These AP 8th Class Biology Important Questions 9th Lesson Production and Management of Food From Animals will help students prepare well for the exams.
AP State Syllabus 8th Class Biology 9th Lesson Important Questions and Answers Production and Management of Food From Animals
8th Class Biology 9th Lesson Production and Management of Food From Animals 1 Mark Important Questions and Answers
Question 1.
From where do we obtain food?
Answer:
We obtain food from plants and animals.
Question 2.
What are the food items that are obtained from animals?
Answer:
We obtain milk, meat and eggs from animals.
Question 3.
What is animal husbandry?
Answer:
Providing food, shelter, protection and breeding of animals is called animal husbandry.
![]()
Question 4.
How did man use animals since long time?
Answer:
Since long time, man used animals not only for obtaining food but also for agriculture, transportation etc.
Question 5.
Why did early man domesticate only some of the animals?
Answer:
The early man domesticated only some of the animals which provide him food, clothing and the animals which are helpful for agriculture and transportation.
Question 6.
In what way the animals are useful to us?
Answer:
Buffalo and cow give us milk, hens give us eggs and meat, goats and sheep provide us meat, ox, bulls, donkeys are useful for agriculture and transportation.
Question 7.
What do farmers believe in our country?
Answer:
In our country farmers believe that animal husbandry is part and parcel of agriculture.
Question 8.
Name the animals that domesticate by the people living in rural areas.
Answer:
People living in rural areas domesticate animals like cows, buffaloes, bullocks, goats, sheep, pigs, hens, etc.
Question 9.
What is the important issue in Animal husbandry?
Answer:
Supplying of nutritious food, accommodating clear and hygienic shelters for animals is important issue in animal husbandry.
![]()
Question 10.
Where do people rear their cattle in the village?
Answer:
Generally villagers send their cattle to rear at the places where grass is easily available.
Question 11.
Where do farmers keep their cattle?
Answer:
Farmers keep their cattle in the sheds.
Question 12.
Name the agricultural practices done by using bullocks and he-buffaloes.
Answer:
Ploughing and levelling the field farmers use bullocks and he-buffaloes.
Question 13.
How do cattle rearers protect their cattle?
Answer:
Cattle rearers make fences in the fields at off crop seasons.
Question 14.
How is the milk production effected?
Answer:
Milk production is effected by viral and bacterial diseases.
Question 15.
In rainy season how are cattle protected from mosquitoes?
Answer:
Cattle can be protected by covering mosquito nets.
Question 16.
Who will provide treatment and health care for cattle?
Answer:
Veterinary doctor will provide treatment and health care for cattle.
![]()
Question 17.
Name the dangerous disease in cows and buffaloes.
Answer:
Galikuntu is a common and dangerous disease in cows and buffaloes.
Question 18.
From which disease sheep and goats will suffer?
Answer:
Sheep and goats will suffer from worm infections (Nattala Vyadhi)
Question 19.
How do our government treats milk production?
Answer:
Our Government treats milk production as an industry.
Question 20.
How much milk is given by traditional species of cows?
Answer:
2 to 5 litres of milk per day.
Question 21.
How much milk is given by murra species?
Answer:
Murra species give up to 8 litres of milk per day.
Question 22.
Name the traditional varieties of cows.
Answer:
Haryana, Jaferabad, Nagapuri are the traditional varieties which give good quantity of milk.
Question 23.
Name the foreign varieties of cows.
Answer:
Jersy (England) and Holstein (Denmark).
Question 24.
What is the milk yield from foreign varieties?
Answer:
They give 8 to 20 litres of milk.
![]()
Question 25.
What is pasteurization?
Answer:
The destruction of disease producing organisms present in the milk. In this process milk is heated at 62° temperature and cooled below 10°C.
Question 26.
In which months milk production is high?
Answer:
In the months of October and November milk production is high.
Question 27.
Who is the father of white revolution?
Answer:
Prof. J.K. Korian is the father of white revolution in India.
Question 28.
How is milk secreted?
Answer:
Milk is secreted from the mammary glands of animals.
