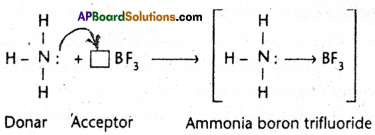
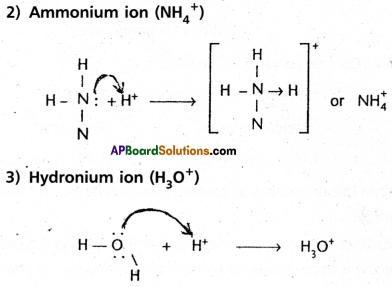
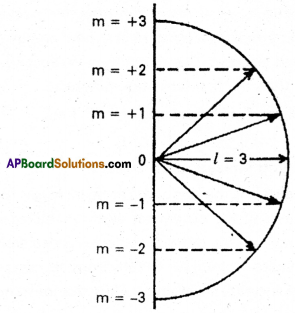
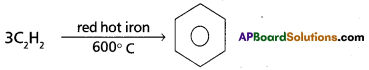
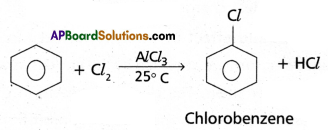
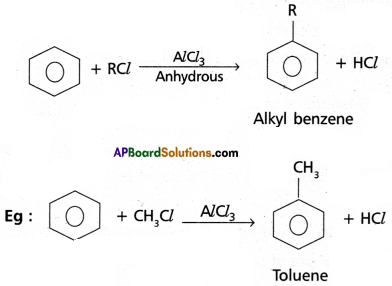
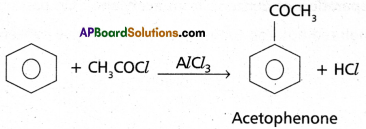
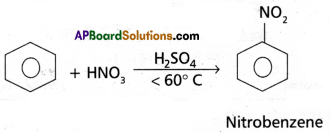
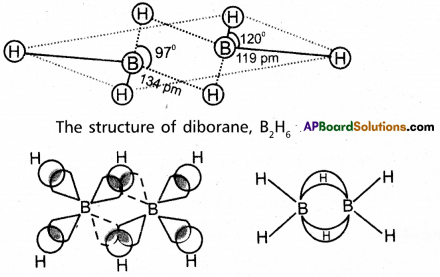
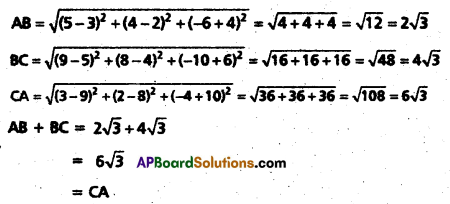
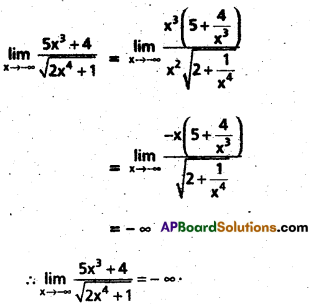
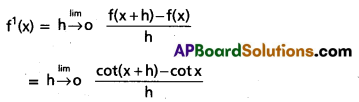
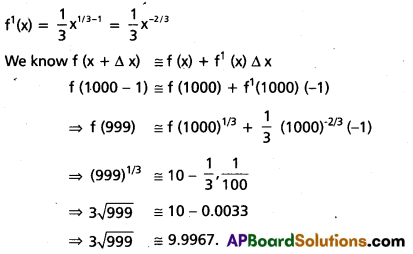
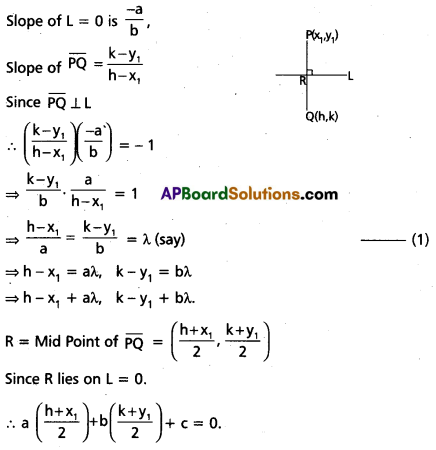
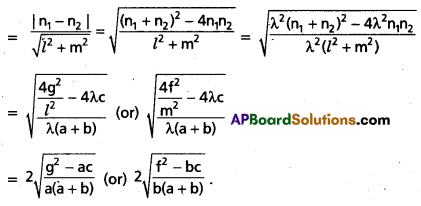
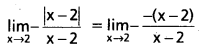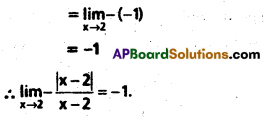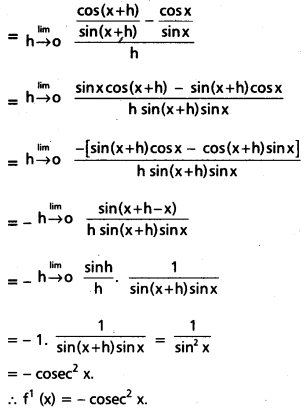Access to a variety of AP Inter 2nd Year Sanskrit Model Papers Set 6 allows students to familiarize themselves with different question patterns.
