Telangana & Andhra Pradesh BIEAP TS AP Intermediate Inter 1st Year Chemistry Study Material Textbook Solutions Guide PDF Free Download, TS AP Inter 1st Year Chemistry Blue Print Weightage 2022-2023, Telugu Academy Intermediate 1st Year Chemistry Textbook Pdf Download, Questions and Answers Solutions in English Medium and Telugu Medium are part of AP Inter 1st Year Study Material Pdf.
Students can also read AP Inter 1st Year Chemistry Syllabus & AP Inter 1st Year Chemistry Important Questions for exam preparation. Students can also go through AP Inter 1st Year Chemistry Notes to understand and remember the concepts easily.
AP Intermediate 1st Year Chemistry Study Material Pdf Download | Jr Inter 1st Year Chemistry Textbook Solutions
AP Inter 1st Year Chemistry Study Material in English Medium
- Chapter 1 Atomic Structure
- Chapter 2 Classification of Elements and Periodicity in Properties
- Chapter 3 Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure
- Chapter 4 States of Matter: Gases and Liquids
- Chapter 5 Stoichiometry
- Chapter 6 Thermodynamics
- Chapter 7 Chemical Equilibrium and Acids-Bases
- Chapter 8 Hydrogen and its Compounds
- Chapter 9 The s-Block Elements
- Chapter 10 The p-Block Elements – Group 13
- Chapter 11 The p-Block Elements – Group 14
- Chapter 12 Environmental Chemistry
- Chapter 13 Organic Chemistry-Some Basic Principles and Techniques
AP Inter 1st Year Chemistry Study Material in Telugu Medium
- Chapter 1 పరమాణు నిర్మాణం
- Chapter 2 మూలకాల వర్గీకరణ – ఆవర్తన ధర్మాలు
- Chapter 3 రసాయన బంధం – అణు నిర్మాణం
- Chapter 4 పదార్ధం స్థితులు : వాయువులు, ద్రవాలు
- Chapter 5 స్టాయికియోమెట్రీ
- Chapter 6 ఉష్ణగతిక శాస్త్రం
- Chapter 7 రసాయనిక సమతాస్థితి, అమ్లాలు – క్షారాలు
- Chapter 8 హైడ్రోజన్ – దాని సమ్మేళనాలు
- Chapter 9 S బ్లాక్ మూలకాలు
- Chapter 10 P బ్లాక్ మూలకాలు – 13వ గ్రూప్
- Chapter 11 P బ్లాక్ మూలకాలు – 14వ గ్రూప్
- Chapter 12 పర్యావరణ రసాయన శాస్త్రం
- Chapter 13 కర్బన రసాయన శాస్త్రం – సామాన్య సూత్రాలు, విధానాలు
TS AP Inter 1st Year Chemistry Weightage Blue Print 2022-2023
TS AP Inter 1st Year Chemistry Weightage 2022-2023 | TS AP Inter 1st Year Chemistry Blue Print 2022
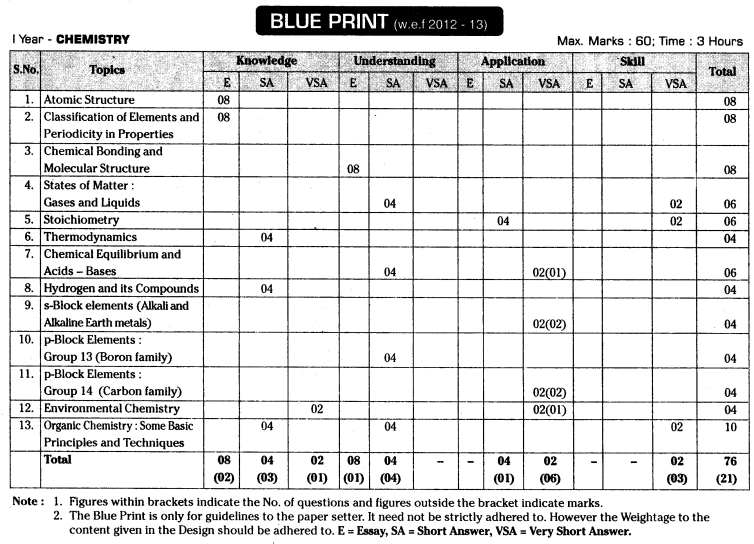
Intermediate 1st Year Chemistry Syllabus
TS AP Inter 1st Year Chemistry Syllabus
Chapter 1 Atomic Structure (20 Periods)
- 1.1 Sub-atomic particles
- 1.2 Atomic models-Rutherford’s Nuclear model of the atom
- 1.3 Developments to Bohr’s model of the atom.