Question 29.
Why do people in our country decorate their cattle during festivals?
Answer:
People believe that cattle are part and parcel of our culture. They treat them as their family members. So they decorate their cattle.
Question 30.
Why do some persons collect bones of dead animals?
Answer:
because bones are used in fertilizer industry.
![]()
Question 31.
What is the use of leather of animals?
Answer:
Leather of cattle is used in the leather industry.
Question 32.
What is Biogas? How is it produced?
Answer:
Biogas is produced from the wastes from cattle, home etc. As this is produced biologically, this gas is called biogas used for domestic purposes.
Question 33.
What are Broilers and layers?
Answer:
Broilers are the hens reared for meat and layers are the hens reared for eggs in poultry.
Question 34.
Name some local variety of poultry varieties.
Answer:
Aseel, Kadaknath, Chittagang, Longshan, Bursa are the pure local varieties.
Question 35.
What is a poultry?
Answer:
Production and rearing of hens on a large scale is called poultry.
Question 36.
In which place India is occupied in production of eggs?
Answer:
India achieved 4th position in the world by producing 41.06 million eggs per annum.
![]()
Question 37.
Name the foreign varieties of hens giving meat.
Answer:
New Hampshire, White plymouth, Rhode island red, while leg horn and Anoka.
Question 38.
What are the major practices in food production?
Answer:
Animal husbandry, poultry, fish culture, bee culture etc., are the major practices in food production.
Question 39.
In which months the egg prices are high?
Answer:
During January to April, egg prices are high.
Question 40.
Why egg prices are more in January to April?
Answer:
This is because of most of the eggs are used for hatching.
Question 41.
What is the temperature for hatchability of eggs?
Answer:
Hatchability of eggs is generally influenced by 37°C to 38°C temperature.
Question 42.
Write a slogan on nutritional Egg.
Answer:
“If you want to be healthy person eat egg every day”.
Question 43.
Name the traditional variety meant for fighting.
Answer:
Aseel (Berisa Kodi) is the Indian traditional variety meant for fighting.
Question 44.
How is hatching done in our rural areas?
Answer:
Our rural areas, the practitioner hatch eggs by placing them under broody hen.
![]()
Question 45.
What is the weight of Emu bird?
Answer:
The weight of Emu bird is nearly 50 kg.
Question 46.
What is the life span of natural wild varieties?
Answer:
Natural wild varieties grow fully in 5 to 6 years.
Question 47.
What is the life span of broilers?
Answer:
Broilers grow fully in just 6 to 8 weeks.
Question 48.
What is Apiculture?
Answer:
Culture of honey bees (apis) is called Apiculture.
Question 49.
What is the use of honey bee production?
Answer:
Development of apiculture is not only for honey production but also very much useful for crop pollination.
Question 50.
Which insects are the best pollinators?
Answer:
Honey bees are the best pollinators of many agricultural crops.
Question 51.
How much honey is produced by Indian honey bee?
Answer:
Indian honey bee produces 3 – 10 kg of honey.
![]()
Question 52.
Which honey bee is produces more honey?
Answer:
European honey bee produces 25 – 30 kgs of honey per annum.
Question 53.
Name the honey bees present in honey bee colony.
Answer:
A honey bee colony consists of one queen bee, several thousands of workers and few hundreds of drones.
Question 54.
What is the primary function of a queen bee?
Answer:
The primary function of a queen bee is to lay eggs.
Question 55.
What is the life span of a queen bee?
Answer:
The life span of queen bee is two-three years.
Question 56.
What are worker bees?
Answer:
The sterile females are called worker bees in the hive.
Question 57.
What is the function of worker bees?
Answer:
They attend to indoor duties during first three weeks of their lives such as secretion of royal jelly feeding of the brood, collecting nectar, pollen and water.
Question 58.
Name the plants that are sources of nectar.
Answer:
Fruit trees like citrus, apple, guava, tamarind, cultivated fields, crops like mustard, gingelly, wheat, cotton, sunflower.
![]()
Question 59.
