These TS 10th Class Social Chapter Wise Important Questions 18th Lesson Emerging Political Trends 1977 to 2000 will help the students to improve their time and approach.
TS 10th Class Social Important Questions 18th Lesson Emerging Political Trends 1977 to 2000
1 Mark Questions
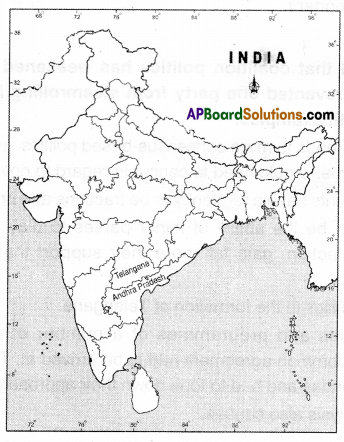
Question 1.
Identify at least any two states presently ruled by regional parties in India on the given Indian political map.
Answer:
Question 2.
What was the contribution of Telecom revolution?
Answer:
The contribution of Telecom Revolution:
The network of telephonic communication in the country using satellite technology Increased.
Question 3.
Mention any two initiations of NT. Rama Rao.
Answer:
- Sale of rice at Rs.2/- kg
- Mid-day meal scheme in government schools.
- Liquor prohibition.
Question 4.
Write about the 73rd amendment of the Constitution.
Answer:
73rd amendment: The 73rd constitutional amendment created institutions of local self-government at the village level and so Gram Panchayat, Mandal Parishad and Zilla Parishad are formed.
Observe the ie given below and answer the questions.
Results of Telangana State Asserrtly and Parliament Elections -2014
| Name of the Party | Assembly Seat won | Parliament Seats won |
| 1. T.R.S. | 63 | 11 |
| 2. Congress Party | 21 | 2 |
| 3. TD.P. | 20 | 2 |
| 4. Others | 15 | 2 |
| Total | 119 | 17 |
Question 5.
Name the two parties that secured more than 15 Assembly seats.
Answer:
Parties that secured more than 15 Assembly seats.
- TRS
- Congress Party
- TDP
Question 6.
Why did TRS secure mor seats In 2014 elections?
Answer:
TRS secured more seats In 2014 elections because it played a key role in Telangana agitation.
Question 7.
Name some non-political movements.
Answer:
Environmental movements, feminist movement, civil liberties movements, literacy movements.
Question 8.
Which became powerful motors of social change?
Answer:
A number of non-political movements emerged and became powerful motors of social change.
Question 9.
Which parties decided to merge together and form the Janata Party?
Answer:
The Congress, Swatantra Party, Bharatiya Jan Sangh, the Bharatiya Lok Dsp, and the Socialist Party decided to merge together and form the Janata Party.
Question 10.
Who supported the Janata Party?
Answer:
The DMX, the SAD, and the CPI (M) chose to maintain their separate identities but supported me Janata Party in a common Iront against the Congress.
Question 11.
Who played an important role in bringing together all the anti-Congress and anti-Emergency parties?
Answer:
Senior leaders like Jayaprakash Narayan and Acharya JB Krlplani played an important role bringing together all the anti-Congress and anti-Emergency parties to fight the elections.
Question 12.
What was the argument of the Janata Party regarding the dismiss of nine state governments?
Answer:
The Janata Party argued that the Congress party had lost its mandate to rule in the States as it had been defeated.
Question 13.
Which created a bad state in A.P.?
Answer:
In Andhra Pradesh, the frequent change of Chief Ministers by the central Congress leadership and the imposition of leaders from above created a bad taste.
Question 14.
Who moved to Assam and Bengal?
Answer:
The Bangladeshis moved to Assom and Bengal.
Question 15.
Expand AASU.
Answer:
All Assom Students Union.
Question 16.
Expand AGP.
Answer:
Assam Gana Parishad.
Question 17.
Name some communities of Assam.
Answer:
Bodas, Khasis, Mizos and Karbis.
Question 18.
Who was Bhindranwale and what was his demand?
Answer:
Bhindranwale, the leader of the grot of militant Sikhs began to preach separatism and also demanded the formation of a Sikh State- Khahstan.
Question 19.
What did the militants try?
Answer:
The instants tried to Impose an orthodox lite code on aM Sdhs and even non-Sikhs of Punjab.
Question 20.
Who made a declaration in April 1986?
Answer:
In April 1966. an assembly at the Akal Takht made a declaration of an independent state 0f Khahstan.
Question 21.
Where were the militants engaged in?
Answer:
The militants were also engaged in large-scale kidnapping and extortion to raise funds for their work.
Question 22.
How were the methods used by the governerment for the suppression of militancy In Punjab?