- 1.3.1 Nature of electromagnetic radiation
- 1.3.2 Particle nature of electromagnetic radiation-Planck’s quantum theory
- 1.4 Bohr’s model for the hydrogen atom
- 1.4.1 Explanation of line spectrum of hydrogen
- 1.4.2 Limitations of Bohr’s model
- 1.5 Quantum mechanical considerations of sub-atomic particles
- 1.5.1 Dual behaviour of matter
- 1.5.2 Heisenberg’s uncertainty principle
- 1.6 Quantum mechanical model of an atom. Important features of the Quantum mechanical model of the atom.
- 1.6.1 Orbitals and quantum numbers
- 1.6.2 Shapes of atomic orbitais
- 1.6.3 Energies of orbitals
- 1.6.4 Filling of orbitals in atoms, Aufbau principle, Pauli’s exclusion principle, and Hund’s rule of maximum multiplicity
- 1.6.5 Electronic configurations of atoms
- 1.6.6 Stability of half-filled and completely filled orbitals.
Chapter 2 Classification of Elements and Periodicity in Properties (20 Periods)
- 2.1 Need to classify elements
- 2.2 Genesis of periodic classification
- 2.3 Modem periodic law and present form of the periodic table
- 2.4 Nomenclature of elements with atomic number greater than 100
- 2.5 Electronic configuration of elements and the periodic table
- 2.6 Electronic configuration and types of elements s.p.d. and f blocks
- 2.7 Trends in physical properties:
- 2.7.1 (a) Atomic radius, (b) Ionic radius, (c) Variation of size in inner transition elements, (d) Ionization enthalpy, (e) Electron gain enthalpy, (f) Electro negativity
- 2.7.2 Periodic trends in chemical properties: (a) Valence or Oxidation states, (b) Anomalous properties of second-period elements – diagonal relationship.
- 2.7.3 Periodic trends and chemical reactivity.
Chapter 3 Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure (20 Periods)
- 3.1 Kossel – Lewis approach to chemical bonding
- 3.2 Ionic or electrovalent bond – Factors favourable for the formation of the ionic compounds-Crystal structure of Sodium chloride – General Properties of ionic compounds.
- 3.3 Bond Parameters – bond length, bond angle, bond enthalpy, bond order, and resonance – Polarity of bonds dipole moment.
- 3.4 Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion (VSEPR) theories. Predicting the geometry of simple molecules.
- 3.5 Valence bond theory – Orbital overlap concept-Directional properties of bonds-overlapping of atomic orbitals strength of sigma and pi bonds-Factors favouring the formation of covalent bonds.
- 3.6 Hybridisation-different types of hybridization involving s, p, and d orbitals -shapes of simple covalent molecules.
- 3.7 Coordinate bond – definition with examples.
- 3.8 Molecular orbital theory – Formation of molecular orbitals. Linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO)- conditions for a combination of atomic orbitals – Energy level diagrams for molecular orbitals – Bonding in some homo nuclear diatomic molecules – H2, He2, Li2, B2, C2, N2 and O2
- 3.9 Hydrogen bonding-cause of formation of hydrogen bond-Types of hydrogen bonds-inter and intra molecular – General properties of hydrogen bonds.
