Telangana SCERT 10th Class Social Study Material Pdf Telangana 9th Lesson Globalisation Textbook Questions and Answers.
TS 10th Class Social 9th Lesson Questions and Answers – Globalisation
Question 1.
What were the reasons for putting barriers to foreign trade and foreign investment by the Indian government? Why did It wish to remove these barriers?
Answer:
Barriers to foreign trade and foreign investment were put by the Indian government to protect domestic producers from foreign competition, especially when industries had just begun to come up in the 1950 and 1960s. At this time, competition imports would have been a death blow to growing industries Hence, India allowed imports only essential goods.
Later in the 1 990s. the government wished to remove these barriers because it that domestic producers were ready to compete with foreign industries. It felt that foreign competition would ii tact improve the quality of goods produced by Indian industries. This decision was also supported by powerful international organisations.
Question 2.
How would flexibility in labour laws help companies?
Answer:
- Flexibility in labour laws can help the companies to decrease their production cost by employing labourers only for short period of time when there is need instead of employing them for long periods of time or yearly basis.
- By using upon labour laws, company heads can negotiate wages and terminate employment, depending on market conditions.
Question 3.
What are the various ways In which MNCs set up or control production in other countries?
Answer:
MNCs can set up and control production In other countries in following ways.
- By setting up now factories/production units.
- By purchasing/acquiring local units of domestic nations.
- By setting up partnerships with local companies.
MNCs have technical, financial and marketing superiority and thus can control production in other countries.
![]()
Question 4.
Why do developed countries want developing countries to liberalise their trade and Investment? What do you think should the developing countries demand in return?
Answer:
- Developed countries want developing countries to liberalise their trade and investment so that goods could be imported and exported easily.
- Also, they could set up their factories and offices in the developing countries for enjoying the benefits of low cost of labour and high demand, i,e, large markets.
- In return, developing countries expect that developed nations should not impose Import duties or other barriers on goods imported from developing nations, by developed countries.
Question 5.
“The impact of globalisation has not been uniform.” Explain this statement.
Answer:
- The impact of globalisation has not been uniform. It has benefited skilled and professional persons In urban areas, It has not benefited much the persons who are unskilled.
- The industrial and service sectors have gained because of globalization, but the agriculture sector has not gained much from globalisation.
- Moreover, globalisation has benefited large industrial units as MNCs have collaborated with beg units only.
- The small and medium-sized industrial units are hit hard as they find it very difficult to
compete with huge MNCs. - Many small units have faced closure while large industrial units have succeeded in expanding their market to many other nations.
Question 6.
How has liberalisation of trade and Investment policies helped the process of globalisation?
Answer:
With the liberalisation of trade and investment policies, the goods could be imported and exported easily between the countries arid foreign investment can be done without much restrictions. The foreign countries could now set up their factories and offices in the domestic country.
This results in interaction of the foreign country with the domestic country which is known as globalisation. In other words, globalisation is the process of rapid integration or interconnection between countries which is possible by the liberalisation of trade and investment.
Question 7.
Globalisation will continue in the future. Can you Imagine what the world would be like twenty years from now? Give reasons for your answer.
Answer:
After 15 to 20 years, world would undergo a positive change which will possess the following features. healthy competition, improved production efficiency, and increased volume of output. income and employment, and better living standards. greater availability of information and modern technology.
Reasons:
Favourable factors for globalisation:
- Availability of human resources both quantity-wise and quality-wise.
- Broad resource and industrial base of major countries.
- Growing entrepreneurship.
- Growing domestic market.
![]()
Question 8.
