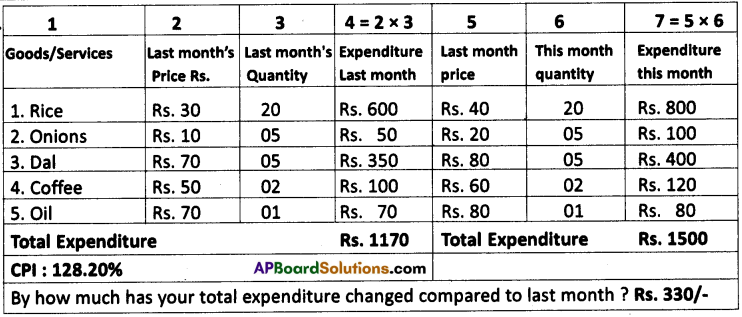
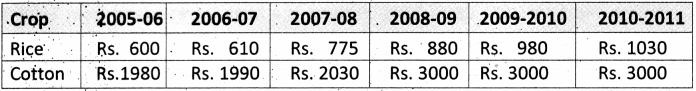
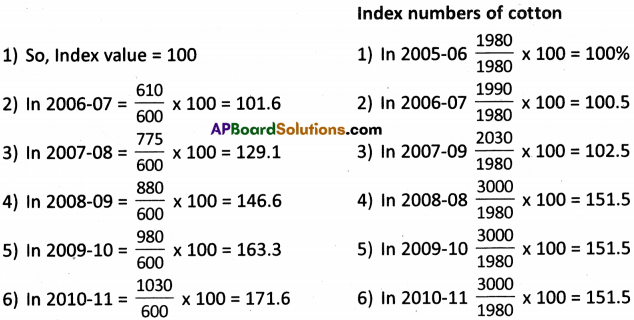
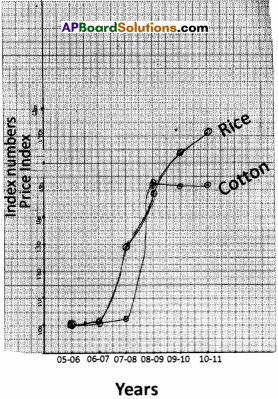
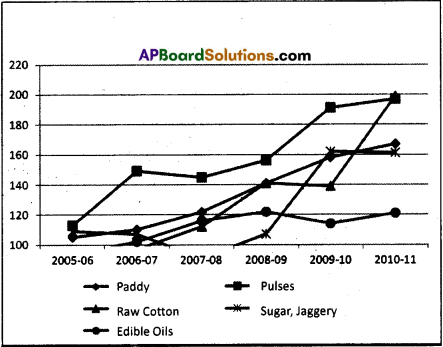
SCERT AP Board 9th Class Social Solutions 19th Lesson Expansion of Democracy Textbook Questions and Answers.
AP State Syllabus 9th Class Social Studies Solutions 19th Expansion of Democracy
9th Class Social Studies 19th Lesson Expansion of Democracy Textbook Questions and Answers
Improve Your Learning
Question 1.
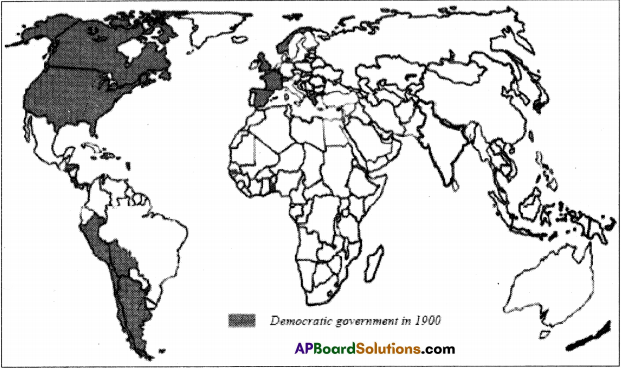
Map 1: Democratic Governments in 1900 – 1950
Map 2 : Democratic Governments in 2011
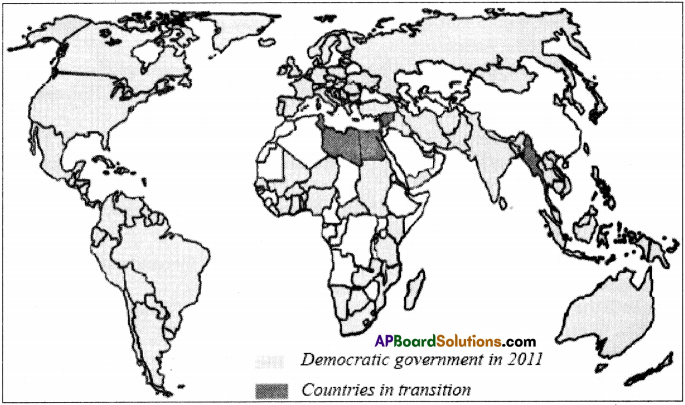
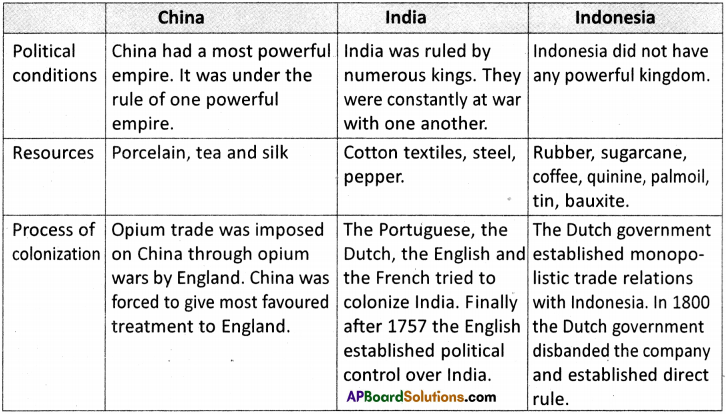
a) On the basis of these maps, identify up to three countries (in some cases you won’t find three countries) that were democratic in these continents for the given years and make a table as given.
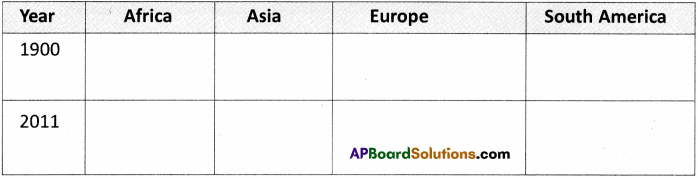
Answer:
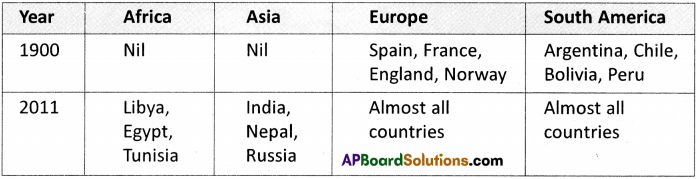
b) identify some African countries with democracy in 2011.
Answer:
Egypt, Libya, Tunisia are countries which got independence in and around 2011.
c) Make a list of big countries that were not democratic in 2011.
Answer:
1) Asian countries :
China, Kazakhstan, Turkmenistan, Saudi Arabia, etc.
2) African countries :
Algeria, Ethiopia, Chad, Zaire, Morocco, Mauritania, Angola, etc.
The above countries were not democratic in 2011.
![]()
Question 2.
Read the maps again and think about the following points.
a) Based on the maps, can we say that the Twentieth century was a significant era for the spread of democracy?
Answer:
- At the beginning of the 20th century only few countries of Europe and America were independent, e.g.: Spain, France, England, Norway, Argentina, Chile, Bolivia and Peru, the USA, Canada, Alasca.