AP Inter 2nd Year Sanskrit Model Paper Set 6 with Solutions
Time : 3 Hours
Max.Marks : 100
Note :
- All questions should be attempted.
- Question Nos. 1, 2 and 3 should be answered either in the medium of instructions of the candidate or in Sanskrit (Devanagari Script) only.
- The remaining questions should be answered in Sanskrit (Devanagari Script) only.
सूचना :
प्रथम, द्वितीय, तृतीय प्रश्नान् विहाय अन्ये सर्वेऽपि प्रश्नाः संस्कृत भाषायामेव समाधातव्याः ।
1. एकस्य श्लोकस्य प्रतिपदार्थं भावं च लिखत ।
अ) परोक्षे कार्यहन्तारं प्रत्यक्षे प्रियवादिनम् ।
वर्जयेत्तादृशं मित्रं विषकुम्भं पयोमुखम् ॥
समाधान:
पदच्छेद (Word Division) : परोक्षे, कार्यहन्तारं, प्रत्यक्षे, प्रियवादिनम्, वर्जयेत्, तादृशं, मित्रं, विषकुम्भं, पयोमुखम् ।
अन्वयक्रम : परोक्षे, कार्यहन्तारं प्रत्यक्षे, प्रियवादिनम्, तादृशं मित्रं, पयोमुखं, विषकुम्भं इव, वर्जयेत् ।
अर्था (Meanings) : परोक्षे = behind, कार्यहन्तारं = one who spoils our work, प्रत्यक्षे = in front of us, प्रियवादिनम् = who speaks sweetly, तादृशम= such, मित्रम् = friend, पयोमुखम = milk topped, with milk at rim, विषकुम्भम् = pitcher of poison, वर्जयेत् = should abandon.
भाव (Substance) : One should abandon such a friend who spoils our work at our back, but speaks sweetly in front of us as he is a vessel filled with poison but having milk at rim.
आ) प्रथमे नार्जिता विद्या द्वितीये नार्जितं धनम् ।
तृतीये नार्जितं पुण्यं चतुर्थे किं करिष्यति ॥
समाधान:
पदच्छेद (Word Division ) : प्रथमे न, आर्जितं, विद्या, द्वितीये, न, आर्जितं धनम्, तृतीये न, आर्जितं पुण्यं, चतुर्थे किं करिष्यति ।
अन्वयक्रम : प्रथमे, विद्या, न, आर्जितम्, द्वितीये, धनं, न आर्जितम्,
तृतीये, पुण्यं, न, आर्जितम्, चतुर्थे किं करिष्यति ।
अर्था (Meanings) : प्रथमे = during the first stage of life, in the first quarter; विद्या = education; न + आर्जितम् = not gained; द्वितीये = in the second stage, second quarter; धनम् = money, ricers; न `आर्जितम् = not gained; तृतीये: = in the third stage of life, in the third quarter; पुण्यं = merit; न + आर्जितम् not gained; चतुर्थे = in the last stage, in the last quarter; किं करिष्यति = what will he do?
(Substance): If a person does not acquire knowledge in the first stage of his life, money in the second stage, and merit in the third stage, what will he do in the last stage?
2. एकं निबन्धप्रश्नं समाधत्त ।
अ) दिलीपस्य धर्मनिष्ठामधिकृत्य लिखत ?
Answer:
Introduction: The lesson Dharmanishta is an extract from the 2nd canto of Raghuvamsa, written by Kalidasa. This lesson describes the moral and devotional character of king Dilipa.
A Lion attacks Nandini: The childless king Dilipa his wife Sudakshina were engaged in the service of Nandini, the cow of sage Vasishta. One day Nandini which went to the forest guarded by the king wished to test the devotion of the king, and entered a Himalayan cave. Thinking that the cow was unassailable to any wild animal, the king took his eyes off her to watch the beauty of the mountain. Then a lion attacked her. Alerted by her cry, the king became ready to kill the lion by shooting an arrow at it. But his hand got fixed on the shaft of the arrow. चित्रार्पितारम्भ इवावतस्थे ।
Then the lion told him that he was a servant of Lord Siva. He was appointed there to protect the Devadaru tree grown by Parvathi. He was made a lion, and any animal that arrived there when he was hungry would become his food.