What are the other products of Apiculture?
Answer:
Bee venom and bee wax are the other products of Apiculture.
Question 60.
How is bee venom used?
Answer:
Bee venom is used for the preparation of “Apistincture” used in homeopathic treatment.
Question 61.
What are the uses of bee wax?
Answer:
The uses of bee wax are production of polish cream, nail polish etc.
Question 62.
Name the parts present in a artificial bee hive.
Answer:
It consists of floor board, brood chamber, super chamber, top cover, inner cover, frames and entrance rod.
Question 63.
Name the pests and predators that attack honey bee colonies.
Answer:
Wax moths, wasps, rubber flies, dragon flies attack honey colonies. King crow, Bee eater are more harmful.
Question 64.
How are fish important for us?
Answer:
Fish constitute an important and rich sources of high quality animal protein.
Question 65.
What are the inland water areas?
Answer:
Rivers, fresh water and brackish water lakes, reservoirs, tanks, ponds, swamps etc., are the inland water areas.
![]()
Question 66.
Name the crustacean fishery.
Answer:
Prawns, lobsters and crabs together constitute the crustacean fishery.
Question 67.
Name the local varieties offish.
Answer:
Murrel (Korramenu), Katla (jalla), Katrana (bochalu), rohu (mosu), seer (vanjram) are the local varieties.
Question 68.
Name the marine fish varieties.
Answer:
Macerel, tuna, saradines are the marine fish varieties.
Question 69.
What are mechanized fishing?
Answer:
Fishermen catch fish by using machines is called mechanized fishing.
Question 70.
Name some marine fishes which are of high economic value.
Answer:
Mullets, Bhetki and peral spots, shel fishes such as prawns mussels and oysters as well as sea weed.
Question 71.
What are estuaries?
Answer:
Brackish water resources where sea water and fresh water mix together are called estuaries.
![]()
Question 72.
What is the reason for growing fish in paddy fields?
Answer:
The reason for this is increasing use of inorganic fertilizers and insecticides in paddy fields.
8th Class Biology 9th Lesson Production and Management of Food From Animals 2 Marks Important Questions and Answers
Question 1.
How do you appreciate the role of poultry to meet the food needs of the present day increasing population ?
Answer:
- The world is facing the problem of over growth in population.
- To meet the increasing population food needs, poultry is the best suitable option.
- So billion hens are reared world wide for eggs and chicken.
- India achieved 4th position in the world by producing 41.06 million eggs per annum.
- India is placed in 5th position in the production of 1000 million kgs of chicken per year.
- Hence, I appreciate the poultry, in fulfilling the food needs of the society.
Question 2.
“Fish has high nutrition values” said Shravya. Do you support Shravya? Why?
Answer:
- The meat of fish contains 15-25% of proteins. Hence they are the rich sources of proteins.
- The meat of fish has vitamins like A and D.
- Fishes are the sources for very important fatty acids and unsaturated fatty acids which are very vital in our body’s metabolic activities.
- Meat of fish can be easily digested. It helps in the growth and development.
![]()
Question 3.
Name the three Indian Major fresh water crops grown in fish culture.
Answer:
- Rohu – Labeo rohita:
- Boche – Catla catla
- Erramosu – Cirrhinus mrigala are the three Indian major crop fishes.
8th Class Biology 9th Lesson Production and Management of Food From Animals 4 Marks Important Questions and Answers
Question 1.
This fish is called Tuna. Collect information about availability catching and marketing of this particular fish.

Answer:
Availability:
English: Big eye Tuna
Latin: Thunnus obesus
size + weight: Average today about 40 -180 c.m. about 1, 4-130 Kg.
Biggest Angled Fish: 197, 3 kg, 236 cm, Peru, 1957 Russel Lee
Maturity: Size 105 cm, weight 25 Kg., age 3 – 4 years
Maximum: Size 230 c.m., Weight 210 Kg., Age 15 years
Catching: 21% Eastern Pacific
38% Western Pacific
22% Indian Ocean
19% Atlantic Ocean
Catching Methods: Longlining, Purse seining and pole-and-line (by-catch)
Share of all Tuna: 2011 about 10% – 398.000 m.t
Main Production: Thailand, Philippines, Indonesia, Mexico, Venezuela, Ecuador, Colombia, Spain, Italy.
