.
- Break the bark away from the sap (live) wood about 3 foot from the ground and about 10 inches wide, by chopping the bark away with an axe or sickle.
- We have to fit collecting bucket tightly to the sap wood so that when gum begins to seep out, it will drip into it.
- Break some shallow notches in a ‘V’ shape, with the point of the ‘V’ directly above the centre of the bucket.
- Leave the bucket attached to the tree until the gum begins to seep out and drains into it.
- Remove any nails or other metal things when we finished from the tree and take down the gum collection bucket.
Question 16.
Collect the information about uses of different kinds alkaloids, take help of library or internet?
Answer:
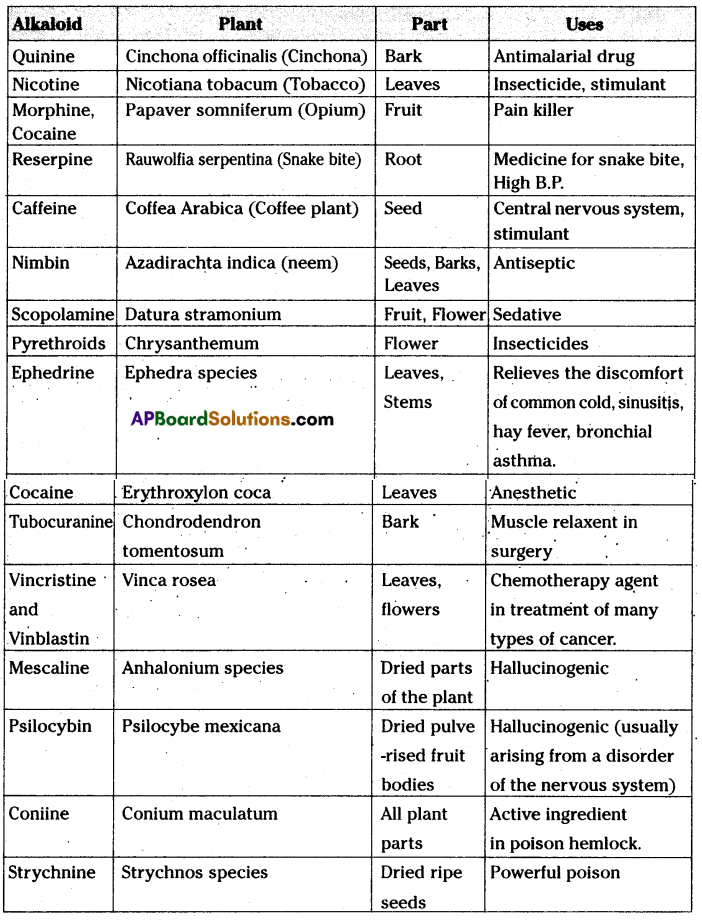
Question 17.
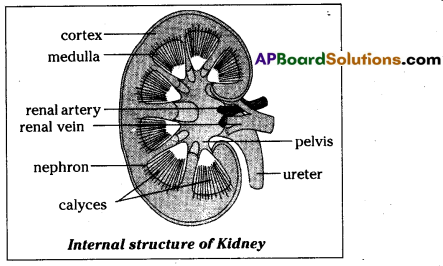
Draw a neat labeled diagram of L.S of kidney?
Answer:
Question 18.
Describe the structure of nephron with the help of a diagram.
Answer:
Structure of nephron: Each nephron has the following parts.
A. Malpiglilan body:
- It consists of a blind cup-shaped broader end of nephron called Bowman’s capsule.
- And a bunch of fine blood capillaries called glomerulus.
- The afferent arteriole (arteriole is the finer branch of an artery) enters Into the
Bowman’s capsule and divides into a network of capillaries. - It comes out of the capsule as efferent arteriole with lesser diameter.
- The bunch of capillaries is called glomerulus.
- Because of the narrower outlet (efferent arteriole) pressure exerts in the glomerulus.
- It functions as a filtration unit.
- Bowman’s capsule which accommodates one glomerulus, is lined by a single layer of squamous epithelial cells called podocyte cells.
- There are fine pores between pod ocyte cells to allow passage of materials filtered out of glomerulus.
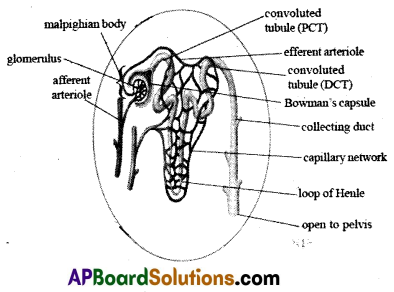
B. Renal tubule:
- It has three parts.