Dilipa’s offer: Then the king said that Siva was to be respected, and at the same time, the property of the teacher was to be saved. He offered his own body as food to the lion requesting the release of the cow. But the lion said that the king was young and an emperor. He seemed to be imprudent in giving up more for little. By showing compassion to the cow, she alone would be saved. But if he lived, he could always save his people from calamities. The king said that a king should protect his subjects.
तद्विपरीतवृत्तेः, प्राणैः उपक्रोशमलीमसैर्वा । He could not offer other cows for Nandini, the daughter of Surabhi to his preceptor. He pleaded with the lion that how he could stand before his teacher when the cow was lost and himself was unhurt. He further said that people like him did not care for physical bodies. पिण्डेष्वनास्था खलु भौतिकेषु ।
The lion agreed and released the cow. But when the king bent his head before the lion, he received a shower of flowers from the Vidyadharas. The delighted cow, followed by the king returned safely to the hermitage.
![]()
आ) पाठ्यभागमनुसृत्य गीर्वाणवाण्याः सारांशं लिखत ?
Answer:
Introduction : The lesson Chitravimsati was written by Sri Jatavallabhula Purushottama Sastry. It is an extract from his work Chitra-satakam. There are two topics in this lesson Girvanavani and Chitraloka. The first part describes the greatness of Sanskrit language.
Girvanabhasha :
The nectar oozing Sanskrit language is spoken by the gods. It is the ocean of the gems of good sayings and the treasure trove of great literature, and is acquired only by the meritorious. संस्कृताख्या सुकृतैकलभ्या | It is the ladder to liberation and the staircase to the heaven: It is relished by people of different tastes. Just as the children inherit the virtues of the mother, so also all the languages inherit the qualities of the divine mother language. In Sanskrit as the words are formed from the roots, they are naturally pure.
A language is the mother because she spreads in the world, and also she protects the dependents like a mother. On this earth, such a mother tongue is Sanskrit only, how can other languages have the title of mother ? वाच्याः कथं मातृपदेन चान्या: ? Even now, those who are experts in that language make the non-learners of the language ashamed by reciting the ancient verses.
Lakhs of people speak it, and lakhs understand it. Lakhs of books in that language are sold every year. How can we live abandoning that language which is always in our body like life, and which is used during marriage ceremony, rituals of manes and gods, and in poetry recitals and philosophical discourses ? Our history is before us with life. How is it dead? In this world, beautiful poetry is removed from dharma and righteous poetry is not beautiful. Except in Sanskrit where else is poetry that is golden and fragrant ?
3. एकं निबन्धप्रश्नं समाधत्त ।
अ) भोजस्य सालभंजिकया उक्तं विक्रमस्य औदार्यं लिखत ।
Answer:
Introduction: The lesson Vikramasya Audaryam is taken from vikramarkacharitam written by Sivadasa. When Bhoja wants to ascend the throne of Vikrama the statue on the fourth step tells this story about the generosity of king Vikrama.
The childless Brahmin:
While Vikramaditya ruled Ujjaini, there was a learned Brahmin in that city, who was virtuous, but who had no children. Once, his wife said to him that there was no heaven for one who had no children सत्पुत्रेण कुलं नृपेण वसुधा लोकत्रयं भानुना । The Brahmin worshipped Lord Siva. The god appeared in his dream and asked him to perform Pradoshavrata. The Brahmin did so and he begot a son, whom he named Devadatta. When his son grew up, the Brahmin performed his marriage, and went on a pilgrimage to Varanasi.
Devadatta’s help to Vikrama :
Once Devadatta went into the forest to collect fuel sticks for sacrifice. At that time, king Vikrama came to the forest for hunting. There he asked Devadatta the way to the city, even though he knew it.
Devadatta himself led him to the city. The king praised him, and appointed him in his court. One day the king praised Devadatta’s help in the assembly saying that he could never repay his debt.
Devadatta kidnaps the prince :
Devadatta wondered whether the king’s praise was true or false. He wanted to test the words of the king. He kidnapped the prince, and gave one of his ornaments to his servant and sent him to the market to sell it. The king’s men who were searching for the prince caught him, and brought him to the king. When the king asked him, the servant said that he was Devadatta’s servant. The king sent for Devadatta, who said that he killed the prince or money. The members of the court said that Devadatta should be sentenced to death. But the king said that Devadatta rescued him in the forest. One should not find faults in those dependent on him. fordy महतां गुणदोषचिन्ता | He said that his son died because of his previous deeds only. He honoured Devadatta and sent him away.
Devadatta returned with the prince, and told the king that he wanted to test the words of the king. He praised the generosity of the king, who said that one should not forget the help done to him. यः कृतमुपकारं विस्मरति स एंव पुरुषाधमः ।
Thus the statue told Bhoja about the generosity of king Vikrama.
