These TS 10th Class Biology Chapter Wise Important Questions 7th Lesson Coordination in Life Processes will help the students to improve their time and approach.
TS 10th Class Biology Important Questions 7th Lesson Coordination in Life Processes
1 Mark Questions:
Question 1.
What happens if the direction of peristalsis is not reversed in animal like cow?
Answer:
If the direction of peristalsis is not reversed (rumination is not done) in animal like cow, the food will not be masticate in the mouth and fermentation of the food with the micro-organisms in the stomach will not be takes place.
Question 2.
What happens if the re is no mucus in the Oesophagus?
Answer:
- The walls of the food pipe secrete a slippery substance called mucus.
- Mucus lubricates and protects the oesophageal walls from damage.
- This helps the food bolus to slide down easily in the tube.
- If there is no mucus. lubrication will not done for the food bolus to slide and walls get damage.
Question 3.
Which part of small intestine absorbs digested food?
Answer:
Microvilli / villi.
Question 4.
Name the chemical which is used to test the action of saliva on flour (ata).
Answer:
Iodine Solution.
![]()
Question 5.
What happens, if there is no peristatic movement in Oesophagus?
Answer:
- The food won’t slidedown in the oesophagus.
- The digestion of food won’t takes place in the stomach and small intestine.
Question 6.
We remove our hand when we touch a hot subject. Find out its reflex action.
Answer:
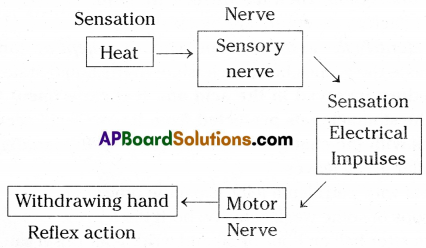
Question 7.
When do we feel hunger fall pangs in stomach?
Answer:
When the level of glucose falls in the blood we feel hunger pangs in stomach.
Question 8.
Which hormone is responsible for hunger pangs in stomach?
Answer:
Ghrelin.
Question 9.
Which plays an important role in carrying hunger signals to brain?
Answer:
Diencephalon (forebrain) and vagus nerve (10th cranial nerve)
Question 10.
Increase in ghrelin levels results in?
Answer:
Sensation of hunger and motivation to consume food.
Question 11.
Which hormone suppresses hunger?
Answer:
Leptin.
Question 12.
interactions between what enhances our perceptions of the food we eat?
Answer:
Interactions between the senses of taste and smell.
![]()
Question 13.
What are the different types of papillae present on the tongue?
Answer:
Filiform papillae, fungiform papillae, phohate papillae and circumvallate papillae.
Question 14.
What is the dental formula of human beings?
Answer:
\(\frac{2,1,2,3}{2,1,2,3}\) (present on one side of the jaw)
Question 15.
Name the different sets of teeth present in mouth.
Answer:
Incisors, canines, premolars and molars.
Question 16.
Write the number of different sets of teeth.
Answer:
Incisors -, 8, canines – 4, premolars – 8. molars – 12.
Question 17.
What is mastication?
Answer:
Grinding, chewing and shredding of food in the mouth by teeth is called mastication.
Question 18.
Which cranial nerve controls the movement of muscles in the jaw?
Answer:
Fifth cranial nerve (- Trigeminal nerve)
Question 19.
What is bolus?
Answer:
Food that is formed due to the mastication of food in the mouth is called bolus.
Question 20.
What is the function of salivary amylase?
Answer:
It breaks down the large starch molecules into smaller subunits usually into sugars.
Question 21.
What kind of tube is oesophagus?
Answer:
It is muscular and elastic.
Question 22.
How does mucus help in passage of food?
Answer:
Mucus lubricates, protects the walls from damage and helps bolus slide down easily to stomach.
Question 23.
What are the two kinds of muscles present in oesophagus
Answer:
Two kinds of smooth muscles are present – Inner layer consists of circular muscles and the outer layer of longitudinal muscles.
Question 24.
What is peristalsis?
Answer:
The involuntary contraction and relaxation of the muscles of oesophagus, stomach and intestine is called peristalsis.
Question 25.
What is chyme?