- First or proximal convoluted tubule (PCT), loop of Henle, which is U shaped, second or distal convoluted tubule (DCT).
- Distal convoluted tubules open into a collecting tube.
- Collecting tubules form pyramids and calyces which open into the pelvis.
- Pelvis leads into the ureter.
- All the parts of the renal tubule are surrounded by a network of peritubular (around tube) capillaries formed from efferent arteriole.
- The peritubular capillaries join to form renal venule, which joins the other venules to form finally the renal vein.
![]()
Question 19.
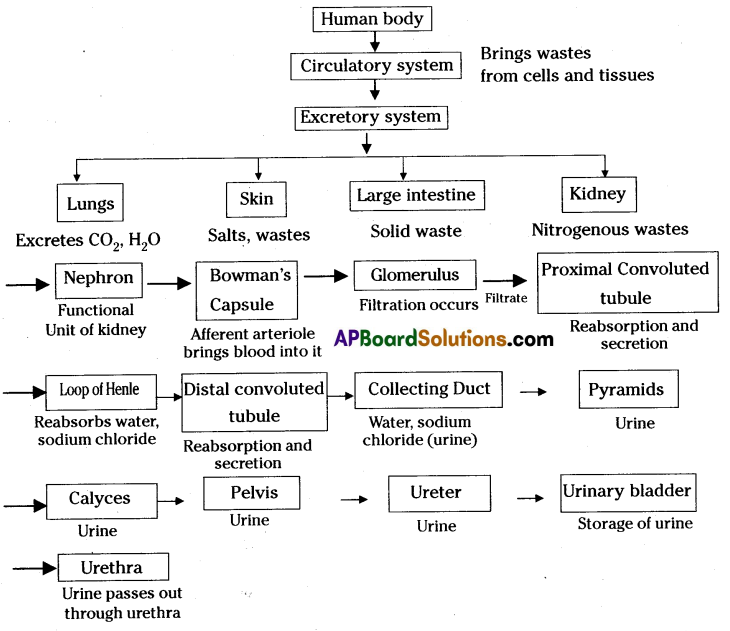
Draw a block diagram showing the pathway of excretory system in human beings.
Answer:
Block diagram showing the pathway of excretory system in human beings.
Question 20.
If you want to explain the process of filtration in kidney what diagram you need to draw.
Answer:
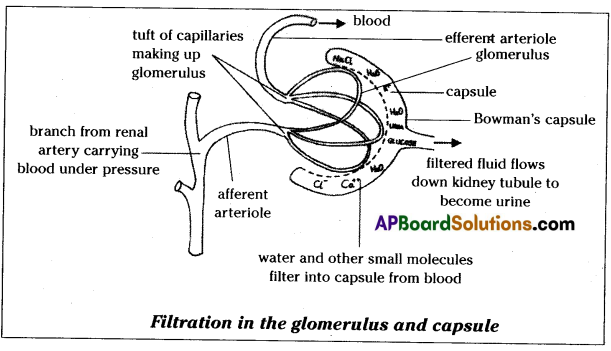
Question 21.
List out the things that makes you amazing in excretory system of human being.
Answer:
- Kidneys remove garbage from our body. They also work towards balancing the amount of vitamins, minerals, fat and protein that are found in the blood. It does this so that our body can easily perform day to day activities.
- The right and left kidneys are assisted by a number of organs in the body which help in disposing waste products.
- Our intestine makes solid waste materials and is excreted through digestive tract.
- Each day our body eliminates around 1.6 to 1.8 litres all of the liquids, minerals and vitamins that are of no use to the body are contained the urine.
- The bladder of a human body is nearly the same size as the average of human brain.
- In one individual’s life span the liver can produce around 184.275 kgs of bile (6500 ounces).
- In our life time an individual could urinate close to 7,850,000,000 gallons of fluid.
- There are two kidneys in the human body. The left kidney is always found higher than the right kidney.
- A really extraordinary fact regarding the excretory system is that upto 400 ml of urine can be held in human bladder.
- Skin is also an excretory organ responsible for elimination of wastes through sweat along with various toxins.
- Urine contains a high amount of urea which can be used by plants as a source of nitrogen. Because of this diluted urine can be used in gardens and potted plants.
Question 22.
You read about ‘Brain dead’ in this chapter. What discussions would you like to have why you think so?