आ) ‘भिषजो भैषज्यम्’ इति पाठ्यभागस्य सारांशं लिखत ।
Answer:
Introduction: The lesson Bhishajah Bhaishajyam was written by Prof. Pullela Sriramachandra. It is taken from his Sriramachandra-laghukavya-sangraha. This lesson describes the story of a selfish doctor, and the fruit he reaped for his selfishness.
The Villager’s Plea: One day some villagers came to Dr. Venkata Rao, and requested him to attend to a boy who was injured in an accident. Venkata Rao childed them for not coming in time. वैद्योऽपि मानव एव | He accused them of trying to get treatment done without paying fee. He insulted them saying the boy would be delicate as the baby of a donkey. When they left as the boy was serious क्षणे क्षणे किल परिक्षीयते बालस्य दशा, Venkata Rao thought nothing would happen if one puppy died.
The poor and intelligent Venkata Rao : Venkata Rao was the son of a poor farmer. He was very intelligent and secured a seat in medical college. His father sold their agricultural land for his education. A rich man married his daughter to Venkata Rao. Venkata Rao’s practice also picked up. Along with money, the three defects grew in him. They were considering others as insects, himself as god, and accepting others praise as the truth. When he spoke of his father as a beggar, his father left him and returned to their village.
Marriage was also a business affair for Venkata Rao. विवाहो नाम वणिग्व्यवहार एव | For him money was everything. He never loved his wife. His son Suresh alone became the object of his affection.
Desire for Power: Venkata Rao thought that money was useless without power. He became an MLA twice. But he could not become a minister. He was unhappy about that. He could not win the seat the third time. He blamed the people for that. His hatred for people grew.
Manjuhasini, the Lady Doctor: At that time, Dr. Manjuhasini joined the government hospital there. She was Venkata Rao’s classmate in medical college. She rejected Venkata Rao’s advances. Venkata Rao was hoping that she might have changed now as he became rich.
The death of his son: Venkata Rato received a phone call from Manjuhasini requesting his help in an emergency case. His driver tried to inform him that his son was not there at the school when he went there after getting the brake repaired. Venkata Rao cut him short saying that the boy would have reached home. But when he went to the hospital he saw the same villagers who came to him earlier in the day, and the body of his dead son.
![]()
4. त्रयाणां प्रश्नानां समाधानानि लिखत ।
अ) भृगुवंशकेतुः कः ?
समाधान:
भृगुवंशकेतुः परशुरामः ।
आ) कीदृशं वस्तु तथैव तिष्ठति ?
समाधान:
हुतं दत्तं च वस्तु तथैव तिष्ठति ।
इ) केन द्रुपदः गर्वाधः जातः ?
समाधान:
द्रुपदः धनश्रिया गर्वान्धः जातः । एवम् अर्जुनः उक्तवान् ।
ई) कृपी गोक्षीरं ददामीत्युक्त्वा पुत्राय किं दत्तवती ?
समाधान:
कृपी गोक्षीरं ददामीत्युक्त्वा पुत्राय पिष्टमिश्रितजलं दत्तवती । तत् पीत्वा अश्वत्थामा तुष्टः अभवत् ।
उ) कालिदासश्लोके भोजेन प्राप्तं समाधानं किम् ?
समाधान:
कालिदासश्लोकेन भोजेन प्राप्तं समाधानम् एवम् अस्ति – द्वयोः सम्भाषणकर्त्रीः मध्ये सूचनां विना न प्रविशेत् इति ।
ऊ) भोजः कोशाध्यक्षं प्रति किं सूचितवान् ?