Answer:
The partly digested food in the stomach is called chyme.
Question 26.
What stimulates stomach muscle into action?
Answer:
Nervous system.
Question 27.
What causes the stomach to churn and mix the food?
Answer:
Peristalsis movements.
Question 28.
The muscles present at the opening of the stomach and the first part of the small intestine or duodenum?
Answer:
Pyloric sphincter.
![]()
Question 29.
Why should only a small quantity of food be passed from stomach to duodenum?
Answer:
For the complete digestion of the food.
Question 30.
What is involved in bringing about peristalsis?
Answer:
Autonomous nervous system.
Question 31.
What is the direction of peristalsis?
Answer:
It is forward direction from mouth it starts.
Question 32.
What happens if the direction of perista is reversed?
Answer:
Food moves in the backward direction.
Question 33.
What is the nature of the chyme?
Answer:
Acidic
Question 34.
Acidic nature of chyme initiates the production of hormones?
Answer:
Secretin and cholecystokinin.
Question 35.
Secretin and cholecystokinin stimulate
Answer:
Pancreas, liver and walls of small intestine to secrete pancreatic juice, bile juice and succus entericus.
Question 36.
What process is involved in the process of absorption?
Answer:
Selective absorption.
Question 37.
The parts that absorb nutrients from the food in small intestine?
Answer:
Finger-like projections called villi absorb nutrients.
Question 38.
Why do you think small intestine is long and coiled?
Answer:
For the remain of food longer thereby enhancing absorption.
Question 39.
What is second brain?
Answer:
The nervous system present below the gut or alimentary canal that control digestion is called second brain.
![]()
Question 40.
What is the other name for second brain?
Answer:
Enteric nervous system.
Question 41.
What controls the exit of stool from the body?
Answer:
Anal sphincter.
Question 42.
What happens during inhalation?
Answer:
During inhalation, oxygen moves across the walls of the alveoli and enters the blood.
Question 43.
What happens during exhalation?
Answer:
During exhalation, carbon dioxide from the blood moves into the alveoli of the lungs and breathed out.
Question 44.
What would be the path of salt removal from gut to the outside of our body?
Answer:
Sait is removed via through the kidneys. skin, etc.
Question 45.
For oxidation of for transport of substance which processes are to be coordinated?
Answer:
Respiration and blood circulation.
Question 46.
Why do you think the stomach is structured like a bag rather than a tube like oesophagus?
Answer:
The stomach is a muscular bag whose principal function in most groups is acidification and macerate ion of the food to the liquid state and temporary storage until it is passed to the intestine. Hence stomach is structured like a bag rather than a tube Like oesophagus.
Question 47.
How do we know that we need food?
Answer:
Hunger pangs are produced in our stomach due to the release of hormone Ghrelin.
This causes sensation of hunger and also we need food.
Question 48.
What could be the range of temperature for us to relish food items?
Answer:
41° F to 140° = F
Question 49.
Ritwik felt hunger pangs but could not take his meal on time. After some time the hunger pangs disappeared and he felt relieved. State the reasons.
Answer:
Ritwik felt hunger pangs due to release of hormone Ghrelin and hunger pangs disappeared due to release of hormone Leptin.
2 Mark Questions:
Question 1.
In the food pipe, the food bolas is propelled into the stomach by peristaltic movement. Represent this action with a diagram.
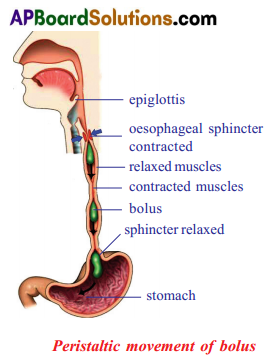
Question 2.
Take two similar green leaves. Apply grease on one leaf and leave the other free.
OR
Add 1 or 2 drops of acid on each lear What kind of change do you observe from this?
Answer:
- The leaf to which grease is applied is not effected with the acid.
- The leaf to which grease is not applied is effected.
- From the above activity we can conclude that mucus secreted by the walls of stomach protect it from the harmful effects of hydrochloric acid in the stomach.
![]()
Question 3.
Identify the diagram and write two functions of it.