Answer:
The Government used very harsh methods for the suppression of militancy n Punjab, many of which were seen as violations of Constitutional rights of citizens.
Question 23.
What did Rally Gandhi begin?
Answer:
Rajiv Gandhi began a peace initiative in Punjab, Assam, and Mizoram and also in the neighboring country of Sri Lanka.
Question 24.
What is called the telecom revolution?
Answer:
Rajiv Gandhi initiated what es called the ‘telecom revolution’ In India which speeded up and spread the network of telephonic communication in the country using satellite technology.
Question 25.
What had been under dispute for some time regarding Babil Masjld?
Answer:
Some sections of the Hindus had begun a campaign for building a temple for Lord Rama in Ayodliya in the place of Babn Masjid.
Question 26.
What is the specialty of Elections held In 1989?
Answer:
The issue of corruption in administration and in political circles became the main plank of the election campaign for non-Congress political forces in the next elections held in 1989.
Question 27.
What is Policy Paralysis?
Answer:
Policy Paralysis means the coalition could not implement any policy which called for serious change for fear of withdrawal of support by one or the other parties.
Question 28.
Which was the first coalition to be re-elected?
Answer:
The UPA was the first coalition to be re-elected.
Question 29.
Who led the Loft Front Government in West Bengal In 1977?
Answer:
Jyoti Basu of CPM led the Left Front Government in West Bengal in 19T7.
Question 30.
On what did the Operation Barga depend?
Answer:
Operation Barga depended heavily on collective action by the sharecroppers and Panchayati Raj Institutions thus avoiding bureaucratic delays and domination of the landowning classes.
Question 31.
Give any two examples for RegIonal Political parties.
Answer:
TRS, TDP, YSRCP, DMK., etc.
Question 32.
Expand the term AIADMK.
Answer:
All India Anna Dravida Munnetra Kazagam.
2 Marks Questions
Question 1.
What are the situations that paved to strengthen the regional parties in present days?
Answer:
The situations that paved to strengthen the regional parties
- Regional aspirations – regional movements.
- Intermediate castes strengthening – gaining political power.
- To gain political power.
- Defections and corruption.
Question 2.
Observe the following table and analyse It.
Table: Seat share of various
Political parties in 2014 (Lok Sabha).
| Political party | Won seats |
| 1. Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP) | 282 |
| 2. Indian National Congress (INC) | 45 |
| 3. Tetugu Desam Party (TDP) | 16 |
| 4. Telangana Rashtra Samithi (TRS) | 11 |
| 5. Left parties (CPI + CPI (M)) | 10 |
Answer:
- In 2014 General elections BJP got with 282 seats, emerged as a largest party and formed the government also.
- Indian national congress got only 45 seats.
- Left parties CPI + CPI (M) joined together got 10 seats.
- The Regional parties like TDP gaIned 16 seats & TRS 11 seats in Lok Sabha elections.
Question 3.
Which qualities of Lal Bahadur Shastri do you like ? Why?
Answer:
After the death of Nehru n 1964, the Congress managed a successful transition with the choosing of Lal Bahadur Sastri as its leader In government. Sastri was immediately put to test with a series of issues which challenged the fundamental values and goals of the Indian nation. These included the Anti-Hindi agitation led by the DMK the South. which threatened the goals of unity and integrity, the shortage of food which came in the way of social and economic transformation, besides a war with Pakistan in 1965.
Question 4.
What are the Important changes that occured In India between 1975-85?
Answer:
Many changes occurred in India between 1975-85. Some of them are:
- Emergency was declared by SMF. Indira Gandhi as she was asked to quit her Prime Minister post by Allahabad high court.
- Jariatha Government came into power In 1979.
- Congress Party came to power in the elections after Janatha govt failure.
- Non-political movements like environment movements, feminist movements, CiVil liberties movement and literacy movements came up.
Question 5.
At present, what Is the n.cesslty of coalition politics?
Answer:
In the present multiparty system In India It is Impossible for any sIne party to win a maiority of seats and form a government of its own but In 2019 electIons BJP has won the election as sine party. it went as coalition.
Question 6.
Write appropriate suggestions to eradicate spread of corruption completely.
Answer:
Suggestions to eradicate spread of corruption:
- Dital payments should be made mandatory.
- Accounts must be accountability.
- All transactions to be made with transparency.
- Public audit is needed.
- Punishment to the corrupted.
Question 7.
Do you think that the reservations will promote the social development? Express your ideas.
Answer:
- Reservations will definitely promote social development
- Scheduled castes and tribes ware downtrodden and suffered in the social stature for centuries.
- To develop themselves and to question the injustice they meted out, reservations will of great help.