समाधान:
कविकुलगुरोः कालिदासस्य सदनं एकलक्षसुवर्णमुद्राः प्रेष्यन्ताम् इति भोजः कोशाध्यक्षं सूचितवान् ।
5. द्वयोः संदर्भ व्याख्यानं लिखत ।
अ) परेषां सहसावज्ञा न कर्तव्या कथञ्चन ।
समाधान:
परिचयः – एतत् वाक्यं विभीषणोपदेशः इति पाठ्यभागात् स्वीकृतम् ।
एषः पाठः – रामायणस्य युद्धकाण्डात् गृहीतः । अस्य कविः वाल्मीकिः ।
सन्दर्भः – प्रदीयतां दाशरथाय मैथिली इति रावणं प्रति उपदिशन् विभीषणः एवं वदति ।
भावः – परेषां बलानि अपरिमेयानि । तेषां सहसा अवज्ञा न कुर्यात् ।
आ) पिण्जेष्वनास्था खलु भौतिकेषु ।
समाधान:
परिचयः एतत् वाक्यं ‘धर्मनिष्ठा’ इति पाठ्यभागात् स्वीकृतम्, एषः भागः कालिदासस्य रघुवंश महाकाव्ये पञ्चमसर्गात् स्वीकृतः ।
सन्दर्भः दिलीपः सिंहं प्रति एवं उक्तवान् ।
भावः पृथिव्यादि भूतविकारेषु शरीरेषु अनपेक्षा खलु ।
विवरणम्ः हे सिंह ! मम थशोरुप शरीरे दयालुः भव । देहं अशाश्वतम्, कीर्तिरेव शाश्वतम् ।
इ) ग्रामे यत्र गृहे समैक्यपरता सा धर्मभूमिर्मम |
समाधान:
परिचयः – एतत् वाक्यं सा मातृभूमिर्मम इति पाठ्यभागात् स्वीकृतम् । अस्य कविः श्रीमान् दोर्बल प्रभाकर शर्मा ।
सन्दर्भः – मातृभूमेः वैशिष्ट्यं वर्णयन् मम मातृभूमिः ज्ञानभूमिः धर्मभूमिः इति वदन् कविः एवं वर्णयति ।
भावः – यत्र गृहे माता भर्तुः सुतानां च इष्टवस्तूनि परिवेषति, पिता वृत्तिप्रदः, भ्रातरः स्नेहसम्पन्नाः ग्रामे शोभायात्राः गृहे एक्यता इत्यादीनि सन्ति, सा मम धर्मभूमिः इति कविः वदति ।
ई) भृत्या हि पक्त्री वद किं न सा स्त्री ।
समाधान:
परिचय : गतत् वाक्यं ‘नित्रविंशतिः’ इति पाठ्यभागात् स्वीकृतम्’ अस्य पाठ्यभागस्य रचयिता जटावल्लभपुरुषोत्तम शास्त्री ।
सन्दर्भ : लोके चित्रविषयान् वर्णयन् कविः एवं वदति । मम सुता महानसे न निरोधनीया, स्त्रियः पूज्याः इति चित्रं वदन्ति । तर्हि भूक्तिः कथं सिद्ध्यति इति कविः पृच्छति ।
भाव : या भृत्या पचति सा स्त्री नास्ति किम् ?
विवरणम् : मदीया कन्या महानसे नैव पाकं कराति ? स्त्रियः पूज्याः, इति वदन्ति, भृत्या पाचिका स्त्री कि ? वद ।
![]()
6. द्वयोः ससंदर्भ व्याख्यानं लिखत ।
अ) सतां सङ्गो हि भेषजम् ।
समाधान:
परिचयः – एतत-वाक्यं, “मन्दविषसर्पकथा” इति पाठ्यभागात् स्वीकृतम् अस्य पाठ्यभागस्य रचयिता नारायणपण्डितः ।
सन्दर्भः – शोकाविष्टं कौण्डिन्यं पति कपिलः एवं अवदत् ।
भावः – सज्जनसांगत्यं एव सज्जनां भेषजम् ।
विवरणम्ः – सर्वे सज्जनसाङ्गत्यं करणीयम् तदा एव जीवनं सुखमयं भवेत् ।
आ) सत्पुत्रेण कुलं नृपेण वसुधा लोकत्रयं भानुना ।
समाधान:
परिचय : इदं वाक्यं “विक्रमस्य औदार्यम्” इति पाठ्यभागात् स्वीकृतम् । अस्य पाठस्य रचयित शिवदास |
सन्दर्भ : ब्राह्मणस्य पत्नी स्व भर्तारं प्रति एवं अवदत् ।
भाव : सत्कुमारिण वशं राज्ञा वसुधा सूर्येण भुवनत्रयं प्रकाश्यन्ते ।
विवरणम् : वाणी व्याकरणेन, हंसमिधुनैः पद्यः पण्डितैः सभा सुपुत्रेण कुलं राज्ञा, भूमिः सूर्येण लोकत्रयं विराजन्ते ।
इ) क्षणे क्षणे किल परिक्षीयते बालस्य दशा ।
समाधान:
परिचयः – वेङ्कटरावस्य भिषजो भैषज्यम् इति पाठ असित अस्य पाठस्य रचयित, श्री पुल्लेल श्रीरामचन्द्रः ।
सन्दर्भः एकः वृद्धः युवकं उद्दिश्य एवं अवदत् ।
भावः – क्षणे क्षणे परीशील्यमाने बलकस्य दशा क्षीयेत ।
विवरणम्ः – वृया अनेन कलहेन, बालकस्य परिस्थितिः सीयते ।
ई) अप्पय्यः साक्षात् परमशिवस्य अवतारः ।
समाधान:
परिचय : एतत् वाक्यम् अप्पय्यदीक्षितेन्द्र इति पाठ्यभागात् स्वीकृतम् । अस्य रचयित्री सङ्का उषाराणी ।
सन्दर्भ : केचन जनाः अन्तिमसमये अप्पय्यदीक्षितम् चिदम्बरे नटराज- प्रतिमायां लीयमानम् अपश्यन् । तस्मिन्नेव समये गृहे अप्पय्यः प्राणविहीनः अभवत् । तेन सः परमेश्वरस्य अवतारः इति विज्ञाः मन्यन्ते स्म ।
भाव : अप्पय्यः साक्षात् परमेश्वरस्य अपरः अवतारः एव ।
7. त्रयाणां प्रश्नानां समाधानानि लिखत ।
अ) कदा प्रभृति अशुभानि निमित्तानि दृश्यन्ते ?