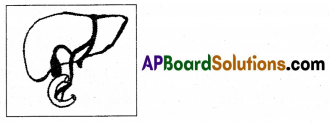
Answer:
Liver:
- Breakdown of larger fats into small globules/emulsification of fats.
- It excretes Bile salts, cholesterol steroid, hormones, extra drugs, vitamins and alkaline salts through urine.
Question 4.
What will happen if islets of Langerhans fail to function?
Answer:
- Insulin may not be produced.
- Human may suffer from sugar diabetes.
- Sugar level increases in blood.
Question 5.
What may happen if villi are absent in small intestine?
Answer:
- Villi increase the surface area of the small intestine for absorption when food passes through it. If villi are absent, food will not be digested completely.
- Digested food will not be absorbed effectively.
- The food taken into the body is expelled out only after completing partial absorption in the small intestine.
- The body will suffer from starvation of nutrients.
Question 6.
Draw the diagram showing peristaltic movement. Write the names of the parts responsible for it.
Answer:

a. Mucus lubricates and protects the walls of oesophagus.
b. Circular muscles and longitudinal muscles of oesophagus help in the movement of food ‘bolus’.
c. Feristalsis is under the control of Autonomous nervous system.
Question 7.
How can the taste of food be detected?
Answer:
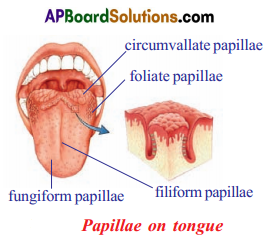
- On the tongue different types of papillae are present to sense different tastes.
- If we want to taste the food material, the food should be dissolve in saliva.
- We can taste the food that is in the form of liquid only.
- Only after the dissolved food enters into the cup-like taste buds (papillae), the sense of taste is carried tothe brain for analysis.
- Then only we will know the taste of the food material.
Question 8.
Write a short note on digestion of food in mouth.
Answer:
- In mouth, saliva is secreted by the action of autonomous nervous system to moisten the food to make chewing and swallowing easier.
- As a result of chewing food forms into a slurry mass called ‘bolus’.
- The enzyme salivary amylase in the saliva breaks down the large starch molecule into smaller subunits usually into sugars.
- During mastication food size becomes convenient to swallow.
Question 9.
Why do we salivate during a nap of (short sleep) daytime?
Answer:
- Nocturnal animals are active during nights but we are active during day time and take rest at night.
- All the systems of our body are active in function during the daytime of our activity. Hence, man is a diurnal animal.
- Our digestive system is also active and ready to receive the food for digestion.
- If we sleep during day time saliva oozes out of our mouth and wets the pillows.
- This will not happen during night time.
Question 10.
Explain the process of exit of waste materials from large intestine.
Answer:
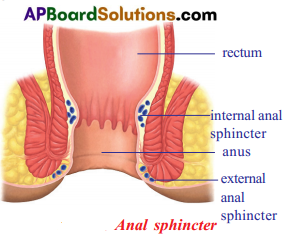
- When the unwanted waste material reach the large intestine, the peristaltic waves move the stool into the rectum.
- Water gets reabsorbed and the remaining waste usually hard mass that gets stored in the last part of the large intestine i.e., the rectum.
- There are two muscular layers helping the exit of stools.
- One is under involuntary control and the other is under in voluntary control.
- These muscular structures help in opening and closing of the aperture of the canal which are called sphincter.
Question 11.
How do we detect the smell of agarbathi?
Answer:
- The fore brain is the main thinking part of the brain.
- It has regions which receive sensory impulses from various receptors.
- Separate areas of the fore brain are specialised for hearing, smell, sight and so on.
- Olfactory receptors send the information about the smell of incense stick to fore brain.
- The fore brain integrates it along with information received from other receptors as well as with information that is already stored in the brain.
Question 12.
Tooth enamel is one of the hardest substances in our body. How does it undergo damage due to eating chocolates and sweets?
Answer:
- The acid is formed in the mouth after a sugary food (chocolates and sweets) has been taken.
- This acid lowers the pH in the mouth.
- Tooth decay starts when the pH of acid formed in the mouth falls below 5.5.
- This is because then the acid becomes strong enough to attack the enamel of our teeth and erode it.