- Reservations both in education, jobs arid legislature help them.
Question 8.
What did the emergence of competitive alternatives ensured?
Answer:
The emergence of competitive alternatives ensured that Indian voters could always exercise a reasonable choice. This also allowed many different political viewpoints and sectional interests to become active in state-level and national politics.
Question 9.
How was the rule of the first non-Congress government?
Answer:
The Janata Party had come to power promising a restoration of democracy arid freedom from authoritarian rule. However, the disunity among the partners had a serious effect on the governance and its rule is most often remembered for internal squabbles and defections. The factional struggle in the party soon culminated in the fall of the government within three years leading to fresh elections in 1980.
Question 10.
What happened whenever there was any political Instability?
Answer:
Whenever there was any political instability or natural calamity in the neighbouring country, thousands of people moved into the State creating huge discomfort for the locals. The local people felt that they would lose their cultural roots and soon be outnumbered by the ‘outsiders.
Question 11.
What was there besides culture and demographics?
Answer:
Besides culture and demographics, there was also an economic dimension. Trade and other establishments were in he hands of non-Assamese communities. The major resources of the State, including tea and oil wore again not benefitting the locals.
Question 12.
What was the dominant thrust of the movement?
Answer:
The dominant thrust of the movement was that Assam was being treated as an internal colony and this had to stop The main demands were that the local people should be given greater preference in employment, the “outsiders should be removed and the resources should be used for the benefit el the locals.
Question 13.
Which has led to violent attempts of ethnic cleansing In Assam?
Answer:
Too much emphasis on ethnic identities had a negative impact on other communities of Assom like the Bodos, Khasls, Mizos, and Karbis. Many of them too demanded autonomous status. They began to assert themselves arid wanted to drive out people of other communities from their areas.
Question 14.
What did Punjab claim?
Answer:
It laid dams to the new capital city of Chandigarh which remained a ‘union territory directly administered by the Centre. Punjab also claimed more water from Bhakra Nangal dam and greater recruitment of Sikhs in the army.
Question 15.
Write about the resolution of Akali Del.
Answer:
The Akali Dei had passed a set of resolutions in 1978 clung the Janata Party rule in the center, calling upon the central government to implement them. Its most significant demand was to amend the Constitution to give more powers to the states and ensure greater decentralization of powers.
Question 16.
What happened after Rajlv Gandhi’s entrance?
Answer:
After Rajlv Gandhi became the Prime Minister, he held talks with SAD and entered into an agreement with Sant Langowal, the SAD president, Though fresh elections were held in Punjab and SAD won them, the peace was short-lived as Longowal was assassinated by the militants.
Question 17.
What did Rajiv Gandhi say In his speech?
Answer:
In a famous speech, Rajiv Gandhi said that out of every Rupee spent on the poor barely 15 paise reaches them it highlighted the fact that despite huge increases in development expenditure,the story of the poor remained the same.
Question 18.
Which factors influenced central government to use armed forces to reduce tensions In Assam?
Answer:
- Three factors influenced the use of armed forces in the Northeastern region.
- Firstly, it was a sensitive border area adjacent to China. Myanrnar and Bangladesh.
- Secondly, rebel groups demanding separation from India procured arm from outside.
- Thirdly, they indulged in large-scale ethnic violence against minority communities.
- The government thought this was the only way to bring about peace in the area.
Question 19.
What was meant by liberalisation?
Answer:
- It meant a lot of things put together like drastic reduction of government expenditure, reducing restrictions and taxes on imports. etc.
- It proved for reducing restrictions on foreign investments in India and allowed foreign countries to set up companies in India.
- It is required to the opening of many sectors of the economy to private investors,
- It brought in foreign goods and Indian businessmen were forced to compete with them.
- It had many positive and negative impacts on India.
Question 20.
One of the greatest weaknesses was undoubtedly the low priority given to primary education and public health.” Comment on It.
Answer:
- The post-Independence era is marked with less priority to education and health.
- The optimum development of country depends mostly on the education and health levels of its population of it.
- It further forms part of Human Development Indicators also.
- So, I suggest more priority should be given to education and health now.
Question 21.
Read the given data to answer the following questions.
Coalition Governments and Some Political Parties form the 1980’s
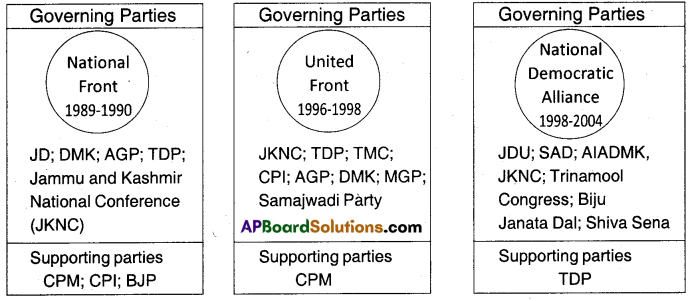
A) Which were the parties that participated In the governments of the National Front and United Front and supported the government from the outside?