Locate the following In the map of world.
i) China
ii) Japan
iii) Brazil
iv) South Africa
Answer:
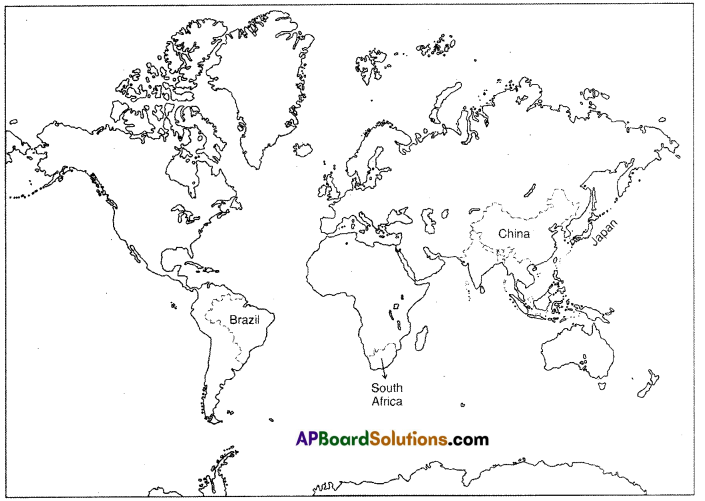
TS 10th Class Social 9th Lesson Globalisation Intext Questions
Page No. 119
Question 1.
Choose any one single item like Mobile phones or vehicles; identify the number of Brands available for this item in the market. Are they owned and manufactured in India or abroad? Discuss with your parents or other adults and find out how many such brands were available 30 years ago.
Answer:
Let’s take cell phones for instance. There are numerous varieties in cell phones. e.g: Nokia, Samsung, Celkon, Videocon, LG, Micromax, Sony Ericson, etc. LG, Videocon, and Onida cell phones are manufactured in India. But the raw materials used in them like chips, motherboards and accessories are mostly imported from foreign countries such as Japan, China, Singapore, Korea, Malaysia, etc.
So the cell phones manufactured in our country are affordable to us. In the past, BSNL and Reliance produced land phones. Later Reliance subscribed to walkie-talkies, mobile phones, etc. Mobile phones weren’t available in our country thirty years ago.
Page No. 121
Read the passage (Ford Motors, across the globe.) In page no. 120 and answer the following questions.
Ford Motors, an American company, Is one of the world’s largest automobile manufacturers with production spread over 26 countries of the world. Ford Motors came to India in 1995 and spent Rs. 1700 crores to set up a large plant near Chennai. This was done in collaboration with Mahindra and Mahindra, a major Indian manufacturer of eeps and trucks.
By the year 2004, Ford Motors was selling 27,000 cars in the Indian markets, while 24,000 cars were exported from India to South Africa, Mexico and Brazil. The company wants to develop Ford India as a component supplying base for its other plants across the globe.
2. Would you say Ford Motors Is an MNC? Why?
Answer:
Yes, we can say Ford Motors is an MNC because its production units have spread over 26 countries of the world. This is the most important feature of an MNC.
![]()
Question 3.
What is foreign Investment? How much did Ford Motors Invest In India?
Answer:
- Foreign investment: Private capital investment by firms of one country into those of another country is
called foreign investment. - Ford Motor invested Rs, 1,700 crores In India.
Page No. 122
Question 4.
By setting up their production plants In India, MNCs such as Ford Motors tap the advantage not only of the large markets that countries such as India provide but also the lower costs of production. Explain the statement.
Answer:
MNCs set up production
- where it s close to the market;
- where the skilled and unskilled labour is available at low costs.
- where the availability of other factors of production is assured.
- The concerned government policies are favourable to the MNCs.
Question 5.
Why do you think would the company want to develop India as a base for manufacturing car components for Its global operations? Discuss the following factors:
a) cost of labour and other resources In India
b) the presence of several local manufacturers who supply auto parts to Ford Motors
c) closeness to a large number of buyers In India and China
Answer:
a) Wages and salaries are much lower In India when compared to in developed countries. Raw material and power is also cheaper.
b) There are many companies which manufacture various auto parts. Because of their lower cost of operation, these companies supply various parts at less price.
c) India and China together have 30/ of the world’s population and they provide a huge market for various companies. Making a production base in India provides easy access to these two markets.