Life cyle: About 7-8
Major Markets: Japan (Sashimi)
Populr Product: Fresh (Whole fish)
Forms: Fresh Fillets (Sashimi)
![]()
Question 2.
Write a note on different methods used to store the fish in your area.
Answer:
- The fish caught should be preserved in chilled conditions.
- After catching the fish, gut is removed. Before transportation, fishes are thoroughly washed in clean and chlorinated waters.
- They are perceived in insulated ice boxes with alternate layers of crushed ice and fishes in 1 : 1 proportion.
- Preservation can also be done by
a) Drying b) Salting c) Smoking d) Canning methods - Before canning, harmful bacteria like clostridum botulinum must be destroyed.
- Cold storage facility and vans with refrigerated chamber have improved the storage and transport of fish.
Question 3.
Visit a poultry farm of your village. Collect the diseases of poultry and their preventive control measures. Prepare them in theform of a table.
Answer:
| Diseases in Poultry birds | Casual organism | Precautionary control measures |
| Fowl cholera | Bacteria | Vaccination for fowl cholera is must. |
| Salmonellasis | Bacteria | Antibiotics with sulphur and vaccines. |
| Coryza | Bacteria | Sulfa drugs and antibiotics are necessary. |
| Fowl fox | Virus | They should be separated from the farm. |
| Ranikhet | Virus | Fowls should be separated from the farm and treatment should be given separately. |
![]()
Question 4.
Write some diseases of tamed animals.
Answer:
- Galikuntu is a common and dangerous diseases occur in cows and buffaloes.
- Sheep and goats suffer from worm infections (Nattala vyadhi).
- Some parasitic diseases cause damage to liver and intestine of tamed animals.
- Viral and bacterial diseases also effect on milk production of cows and buffaloes.
These are some examples for diseases in domestic animals.
8th Class Biology 9th Lesson Production and Management of Food From Animals Important Questions and Answers
Question 1.
How are the microorganisms like bacteria killed and how can the milk be preserved at milk chilling centres?
Answer:
- Pasteurization of milk ensures the destruction of disease producing organisms present in milk.
- In this process, milk is heated at 72°C for 30 minutes.
- Prior to this, the milk was being cooled to below 10°C.
- This process was invented by Louis Pasteur.
Question 2.
Dung is used as biofuel. You know that it is an accessory product. Write about such accessory products produced in animal husbandry.
Answer:
1. The supplimentary products produced from animal husbandry are meat, dung, leather, bones, horns, etc,
2. Animal husbandry is also contributing to different industries like
- Dairy industry: Milk and milk products are produced.
- Slaughter houses: Production of meat.
- Leather industry: Tanning of leather and making shoes, belts and suitcases, etc.
- Fertilizer industry : Bones of cattle are used in the production of chemical fertilizers.
- Bio gas industry: Cattle dung is used in the production of biogas.
- Toys industry: The horns of cattle are used to make toys and ornamental items.


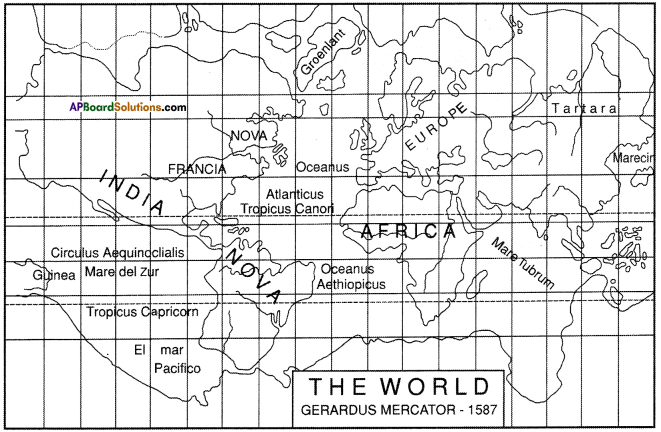
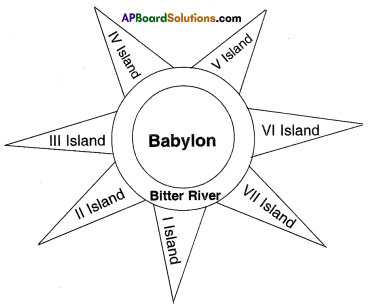 The Babylonian clay tablet was dated from the Persian period. It was flat and round. The inner circle had all the places they knew about. The city of Babylon was shown in the middle. Beyond the inner circle was ‘Bitter river, or ‘Salt water ocean’ in which were seven triangular islands.