Answer:
To National Front: CPM. CPI, and BJP.
To United Front: CPM.
B) Mention the name of the party that participated In the above three governments.
Answer:
J.K.N.C.
Question 22.
What are the newest states of India? When were they formed?
Answer:
| State | Year of formation |
| 1. Uttararichal/Uttarakhand | 2000 |
| 2. Jharkhand | 2000 |
| 3. Chattisghar/Chattisghad | 2000 |
| 4. Telangana | 2014 |
Question 23.
Write about people’s welfare schemes started by present Governments.
Answer:
- Supply of rice at the cost of Rs. 1/. per Kg to the white ration card holders.
- PensIons for the old age people and widows.
- Free Textbooks, uniforms, and midday meal scheme in government schools.
- Housing schemes for the poor people.
- Health scheme for the poor people.
- Fees reimbursement to the poor for higher education, etc.
4 Marks Questions
Question 1.
Telecom revolution has brought several changes In human lIfe nowadays. Explain them.
Answer:
Changes brought by telecom revolution:
- Saves time
- Fast communication
- Online services
- Prosperous life
- Addiction
- Obesity
- Cost of living increased
- Affected human relations
Question 2.
Read the paragraph given below and Interpret.
On one hand, India was forced to open up and liberalise’ Its economIillowing freer flow of foreign capital and goods Into India, On the other hand, new social groups asserted themselves politically for the first time, and finally, religious nationalism and communal political mobilisation became important features of our political hie. Ail this put the Indian society into great turmoil, we are still coming to grips with these changes and adapting ourselves to them.
Answer:
According to the given paragraph, there is a force upon Indian rulers to liberalise the economy. Foreign capital and good should be flown into our country without barriers. Religious nationalism, communal political mobilization have become important features of our life. All these put our society into a great violent disturbance. We are adjusting every time to the situations.
There are so many reasons for the liberalisation of Indian economy. Our government goes to International Banks for loans to develop the country. There they put same conditions. We accept them because of our needs. if India Is self sufficient m all the corners. it will not happen. India is a developing country. For about two hundred years it was exploded by the British.
After Independence. our Government concentrated on agriculture arid industrial development categorically. In the last decade of the 20th-century political changes took place with regard to economic liberalisation, After falling of VP Singh government, PV. Narasimha Rao became the Prime Minister of India.
It was Congress government. He negotiated with the International Monetary Fund for loans to face the crisis. The IMF laid down certain conditions. They are reduction of government expenditure, cuts in subsidies, reducing restrictions on foreign goods, and foreign investment and privatisation of telephone and banking, etc. All this is an effect of Globalisation.
Along with economical disturbances, there are social disturbances. Religion was used In politics. Communal mobilization was also there, All Indians are one and same … such feeling was seemed to be disappearing.
India declared it as a secular country. All the religions are treated equally. No discrimination on the basis of caste or religion, All Indians are equal. At the time of elections religious polarisation is common Caste and religion-based politics is very dangerous to the national integration.
In conclusion, it‘s necessary to invite the foreign investment or import foreign goods but it is to be accepted in the fields where we are not concentrating. The foreign or multinational companies are coming to India to make chips of potato and marketing them.
In what way Is it useful to our country? That we can do here. Heavy industries. mining and computer-based technology are some of the areas in which we are not doing well. Let the MNCs corner and do something with these areas, but they are trying to make cash for themselves.
Question 3.
Observe the following table and write a paragraph analyzing It.
Summary of the 2014 – Indian General Elections
| Party | Alliance | Votes(%) | Seats |
| BJP | NDA | 31% | 282 |
Answer:
The given table describes the summary of the 2014 general elections In India. In the given table two parties that Is Bharatiya Janata Party and the Indian National Congress are compared. It Is not only the party comparison but their alliances are also mentioned.
The Bharatiya Janata Party alliance is National Democratic Alliance whereas the United Progressive Alliance Is related to Indian National Congress. In these elections, The NDA got 31% of the votes whereas the UPA got 19.31%. II we observe the seats, the BJP with its alliance won 282 whereas the INC won only 44. These elections are very crucial because the voter strongly rejected the pre independence party which ruled India since 1947.
For a long time it was a single largest party to win the seats ¡ri Lok sabtia. The voters cleverly gave mandate to the Bharaüya Janata Party with the hopes that their future may be changed. The BJP announced the Prime Ministerial candidate, Narendra Modi wi advance. He achieved and succeeded in Gujarat as Chief Minister.