Chapter 4 States of Matter: Gases and Liquids (15 Periods)
- 4.1 Intermolecular forces
- 4.2 Thermal Energy
- 4.3 Intermolecular forces Vs Thermal interactions
- 4.4 The Gaseous State
- 4.5 The Gas Laws
- 4.6 Ideal gas equation
- 4.7 Graham’s law of diffusion – Dalton’s Law of partial pressures
- 4.8 Kinetic molecular theory of gases
- 4.9 Kinetic gas equation of an ideal gas(No derivation)- Deduction of gas laws from Kinetic gas equation.
- 4. 10 Distribution of molecular speeds – rms, average and most probable speeds -Kinetic energy of gas molecules.
- 4.11 Behaviour of real gases – Deviation from Ideal gas behaviour – Compressibility factor Vs Pressure diagrams of real gases.
- 4.12 Liquefaction of gases
- 4.13 Liquid State – Properties of Liquids in terms of intermolecular interactions – Vapour pressure, Viscosity, and Surface tension (Qualitative idea only. No mathematical derivation).
Chapter 5 Stoichiometry (15 Periods)
- 5.1 Some Basic Concepts – Properties of matter – uncertainty in Measurement – significant figures, dimensional analysis
- 5.2 Laws of Chemical Combinations – Law of Conservation of mass, the law of definite proportions, the law of multiple proportions, Gay Lussac’s law of gaseous volumes, Dalton’s atomic theory, Avogadro law, principles, and examples.
- 5.3 Atomic and molecular masses- mole concept and molar mass concept of equivalent weight.
- 5.4 Percentage composition of compounds and calculations of empirical and molecular formulae of compounds.
- 5.5 Stoichiometry and stoichiometric calculations.
- 5.6 Methods of expressing concentrations of solutions-mass percent, mole fraction, molarity, and normality.
- 5.7 Redox reactions-classical idea of redox reactions, oxidation, and reduction reactions-redox reactions in terms of electron transfer.
- 5.8 Oxidation number concept.
- 5.9 Types of Redox reactions-combination, decomposition, displacement, and disproportionation reactions.
- 5.10 Balancing of redox reactions- oxidation number method, half-reaction(ion-electron) method.
- 5.11 Redox reactions in titrimetry
Chapter 6 Thermodynamics (10 Periods)
- 6.1 Thermodynamic terms
- 6.1.1 The system and the surroundings
- 6.1.2 Types of systems and surroundings
- 6.1.3 The state of the system
- 6.1.4 The Internal Energy as a state function, (a) Work (b) Heat (c) The general case, the first law of Thermodynamics
- 6.2 Applications
- 6.2.1 Work
- 6.2.2 Enthalpy. H- a useful new state function
- 6.2.3 Extensive and intensive properties.
- 6.2.4 Heat capacity
- 6.2.5 The relationship between Cp and Cv
- 6.3 Measurement of “U and H”: calorimetry.
- 6.4 Enthalpy change, ‘rH’of reactions-reaction Enthalpy, (a) Standard enthalpy of reactions, (b) Enthalpy changes during transformations, (c) Standard enthalpy of formation, (d) Thermo chemical equations, (e) Hess’s law of constant heat summation.
- 6.5 Enthalpies for different types of reactions, (a) Standard enthalpy of combustion (“cH°) (b) Enthalpy of atomization (“a Ho). Phase transition, sublimation, and ionization, (c) Bond Enthalpy (“bond H6) (d) Enthalpy of solution (“sol Ho), and dilution.
- 6.6 Spontaneity, (a) Is a decrease in enthalpy a criterion for spontaneity? (b) Entropy and spontaneity are the second law of thermodynamics, (c) Gibbs Energy and spontaneity.
- 6.7 Gibbs Energy change and equilibrium.
- 6.8 Absolute entropy and the third law of thermodynamics.
Chapter 7 Chemical Equilibrium and Acids-Bases (15 Periods)
- 7.1 Equilibrium in a physical process
- 7.2 Equilibrium in chemical process – dynamic equilibrium.
- 7.3 Law of chemical equilibrium- Law of mass action and equilibrium constant.