समाधान:
यदा प्रभृति सीता आगता तदा प्रभृति अशुभानि निमित्तानि दृश्यन्ते ।
आ) धर्मनिष्ठा इति पाठ्यांशः कस्मात् संगृहीतः ?
समाधान:
धर्मनिष्ठा, इति पाठ्यभागः, रघुवंशमहाकाव्ये तृतीयसर्गत् संगृहीतः ।
इ) पृथिव्यां त्रीणि रत्नानि कानि ?
समाधान:
पृथिव्यां त्रीणि रत्नानि जलं, अन्नं, सुभाषितम् ।
ई) देवः कुत्र सहायकृत् भवति ?
समाधान:
उद्यमं, साहस, धैर्यं, बुद्धिः, शक्तिः, पराक्रमः यत्र वर्तन्ते तत्र सहायकृत् भवति ।
उ) मानवानां प्रकृतिशुभगुणाः के ?
समाधान:
क्षान्तिः, संस्कारगन्धः, संतृप्तिः, मृदुवाक् इत्यादयः मानवानां प्रकृतिगुणाः ।
ऊ) लोके चित्रमतिः कः ?
समाधान:
ईश्वरे भक्तिः सर्वेषां अस्ति, ईश्वरप्रतिपादित वेदे भक्तिः नास्ति, एतत् लोके चित्रगतिः ।
8. त्रयाणां प्रश्नानां समाधानानि लिखत ।
अ) हितोपदेशे कति भागाः सन्ति ? ते च के ?
समाधान:
हितोपदेशे चत्वारः भागाः सन्ति । ते
1. मित्रलाभः 2. मित्रभेदः 3. विग्रहः 4. सन्धिः
आ) ब्राह्मणं प्रति तत्प्रेयसी किं जगाद ?
समाधान:
ब्राह्मणं प्रति तत्प्रेयसी एवं जगाद – अपुत्रस्य गतिर्नास्ति स्वर्गो नैव च नैव च । सत्पुत्रेणैव कुलं प्रकाशते इति ।
इ) धर्मपालस्य कति पुत्राः ? ते च के ?
समाधान:
धर्मपालस्य त्रयः पुत्रः आसन् । ते च सुमन्त्रः, सुमित्रः कामपालः च ।
![]()
ई) श्रीधरः स्वमातुः मरणसमये कि कुर्वन्नासीत् ?
समाधान:
श्रीधरः स्वमातुः मरणसमये विश्वविद्यालये शोधग्रन्थसमर्पणकार्यं कुर्वन् आस्ते ।
उ) वेङ्कटरावस्य पिता कः ?
समाधान:
वेङ्कटरावस्य पिता सुब्बरायशास्त्री ।
ऊ) अप्पय्यदीक्षितः आन्ध्रभाषां कथं प्रशशंस ?
समाधान:
आन्ध्रत्वम् आन्ध्रभाषा च नाल्पस्य तपसः फलम् इति अप्पय्यः आन्ध्रभाषां प्रशसंश
9. एकेन वाक्येन समाधानं दत्त ।
अ) सुखधर्मनाशनं केन भवति ?
समाधान:
सुखधर्मनाशनं कोपेन भवति ।
आ) दिलीपस्य धर्मपत्नी का ?
समाधान:
सुदक्षिणा
इ) सर्वत्र का पूज्यते ?
समाधान:
विद्या
ई) चिरसम्प्रदाय रुचिराः के ?
समाधान:
चिरसम्प्रदायरुचिराः संस्काराः ।
उ) “चित्रविंशतिः” इति पाठ्यभागः कस्मात् स्वीकृत: ?
समाधान:
गीर्वाणवाणी – चित्रलोक:
10. एकेन वाक्येन समाधानं दत्त ।
अ) हितोपदेशः केन विरचितः ?
समाधान:
नारायणपण्डितेन
आ) देवदत्तः राजानं कुत्र अनीनयत् ?
समाधान:
नगरम्
इ) दशकुमारचरितं केन विरचितम् ?
समाधान:
दण्डिना
ई) श्रीधरस्य ज्येष्ठभ्रातृवत् कः वर्धते ?
