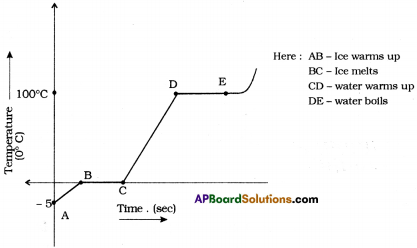
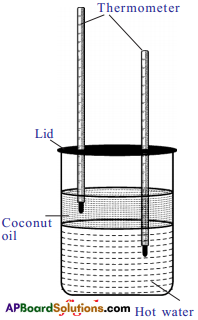
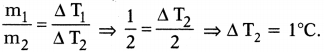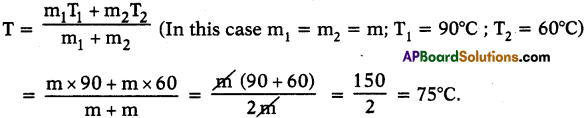SCERT AP Board 9th Class Social Solutions 8th Lesson Service Activities in India Textbook Questions and Answers.
AP State Syllabus 9th Class Social Studies Solutions 8th Lesson Service Activities in India
9th Class Social Studies 8th Lesson Service Activities in India Textbook Questions and Answers
Improve Your Learning
Question 1.
What is meant by the term “service activities”?
Answer:
1. Services rendered by different people in a specified activity are known as service activities.
E.g.: a) Teachers’ Services.
b) Health and Medical Services rendered by doctors and para-medical staff.
c) Services of people working in army, navy, and airforce.
d) Financial activities of banks and insurance companies.
e) Trading activities, etc.
All the above services can be termed as Service Activities.
2. Service activities do not produce any tangible commodity like paddy or cloth.
3. Service activities here refer to ‘the nature of work” done.
4. “Service activities” in this context of work does not mean something that is done “free of cost” or “out of love or devotion.”
5. All the above people earn money by rendering these “service activities.” This is their livelihood.
6. These service activities are required for agriculture and industrial activities.
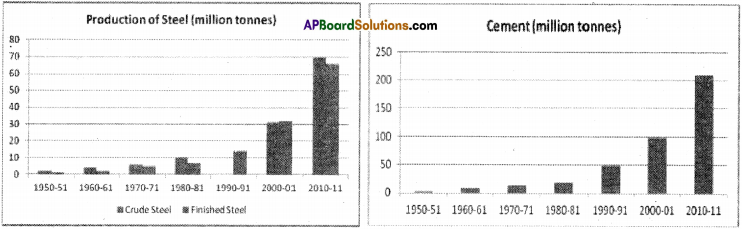
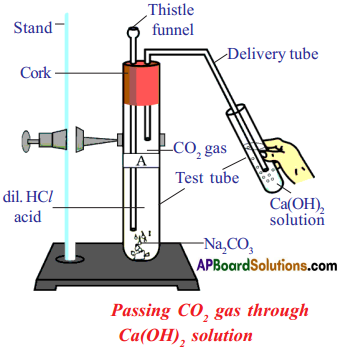
![]()
Question 2.
List five service activities and give your reasons why they are not be considered as either agricultural or industrial activities.
Answer:
1. Health and Medical Services :
A doctor examines patients, prescribes medicines and monitors their progress. Other para-medical staff help doctors.
2. Trade :
Goods whether agriculture or manufacture goods are to be transported to distributors. Distributors in turn supply goods to wholesaler who in turn supplies them to retailers. And consumers purchase from the retailer. These are trading activities.
3) Financial Services :
Banks issue loans to all farmers and entrepreneurs and facilitate agriculture and industrial activities. Insurance companies insure goods against risk.
4) Defence :
Activities and people who work in all the armed forces like army, navy, and airforce.
5) Personal Services :
Workers who do domestic work, laundry, cleaning, dyeing, hair dressing, etc.
a) In all the above examples we can see that services are rendered.
b) Nothing new is produced here. In agriculture, we produce some crop and in industrial activity, we work upon raw materials and convert them into finished goods. Here in the above examples, nothing tangible is produced.
c) The above examples are special kind of activities that help agriculture and industry and also provide a lot of service that people require.
So we cannot consider the service activities as either agricultural or industrial activities.
Question 3.
How can service activities help in the overall development of a country?
Answer:
- Overall development of a country depends on developmental initiatives involving setting up of many establishments like educational institutions, hospitals, etc.
- Other developmental activities include provision of infrastructure facilities such as transportation, telecommunications, banks, insurance services, and other services like trading, book keeping, and public administration.