![]()
Question 13.
What do you think would happen if the salivary glands do not function in our mouth?
Answer:
- If the salivary glands do not function in our mouth saliva will not release in the mouth.
- Saliva is important to lubricate our mouth, help with swallowing, protect our teeth against bacteria and acid in the digestion of food. This will not occur as the saliva is not produced by salivary glands.
Question 14.
If we swallow food material directly without mastication, what will happen?
Answer:
If we swallow food material directly without mastication,
- Digestion process will not start.
- Makes the digestion process much complicated if the food is not made into bolus in the mouth.
- Absorption of nutrients from food is difficult.
- It will not promote feelings of fullness after eating
Question 15.
The mere smell or sight of food stimulates hunger. Describe the process in a flow chart.
Answer:
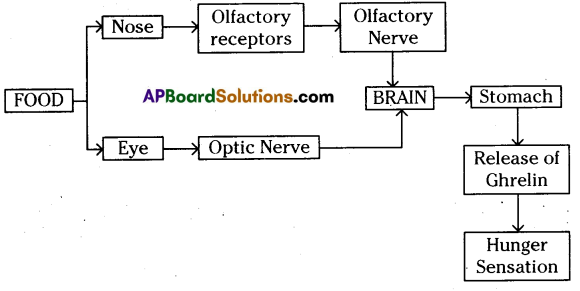
4 Mark Questions:
Question 1.
Give appropriate reasons for the below statements.
i. Hunger sensations reach brain when the stomach becomes empty.
Answer:
Ghrelin is secreted from walls of stomach.
ii. Hunger sensations stops after the stomach becomes full.
Answer:
Leptin hormone is secreted which supresses hunger.
iii. Food is not taste good when we suffer with cold.
Answer:
During cold olfactory receptors are blocked.
iv. We cannot identify the taste of grape when it is kept of tongue?
Answer:
We cannot taste the grapes because it is not in the liquid state.
Question 2.
Write the procedure involved in the acid and leaf experiment to understand the concept “how the stomach gets protected from its own acid secretions”. Compare the observations with the changes that takes place iii human digestive system.
Answer:
- Take two similar green leaves.
- Grease one leaf with petroleum jelly, leave the other free.
- Add 1 or 2 drops of some weak acids on both the leaves.
- Observe them after half-an-hour or so and write your observations.
- The leaf to which petroleum jelly was not applied effected by the acid.
- We observe the colour of the leaf changes.
- The other leaf was not affected by the acid because of petroleum jelly.
From the above activity we can conclude that mucus secreted by the walls of stomach protect it from the harmful effects of hydrochloric acid.
Question 3.
What is peristaltic movement? Compare the similarity of bolus movement in oesophagus with cycle tube and potato experiment which you have conducted in school.
Answer:
Peristalsis: Contraction and relaxation of circular and longitudinal muscles bring in a wave-like motion that propels the food bolus into the stomach from oesophagus by the action called as peristalsis.
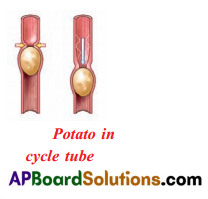
Experiment:
Aim : Making a mode of oesophagus to observe how bolus moves forward.
Material required: Potatoes, cycle tube lubricate oil
Procedure:
- Take a piece of waste cycle tubes and insert one or two potatoes into it.
- Lubricate the inner side of the tube with oil.
- In the same way smear oil over potatoes.
- Insert oil coated potatoes in the tube.
- Now try to push the potatoes by squeezing the tube from behind the
Observation : Oil acted as lubricant to push the potato easily in the forward direction.
Conclusion : The muscles in the wall of the oesophagus have bring in a wave like movement due to contraction and relaxation, that propels the food bolus into the stomach. This action is called peristalsis.
I. Conceptual Understanding
Question 1.
Vasu is doing experiment, lab activities in his classroom. He is tired due to hungry. How does hungry feeling occur ? How will one know?
Answer:
Levels of different substances are generally maintained in the blood mainly by our digestive system. One of the major substance is glucose. When its levels in the blood fall, we get hunger pangs in stomach.