Answer:
- When some one is brain dead, there is no blood flow or oxygen to their brain.
- The brain stops functioning ¡n any capacity.
- Because the ventilator is breathing for the person organs such as the heart and liver continue to receive oxygen and one able to function for a few days after the
brain has dead. - Unless damaged by injury we can transplant organs like kidney, liver, heart, lungs, pancreas, skin, bone, intestine and eyes (Retina) from brain’ dead patients.
- The process of transplantation of organs from brain dead patients to another is called cadaver transplantation.
- There is very less awareness among people about organ donation.
- Society needs much awareness in organ donation so that we can save many lives who are in need of different organs for their survival.
- Those who are willing to donate their organs have to sign in an application form at transplantation facility hospital.
- Some voluntary organisation like jeevandan.org working on this aspect.
![]()
Question 23.
We people have very less awareness about organ donation, to motivate people write slogans about organ donation?
Answer:
- Organ donation saves lives.
- Give a life, gift of life.
- Donate organs today for better tomorrow.
- The measure of a life, after all is not its duration but its donation.
- Change your thoughts and you change your world.
- Organ donation is icky (disagreeable) but recycle yourself is sticky.
- Support organ donation across our great nation.
- Give my eyes to a man who has never seen a sun rise.
- Give my heart to a person whose own heart has caused nothing but endless days of pain.
- The gift that lives on.
Question 24.
After learning this chapter what habits you would like to change or follow for proper functioning of kidneys?
Answer:
- I always eat the home-cooked meals. Canned foods, fast foods, restaurant foods and highly processed food cause malfunctioning of kidney I avoid eating the above food items.
- I should adopt to take low salt diet to help controlling blood pressure and slow down a kidney damage.
- Eating food that are lower in protein can help to decrease levels of urea and improve kidney function.
- I replace high protein foods like meat, eggs and milk products with lower protein options like grains and vegetables.
- I avoid eating products that contain refined sugar such as cakes, pies, cookies, candies and pastries. I replace the above food items with fruits containing simple carbohydrates.
- High sodium content in the food damages kidneys. Hence I avoid foods that are high in sodium Including potato chips, bacon (cured meat from back or sides of pig), cheese, meat, canned vegetables, canned soups, frozen dinners and table salt.
- Spices that do not contain sodium can be used to add flavour to food without increasing sodium intake.
- I avoid taking high phosphorus foods such as cheese, cola soft drinks, butter and I replace them with lower phosphorus foods such as soft drinks, sharbat etc.
- Potassium levels in the body are kept at normal levels by kidneys. So I eat food with how potassium levels.
- Potassium levels are low In apples, watermelon, cucumber, grapes, cherries and carrot. High potassium levels cause Irregular heart beats.
Fill in the blanks :
1. Earthworm excretes t ts waste material through …………….
2. The dark coloured outer zone of kidney is called …………….
3. The process of control of water balance and ion concentration within organism is called …………….
4. Reabsorption of useful product takes place in ……………. part of nephron.
5. Gums and resins are the ……………. products of the plants.
6. Bowman’s capsule and glomerulus taken together make a …………….
7. The alkaloid used for malaria treatment is …………….
8. The principle involved in dialysis is …………….
9. Rubber is produced from ……………. of Heavea braziliensis of rubber plants.
10. ……………. performed first Kidney Transplantation.
Answer:
1. nephridia
2. cortex
3. osmoregulation
4. tubular
5. secondary metabolic
6. malphigian tubule
7. quinine
8. separation
9. latex
10. Dr. Charles Hufnagei
![]()
Choose the correct answer:
Question 1.
The structural and functional unit of human kidney is called ……………..
A. Neuron
B. Nephron
C. Nephridia
D. Flame cell
Answer:
B. Nephron
Question 2.
The excretory organ in cockroach
A. Maiphigian tubules
B. Raphids
C. Ureters
D. Nephridia
Answer:
A. Maiphigian tubules
Question 3.
Which of the following is the correct path taken by urine in our body
i. Kidneys
ii. Ureters
iii. Urethra
iv. Urinary bladder
A. i, ii, iv, iii
B. i, ii, iii, iv
C. iv, iii, i, ii
D. ii, iii, i, iv
Answer:
A. i, ii, iv, iii
Question 4.
Maiphlgian tubes are excretory organs in ………..
A. Earthworm
B. Housefly
C. Flatworm
D. Flame cell
Answer:
B. Housefly
Question 5.