- After World War II almost all countries fought against colonial powers and got independence.
- Though there are still some non-democratic countries, we can call 20th century as an era of democracy.
b) During the early 20 century, democracy was mostly in the continents like Europe and Americas. While in certain continents like Africa and Asia there were almost no democratic countries.
c) Even today there are certain areas that have not established democratic governments such as Saudi Arabia and Ethiopia.
Question 3.
Most countries often claim themselves to be democratic by conducting elections. How did this occur in the context of Myanmar and Libya?
Answer:
- Both the countries Myanmar and Libya claim themselves as independent and democratic.
- But in practical view, they are not democratic countries.
- Unlike democratic countries –
a) They did not allow multi-party elections and one party usually ruled for several years.
b) Even they did not allow free elections.
c) Sometimes they did not allow the elected representatives to form governments.
Ex : NLD, led by Suu Kyi got 80% seats, was not allowed to form government.
d) They did not allow freedom of expression or freedom to form organizations, or freedom to protest against government.
Both the countries did not have any conditions for a democracy to flourish. Hence they cannot claim themselves to be democratic by conducting elections.
Question 4.
Why do you think the rulers try to control the media? Do you know how is media controlled in your area?
Answer:
- Mass Media is powerful weapon which can make or break any governments.
- Restrictions on media helps them to remain in power.
- Hence the rulers always try to control the media.
- So many times in India too government censors certain news. This generally happens without the notice of common man.
![]()
Question 5.