Question 6.
In what ways will the production of cars by Ford Motors in nca lead to Inter linking of production?
Answer:
The company is making engines and body at its plant. it is processing other components from various suppliers which operate in India. Even designing some of the new models has been done India. So India is providing a perfect base for all the operations related to production of cars for the Ford Motor. Hence It can be said that proper interlinking of production is happening in India for this company.
Question 7.
In what ways is an MNC different from other companies?
Answer:
An MNC does different operations related to its business at different locations across the globe. Other companies limit their operation to a single country or to a few countries. By doing so, an MNC is able to take advantage of cost-benefit and also of easier access to important markets, Ths may not be possIe for other companies.
![]()
Question 8.
Nearly all major multinationals are American, Japanese or European, such as Nike, Coca-Cola, Pepsi, Honda, Nolda. Can you guess why?
Answer:
Industrialization began from Europe and then spread to America and later to Japan. By the time India became independent, many companies of these countries had already become financially strong. This is the reason that most of the MNCs are from America, Europe or Japan.
Question 9.
What was the main channel for connecting the countries in the past? How is it different now?
Answer:
Trade was the main channel which connected the countries in the past. Things have not changed much in the present as well. Trade still is the major channel to connect the countries. However, tourism arid study also contributes towards making the world a more interconnected place now.
Question 10.
Distinguish between foreign trade and foreign Investment.
Answer:
Foreign trade implies exchange of goods and services across nations. Foreign investment implies transfer of capital from one nation to another.
Question 11.
In recent years, China has been importing steel from India. Explain how the Import of steel by China will affect:
(a) steel companies in China.
(b) steel companies in india.
(c) industries buying steel for production of other industrial goods in China.
Answer:
(a) Because of cheap availability of steel from India, Chinese steel industry will prosper.
(b) Steel industries in India will obviously suffer due to lack of availability of steel,
(c) Other industries of China which are dependent on steel will also prosper.
Question 12.
How will the import of steel from India into the Chinese markets lead to integration of markets for steel In the two countries?
Answer:
Steel is often called the backbone of modern industry. Tools, machinery, equipments, tombs of transport and infrastructure largely need steel. If we export steel to China, it will increase foreign trade. Development in China will further benefit increase demand for steel and exports from India, Steel Industries will help In manufacturing of other goods which will be further create foreign exchanges, thus integrating trade between two countries.
Question 13.
What is the role of MNCs in the process of globalisation?
Answer:
- MNCs are playing a major role In the process of globalisation. MNCs have been looking for locations around the world, which would be cheap for their production.
- As a result of greater foreign investment and greater foreign trade, there would be greater integration of production and markets across countries,
- More and more goods and services, investments and technology are moving between the Countries.
- Most regions of the world are in closer contact with each other than a decade back.
- Foreign investment in the countries has been rising.
- Foreign trade between the countries has been rising.
- The activities of most of the MNCs involve substantial trade in goods and also services.
Question 14.
What are the various ways in which countries can be linked? LIflt
Answer:
The various ways in which countries can be linked are
- by trade relations
- by exchange of services
- through communication
- through general tourism
- through economic aid and mutual borrowing
- through education in worldwide institutions,
Question 15.
Choose the correct option: Globalisation, by connecting countries, results in
(a) lesser competition among producers.
(b) greater competition among producers.
(c) no change in competition among producers.
Answer:
(b) greater competition among producers.
![]()
Page No. 125
Question 16.
In this example, underline the words describing the use of technology In production.
Answer:
A news magazine published for London readers is to be designed and printed in Delhi. The text of the magazine is sent through Internet to the Delhi office. The designers in the Delhi office get instructions on how to design the magazine are ven from the office in London using te4ecomrnurcation facilities. The designing is done on a computer. After printing, the magazines are sent by air to London. Even the payment of money for denying arid Dnnting from a bank is London to a bank in Delhi is done instantly through the internet
(e-banking)
Question 17.