The Babylonian clay tablet was dated from the Persian period. It was flat and round. The inner circle had all the places they knew about. The city of Babylon was shown in the middle. Beyond the inner circle was ‘Bitter river, or ‘Salt water ocean’ in which were seven triangular islands.






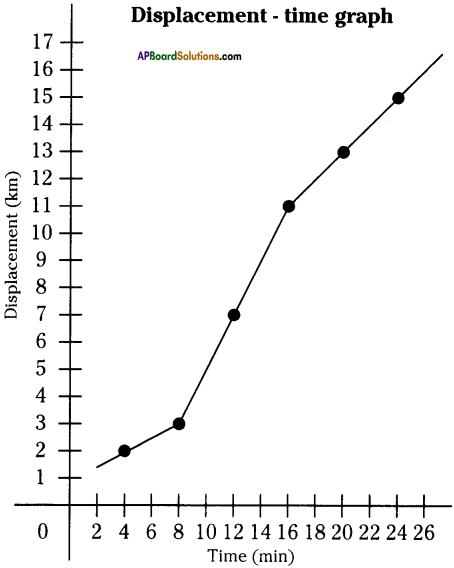
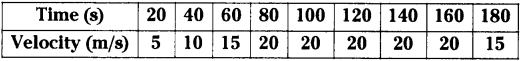
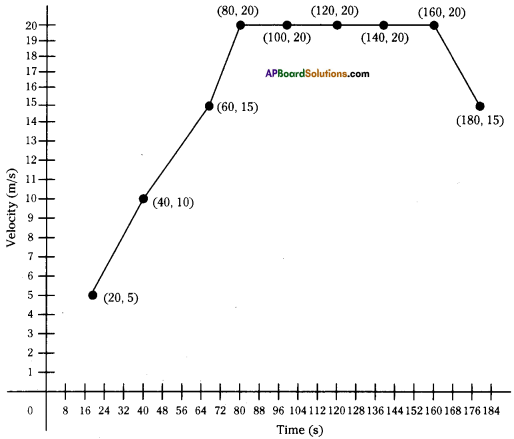
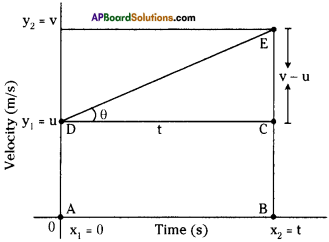












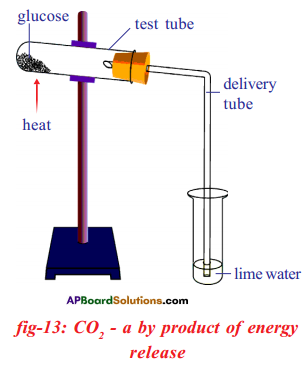

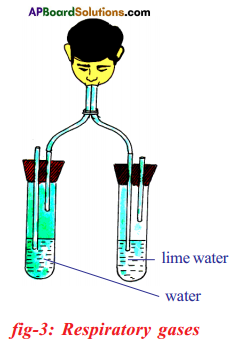 (a) Which gas turns lime water milky in this experiment?