Write an imaginary dialogue between a person from Libya and Myanmar comparing the events and struggle for democracy in their respective countries.
Answer:
Person from Libya : Hai, I am xxxx, as I have already told you the monarchy is over thrown in our country.
Person from Myanmar : Yes, I came to know about that who is ruling your country now.
Libya : Gaddafi has taken control of our country. What about your country.
Myanmar : In 1962, the government was overthrown and ‘Ne Win’ military rule is going on.
Libya : First of all we thought he could rule us. He laid foundation for development. What is your country’s position?
Myanmar : Under military rule, our country did not make any progress.
Libya : UNO is supporting our people’s to demands.
Myanmar : Other countries are also showing sympathy us.
Libya : We protested against.
Myanmar : Suu Kyi is in house arrest she played good role.
Libya : Gaddafi is overthrown in 2012. O.K. Bye.
Myanmar : We got new government in 2012. Bye.
Question 6.
How do literacy and mass education help for the functioning of democracy?
(OR)
How do the literacy help for the effective functioning of democracy?
Answer:
- Literacy and education play an important role in the development of individual and society.
- Knowledge liberates citizens from ignorance.
- Any society needs a vigilant, conscious, and informed public for the successful functioning of the democracy.
- Education enables people to think critically, rationally, and scientifically.
- The right to vote can be properly exercised when voter can read newspapers, follow national and international developments, and participate in democratic process effectively.
Hence the proper functioning of democracy always depends on the literacy and mass education.
![]()
Question 7.
What is the difference between democracy and dictatorship?
Answer:
Differences between democracy and dictatorship :
| Democracy | Dictatorship |
| 1. Democracy is a political system in which sovereignty vests with people. | 1. Dictatorship is a political system in which sovereignty vests in one single person’s hands. |
| 2. Free and fair elections are necessary for the successful running of the democracy. | 2. Dictatorship does not require elections. |
| 3. Democracy operates on the recognition of dissent. | 3. Right of disagreement is not recognized. |
| 4. Public opinion has important place in democracy. | 4. Pubic opinion is not taken into consideration. |
| 5. A high degree of social and economic equality is also essential for true democracy. | 5. Dictatorship leads to concentration of power and wealth in few hands. |
Question 8.
What is the role played by Aung San Suu Kyi in fighting for democracy in Myanmar?
Answer:
- Aung San Suu Kyi, daughter of Aung San who took the lead in staging protest against the military rule.
- Suu kyi fought for reforms in Burma.
- She established a new political party “National League for Democracy (NLD) and won majority (80%) of the seats even though she was in prison.
- Suu Kyi was released from house arrest after the elections of 2010.
- She questioned on the malpractices of elections.
- In 2011 Suu Kyi’s ‘NLD’ contested in the elections and have won 43 out of 45 parliamentary seats that were vacant.
- The freeing of Suu Kyi and the successful participation of NLD in elections are considered the beginning of democracy in Burma.
Question 9.
Read the last paragraph of this chapter and answer the question.
Today, it is increasingly becoming clear to the people that democracy which respects the freedom and rights of all people may be the best way to solve some of the complex problems the countries face. Today, a new kind of democracy is being forged across the world in which even the poorest and the most vulnerable people will have a voice and will be able to influence policies and ensure justice and peace for all.
What is a new kind of democracy?
Answer:
- The poorest and the most vulnerable people will have a voice.
- The poorest will be able to influence the policies.
- The new kind of democracy will ensure justice and peace for ail.
![]()
Question 10.
Read the newspapers and note down any news regarding struggle for democracy in Libya or Egypt or any other country. Prepare a file of such news clippings and display in the classroom.
Answer:
Struggle for democracy in Libya :
A few months ago the National Transitional Council (NTC), which has governed Libya since the first few weeks of the revolt in 2011, announced that the assembly would not draft the constitution itself but instead appoint a 60-member committee to draft it. The members of this committee were supposed to be chosen from outside the assembly and represent the country’s three geographic regions of Libya – Tripolitania, Cyrenaica, and Fezzan — in equal numbers. Yet, a few weeks ago, the NTC changed policy again at the last moment, declaring that the members of the constitutional committee would not be appointed by the assembly but directly elected by the people, though it’s not clear when. Confused? So are Libyans.
There are rumors in Libya that most members of the NTC are not happy about the idea of dissolving the institution and going back home. It’s just a rumor, but the group’s decision to revoke constitution-writing powers from the new assembly is making people suspicious, and that’s the point. The NTC likely fears too much power going to Islamists, who are notoriously less friendly toward the NTC than are other groups. We can’t know the NTC’s motivations for sure, but their recent moves diminished the power of the new assembly, which they may have feared would be dominated by Islamists, who swept national elections in neighboring Tunisia and Egypt. A more democratic Libya would re¬ject the NTC’s odd rule-changing and reinstate the elected assembly’s power to write the constitution. After all, this is what Libyans voted for. So should the same Western powers that supported the Libyan revolt.