- All these activities are service activities that help agriculture and industry and facilitate overall development of our country.
Question 4.
How are agricultural and industrial activities related to services?
Answer:
Agricultural and industrial activities need the services of various sectors.
- Transportation helps in assembling raw material from the mines to industrial spots and to carry finished goods from industry to markets.
- Road and other services to transport finished products.
- Marketing services.
- Import and export services.
- Storage services like godowns.
- Financial services like banking loan and insurance services.
- Health and education services.
- Communication system, information technology.
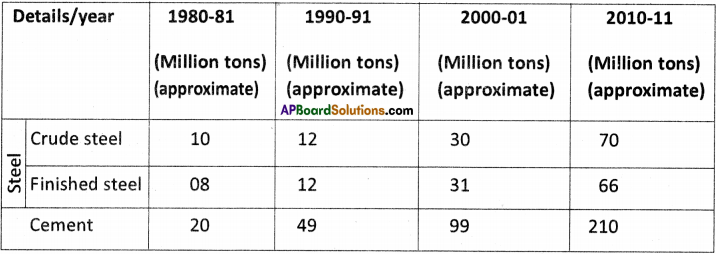
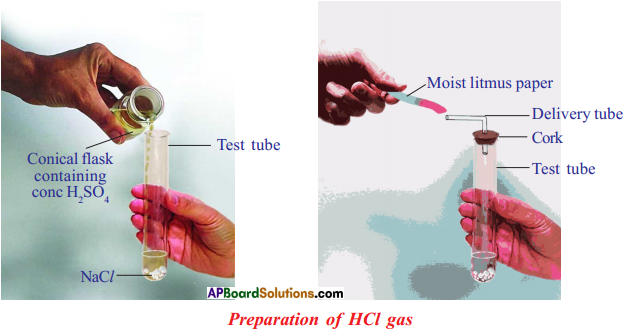
![]()
Question 5.
‘The growth of service sector is sustainable and can make India as a rich country.’ Do you agree with this statement? Elaborate.
Answer:
- There is a lot of change in technology and by exporting our services i.e., “BPOs” or “Outsourcing” we are earning foreign exchange.
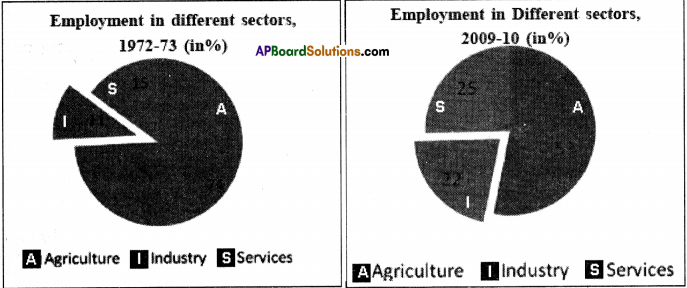
- Service Sector constitutes one-fourth of the jobs people do in India.
- 90.5 lakhs and 25.3 lakhs of people are involved in community, social, personal services, and transport and communications respectively.
- So many jobs are available for educated people in service sector.
- Due to the development of telecommunications and information technology, the world has become a global village.
- Due to the establishment of Multinational Companies, we are getting projects from foreign countries.
- The standard of living of the people has been increased for the last two decades. Hence the growth of service sector is sustainable and can make India a rich country.
Question 6.
Why are service sector activities becoming important?
Answer:
- Service sector activities include all the services like Banking and Finance, Trade and Commerce, Transport and Communications, Health, Education, Personal services, etc.
- Service sector activities do special kind of activities that help agriculture and industry and provide a lot of services that people require.
- Provision of education and health fulfils the aim of social welfare.
- Trade and commerce help in bringing buyers and sellers together.
- Transportation is necessary forthe movement of men and material from one place to another.
- The development of telecommunications has cut the geographical boundaries and helps in globalization.
- They provide information about new markets and products.
- They are considered as means of modernization.
- They provide employment opportunities and are very useful in rising the standard of living of the people.
Due to the above reasons the service sector activities are becoming important.
Question 7.
Service activities cannot expand beyond a level unless agriculture and industries. Explain.
Answer:
- Development of a country is always measured on production of goods and services.
- Increase in production is possible only through the development of agriculture sector and industrial sector.
- Service activities are necessary to modernize agriculture and industrial sector.
- Development services without increase in production is a waste.
- Hence service activities cannot expand beyond a level unless agriculture and industries develop.
- In fact, all three sectors should go hand in hand.