- 7.4 Homogeneous equilibria, the equilibrium constant in the gaseous system, Relationship between K and Kc.
- 7.5 Heterogeneous equilibria.
- 7.6 Applications of equilibrium constant.
- 7.7 Relationship between equilibrium constant K reaction quotient Q arid Gibbs energy G.
- 7.8 Factors affecting equilibrium Le-chatelier’s principle applies to the industrial synthesis of ammonia and sulphur trioxide.
- 7.9 Ionic Equilibrium in solutions.
- 7.10 Acids, bases, and salts – Arrhenius, Bronsted- Lowry, and Lewis concepts of acids and bases.
- 7.11, Ionisation of acids and bases – Ionisation constant of water and ifs ionic product- pH scale -ionisation constants of weak acids-ionization of weak bases-relation between Ka and Kb -di and polybasic acids and di poly acidic bases-factors affecting acid strength-common ion effect in the ionization of acids and bases-hydrolysis of salts and pH of their solutions.
- 7.12 Buffer solutions-designing of buffer solution-preparation of the acidic buffer.
- 7.13 Solubility equilibria of sparingly soluble salts, solubility product constant common ion effect solubility of Ionic salts.
Chapter 8 Hydrogen and its Compounds (8 Periods)
- 8.1 Position of hydrogen in the periodic table.
- 8.2 Dihydrogen-occurrence and isotopes.
- 8.3 Preparation of dihydrogen
- 8.4 Properties of dihydrogen
- 8.5 Hydrides:ionic. covalent, and non-stiochiometrichydrides
- 8.6 Water-physical properties; structure of water, ice. Chemical properties of water; hard and soft water temporary and permanent hardness of water
- 8.7 Hydrogen peroxide: Preparation; physical properties; structure and chemical properties; storage and uses
- 8.8 Heavy water
- 8.9 Hydrogen as a fuel
Chapter 9 s-Block Elements (Alkali and Alkaline Earth Metals) (8 Periods)
Group 1 Elements:
- 9.1 Alkali metals; electronic configurations; atomic and ionic radii; ionization enthalpy hydration enthalpy; physical properties; chemical properties; uses.
- 9.2 General characteristics of the compounds of the alkali metals; oxides; halides; salts of oxy acids.
- 9.3 Anomalous properties of lithium: differences and similarities with other alkali metals, diagonal relationship; similarities between lithium and magnesium.
- 9.4 Some important compounds of sodium- Sodium Carbonate; Sodium Chloride; Sodium Hydroxide; Sodium Hydrogen Carbonate.
- 9.5 Biological importance of Sodium and Potassium.
Group 2 Elements:
- 9.6 Alkaline earth elements; electronic configuration; ionization enthalpy; hydration enthalpy; physical properties; chemical properties; uses.
- 9.7 General. characteristics of compounds of the alkaline earth metals: oxides, hydroxides, halides, salts of oxyacids (carbonates; sulphates, and nitrates).
- 9.8 Anomalous behavior of beryllium; its diagonal relationship with aluminium.
- 9.9 Some important compounds of calcium: Preparation and uses of calcium oxide; calcium hydroxide; calcium carbonate; plaster of Paris; cement.
- 9.10 Biological importance of calcium and magnesium.
Chapter 10 p-Block Elements Group 13 (8 Periods)
Boron Family
- 10.1 General introduction – electronic configuration, atomic radii, ionization enthalpy, electronegativity; physical & chemical properties.
- 10.2 Important trends and anomalous properties of boron.
- 10.3 Some important compounds of boron-borax, orthoboric acid, and diborane.
- 10.4 Use of boron, aluminium, and their compounds.
Chapter 11 p-Block Elements Group 14 (8 Periods)
Carbon Family
- 11.1 General introduction – electronic configuration, atomic radii, ionization enthalpy, electronegativity; physical & chemical properties.
- 11.2 Important trends and anomalous properties of carbon.