Libya has come a long way since Gaddafi’s fall, but it still hasn’t been able to solve two major security problems: the armed militias that still roam the country and the state’s deteriorating control of its national borders. Fortunately, this is where new assembly can step in, finding agreement among the various parties and militias and forming a govern-ment, one that is as inclusive as possible, to administer and rebuild Libya. The interna-tional community can help, including by training and equipping the police and security forces, both of which were devastated by the recent conflict.
A successful election is just the start of dealing with one of Libya’s most important challenges right now: national unity. Regional and local claims and jockeying for power threaten to undermine the legitimacy of and support for the national government. A few thousand inhabitants of the eastern provinces care calling for a federalist state, if not of outward secession. While this is definitely a minority position, it is a very dangerous one because it could easily, at the administration’s first real difficulty, split the government and the people, thus slowing or even reversing Libya’s progress toward stability. Most Libyans, as well as the interested Western nations, are rightly happy with Libya’s progress toward becoming a stable, unified, democratic state. But if they want that progress to continue, they’ll all have to work together.
9th Class Social Studies 19th Lesson Expansion of Democracy InText Questions and Answers
Question 1.
What kind of problems do you think these pose for establishing democratic government? (Text Book Page No. 235)
Answer:
- Bringing democratic participation of all the people under conditions of tribalism, normalism, illiteracy, and restrictions on women was difficult.
- Encouraging participation of common people in public affairs through peoples councils and elected Peoples Assembly in the centre in also difficult.
Question 2.
Even though the people had benefited much from the Gaddafi government, why do you think they rose in rebellion against it? (Text Book Page No. 237)
Answer:
- The government of Gaddafi was not ready to trust these democratic bodies.
- “Revolutionary Councils” were appointed.
- The democratic bodies had to implement the decisions of these non-elected leaders.
- The RCC used brute armed force to arrest, torture, and kill political opponents.
- There was no freedom of press and no one could start any trade union or other associations.
- The civic amenities were deplorable.
Hence rebellions rose against the government of Gaddafi.
![]()
Question 3.
Even though the Gaddafi government claimed to be a democratic government, what aspects of democracy were absent? What aspects of democratic government were present in it? (Text Book Page No. 237)
Answer:
Aspects of democracy absent in the government of Gaddafi:
- Democratic bodies had to implement the decisions of non-elected leaders.
- Freedom of press, freedom to form trade unions and associations were prohibited.
- No political parties were allowed to function in Libya.
- This led to concentration of power and wealth in the hands of few.
Aspects of democracy present in the government of Gaddafi :
- Free universal education was provided.
- Free medical care for all was also provided.
- Oil profits were distributed to all the citizens.
- Subsidised housing schemes were introduced.
- Women were given with equal opportunities and status in the society.
Question 4.
Why are civil liberties important for democracy? Explain in the context of Libyan experience. (Text Book Page No. 237)
Answer:
- “Liberty” is one of the aspects of democracy.
- Civil liberties include liberty of thought, speech, expression, faith, belief and worship.
- These “liberties” were missing in Libya.
- Liberty of expression was brutally crushed.
- The RCC was also very intolerant of criticism and opposition.
- People were not at liberty to express their discontent.
Thus lack of civil liberties led to the downfall of the government of Gaddafi in Libya.
![]()
Question 5.
Why do you think democracy was not able to establish itself in Burma after its independence? (Text Book Page No. 240)
Answer:
- Burma became independent just 5 months after Indian independence.
- It appeared that Burma too would emerge as a democratic republic.
- However, the Burmese did not have a united political party to lead them at the time.
- Burma consisted of a large number of small states and ethnic linguistic regions.
- Aung San, the leader of the nationalist movement and the leader of the ethnic group was assassinated.
- Burmese military began its slow advance into the ethnic states to rule by force.
- They were illiterate, no able leader, no power to fight with military, etc., were the reasons for the failure to establish democracy in Burma.
- Finally, in 1962, the elected government was overthrown by a coup, and army “General Ne Win” took over the charge of the country.
Question 6.
Why do you think democracy was not able to establish itself in Libya after its independence? (Text Book Page No. 240)
Answer:
- Libya got its independence in 1951 and the power was transferred to king Idris.
- In the year 1969 under the leadership of Gaddafi monarchy was abolished and the country was declared as the “Socialist Libyan Arab Republic”.