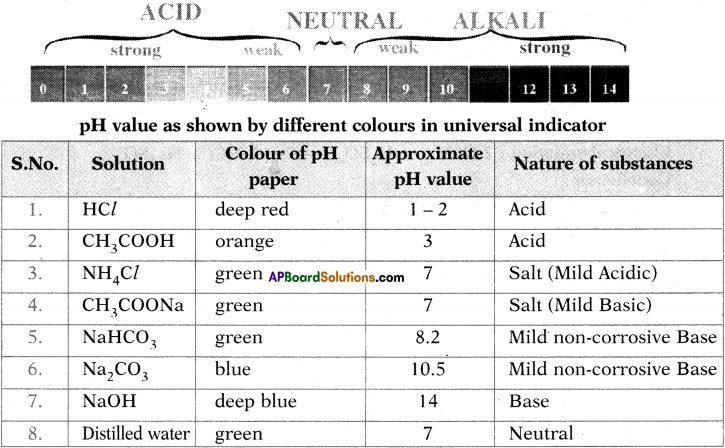
![]()
Question 8.
How can service sector reduce educated unemployment in India?
Answer:
- There has been tremendous change in the communication technology which has opened a wide range of jobs for educated people.
- Business Process Outsourcing (BPO) has brought in new kinds of employment opportunities.
- They provide services to people located across the globe using telecommunication links.
- The entertainment industry creates jobs to work in various print media firms, cable television channels.
- We see number of internet cafes and telephone booths in most of the cities and towns.
- The advertising industry has also brought new job opportunities.
- Many new jobs are available in Banking and insurance sectors.
Hence service sector can reduce educated unemployment in our country.
Question 9.
Is there any migration of labourers from your area? Find out the reasons for the migration.
Answer:
Yes, there is migration of labourers from our village.
Reasons for migration :
- People migrate from rural areas mainly due to insufficient employment opportuni¬ties, inadequate income available in rural employment.
- People also migrate with the expectation of higher incomes and more opportunities for family members and may be better services.
- For some people from rural areas moving to cities and towns, to work in industry and other services activities have been recognised as a natural response to increase their income and for better family prospects.
Question 10.
Read the 9th paragraph of this chapter ‘Working people engaged’ and answer the following.
| Working people engaged in service activities do not produce a commodity, like that in agriculture or in industry. They do special kind of activities that help agriculture and industry and also provide a lot of service that people require. Another example is the banking and finance related service activities required by people and business organisations. You have read about this in Class VIII chapter “Money and Banking”. Similarly there are the cell phone, internet and all other types of telecommunication service providers. |
What are the service activities required for agriculture and industries?
Answer:
- Banks and other financial institutions finance the agriculture and industrial activities by lending of funds.
- Transportation services help in the development of the agriculture sector through effective distribution of food grains and perishable goods from the producing areas to the markets without interruption.
- Transportation helps in the distribution of raw material to the industrial units.
- Service sector activities provide information about new markets and products.
- A variety of trading activities like distributors, wholesalers and retailers also constitute a major segment of service activities.
- These activities help in bring buyers and sellers together.
- Proper power supply to various industrial units facilitates industrial growth.
Question 11.
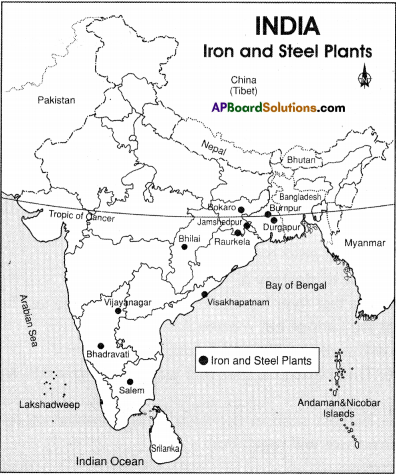
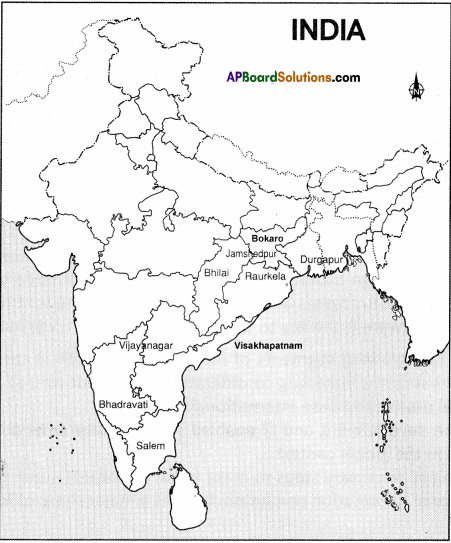
Observe the map given in the (text) page 104. Locate the software technology parks of our country in the India outline map.