समाधान:
श्रीधरस्य ज्येष्ठभ्रातृवत् तस्य मातुः कासः वर्धते ।
उ) भिषजः भैषज्यम् इति पाठ्यांशः केन विरचितः ?
समाधान:
पुल्लेल श्रीरामचन्द्रः
11. अधोनिर्दिष्टं कथां पठित्वा प्रश्नानां समाधानानि दत्त |
प्रश्नाः,
(1) वृक्षे प्रतिवसतः पक्षिणो नाम किम् ?
समाधान:
वृक्षे प्रतिवसतः पक्षिणो नाम सिन्धुकः ।
(2) कस्मिन् सुवर्णमुत्पद्यते ?
समाधान:
पुरीषे सुवर्णमुत्पद्यते ।
(3) पक्षिणमुद्दिश्य कः समाययौ ?
समाधान:
पक्षिणमुद्दिश्य व्याधः समाययौ ।
(4) स पक्षी कुत्र पुरीषमुत्ससर्ज ?
समाधान:
स पक्षी व्याधस्य अग्रत एव पुरीषमुत्ससर्ज ।
(5) व्याधः वृक्षे कं बबन्ध ?
समाधान:
व्याधः वृक्षे पाशं बबन्ध |
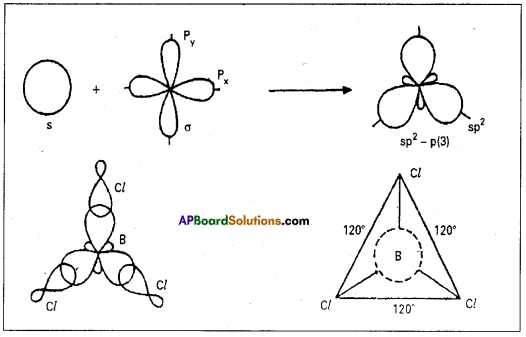
12. नामनिर्देशपूर्वकं त्रीणि सन्धत्त ।
अ) शरत् + चन्द्रः
समाधान:
शरच्चन्द्रः = श्चुत्व सन्धिः
आ) उत् + डयनम्
समाधान:
उड्डयनम् = ष्टुत्व सन्धिः
इ) तत् + मात्रम्
समाधान:
तन्मात्रम् = अनुनासिक सन्धिः
ई) षट् + आननः
समाधान:
षडाननः = जश्त्व सन्धिः
उ) सः + अपि
समाधान:
सोऽपि = विसर्ग सन्धिः
ऊ) हरिः + गच्छति
समाधान:
हरिर्गच्छति = विसर्गरेफादेश सन्धिः
![]()
13. नामनिर्देशपूर्वकं त्रीणि बिघटयत ।
अ) सज्जनः
समाधान:
सद् + जनः = श्चुत्व सन्धिः
आ) तट्टीका
समाधान:
तत् + टीका = ष्टुत्व·सन्धिः
इ) अजन्तः
समाधान:
अच् + अन्तः = जश्त्व सन्धिः
ई) षण्मुखः
समाधान:
षट् + मुखः = अनुनासिक सन्धिः
उ) कोऽपि
समाधान:
कः + अपि = विसर्ग सन्धि:
ऊ) पितुरिच्छा
समाधान:
पितुः + इच्छा = विसर्गरेफादेश सन्धिः