How Is information technology connected with globalisation? Would globalisation have been possible without the expansion of IT?
Answer:
- Globalisation is the process of growing integration of one country’s economy with world economy.
- Information and communication technology has played a major role in spreading out production of services across countries.
a) The development in IT. in the areas of telecommunications, computers, Internet have
been changing rapidly.
b) Telecommunication facilities are used to contact one another around the world, to access information instantly, and to communicate from remote areas. This has been facilitated by satellite communication devices.
c) Internet also slows us to send instant email and talk across the world at negligible costs. Globalisation would not have been possible without the expansion of IT.
Page N0. 126
Question 18.
What do you understand by liberalisation of foreign trade?
Answer:
Removing barriers or restrictions set by the government on foreign trade and foreign investment is known as liberalisation of foreign trade.
Question 19.
Tax on imports is one type of trade barrier. The government could also place a limit on the number of goods that can be Imported. This Is known as quotas. Can you explain, using the example of Chinese toys, how quotas can be used as trade barriers? Do you think this should be used? Discuss.
Answer:
A fixed quantity for import is called quota. This can be done in case of Chinese toys. This will have both negative and positive impacts. Once trade restrictions shall be there, the Indian toy manufacturers will be in a position to sell their products. This will help the Indian toy manufacturers and employees. But as the experience of better quality at lesser price in case of Chinese toys shows, this step would be detrimental for consumer’s interest.
![]()
Page No.127
Question 20.
Fill in the blanks.
WTO was started at the initiative of ………………………. (i) ……………….. countries. The aim of the WTO is to …………………. (ii)……………… WTO establishes rules regarding ………….(iii) ………… for all countries, and sees that ……………… (iv) …………….. In practice, trade between countries is not …….. (v) ………….. Developing countries like India have ……………. (vi) ……………………….. whereas developed countries, in many cases, have continued to provide protection to their practices.
Answer:
(i) developed;
(ii) liberalise international trade;
(iii) international trade;
(iv) these rules are properly obeyed;
(v) fair:
(vi) removed trade barriers,
Question 21.
What do you think can be done so that trade between countries is fairer?
Answer:
All countries should remove trade barriers to make for a fair international trade. Developed countries should desist from forcing the developing countries in agreements which they themselves may not obey.
Question 22.
Read the passage on (The agriculture sector …. and fair trade ?) page 127 and answer the following question.
The agriculture sector provides the bulk of employment in India. Compare this with a developed country such as the US with the share of agriculture in GDP at 1% and its share in total employment a tiny 0.5% And yet this very small percentage of people who are engaged in agriculture in the US receive massive sums of money from the US, government for production and for exports to other countries.
Due to this large amount of money that they receive, US farmers can sell the farm products at abnormally low prices. The surplus farm products are sold in the markets In other countries at low prices, adversely affecting farmers in these countries.
Developing countries are, therefore, asking the governments of developed country, We have reduced trade barriers as per WTO rules. But you have ignored the rules of WTO and have continued to pay your farmers vast sums of money. You have asked our governments to stop supporting our farmers, but you are doing so yourselves. is this free and fair trader?”
In the above example, we saw that the US government gives massive sums of money to farmers for production. At times, governments also give support to promote production of certain types of goods, such as those which are environmentally friendly. Discuss whether these are fair or not.
Answer:
Supporting its own farmers at the cost of fair international trade cannot be termed as a fair practice. Supporting the production of environmentally-friendly products is beneficial for the whole world and every country should follow such practices.
![]()
Page No. 128
Question 23.
How has competition benefitted the people in India?
Answer:
Competition has benefitted the Incans in a positive way. To understand this, let us take the example of the availability of two-wheelers. Before liberalization, there were only the following brands of two-wheelers – Bajaj, Rajdoot. Bullet and Yezdl. li someone wanted to buy a Bajaj scooter, the waiting period used to be for a couple of years. Once the markets opened up. many companies came to India. Right now, one can buy a two-wheeler of his choice at his own convenience, Two wheelers can be seen even in remote areas of India. All of this could be possible because of competition.