Answer:
Students Activity
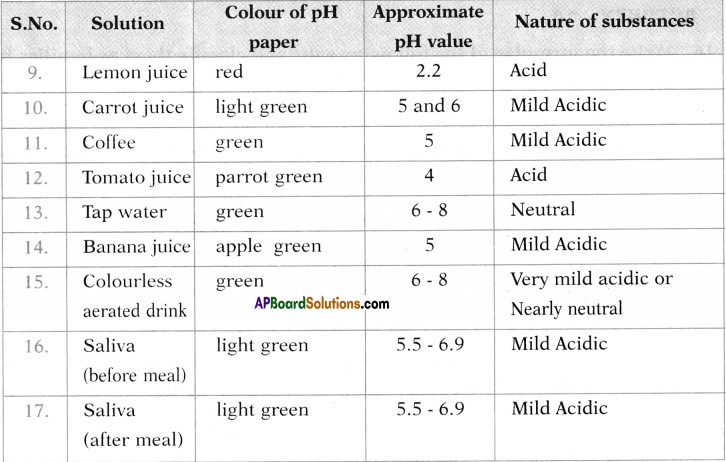
![]()
Question 12.
Discuss with any seven people identify with sector they are employed in. Write a brief note or design a poster about their work. What relationship do you see between their employment and place of residence?
| Name of the person | Nature of work done | Agriculture/Industry/Services |
Explain your reason for the classification.
Answer:
| Name of the person | Nature of work done | Agriculture/Industry/Services |
| “X” | Works in steel plant | Industry |
| “Y” | Carpenter | Services |
| “Z” | Landlord | Agriculture |
| “A” | Works in telephone exchange | Services |
| “B” | Teacher | Services |
| “C” | Goldsmith | Services |
| “D” | Works in the land of others | Agriculture |
| “E” | Match box making | Industry |
1) Primary sector :
This includes those activities that are undertaken by directly using natural resources, e.g.: Cultivation of paddy. This is known as primary sector because it forms the base of subsequent products that are made from it. This sector is also called Agriculture and Related sector.
2) Secondary sector :
This sector covers those activities in which natural and primary products are changed into other forms through ways of manufacturing.
e.g.: manufacturing paper from bamboo. This sector is also known as industrial sector.
3) Tertiary sector :
This sector includes those activities that help in the development of the primary and secondary sectors, e.g.: railways. Since they provide services to help the production, this sector is also called service sector.
9th Class Social Studies 8th Lesson Service Activities in India InText Questions and Answers
Question 1.
There are eight categories of service activities given below. Some details are filled in, others are left out. Fill in the blank ones after discussing with your teacher. (Text Book Page No. 97 & 98)
Answer:
1. Education:
Institutions – schools, colleges, universities, technical institutions come under this category. This means those who are working in these institutions such as teachers, all the administrative staff and their activities constitute services.
2. Health and Medical Services :
Primary health centres. General hospitals. Old aae homes, etc.
3. Trade :
A variety of selling activities both wholesale and retail that we see around. National and International business, etc.
4. Public Administration :
Public services under village and town panchayats, state and central governments come under this category. Examples: people who work in police stations, workers of various other government departments such as village administrative officers, revenue inspectors, tehsildars, Collectors, those who work in all kinds of courts, assistants, clerks, accountants, typists, peons, drivers etc.
5. Defence :
Activities and people who work in all the armed forces like army, navy and air force.
6. Financial activities :
Banks and different saving schemes, postal, life insurance, etc.
7. Personal Services :
Workers who do domestic work, laundry, cleaning, dyeing services, hair dressing, running beauty parlours, tailoring shops, photo, and video studios.
8. Activities such as:
People working in entertainment and information technology industry – production of films, TV serials, those working in media, newspapers, television channels, and advertisement agencies are also included in services.
![]()
Question 2.
What do you think about Foreign Direct investment {FDI} in Retailing Activities? Can government do anything to address this issue? (Text Book Page No. 101)
- In my opinion, there will be gainers and losers from FDI in retail.
- Overall gains will outweigh to losses.
- In course of time the losess too will benefit.
- It was opined that large and medium sized farmers will initially benefit the most, while the small farmers or landless labour will be the losers.
- However, the purchases by the big super markets will increase demand for agricultural products, which in turn will expand agricultural out put, and increase demand for labour.
- This will increase agricultural wages in the long run.