So the voters accepted him as Prime Minister also. They believed hm. Congress lost faith of the people because of its failures. During Congress period there was a lot of corruption, scams and nepotism, etc. Many of the Congress members of Parliament were in court cases. Rajiv Gandhi himself declared that corruption is highly established in India. So Bharatiya Janata Party with its alliance should worli for the development of the country as the opportunity is given to them by the voters.
Question 4.
Read the following paragraph and write your opinion.
The twentieth century closed with India which was drawn into the world market, India which seemed to have a thriving democracy in which voices of different sections of the population were making themselves heard and in which, divisive and communal political mobitisabon were threatening to destroy social peace.
It had stood the test of time for over fifty years and had built a relatively stable economy and deeply rooted democratic politics. It still had not managed to solve the problem of acute poverty and gross inequality between castes, communities, regions and gender.
Answer:
The given paragraph depicts about divisive and communal politics. These may destroy the social peace. After the independence in India. stable government continued for 30, 40 years and unstability began. Main problem of solving poverty and inequalities with regard to caste, region‘s not yet solved.
My opinion is that the politics are only vote-bank-based. Sometimes the political leaders are there behind the communal riots. To throw out some Chief Minister of the same party, their party leaders encourage these nota. Caste-based politics are shown at the time of tickets given to party candidates. Caste unions and the caste group heads are distributed money to lure them to get their votes. Some constituencies are fixed for some regions because of their dominance in number. It s really a threat to democracy. Holy places of worship are also in some cases used to spread communal messages. That destroys social peace. My suggestion is that people should get awareness about this and act accordingly.
Question 5.
Observe the following table and analyse It.
The trend of Coalition Governments, 1989 – 2004
| Coalition Government | Duration | Governing parties | Supporting parties |
| 1. National Front | 1989 -90 | JD, DMK, AGP, TDP,JKNC | CPM, CPI, BJP |
| 2. United Front | 1996 – 98 | JKNC, TDP, TMC, CPI, AGP. DMK, MGP | CPM |
| 3. National Democratic Alliance | 1998- 2004 | JDU, SAD, TMC,AIADMK, JKNC, BJD, Shiva-Sena | TDP |
Answer:
- The given table is about the trend of Coalition Governments during the period of the years from 1989 to 2004.
- The details of three coalition governments and their duration, etc. are given in the table.
- During 1989-1990 Janata Dal-led National Front formed the government. The governing parties in this government were JD. DMK, AGP, TDP, JKNC. CPM, CPI and BJP supported this government.
- United Front formed the coalition government during 1998-1998. JKNC. TOP, TMC. CPI, AGP, DMK, MGP were the governing parties in this government. CPM supported this government.
- During 1998-2004 BJP-Ied National Democratic Alliance formed the government. The governing parties we this government were JOU, SAD. AIADMK. JKNC, TMC, BJD, and Shiva Sena. TDP rendered support to the NDA government.
- The I 990s were years of very significant change in the post-Independence India.
- With the transformation to a competitive multi-party system, it became near impossible for any single party to win a majority of seats and form a government of its own.
- Since 1989, all governments that had formed at the national level have been either coalition or minority governments.
Question 6.
explain the effects along with the reasons for the emerging era of coalition politics.
Answer:
Reasons for the emergence of coalition era of politcs:
- Multi-party system
- No single party securing required majonty.
- Significance of regional parties increased.
- Congress party gradually lost peoples mandate after 1960s.
Effects:
- No political stability
- Isolating the ideologies
- Giving importance to party’s Interest at the cost of nation’s interest.
- Coming to power in spite of securing less mandate.
Question 7.
Suggest measures for’ better democracy and ethical governance.
Answer:
Government chosen by voters is democratic government. it is expected to work for the people’s welfare. In democracy, voters should be educated. In many countries, voters are not literate.
If people are literate and educated, then it becomes strength to democracy. Those who cross 18 years of age gel right to vote by enrolling in electorate. In India many people enrolled in electorate and get right to vote. The voters are not casting their votes. In urban areas voting percentage is very low. In democracy every voter must vote.
Contesting candidates lure the voters by offering many articles to them. The voters must elect honest candidates. Accountability is very important to the voters as well as the rulers.
The expenditure should be shown to the people. It is kept for social audit. All people can check the accounts. Expenditure particulars should be shown by displaying by the side of the roads pertaining to road construction. In the same way it is to display in all departments. If any political leader detects from one party to another, strict punishment should be imposed.