Ghrelin is secreted from the certain cells in the wall of the stomach. Hunger contractions (hunger pangs) start to occur in the stomach due to the secretion of Ghrelin hormone. Increase in ghrelin levels results in sensation of hunger and motivation to consume food.
![]()
Question 2.
Write about the experiment conducted by Ivan Pavlov on conditioned reflex.
Answer:
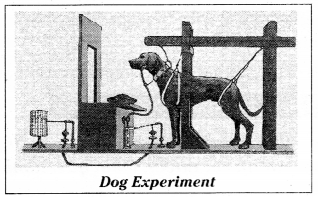
- Ivan Pavlov was a Russian scientist conducted experiments on conditioned reflexes.
- He discovered that dogs produced extra saliva when they were offered food.
- Pavlov noticed that they also did the same when the person who fed them came into the room, even if the person had not brought any food.
- Pavlov went on to ring a bell at the start of feeding time, and eventually the dogs produced extra saliva when they heard the bell, before any food was brought.
- A dog salivating when it hears a bell is not a natural response.
- They would not do this without being conditioned to do so.
- The behaviour has been learned. It is called a conditioned response.
Question 3.
Write briefly about the functional and structural aspects of oesophagus.
Answer:
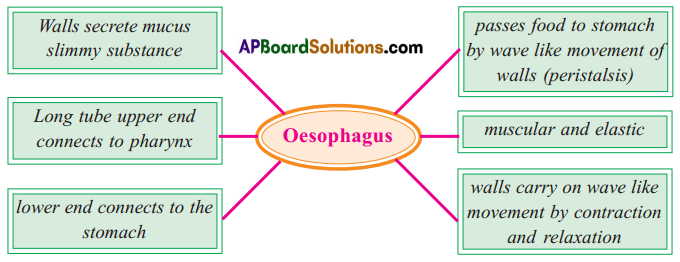
- Oesophagus is a long muscular and elastic tube-like part of the digestive system which lies between pharynx and stomach.
- The wall of the oesophagus is made up of two kinds of smooth muscles.
- The inner layer consists of circular muscles and the outer layer of longitudinal muscles.
- The walls of the oesophagus secrete mucus, a slimy substance which helps in the easy movement of food into the stomach.
- Walls of oesophagus carry on wave-like movement by contraction and relaxation. These movements are known as peristalsis.
- Due to the peristalsis movements food passes from oesophagus into stomach.
Question 4.
Explain briefly about the structure of stomach.
Answer:
- Our stomach is not a bag with specific volume. It is a like a pouch which is elastic in nature.
- The size of the stomach increases based on the food we intake.
- Digestive juices are produced depending on the quantity of food material.
- The walls of the stomach secrete juice containing hydrochloric acid.
- Mucus secreted by some cells in the walls of the stomach form a thin lining on the walls of the stomach. This counters the action of acid.
- The food is thoroughly mixed with the digestive juices by peristaltic movements of muscles in stomach.
- The digestive juices of the stomach turn food into a smooth liquid mass called chyme.
II. Asking Questions and Making Hypothesis
Question 1.
‘Brain dead’ means 100% nonfunctioning of Brain. If you get a chance to meet any neurologist/Jeevandan volunteer, what questions you will ask about ‘brain dead’ patient?
Answer:
If get a chance to meet any neurologist, I will ask following questions.
- Will neurons of brain dead respire? or not?
- What about heart beat?
- Will heart beat take normally?
- Will blood circulate in the body or not?
- What is meant by ventilator?
- How much time does his (patient’s) organ survive after brain death?
- How much time is required to transplant brain dead patient’s organs?
- Which organs can transplant from brain dead?
- Is it necessary to match his blood group with recipient?
- Whom to consult to donate organs?
- Can anybody donate his organs?
![]()
III. Experimentation And Field Investigation
Question 1.
What is peristaltic movement ? Explain the food movement in alimentary canal comparing with the experiment of moving potatoes in cycle tube.
Answer:
Peristaltic movement is the contraction and relaxation of the muscles of the digestive system. The movement of food through food pipe is known as peristaltic movement.