- But the people were concerned about their own tribe and its honour than about the welfare of the people.
- Most of the people were poor nomadic animal herders who were also illiterates.
- Women were confined to purdah and were not allowed to participate in public activities.
- On top of this the government of Gaddafi was not ready to trust the bodies of democracy. Hence the democratic participation of all people under these conditions was difficult.
Question 7.
How did students and youth play an important role in bringing democracy to both Libya and Burma? (Text Book Page No. 240)
Answer:
- People from across the country began to interact through internet and mobile phones to share their misery.
- Use of internet and Facebook helped them to get the support of the people all over the world.
- The youth and people started protesting against delay in the building of houses and political corruption.
- In Burma, the students took the lead in staging protest against the military rule. Finally military power was overthrown in both the countries and democracies are established.
Question 8.
What similarities of events do you find in the description of events in Libya and Burma? (Text Book Page No. 240)
Answer:
- In both the countries, students, youth and people participated in the protest movements.
- Use of mobiles and internet and social networking sites like Facebooks were common.
- “UNO” supported both the countries and declared Libya as “No fly zone” and ordered for a referendum in Burma.
- Economic sanctions were imposed on both the countries.
- In both the countries the protest was to overthrow the military regime and establish a democratic form of government.
- Lastly both the countries successfully conducted elections in a fair way and elected their new leader.
![]()
Question 9.
Underline the statements that are related to political party and voting in both Libya and Burma. (Text Book Page No. 240)
Answer:
a) Libya
- RCC – Revolutionary Command Council.
- Election – 2012 new government sworn in on Nov. 2012. Over 100 political parties participated and 200 representatives were elected.
b) Burma
- 1951, 56 and 60 elections were held.
- 1990 elections – NLD party established by Suu Kyi.
- 2010 elections were held.
- In 2011 ‘NLD’ won 43 out of 45 seats.
Question 10.
Track the changes that you may have heard about Libya and Burma during the year 2012 and write it. (Text Book Page No. 240)
Changes in Libya :
- In 2012 the National Transitional Council (NTC) handed overthe powerto Libya’s newly elected Parliament the General National Congress (GNC).
The Congress appointed a Prime Minister Ali Zidan, who formed an interim government.
Changes in Burma :
Burma’s Pro-democracy leader Aung San Suu Kyi greeted supporters from her vehicle during her election campaign in Aung Pan in the southern Shan State of Burma (Myanmar) on March 1, 2012.
Question 11.
Dictators try to control press and TV media. Do you know other ways of sharing information and ideas between people? (Text Book Page No. 237)
Answer:
- Mobile phone occupies the first place in sharing information and ideas.
- ‘Fax’ is one of the ways of sending message from one place to another.
- Today internets are available everywhere.
- We can send e-mails to exchange information and ideas.
- Social networking sites play important role in sharing informations.
Ex : Facebook, Twitter, etc.
![]()
Question 12.
The Tunisian struggle began with the death of one trader. The struggle gained strength largely through the use of social networking websites like Facebook. Why do you think it is not easy for governments to control them? (Text Book Page No. 237)
Answer:
- Technology has changed much.
- For development, every country has to work on internet.
- Computer have become a part of our life.
- Hence it is difficult to control social networking websites.
Question 13.
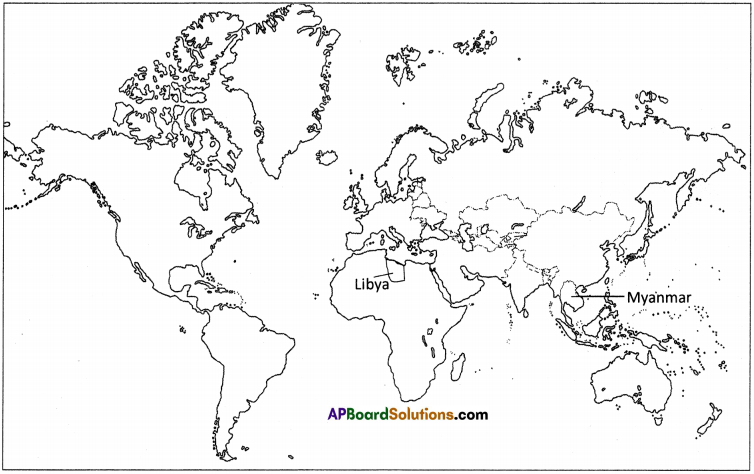
Locate “Libya” and “Myanmar” in the world map. Which continents are they located on? (Text Book Page No. 234)
Answer:
Libya is in Africa continent.
Myanmar is in Asia continent.