Major component of urine is ………………….
A. Urea
B. Sodium
C. Water
D. Creatine
Answer:
C. Water
Question 6.
Special excretory organs are absent in ……………..
A. Birds
B. Amoeba
C. Sponges
D. A and B
Answer:
B. Amoeba
Question 7.
Which of the following hormones has direct impact on urination?
A. Adrenal
B. Vasopressin
C. Testosterone
D. Oestrogen
Answer:
B. Vasopressin
Question 8.
Amber colour to urine due to …………..
A. Urochrome
B. Bilirubin
C. Biliverdin
D. Chlorides
Answer:
A. Urochrome
![]()
Question 9.
Sequence of urine formation in nephron is ……………
A. Glomerular filtration → Tubular reabsorption → Tubular secretion
B. Tubular reabsorption → Tubular secretion → Glomerular filtration
C. Tubular secretion → Glomerular filtration → Tubular reabsorption
D. Tubular reabsorption → Concentration of urine → Tubular secretion
Answer:
A. Glomerular filtration → Tubular reabsorption → Tubular secretion
Question 10.
Part of the nephron that exists in outer zone of kidney.
A. Loop of the Henle
B. PCT
C. DCT
D. Bowman’s capsule
Answer:
D. Bowman’s capsule
Question 11.
After having lunch or dinner one can feel to pass urine, because of ……………
A. Stomach pressures on bladder
B. Solids become liquids
C. Water content in food material
D. Sphincter relaxation
Answer:
D. Sphincter relaxation
TS 10th Class Biology 4th Lesson Excretion Intext Questions
1 Mark Question and Answers :
Question 1.
What products would cause harm to the body, if they are not removed ?
Answer:
Nitrogenous compounds like ammonia, urea, uric acid, bile pigments, excess salts are toxic to the body. So they should be removed.
Question 2.
What happens if harmful products are not removed from our body every day ?
Answer:
If harmful products are not removed from our body they get accumulated in the body and becomes toxic. This leads to the death of the person.
Question 3.
What are the substances present in blood ?
Answer:
The substances present in blood are Glucose, Sodium, Potassium, Chlorides, Urea, Creatinine, Uric acid, Cholesterol, Triglycerides, Calcium Phosphorous, Bilirubin, Proteins, Albumin.
![]()
Question 4.
What are the substances present in urine ?
Answer:
Protein, Creatinine, Calcium, Phosphorous, Uric acid, Sodium, Potassium are the sub-stances present in urine.
Question 5.
What are the substances present both in blood and urine ?
Answer:
Sodium, Potassium, Chlorides, Urea, Uric acid, Calcium, Phosphorous are the substances present in blood and urine is common.
Question 6.
Which substances are present above the normal limits both in the blood and urine ?
Answer:
Sodium, Protein, Potassium, Urea, Uric acid, Cholesterol, Phosphorus, Calcium are present above the normal limits both in the blood and urine.
Question 7.
What do you think a reading above normal limits indicates ?
Answer:
If any material is above the normal limits, it causes health problem which leads to a disease and damage of the organs.
Question 8.
What are the materials needed to be removed from our body ?
Answer:
Carbon dioxide, water and nitrogenous compounds such as ammonia, urea and uric acid are the waste materials needed to be removed from our body.
Question 9.
Think why the diameter of the efferent arteriole is less than that of afferent arteriole ?
Answer:
The diameter of the efferent arteriole is less than afferent arteriole so as to create pressure in the glomerulus to filter the waste materials. Due to this, blood remains in glomerulus more time.
Question 10.
Why is the nephron considered to be the structural and functional unit of the kidney ?
Answer:
The nephron gives structure to the kidneys and it is the functioning unit like filtering the nitrogenous waste materials from the blood. So nephron is considered to be the structural and functional unit of the kidney.
Question 11.
Why more urine is produced in winter ?
Answer:
When we are in cold environment, blood flow to our internal organs is increased, to keep our organs warm. The increase in the blood flow to the kidneys causes more blood to be filtered. Thus more urine is produced in winter.
Question 12.
What happens if reabsorption of water does not takes place ?
Answer:
Our body is filled with water and our hands or feet may swell.
Question 13.
Is there any long term solution for kidney failure patients ?
Answer:
The best long term solution for kidney failure is kidney transplantation. A functioning kidney which is a good match to the body is used in transplantation from a donor preferably a closed relative.
Question 14.
What are the other excretory organs of human body ?