To set right this issue, the government has to take following steps.
- Best storage facilities also should be provided by the govt.
- Govt should take measures that market will not go in the hands of few people.
- Govt must keep Foreign Direct Investment under its control.
Question 3.
Who, in your opinion should set up new medical institutions – privatesectoror government? Why? (Text Book Page No. 102)
Answer:
The following organizations shall be eligible to apply for permission to set up a medical college.
- A state govt. / union territory.
- A university
- An autonomous body promoted by central and state governments.
- A society registered under the Societies Registation Act, 1860.
- A public religious or charitable trust registered under the Trust Act, 1882.
- Companies registered under Company Act.
I think that the government should set up new medical institutions.
Reason:
Because it is not easy to any private sector persons to satisfy the norms of the Medical Counsil of India.
![]()
Question 4.
The following table shows the number of workers (in lakhs) employed in different service activities in large enterprises in 1991 and 2010. Read the table carefully and answer the questions that follow. (Text Book Page No. 100)
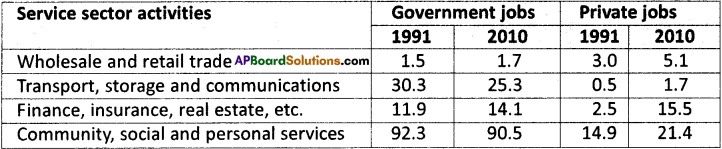
a) Which service activity gave maximum employment in 2010?
Answer:
Community, social and personal services gave maximum employment.
b) Has the number of government jobs increased or decreased over the years?
Answer:
The number of government jobs has been drecreased from 136 lakhs in 1991 to 131.6 lakhs in 2010.
c) What kind of jobs has government generated the most during this period?
Answer:
The jobs in finance, insurance, and real estate have been increased from 11.9 lakhs to 14.1 lakhs for the last 20 years.
d) What kind of jobs were people able to get in the private service activities?
Answer:
People were able to get private jobs in all service sector activities like trading, transportation, finance and personal services.
e) Are there any differences between jobs provided by the government and private employers? Discuss.
Answer:
a) The number of job opportunities in the private sector has been increased from 20.9 lakhs in 1991 to 43.7 lakhs in 2010.
b) The salaries of the private jobs are good but the employees are expected to work very long hours.
c) Government jobs have security whereas private jobs do not give any security to their employees.
Question 5.
Talk to some retail shop owners in your neighbourhood. Discuss their opinions on foreign retailing shops in your class. (Text Book Page No. 102)
Owner of shop – 1 : “Traders and kirana store owners are not fully prepared to face foreign retailers.”
Owne^sfiop – 2’/ “6ur shops are safe. Our customers will not visit those shops.”
Owner of shop – 3 : “The customer will get the knowledge of quality of the provisions. Those shops are maintaining least quality things.”
– We discussed all these points in the classroom.
Question 6.
What is your opinion on foreign companies setting up retail shops in India? How do you think that they generate employment in India? (Text Book Page No. 102)
Answer:
- Foreign direct investment will definetly help the farmers in long run.
- It is argued that there will be loss of jobs in traditional, smaller retail sector.
- However, the purchases by the big supermarkets will increase demand for agricultural products, which in turn will expand agricultural output, which in turn may increase demand for labour.
- This will increase wages in the long run.
![]()
Question 7.
Prepare a table with two columns and list out the advantages and disadvantages of allowing foreign company retail stores in India. (Text Book Page No. 102)
Answer:
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| 1. Foreign direct investment will increase demand for farm products. | 1. The small farmers and landless labour will be the losers. |
| 2. Basing on demand the production of farm goods will be increased. | 2. FDIs will influence the farmers and may buy produce at low costs. |
| 3. Better storage facilities will be provided. | 3. They will not invest much on storage facilities but charge high rates for storage. |
| 4. Better storage facilities will minimise waste of farm produce. | 4. There will be loss of jobs in traditional and small retail sectors. |
| 5. Farmers will be saved from the traps of moneylenders. | 5. The foreign companies will sooner or later misuse – their power to buy in large quantities. |
Question 8.
Why is it necessary to establish more medical institutions in India? (Text Book Page No. 102)
Answer:
- The government of India recognizes ‘Health for all’ as a national goal.
- The medical education and health care in India are facing serious challenges in content and competencies.
- There is a need to balance for more medical colleges with the maintenance and improvement of quality standards.
- There are disparities between different states and rural/urban areas with regard to access to basic medical services and quality health care.
To overcome all these problems, it is necessary to establish more medical institutions in India.