Food movement in alimentary canal:
- The walls of the food pipe secrete a slippery substance called mucus. Mucus lubricates and protects the oesophageal walls, Irvin
- This helps the food bolus to slide down easily 3ust as the oiled potatoes that move in the tube. Oil acted as lubricant to push the potatoes easily in the forward direction.
- The wall of the oesophagus is made up of two kinds of smooth muscles. The inner layer consists of circular muscles and the outer laver of longitudinal muscles.
- Contraction of the circular muscles results in narrowing of the oesophagus just behind the bolus.
- So the food is squeezed downwards.
- Contraction of the longitudinal muscles in front of the bolus widen the tube, this results in shortening of that particular part of the oesophagus.
- Contraction and relaxation of these muscles bring in wave-like motion that propels the food bolus into the stomach by the action called as peristalsis.
- This is involuntary and under the control of autonomous nervous system.
Question 2.
How can you prove, show that stomach is protected from iron damage being caused by secretion of its own acid?
Answer:
Aim: How stomach is protected from damage being caused by secretion of it’s own acid.
Apparatus Required: Petroleum jelly, 2 leaves. Dil. acid dropper, petridish.
Procedure:
- Take 2 similar leaves.
- Grease one leaf with petrolium jelly leave the other tree. Keep then in a petridìsh.
- Add 1 or 2 drops of weak acid on both the leaves.
Observations:
After half an hour, leaf without greasing manages and leaf with greasing remain unchange.
Inference: Mucus secreted by some cell in the walls of stomach or a thin lining on the walls of stomach. This counter the action of acid. The function of petroleum jelly can be compared to that of mucus lining in stomach walls.
Hence the stomach is protected from damage being caused by the secretion of its own acids.
IV. Information Skills And Projects
Question 1.
Prepare a table information containing different kinds of teeth, number their shape and function.
Answer:
| S.No | Name Of teeth | Number | Shape | Function |
| 1. | Incisors | 8 | Chisel, sharp edges | Biting |
| 2. | Canines | 4 | Sharp. Pointed edges | Tearing |
| 3. | Prernolars | 8 | Diamond shape blunt and flat | Chewing and grinding |
| 4. | Molars | 12 | Rectangular. blunt and flat |
Chewing and grinding |
V. Communication Throught Drawing, Model Making
Question 1.
Draw peristaltic movement of food in stomach. Describe movement of food in stomach.
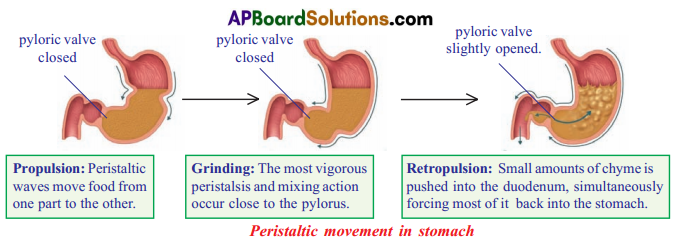
Answer:
- The stomach acts like a washing machine, churning the food around to break it into even smaller pieces.
- Mechanical mixing of food in stomach occurs by peristalsis, which is waves of muscular contractions that move along the stomach wall.
- The contractions of the stomach muscles squeeze and mix the food with the acids and juices of the stomach.
- The digestive juices turns the food into smooth porridge-like consistency called chyme.
- As the process of digestion in the stomach nears completion, the contractions of the stomach decrease.
![]()
Question 2.
Describe with diagram how villi are helpful in absorption of digested food in small intestine.
OR
How is digested food absorbed in small intestine?
Answer:
- The small intestine is the main region for the absorption of digested food.
- The inner surface of the small intestine contains thousands of finger-like projections called villi
- These villi increase the surface area so that the food retained in the folds can remain longer thereby enhancing absorption.
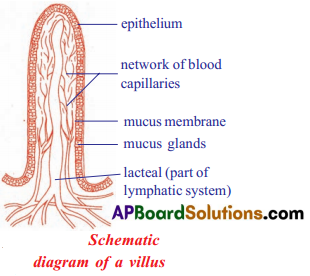
- Blood vessels and lymph vessels are present in the form of a network in the villi.
- Products of digestion are absorbed first into the villi and from there into the blood vessels and lymph vessels.