Answer:
Lungs, Skin, Liver are the other excretory organs of human body.
![]()
Question 15.
People in cold countries get very less/no sweat What changes occur in their skin and in other excretory organs ?
Answer:
In cold countries due to cool environment, the blood vessels are narrow and sweat production is reduced or no sweat. Thus, the skin keeps the body warm.
Question 16.
Do roots secrete ?
Answer:
Yes, roots also can secrete a portion of their peculiar secretions back into the soil.
Question 17.
Why do we get peculiar smell when you shift the potted plants ?
Answer:
Some peculiar secretions are secreted and sent out from roots into soil. When we shift the potted plant we get peculiar smell due to the chemical reaction of the secretion in the soil to make it fertile.
2 Mark Question and Answers :
Question 1.
What products would the organism be able to take up for other activities ?
Answer:
Oxygen produced in the photosynthesis process is used by all the living organisms on the earth for breathing. Without oxygen life would not be possible on the earth. No organism can survive. Carbon dioxide produced in respiration will be taken up by plants to prepare food materials, in the process of photosynthesis. Plants are called autotrophs because they produce food for all the animals and human beings directly or indirectly.
Question 2.
Where are these materials removed from ?
Answer:
Carbon dioxide is eliminated through lungs while small amounts of water is eliminated through body surface (sweating) and through lungs during respiration. An excretory organ system is present for excreting the nitrogenous wastes along with salts, excess water.
Question 3.
Why do you think the body must remove waste substances ?
Answer:
For the smooth functioning of the body the body should be healthy. Waste materials are the toxic substances, which are harmful to the body. So they should be eliminated. If they remain in the body, it leads to the unhealthy conditions to the organisms.
Question 4.
What happens if both kidneys fail completely ?
OR
What happens if both kidneys fail completely in human beings ?
Answer:
- Complete and irreversible kidney failure is sometimes called end stage renal disease (ESRD).
- If kidneys stop working completely, our body is filled with extra water and waste products. This condition is called uremia.
- Our hands or feet may swell.
- The person feels tired and weak because the body needs clean blood to function properly.
- The failure of kidneys leads to accumulation of poisonous wastes in the body and leads to death.
Question 5.
Collect information on sebum and prepare a news bulletin, display it on bulletin board.
Answer:
Sebaceous glands are present in the skin. These glands are also known as oil glands. They produce an oily substance called sebum. The sebaceous gland is like a sack. It has a duct through which it opens into the hair folicle. The sebum is sent outside through the hair folicle to the outside of the skin. Sebum prevents the skin from becoming dry.
![]()
Question 6.
Why do plants shed their leaves and bark periodically ?
Answer:
The leaf is a fragile organ and is at risk from desiccation arid freezing during winter months. To prevent damage most decidous trees shed their leaves in a process called abscission. The tree first withdraws valuable pigments like chlorophyll from leaf before forming a thin band of dead cells at the base of the stem separate the leaf to the stalk. The leaf tissue then dies and drops to the forest floor where it decomposes. Any useful nutrients are then reabsorbed by roots.
Question 7.
Name the alkaloids which are harmful to us.
Answer:
Nicotine is harmful. It causes lung cancer, throat cancer, tongue cancer and affects the nervous system.
Morphine which is used as pain killer, may affect kidneys if they are used more.
Nitrogenous substances are also found in the walls of pollen grains; they are protein substances and when they enter our body they cause allergy.
Question 8.
Do you think is there any relation between reduction in yielding and root secretions ?
Answer:
Yes, there is a relation between reduction in yielding and root secretions. For example, plants like apple where a single apple crop is yielded for 4 or 5 years continuously in the same soil, it fails to produce fruits. It will not give proper yield even if you use lot of fertilizers.
4 Mark Question and Answers :
Question 1.
Where is the transplanted kidney fixed in the body of a kidney failure patient?
Answer:
Kidney transplantation Involves placing a healthy kidney into the body where it can perform all of the functions that a failing kidney cannot. The new kidney is placed on the lower right or left side of the abdomen where it is surgically connected to nearby blood vessels.
Placing the kidney in this position allows it to be easily connected to blood vessels and the bladder. The vein and the artery of the new kidney are attached to the body’s vein and artery. The new kidney’s ureter is attached to the body’s bladder to allow urine to pass out of the body.
Question 2.
What about the failure of kidneys ?