- 11.3 Allotropes of carbon
- 11.4 Uses of carbon
- 11.5 Some important compounds of carbon and silicon-carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide, Silica, silicones, silicates, and zeolites.
Chapter 12 Environmental Chemistry (8 Periods)
- 12.1 Definition of terms: Air, Water, and Soil Pollutions
- 12.2 Environmental pollution
- 12.3 Atmospheric pollution; tropospheric pollution; gaseous air pollutants (oxides of sulphur; oxides of nitrogen; hydrocarbons; oxides of carbon (CO; CO2), Global warming and greenhouse effect.
- 12.4 Acid Rain-particulate pollutants-smog.
- 12.5 Stratospheric Pollution: formation and breakdown of ozone-ozone hole-effects of depletion of the ozone layer.
- 12.6 Water Pollution: causes of water pollution; international standards for drinking water.
- 12.7 Soil Pollution: pesticides, industrial wastes.
- 12.8 Strategies to control environmental pollution – waste management- collection and disposal
- 12.9 Green chemistry: green chemistry in day-to-day life; dry cleaning of clothes; bleaching of paper; synthesis of chemicals.
Chapter 13 Organic Chemistry-Some Basic Principles and Techniques and Hydrocarbons (25 Periods)
- 13.1 General introduction
- 13.2 Tetravalency of carbon: shapes of organic compounds
- 13.3 Structural representations of organic compounds
- 13.4 Classification of organic compounds
- 13.5 Nomenclature of organic compounds
- 13.6 Isomerism
- 13.7 Fundamental concepts in organic reaction mechanisms
- 13.7.1 Fission of covalent bond
- 13.7.2 Nucleophiles and electrophiles
- 13.7.3 Electron movements in organic reactions
- 13.7.4 Electron displacement effects in covalent bonds
- 13.7.5 Types of Organic reactions
- 13.8 Methods of purification of organic compounds
- 13.9 Qualitative elemental analysis of organic compounds
- 13.10 Quantitative elemental analysis of organic compounds
Hydrocarbons
- 13.11 Classification of Hydrocarbons.
- 13.12 Alkanes- nomenclature, isomerism (structural and conformations of ethane only)
- 13.12.1 Preparation of alkanes
- 13.12.2 Properties-physical properties and chemical reactivity, substitution reactions- halogenation (a free radical mechanism), combustion, controlled oxidation, isomerization, aromatization, reaction with steam, and Pyrolysis.
- 13.13 Alkenes- Nomenclature, the structure of ethane, Isomerism (structural and geometrical).
- 13.13.1 Methods of preparation.
- 13.13.2 Properties: Physical and chemical reactions, the addition of hydrogen, halogen, water, sulphuric acid, Hydrogen halides Mechanism-ionic and peroxide effect, Markovnikov’s anti-Markovnikov’s or Kharasch effect). Oxidation, ozonolysis, and polymerization.
- 13.14 Alkynes- nomenclature and isomerism, the structure of acetylene. Methods of preparation of acetylene.
- 13.14.1 Physical properties, chemical reactions- the acidic character of acetylene, addition reactions of hydrogen, halogen, hydrogen halides, and water. Polymerization.
- 13.15 Aromatic hydrocarbons: Nomenclature and isomerism. Structure of benzene, resonance, and aromaticity.
- 13.15.1 Preparation of benzene, Physical properties, Chemical properties: Mechanism of electrophilic substitution. Electrophilic substitution reactions- nitration, sulphonation, halogenation, Friedel-Craft’s alkylation, and acylation.
- 13.15.2 Directive influence of functional groups in mono substituted benzene, Carcinogenicity and toxicity.
We hope that this Telangana & Andhra Pradesh BIEAP TS AP Intermediate Inter 1st Year Chemistry Study Material Textbook Solutions Guide PDF Free Download 2022-2023 in English Medium and Telugu Medium helps the student to come out successful with flying colors in this examination. This Jr Inter 1st Year Chemistry Study Material will help students to gain the right knowledge to tackle any type of questions that can be asked during the exams.