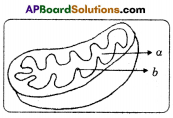
(a) Which gas turns lime water milky in this experiment?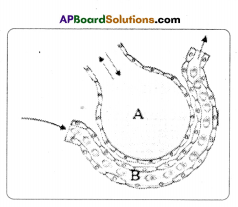 A) To which biosystem is this picture related?
A) To which biosystem is this picture related?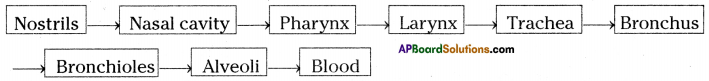
 a) What is the aim of this experiment?
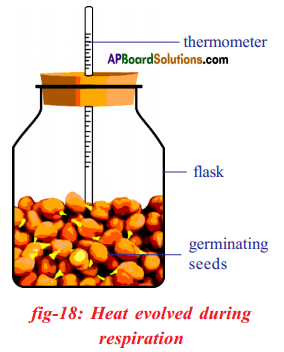
a) What is the aim of this experiment?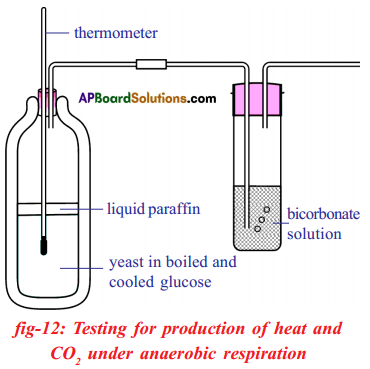 a) What do you prove by conducting this experiment?
a) What do you prove by conducting this experiment?
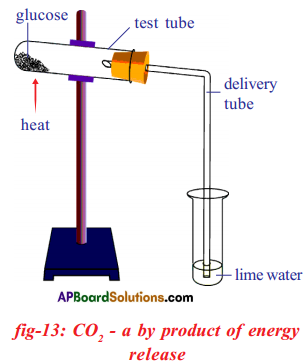 i) Which process do we know with the help of this experiment?
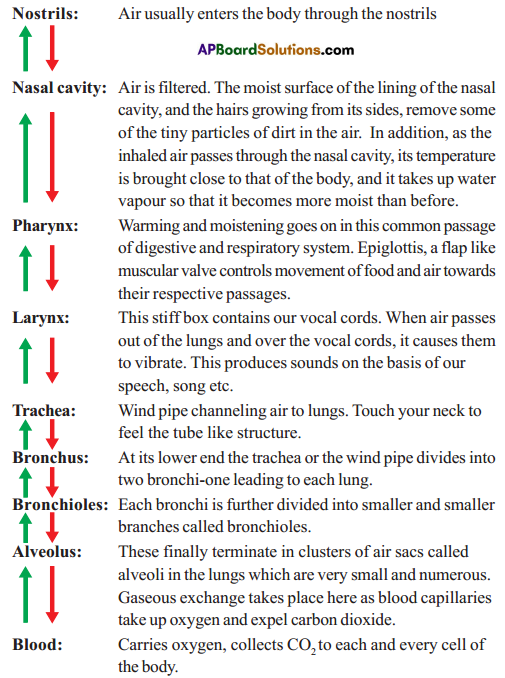
i) Which process do we know with the help of this experiment?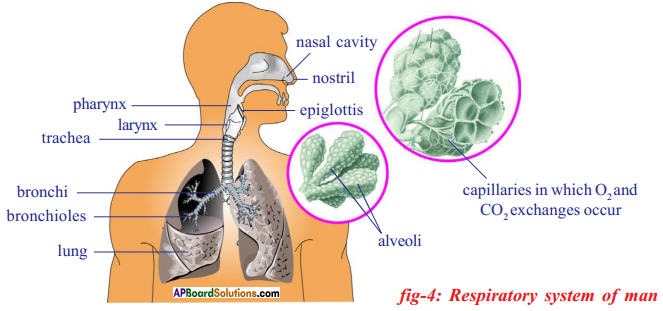

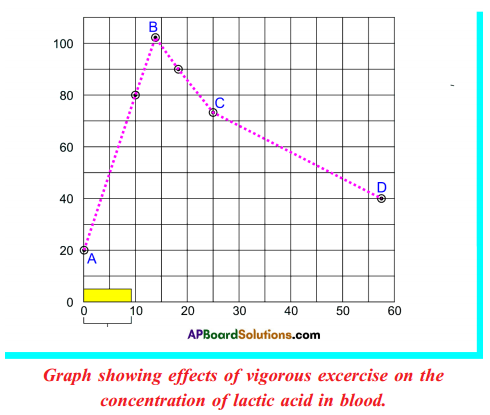
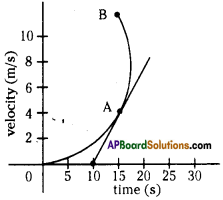
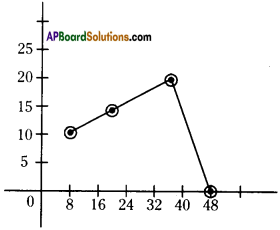
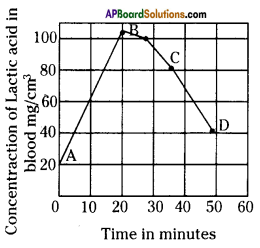 Graph showing effects of vigorous excercise on the concentration of lactic acid in blood.