Government should bring awareness among the rural people about democracy and in cities arid towns it is essential to increase voting percentage. If any political leader or minister or MLA is not discharging the duties well, he/she should be recalled.
Question 8.
Explain about Assam movement In detail.
Answer:
Assam movement:
It is the struggle between Assamese and non-Assamese. This non-Assamese were none other than the people of Bangladesh. The youth of Assam formed All Assani Students Union (AASU) and was in the forefront of agitation. It led a nurrther of stnkes. agitations and marches to remove the so-called outsiders, The problem of outsiders is not a cultural one but of economic issue. Every country or state wants to protect their cultural roots. The Assamese were most of them, Hindus and the outsiders were Muslims. The local people
were afraid of their cultural roots.
Now they affect the trade and so the livelihoods of the locals had been in trouble. It is not only the problem of Assam, it happens at many states. Outsiders dominate a few areas of business and so the locals lose opportunities. In Assam the locals were not given priority or preference in errçioyment. This was the demand of the Assamese. Gradually these demands led to communal polarisation as most of the outsiders are from Bangladesh Muslims. The movement between the Assamese and outsider Muslims led to form an idea of anti-Indian stand.
Central Government took initiation and went on for talks for three years. An agreement was signed by the central government and the students union. In the next elections Assam Gana Parishad (an offshoot of AASU) came to power, In conclusion, the formation of Bangladesh erstwhile Pakistan was taken place on the basis of religion.
Ones religion can be given respect by all but it led to many disturbances. The Muslims, the outsiders of Assam occupied most of the areas of trade and business and there was distress and disappointment among the Assamese. The outsiders would have settled in Bangladesh only. They wanted their country to be separated and still, they are coming to India illegally. Recently both the Prime Ministers of India and Bangladesh say together and solved a few problems. If any problem arises, they should sit together and problems can be solved.
Question 9.
How was the peirod between 1975 to 1985 for Indian democracy?
Answer:
The period between 1975 to 1985 was a testing time for Indian democracy. It began with the state of Emergency ¡n which basic democratic rights were denied and ended with the historic electoral victory of the Congress led by Rajiv Gandhi. Though it began and ended with the rule of the Congress party it saw the emergence of viable alternatives to the Congress at both the Centre and in the States. This effectively prevented India from sliding into a ‘single party democracy’.
Question 10.
What were the soul challenges to national unity?
Answer:
The people of many states felt alienated and wanted either greater autonomy from the centre or even wanted to go separate from India itself. The non-Congress regional parties (like SAD and DMK )meanwhile attempted to come together to form a common front in support of greater say in national level decision making, greater financial autonomy, lower interference State matters and stopping the misuse of the powers of the Governor and arbitrary imposition of President’s Rule.
Question 11.
Write about NTR and TDP.
Answer:
N.T. Rama Rao (NTR), popular firn actor, began the Telugu Desam Party (TDP) on his 60th birthday in 1982. He said that the TDP stood for the honour and sell respect of the Telugu-speaking people (Teluguvari atma gauravam). He argued that the State could not be treated as lower office of the Congress party. Equally important were his promise of some very important welfare measures for the poor Including midday meal scheme in government schools, sale of rice at Rs 2 per Kg to the poor, and liquor prohibition. These
populist measures helped the TOP sweep the 1982 elections. However, he was surreptitiously dismissed by the Governor in 984 when he was away N the United States for a surgery.
Question 12.
What happened In 1985 In the case of Shah Bano?
Answer:
In 1985 the Supreme Court passed a Judgement on a case filed by Shah Bano who had been divorced by her husband ordering that she should be paid maintenance by her ex-husband, While the progressive Muslims welcomed the decision, others protested against this judgement saying that it went against Islamic law and that If this was allowed then there may be further interference In the religious life of the community.
Question 13.
What was the result of Operation Barga?
Answer:
As a result of Operation Barga, the landlords were largely prevented from forcibly throwing the bargadars off the land. In fact, the bargadar rights were made hereditary and thus perpetual. Secondly, the State guaranteed that the bargadars would receive a fair share of the crop (75 percent if the bargadar provided the non-labor inputs and 50 percent if the landlord provides those inputs). In all, approximately half of rural households in West Bengal have received land reform benefits.
Question 14.
Write about the structural adjustment programme.
Answer:
The IMF laid down certain stringent conditions (called ‘structural adjustment programme’), forcing India to accept a policy of liberalisation. This meant
a) drastic reduction of government expenditure-including cuts in subsidies to farmers, expenditure on public services, health, etc.
b) reducing restrictions and taxes on Import of foreign goods
c) reducing restrictions on foreign Investments in India
d) opening of many sectors of the economy (like telephone, banking, airlines, etc) to private investors (these were government monopolies earlier).