Question 24.
Should mole Indian companies emerge as MNCs? How would it benefit the people In the country?
Answer:
It‘s desirable that more Indian companies emerge as MNCs. This will help those companies in expanding their market and financial muscle. This will make India a stronger economy. A stronger economy is always beneficial for its people. The Indian MNCs too can directly benefit people through various corporate Social responsibility programmes.
Question 25.
Why do governments try to attract more foreign investment?
Answer:
More foreign investment helps in increasing the economic activities. This helps in employment generation. So the governments try to attract more foreign investment.
Question 26.
Elsewhere, we read that what may be development for one may be destructive for others. The setting of SEZs has been opposed by some people in India. Find out who are these people and why are they opposing It.
Answer:
When an SEZ is being made in a particular location a vast tract of land needs to be acquired. Land acquisition means a large population Is forced to relocate from many villages. Displacement is always painful for people. Moreover, people who are evacuated do not get proper compensation for their land. Rehabilitation is never adequate and timely. So, many people oppose various developmental activities.
Question 27.
Write an Imaginary caption for the image here. What does it tell about the globalisation.

A. Craze tor artificial drinks spoils healthCrave (or natural drinks Is good for health. Globalizaton leads to run behind products like pizzas, burgers, and cool drinks, They spoil health on the other hand, they badly hit small vendors that depend on setting natural products like coconuts, palm fruits, mango el1y, groundnut cakes. etc.
Page No. 129
Read the passage about Ravi on page 128 and answer the following questions.
Question 28.
What are the ways In which Ravis small production unit was affected by rising competition?
Answer:
Ravi’s small production unit was affected by rising convetiton in the following ways:
a) His customers have changed their product. as they are now manufacturing TV sets for- the MNC brands, who do not use the capacitors produced by Ravi’s unit.
b) His production arid sales have also reduced due to his capacitors being costlier than the imported variety, due to the removal of import duties on imported capacitors.
c) He is going into loss due to not recovering his costs with such a small amount of production. He may even have to close down his unit like his friends have done.
Question 29.
Should producers like Ravi stop production because their cost of production is higher compared to producers in other countries? What do you think?
Answer:
I think it is better to use machines of high technology to reduce his cost of production. It is better to acquire another loan from banks and to repay it in easy installments.
Question 30.
Recent studies point out that small producers In India need three things to compete better in the market : (a) better roads, power, water, raw materials, marketing and Information network. (b) improvement and modernization of technology, and (c) timely availability of credit at reasonable interest rates. Explain how these three things would help Indian producers.
Answer:
These three things will help the lack producers to compete better in the market as follows.
a) Better infrastructure will help them to work more efficiently and timely so that they can compete with foreign Companies In the market.
b) Better technology will help the producers to create better quality products efficiently at cheaper rates.
c) Better finance will enable them to run their production smoothly without delays, thus
improving their competitiveness.
![]()
Question 31.
Do you think UPIC. will be Interested in Investing In these? Why?
Answer:
MICa will not be interested in investing in these because the Indian produces will then compete with ram as equate in the same make (. thus reducing their market share.
Question 32.
Do you think the government basa rote In making these facilities available? Why?
Answer:
- The government has a role in making these facilities available.
- If the government makes these facilities available, then many small Indian producers develop themselves.
- They would be able to compete with foreign MNC’s.
- As governments are nowdays welfare states, they have a role in making these facilities available.
Question 33.
Think of any other steps that the government could take. Discuss.
Answer:
- The government could lrrçoee sanctions or restrictions on MNCs.
- Make that MNCs should behave with corporate social responsibility.
- Government should protect the foretaste of She people end that MNCs prospers
- It Should adopt the policy whIch provides lot initial consent.