Answer:
In most cases the old kidneys will not be removed. This is because even failed kidneys release chemicals that help the body work. However if those kidneys have a disease that cause on going problems such as persistent kidney infections or intestinal blockage,then the transplanting would be considered removing the old kidney. The two most common medical Conditions requiring “native nephrectomy” or “congenital reflux” disease and polycystic disease.
Question 3.
Can donor lead normal life with single kidney without any complication
Answer:
Once a living donor candidate has been completely evaluated and cleared, the chance of the donation affecting his or her life span or life style is extremely low with any surgery and anaesthesia, however, there are risks. Nationally the risk of having a life threatning problem with donating a kidney is one in three thousand.
The risk of minor complications such as a minor wound infection is about 2 to 4%. Because the kidney donor operation is a major surgical procedure; donors find they have less energy and need about 4 to 6 weeks to return to their full resurgical activity level.
![]()
Question 4.
Do plants excrete like animals?
Answer:
- Plants do not have specific organs to excrete the waste materials which are formed during metabolism.
- As in animals carbon dioxide, water, ammonia and other nitrogenous wastes are also formed in plants.
- In plants, carbon dioxide released during respiration is sent out through stomata of leaves.
- Plants discharge the excess water in the form of water vapour during transpiration by leaves. Due to this, the heat in the plants is reduced.
- In germinating seeds carbon dioxide formed during respiration is released into atmosphere.
- Plants have the capacity to utilise the by- products of one metabolic activity as the raw materials for another metabolic activity.
- For example, oxygen released during photosynthesis utilised for respiration; carbon dioxide released during respiration is utilised for photosynthesis. Plants convert nitrogen and ammonia into nitrates.
Question 5.
How do plants manage or send out waste products from its body?
Answer:
- Plants can get rid of excess water by a process like transpiration and guttation. Waste products may be stored in leaves, bark and fruits.
- When these dead leaves, bark, and ripe fruits fall off from the trees, then waste products in them are got rid off.
- In some plants, waste gets stored in the fruits in the form of solid bodies called raphides.
Example : Yam. - Several compounds are synthesized by the plants for their own use specially for defense.
- Several plants prepare chemicals and store them in shoots, leaves, seeds for protection against herbivores.
- Most of the chemicals are unpleasant to taste and hence herbivores do not prefer to eat such plants. Some of the chemicals are toxic and may even kill the animal that eats them.
- Some of the plants release attractants for other organisms which will help the plants for pollination.
- For example, plants having root nodules secrete chemicals to attract rhizobia into the surroundings of the roots and form a symbiotic relationship with the rhizobium.
TS 10th Class Biology 4th Lesson Excretion Activities
Activity 1.
How do you study the external and internal features of a kidney?
OR
Explain the procedure and observations of the experiment conducted to observe internal structure of the Kidney.
Answer:
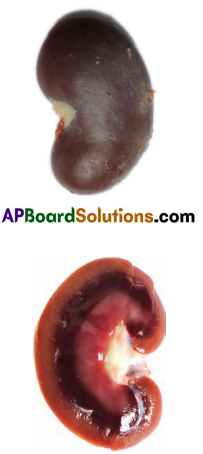
Materials required : Freshly collected specimen of sheep/goat’s kidney from the butcher or 3D model of a kidney, sharp blade/ scalpel, tray and a jug of water. Procedure for observation:
- Before bringing the kidney to the lab wash it thoroughly so that, blood is completely drained from it.
- Put the kidney in the tray and observe it carefully.
- Note down the observations in the notebook.
- With the help of sharp blade take the longitudinal section of the kidney and observe internal structure.
- Draw what you have observed and compare it with the figure.
- After observing the L.S. of kidney answer the following questions given under.
![]()
Question 1.
What is the shape of kidneys?
Answer:
The shape of kidneys are bean shape.
Question 2.
What is the colour of kidney?
Answer:
Colour of kidney is reddish brown.
Question 3.
Do you find any attachments on upper portion of kidney?
Answer:
Yes. Adrenal glands are attached to kidneys Ofl upper portion.
Question 4.
Is the Internal structures similar to fig – 2?
Answer:
Yes. It is similar to internal structure of fig – 2.
Question 5.
What is the colour of the outer part In LS. of kidney?
Answer:
The colour of the outer part of the kidney is Dark.
Question 6.
In L.S. of kidney where do you find dark brown colour portion?
Answer:
Dark brown colour portion is found on the outer zone of kidney.
Question 7.
How many tubes are coming out from kidney fissure?
Answer:
Two tubes are coming from kidney.