Question 15.
How had the other backward castes asserted themselves In Indian politics?
(OR)
What was MandM Commission? Why was li set up? What ware Its recommendations?
Answer:
- The Janata Dal focused on the need for inclusive development and ensuring opportunities for people from backward communities.
- The VP Singh government started implementing 27% reservation in government employment from socially and educationally backward castes that were identified by Mandal Commission
- This sparked numerous protests, especially in north India.
- Many of the OBC castes had become rich from land reforms and green revolution in 1970s and 80s.
- They did not have adequate representation ¡n education, government service and even in politics.
- They now began to demand their share in these spheres.
- With the implementation of Mandai Comrrisslon recommendations, all political parties came to accept the assertion of the OBCa In Indian politics.
Question 16.
Coalition governments induce political instability – Elucidate.
Answer:
- Since 1989, all governments at national level were coalition minority governments.
- A further of regional and national parties had come together.
- So political ideologies and programmes of all parties had to be accommodated.
- A common agreement had to be arrived at.
- No party could pursue extreme agendas.
- They need to tone down their approaches.
- They ought to be suffered with policy paralysis.
- Many coalitions did not last their full time.
- Thus we can say the coalition governments induced political instability.
Question 17.
How do political parties reap on communal polarization? Provide an example.
Answer:
- The Hindus were led by Bharatiya Janata Party.
- In the year 1984 Lok Sabha elections, they won only 2 seats.
- It made great strides when it took up the Ayodhya issue.
- It decided to campaign foc the building of Rama temple at the site of Babri Mosque.
- It claimed that it was the birthplace of Lord Rama.
- L.K. Advani in 1990. led a ‘Rathyatra’ from Somnath to Ayodhya.
- This campaign was accompanied by intense communal polarization.
- It caused a large nunÙer of communal conflicts,
- In 1991 general elections, BJP’s strength went up to 120.
- It was then Rajlv Gandhi was killed and sympathy wave followed the Congress, still, BJP withstood it.
Question 18.
What were the implications of 1977 general elections?
Answer:
- It was a historical election for democracy.
- The Congress party was defeated at the national level for the first time.
- Janata Party became victorious and tried to consolidate itself.
- It dismissed nine Congress governments in states.
- he argued that Congress had lost its mandate to nine in the states as it had been defeated.
- its stand is somewhat proved correct by the results.
- Except in Tamil Nadu and West Bengal Janata Party came to power in states.
- The disunity among the partners had a serious effect on governance.
- The government tell within 3 years, which led to a fresh election in 1980.
Question 18.
Why was the public sympathy to Punjab militant Sikhs declined?
Answer:
- They formed armed attachments and engaged in terrorist activities.
- They dashed with police and other religious groups.
- Those who were not confirmed to militant approved behaviour were killed.
- There were civil casualties in derailing trains, exploding boirts, etc.
- They were engaged in kidnapping and extortion to raise funds.
- All this gradually alienated then from masses and even Sikhs.
- Over a period, public sympathy declined rapidly.
- Peace was finally returned to Punjab by the end of 1 990s.
Question 19.
On the map of India locate the following.
1) Telangana
2) Assam
3) Punjab
4) Tamil Nadu
5) West Bengal
6) Utter Pradesh
7) Nagaland
8) Mizoram
9) Bihar
10) Gujarat
11) Maharashtra
12) Ayodhya
13) Andhra Pradesh
Answer:
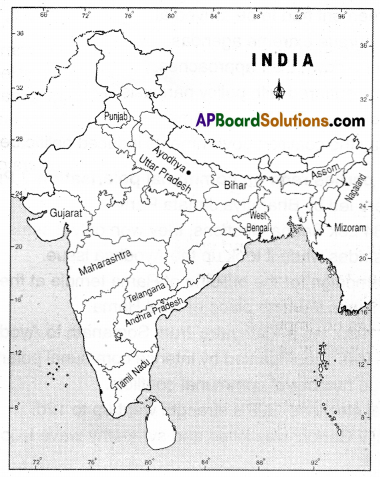
Question 20.
Read the following paragraph and write your comments.
Besides culture and demographics, there was also an economic dimension to this Trade, and other establishments were in the hands of non-Assamese communities. The Major resources of the state unduly Teland oil did not benefit the locals. The tea Industry was mainly based In Kolkata and the oil industry had very few locals involved despite being n the hands of the public sector.
Answer:
This paragraph points out the problems of Assamese for their survival and existence. It is focusing on economic dimension. The trade was under the control of non – Assamese. The tea Industry was in Kolkata and very few locals were there in public sector oil industry.