Graph showing effects of vigorous excercise on the concentration of lactic acid in blood.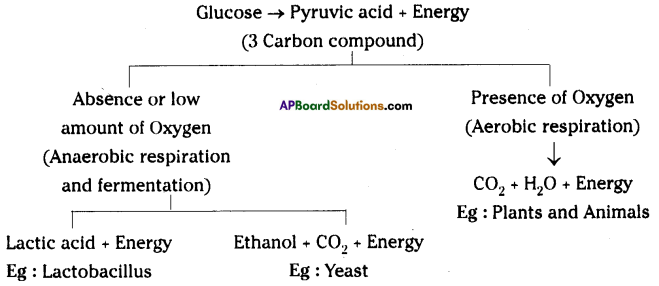
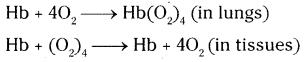

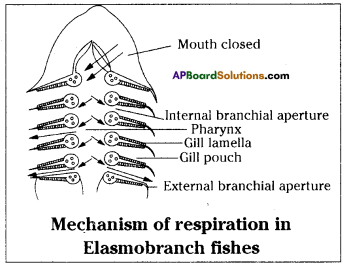
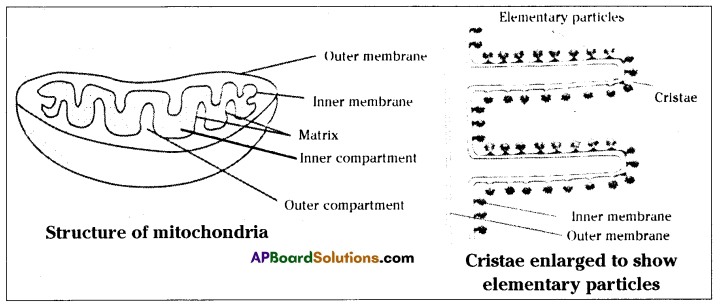
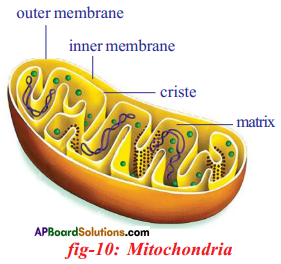 Oxidation of glucose molecule occurs in the mitochondria, ot cell. This is known as cellular respiration. The energy produced during cellular respiration stored in the form of ATP molecule. Energy producing cellular respiration occurs in mitochondria hence we call it cell of power or power house of the ceil.
Oxidation of glucose molecule occurs in the mitochondria, ot cell. This is known as cellular respiration. The energy produced during cellular respiration stored in the form of ATP molecule. Energy producing cellular respiration occurs in mitochondria hence we call it cell of power or power house of the ceil.