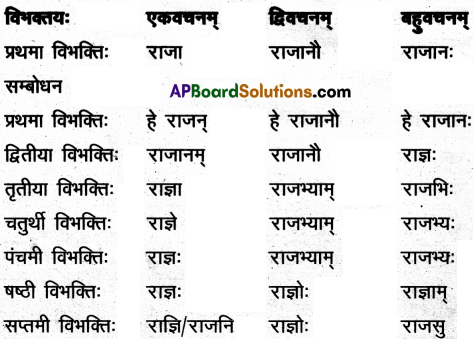
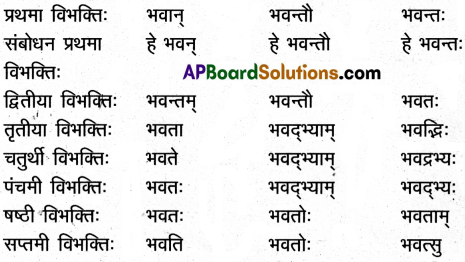
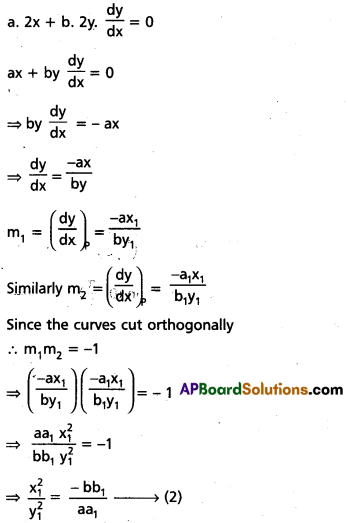
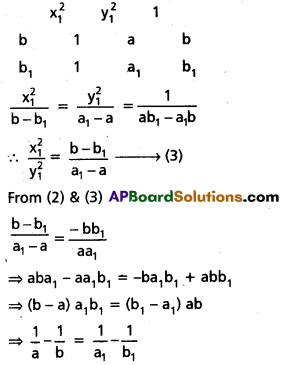
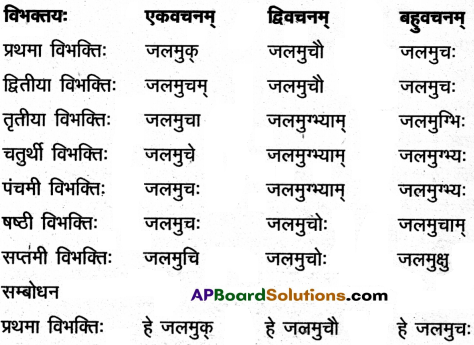
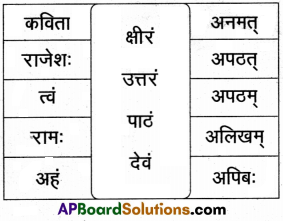
14. द्वयोः शब्दयोः सर्वविभक्तिरूपाणि लिखत ।
अ) वाणिक
समाधान:

आ) खज्
समाधान:
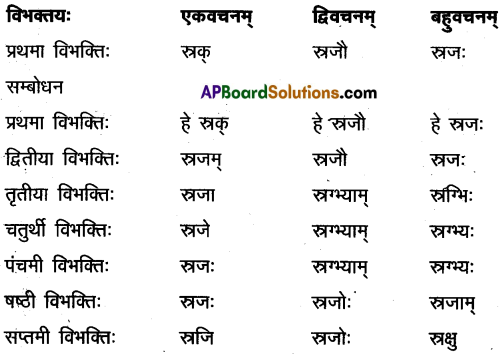
इ) जगत
समाधान:

ई) यद् (न.पुं.)
समाधान:

15. समासनामनिर्देशपूर्वकं त्रयाणां विग्रहवाक्यानि लिखत ।
अ) वृक्षमूलम्
समाधान:
वृक्षस्य मूलम् = षष्ठीतत्पुरुष समासः
आ) अल्पवातः
समाधान:
अल्पश्च असौ वातश्च = विशेषणपूर्वपदकर्मधारय समासः
इ) त्रिलोकी
समाधान:
त्रयाणां लोकानां समाहारः = द्विगु समासः
![]()
ई) धर्मार्थकामाः
समाधान:
धर्मः च अर्थः च कामः च = द्वन्द्व समासः
उ) शाकप्रति
समाधान:
शाकस्य लेशः = अव्ययीभाव समासः
ऊ) उपदशाः
समाधान:
दशानां समीपे ये सन्ति ते = संख्योत्तरपदबहुव्रीहि समासः
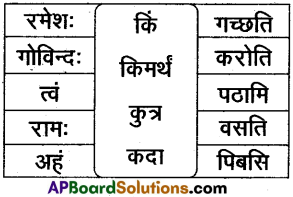
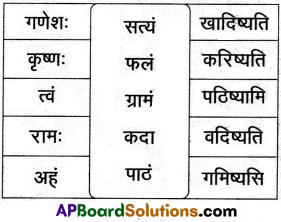
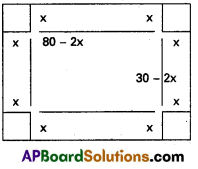
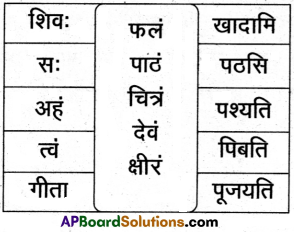
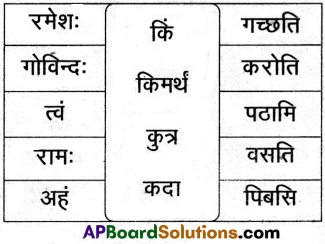
16. अधो निर्दिष्ट पट्टिकामाधारीकृत्य पञ्चसाधुवाक्यानि लिखत |
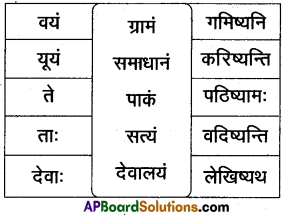
समाधान:
प्रश्नाः
1. वयं सत्यं पठिष्यामः
2. यूयं समाधानं लेखिष्यथ
3. ते ग्रामं गमिष्यन्ति
4. ताः पाकं करिष्यन्ति
5. दावाः सत्यं वदिष्यन्ति