It s the struggle between Assamese and non-Assamese. This non-Assamese were none other than the people of Bangladesh. The youth of Assam formed AH Assam Students Union (AASU) and was In the forefront of agitation. It led a number of strikes.
agitations and marches to remove the so-called outsiders. The problem of outsiders is not a cultural one but of economic issue. Every country or state wants to protect their cultural roots. The Assamese were most of them, Hindus, and the outsiders were Muslims. The local people were afraid of their cultural roots, Now they affect the trade and so the livelihoods of the locals had been In trouble.
It is not only the problem of Assam. it happens at many states. Outsiders dominate a few areas of business and so the locals lose opportunities. In Assam the locals were not given Priority or preference in employment. This was the demand of the Assamese, Gradually these demands led to communal polarisation as most of the outsiders are from Bangladesh Muslims. The movement between the Assa mese and outsider Muslims led to form an idea of anti-Indian stand.
Central Government took initiation and went on for talks for three years. An agreement was signed by the central government and the students union. In the next elections, Assam Gana Parishad (an offshoot of AASU) came to power.
In conclusion, the formation of Bangladesh erstwhile Pakistan was taken place on the basis of religion. Ones religion can be given respect by all but it led to many disturbances. The Muslims, the outsiders of Assom occupied most of the areas of trade and business and there was distress and disappointment among the Assamese.
The outsiders would have settled In Bangladesh only, They wanted their country to be separated and still, they are coming to India illegally. Recently both the Prime Ministers of India and Bangladesh sat together and solved a few ‘blems. If any problem arises, they should sit together and problems can be solved.
Question 21.
Read the following paragraph and write your comments.
small parties tried to gain undue advantage as the withdrawal of their support could cause the ta of the government. Sometimes this also caused’ policy paralysis’ as the coalition could not implement any policy with called for serious change for fear of withdrawal of support by one or the other partners.
Answer:
This paragraph is discussing the importance of coalition politics and its effect. Parties try to gain benefit from sensitive issues also. This paragraph talks about policy paralysis, Though It is a smell party with less number of elected members also dominates and try to threaten the government. The government also feels fear that at any time the coalition parties may withdraw their support.
This situation came in India because of two reasons. One, the national parties have been decreasing in gaining mandate in elections except In a few cases. The second reason is that some local or regional parties are playing a crucial role with local issues.
Now It has become compulsory f or the National Parties to take support from regional parties. In 1970s, it happened to take support of many parties and so they came together with common understanding and formed Janata Party. Jaya Prakash Narayan and Adiarya JB Krlpalany played crucial and important role in bringing all the anti-congress and anti-emergency parties to fight elections. Though some of the parties are dlametncaMy opposite in their viewpoints on social and political issues, they are united and succeeded.
Based on regional issues, some regional parties like Telugu Desam Party, Assam Gana Parishad, Akalidal, and Telangana Rastra Samithi are formed. With their view pewits, they came to power and strongly rooted among the rural mass also. People began ignoring the national parties and the parties started tie-ups with regional parties, Some parties came to an understanding before elections and in some cases, it is after the elections also took place.
In many cases, the National or Regional parties when they came to power, they face the issue of policy paralysis. Even the small parties also threaten the ruling party they withdraw their support if they don’t fulfill their demands. Now common mining programme has become mandatory to the coalition governments. VP Singh started the coalition governments in India, Though two major coalition groups of UPA and NDA, are working in India, sometimes we hear about third front also.
Wi conclusion, the parties should understand the needs of the people and act accordingly. National Parties also categorically prioritize the issues taking the local parties into consideration. Regional parties also should work with national interest Though they give importance to their regional issues national integration and sovereignty of the country are to be considered.
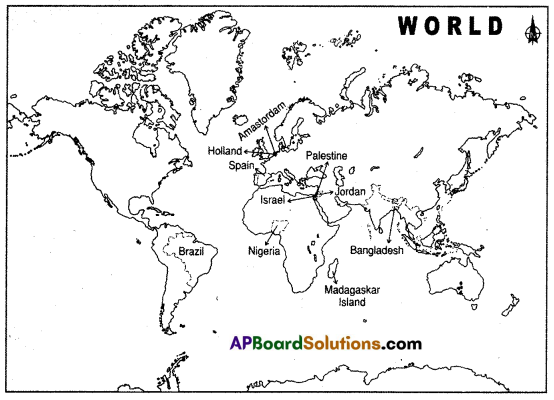
Question 22.
Locate the following in the given map of World.
1) Madagascar Island
2) Nigeria
3) Holland
4) Amsterdam
5) Brazil
6) Jordan
7) Israel
8) Spain
9) Palestine
10) Bangladesh
Answer: