These AP 9th Class Telugu Important Questions 9th Lesson భూమి పుత్రుడు will help students prepare well for the exams.
AP State Syllabus 9th Class Telugu 9th Lesson Important Questions and Answers భూమి పుత్రుడు
9th Class Telugu 9th Lesson భూమి పుత్రుడు Important Questions and Answers
I. అవగాహన – ప్రతిస్పందన
క్రింది అపరిచిత పద్యాలను చదివి, ప్రశ్నలకు జవాబులు రాయండి.
తన కోపమె తన శత్రువు
తన శాంతమె తనకు రక్ష, దయ చుట్టంబౌ
తన సంతోషమె స్వర్గము
తన దుఃఖమె నరకమండ్రు తథ్యము సుమతీ.
ప్రశ్నలు – జవాబులు:
1. శత్రువు ఎవరు?
జవాబు:
కోపం
2. ఏది రక్ష?
జవాబు:
శాంతం
3. దయ ఎలాంటిది?
జవాబు:
చుట్టము
4. స్వర్గ నరకాలు అంటే ఏవి?
జవాబు:
సంతోషం, దుఃఖం
2. లావు గల వాని కంటెను
భావింపగ నీతిపరుడు బలవంతుండౌ
గ్రావంబంత గజంటును
మావటివాడెక్కినట్లు మహిలో సుమతీ.
ప్రశ్నలు – జవాబులు:
1. బలవంతుడు ఎవరు?
జవాబు:
నీతిపరుడు
2. ఏనుగు నడిపేవాడు?
జవాబు:
మావటివాడు
3. సుమతీ శతక కర్త?
జవాబు:
బద్దెన
4. ‘గ్రావం’ అర్థం?
జవాబు:
కొండరాయి
![]()
3. ఈ కింది సమీక్షనుచదివి ఇచ్చిన ప్రశ్నలకు జవాబులు రాయండి. (S.A. II – 2017-18)
మిద్దెతోటల పెంపకం ఇలా
మిద్దెతోటల పెంపకం సాగులో సేంద్రియ పద్ధతుల్ని ప్రోత్సహిస్తున్న రైతు నేస్తం ఫౌండేషన్ ప్రచురించిన ఈ పుస్తకాన్ని మిద్దెతోట సాగుచేస్తున్న తుమ్మేటి రఘోత్తమరెడ్డి తమ అనుభవాన్ని రంగరించి రాశారు. దీనిలో మిద్దెతోటల పెంపకం గురించి సూచనలిచ్చారు. అటువంటి రైతులకు మంచిసూచనలిచ్చారు. మిద్దెతోట పుస్తకం వెల రూ. 349/-
ప్రశ్నలు:
1. ‘మిద్దెతోట’ అనేది ఏమిటి ?
2. ‘మిద్దెతోట’ను ఎవరు ప్రచురించారు?
3. ‘మిద్దెతోట’ ఖరీదెంత?
4. పై సమీక్ష వలన ఎవరికి ప్రయోజనం?
జవాబులు:
1. భవనం పైన గల ఖాళీస్థలంలో ఏర్పాటు చేసుకున్న కుండీల మొదలైన వాటిలో చేసే మినీ వ్యవసాయం.
2. రైతు నేస్తం ఫౌండేషన్
3. రూ. 349/
4. మిద్దెతోట రైతులకు.
II. స్వీయరచన
క్రింది ప్రశ్నలకు నాలుగైదు వాక్యాలలో సమాధానాలు రాయండి.
ప్రశ్న 1.
తన కష్టంతో లోకానికి భుక్తిని పంచే భూమి పుత్రుని గూర్చి విశదపరచిన కవిని గూర్చి రాయండి. (S.A. II – 2017-18)
(లేదా)
అన్నదాతయైన భూమి పుత్రుడు’ ఔన్నత్యాన్ని అభివర్ణించిన కవిని పరిచయం చేయండి. (S.A. II – 2015-16)
జవాబు:
కవి : శ్రీ దువ్వూరి రామిరెడ్డి
కాలం : 9. 11. 1895 నుండి 11.9.1947
జన్మస్థలం : నెల్లూరు
రచనలు : నలజారమ్మ, వనకుమారి, కృషీవలుడు, జలదాంగన, యువక స్వప్నం, కడపటి వీడ్కోలు, పానశాల, నక్షత్రశాల, నైవేద్యం, భగ్న హృదయం, పరిశిష్టం, ప్రథమ కవిత్వం.
బిరుదు : కవికోకిల
శైలి : సరళ సుందరంగా ఉంటుంది. విశ్వశాంతి, దేశభక్తి, మానవతావాదం, అభ్యుదయం వీరి రచనల్లో కనిపిస్తాయి.
ప్రశ్న 2.
రైతుతో ఎవరెవరు సాటిరారని కవి అన్నారు?
జవాబు:
రైతును తమ్ముడా ! అని సంబోధిస్తూ, లోకంలో కొందరు చిత్రంగా ఉంటారు. వీరిలో కొందరు చిన్నతాడు కట్టిన చిన్న చెంబుతో నేల నూతిలో నీళ్ళు తోడేవారు (ఉపయోగం లేని పని), కొందరు తలకు, మోకాలకీ ముడి పెట్టేవారు (సందర్భ శుద్దిలేని పని), ఇంకొందరు చిటికెలతో పందిళ్ళు అల్లేవారు (కబుర్లే పని), అంటే వీళ్ళంతా కేవలం మాటల చమత్కారంతో అరచేతిలో స్వర్గం చూపించేవారు. కానీ చేతులతో సమాజ సేవ చేస్తున్న నీకు వీరెవ్వరూ సాటిరారని కవి అన్నారు.
![]()
ప్రశ్న 3.
రైతుకు ఏవి కొరత?
జవాబు:
సమాజం సుఖసంతోషాలతో ఉండటానికి రైతే కారణం. కానీ అతని కష్ట ఫలితాన్ని ఇతరులు అనుభవించి సుఖపడతున్నారు. రైతు క్షేమాన్ని, శ్రేయస్సును కోరేవారు ఎవరూ లేరు. కనీసం కన్నెత్తి అయిన చూడరు. ఆప్యాయంగా పలకరించరు. చివరకు తిండికీ, బట్టకు ఎప్పుడూ కొరతే.
ప్రశ్న 4.
“అట్టి కృతఘలన్………… పద్యం ద్వారా రైతు ఎలాంటి వాడని అర్థమైంది?
జవాబు:
చేసిన మేలు మరచేవారిని రైతు అసలు పట్టించుకోడని ఈ పద్యం ద్వారా అర్థమైంది. మరియు పొలం పనులలో అతని శరీరం ఎముకలగూడుగా మారినా, వానలు ముంచెత్తినా, కరవు పీడించినా వాటిని లెక్కచేయడని తెలిసింది. ఇంకా కాయకష్టాన్నే నమ్మి, స్వార్జితమైన పట్టెడన్నమే తిని రైతు నిజంగా ‘భూమి పుత్రుడె’ అని గ్రహించాను.
ప్రశ్న 5.
‘భూమి పుత్రుడు’ ప్రక్రియను గూర్చి రాయండి.
జవాబు:
‘భూమి పుత్రుడు’ పాఠ్యభాగం ‘కావ్యం’ ప్రక్రియకు చెందినది. కవి యొక్క కర్మము – కావ్యము. దీనిలో వర్ణనయే ప్రధానాంశముగా కల్గి, మనసుకు హత్తుకునేలా రచన సాగుతుంది.
ఈ క్రింది ప్రశ్నలకు పది లేక పన్నెండు వాక్యాలలో సమాధానాలు రాయండి.
ప్రశ్న 1.
రైతును ఆదర్శంగా తీసుకొని ప్రజలు జీవించడం అవసరం ఎంతైనా ఉంది. దీనిని నీవు సమర్థిస్తావా ? వివరించండి.
జవాబు:
‘రైతే దేశానికి వెన్నెముక’, ‘పల్లెలే దేశానికి పట్టుకొమ్మలు’ – అన్న మాటలు అందరూ అనే మాటలు, వినే మాటలు. రైతు, పల్లెలోని గొప్పదనాన్ని మాటల్లో చెప్పడం తప్ప ఎవరూ వారికి సాయం చేతల్లో చూపించరు. పల్లె సౌందర్యాన్ని ఆస్వాదిస్తామేగాని, అక్కడి ప్రజల బాగోగులు చూడము. పల్లె ప్రజల్లో ఇచ్చి పుచ్చుకొనే తత్వం ఉంటుంది. ఒకరికొకరు పనులలో సాయం అంది పుచ్చుకుంటారు. రైతును ఆదర్శంగా తీసుకోవడం అంటే భేషజం లేని జీవితం గడపటమే. ఉన్నా లేకపోయినా ఒకేలా ఉండడం రైతు జీవితం. నలుగురి క్షేమం కోరేవాడు. ఈ లోకంలో రైతు తప్ప ఇంకెవరుంటారు. మనం రైతులాగా నిస్వార్థంగా, తృప్తిగా జీవించగలిగితే మనమున్న చోటే స్వర్గం అవుతుంది.
రైతు తాను పండించిన పంటను గిట్టుబాటు ధర రాకపోయినా తృప్తిపడి, మరుసటి సంవత్సరం పంట ఇంకా బాగా మొదలుకొని, చిరవకు పంట చేతికి వచ్చే దాకా పండించాలని తాపత్రయపడతాడు. పంట వేయడానికి ముందు పొలం దున్నటం రైతు గుండె ఎంతగా అల్లాడుతుందో ఎప్పుడైనా మనం ఆలోచిస్తామా. పంట పదును మీదున్నప్పుడు వానో, వరదో వస్తుందనే ఊహే ప్రాణాన్ని విలవిలలాడిస్తుంది. అయినా వీటన్నింటిని భరించి, తోటివాళ్ళమైన మనందరి ఆకలి తీర్చే రైతు మనందరికి భగవంతుడు ఇచ్చిన సోదరుడు.
మనం గుర్తించినా, గుర్తించకపోయినా తన సంసారాన్ని ఒక ప్రక్క వ్యవసాయాన్ని ఒక ప్రక్క నడుపుతూ , సమాజాన్ని నడిపిస్తున్నాడు. నిస్వార్థం అతని మనసు, సంతృప్తి అతని ఆలోచన, అందరూ బాగుండాలి అనేది అతని ఆకాంక్ష. మనం గమనిస్తే ఏదైనా సమస్య వచ్చినపుడు పెద్దల సమక్షంలో చర్చకు వస్తే అప్పుడు మధ్యమ మార్గంగా తీర్పు చెప్పడానికి “రైతు పద్ధతిలో మాట్లాడుకుందాం” అంటారు. దీనిని బట్టే మనం అర్థం చేసుకోవచ్చు రైతు ఎంత గొప్ప వ్యక్తో.
![]()
ప్రశ్న 2.
రైతు దేశానికి వెన్నెముక అంటారు కదా! అంతటి ప్రాధాన్యత వహించిన భూమి పుత్రుడుని గురించి దువ్వూరి రామిరెడ్డి గారెలా ఆవిష్కరించారో మీ స్వంత మాటల్లో రాయండి. (S.A. II – 2018-19)
జవాబు:
రైతు దేశానికి వెన్నెముక. నలుగురి క్షేమం కోరేవాడు. ఈ లోకంలో రైతు తప్ప ఇంకెవరుంటారు. మనం రైతులాగా నిస్వార్థంగా, తృప్తిగా జీవించగలిగితే మనమున్నచోటే స్వర్గం అవుతుంది. రైతు తాను పండించిన పంటకు గిట్టుబాటు ధర రాకపోయినా తృప్తిపడి, మరుసటి సంవత్సరం పంట ఇంకా బాగా పండించాలని తాపత్రయ పడతాడు. పంట వేయడానికి ముందు పొలం దున్నడం మొదలుకొని ధాన్యం ఇంటికి తెచ్చేవరకు రైతు గుండె ఎంతగా అల్లాడుతుందో ఆలోచిస్తేనే గుండె జారిపోతుంది.
ఉన్నా లేకపోయినా ఒకేలా ఉండడం రైతు జీవితం. పంట పదును మీదున్నప్పుడు వానో, వరదో వచ్చినప్పుడు అతని మానసిక స్థితి స్థిరంగా ఉంటుంది. అతని ధ్యాస పంటను రక్షించడమే, లేకపోతే నలుగురికి అన్నం లేకుండా చేసినవాణ్ణి అవుతానని బాధ్యత పడతాడు. సృష్టి స్థిల కారులలో విష్ణువు స్థితికర్త. అంటే మనల్ని పోషించేవాడని అర్థం. ప్రస్తుత కాలంలో మనకు రైతే స్థితికర్త,
మనం గమనిస్తే ఏదైనా సమస్య వచ్చినప్పుడు పెద్దల సమక్షంలో చర్చకు వస్తే అప్పుడు మధ్యమ మార్గంగా తీర్పు చెప్పడానికి ‘రైతు పద్ధతిలో మాట్లాడుకుందాం’ అంటారు. దీనిని బట్టి మనం అర్థం చేసుకోవచ్చు. రైతు ఎంత గొప్ప వ్యక్తో. అందుకే దువ్వూరి రామిరెడ్డిగారు “చేతులతో సమాజసేవ చేస్తున్న నీకు వేరెవ్వరూ సాటిరారని” అన్నారు.
III. భాషాంశాలు (పదజాలం, వ్యాకరణం)
1. పర్యాయపదాలు:
ఈసు : అసూయ, ఈర్య
కన్ను : అక్షి, నేత్రం, నయనం
మనుజుడు : మానవుడు, నరుడు, మనుష్యుడు
కృషి : వ్యవసాయం, సేద్యం, కరిసనం
నుతి : పొగడ్త, ప్రశంస
క్షామం : కరవు, అనావృష్టి
తాత : తండ్రి తండ్రి, పితామహ
క్ష్మా : ధారణి, నేల, భూమి
2. వ్యుత్పత్త్యర్థాలు :
కావ్యం : కవి యొక్క కర్మము (గ్రంథం)
అతిథి : తిథి, వార, నక్షత్రము నియమాలు లేక ఇంటికి భోజనానికి వచ్చేవాడు
కృతఘ్నుడు : చేసిన మేలు మఱచువాడు
క్ష్మా : భారమును వహించుటయందు క్షమ (ఓర్పు) కలది (భూమి)
సత్యం : సత్పురుషులయందు పుట్టునది (నిజం)
పుత్రుడు : పున్నామ నరకం నుండి రక్షించువాడు (కుమారుడు)
3. నానార్థాలు :
ఆత్మ : మనస్సు, పరమాత్మ, బుద్ధి, దేహం
రసము : చారు, పాదరసం, శృంగారాది రుచి, కోరిక
కాలము : సమయం, నలుపు, చావు
4. ప్రకృతి – వికృతులు :
భూమి – బూమి
మృత్తిక – మట్టి
కాంక్ష – కచ్చు
కష్టము – కసుటు
భోగం – బోగం (సుఖం)
విద్య – విద్ధియ, విద్దె
పుత్రుడు – బొట్టె, బొట్టియ, పట్టి
గౌరవం – గారవం
బ్రధ్న – పొద్దు
శ్రీ – సిరి
విశ్వాసం – విసువాసం
స్పర్థ – పంతం
5. సంధులు :
హిత + అర్థ = హితార్థ – సవర్ణదీర్ఘ సంధి
దైనిక + ఆవశ్యకం = దైనికావశ్యకం – సవర్ణదీర్ఘ సంధి
కష్ట + ఆర్జితం = కష్టార్జితం – సవర్ణదీర్ఘ సంధి
రస + ఆస్వాద = రసాస్వాద – సవర్ణదీర్ఘ సంధి
దుర్భర + అవస్థ = దుర్భరావస్థ – సవర్ణదీర్ఘ సంధి
కన్నెత్తియున్ + చూతురే = కన్నెత్తియుంజూతురే – సరళాదేశ సంధి
తోపు + తోపు = తోదోపు – ప్రాతాది సంధి
పస్తు + ఉన్న = పస్తున్న – ఉత్వసంధి
ప్రొద్దు + పొడిచిన = ప్రొద్దువొడిచిన – గసడదవాదేశ సంధి
ప్రొద్దు + క్రుంకు = ప్రొద్దుగ్రుంకు – గసడదవాదేశ సంధి
జీవ + కట్టి = జీవగట్టు – ఉత్వసంధి
కన్ను + ఎత్తి = కన్నెత్తి – ఉత్వసంధి
శ్రమ + ఆర్జితం = శ్రమార్జితం – సవర్ణదీర్ఘ సంధి
6. సమాసాలు:
భూమిపుత్రుడు = భూమి యొక్క పుత్రుడు – షష్ఠీ తత్పురుష సమాసం
ధారుణీపతి = ధరణికి పతి – షష్ఠీ తత్పురుష సమాసం
పవిత్రమూర్తి = పవిత్రమైన మూర్తి – విశేషణ పూర్వపద కర్మధారయ సమాసం
శూరమణి = శూరుల అందు శ్రేష్ఠుడు – సప్తమీ తత్పురుష సమాసం
జీవన స్పర్థ = జీవనమునందు స్పర్థ – సప్తమీ తత్పురుష సమాసం
జీవన సంగ్రామం = జీవనమనే సంగ్రామం రూపక సమాసం
హాలిక వర్య – రైతులలో శ్రేష్ఠ – షష్ఠీ తత్పురుష సమాసం
![]()
7. అలంకారాలు:
జీవన సంగ్రామం – రూపకాలంకారం. ఉపమాన ఉపమేయాలకు అభేదం చెప్పుట.
జీవనం – ఉపమేయం
సంగ్రామం – ఉపమానం
ఈ రెండింటికి అభేదం చెప్పబడినది. కనుక ఇది రూపకాలంకారం.
9th Class Telugu 9th Lesson భూమి పుత్రుడు 1 Mark Bits
1. ఆధునిక కాలంలో కృషి చేయడానికి ఎవరూ కృషి చేయడం లేదు – గీత గీసిన పదాలకు నానార్థపదాలు గుర్తించండి. (S.A. II – 2017-18)
ఎ) కష్టం – కారణం
బి) వ్యవసాయం – సాయం
సి) వ్యవసాయం – వ్యవహారం
డి) వ్యవసాయం – ప్రయత్నం
జవాబు:
డి) వ్యవసాయం – ప్రయత్నం
2. లక్ష్మి అనుకున్న కర్జము నెరవేరింది. (ప్రకృతి పదం గుర్తించండి) (S.A. II – 2017-18)
ఎ) కారణం
బి) కార్యం
సి) కయ్యం
డి) కాలం
జవాబు:
బి) కార్యం
3. ‘మనిచిరి నీ పితామహులమాంద్య సుశీలురు సర్వవృత్తిపా’. (ఏ పద్యపాదమో గుర్తించండి.) (S.A. III – 2016-17)
ఎ) మత్తేభము
బి) శార్దూలము
సి) ఉత్పలమాల
డి) చంపకమాల
జవాబు:
డి) చంపకమాల
![]()
4. అఖిల వాణిజ్యములు సిరికాట పట్లు. (ఆధునిక వచనాన్ని గుర్తించండి) (S.A. II. 2017-18)
ఎ) అఖిలమైన వాణిజ్యంబులు సిరికాట పట్లు
బి) అఖిలంబైన వాణిజ్యమ్ములు సిరికినాట పట్లు
సి) అఖిల వాణిజ్యాలు సిరికాట పట్లు
డి) అఖిల వాణిజ్యముల్ సిరికి నాటపట్టులు
జవాబు:
సి) అఖిల వాణిజ్యాలు సిరికాట పట్లు
5. “చిన్నప్పటి నుండీ నాకు బోటనీ అభిమాన విషయం” అన్నాడు రచయిత. (పరోక్ష కథనంలోకి గుర్తించండి) (S.A. II – 2017-18)
ఎ) చిన్నప్పటి నుండీ తనకు బోటనీ అభిమాన విషయమని అన్నాడు రచయిత.
బి) రచయితకు బోటనీ అభిమాన విషయమన్నాడు.
సి) రచయిత బోటనీ నాకు అభిమాన విషయమన్నాడు.
డి) బోటనీ అభిమాన విషయమని రచయిత అన్నాడు.
జవాబు:
ఎ) చిన్నప్పటి నుండీ తనకు బోటనీ అభిమాన విషయమని అన్నాడు రచయిత.
భాషాంశాలు (పదజాలం, వ్యాకరణం)
1. ఆర్థాలు :
6. అన్ని వృత్తులలో పావనమైనది వ్యవసాయం – గీత గీసిన పదానికి అర్థం గుర్తించండి.
A) ధర్మం
B) పవిత్ర
C) మలినం
D) న్యాయం
జవాబు:
B) పవిత్ర
7. శ్రమ పడకుండా ఫలములు తమంతట తాముగా రావు – గీత గీసిన పదానికి అర్థం గుర్తించండి.
A) దారులు
B) పండ్లు
C) దేవతలు
D) ఫలితాలు
జవాబు:
D) ఫలితాలు
8. బావులకు ఉగ్గాలు ఏర్పాటు చేసేవారు – గీత గీసిన పదానికి అర్థం గుర్తించండి.
A) బకెట్లు
B) బిందెలు
C) చేదలు
D) గంగాళాలు
జవాబు:
C) చేదలు
9. రాజు చేతిలోని ధర్మదండం కన్నా నీ చేతి హలం గొప్పది – గీత గీసిన పదానికి అర్థం గుర్తించండి.
A) నాగలి
B) కొడవలి
C) గొడ్డలి
D) కర్ర
జవాబు:
A) నాగలి
![]()
10. ఇరుగుపొరుగు వారి సంపదకై ఈసు పొందవు – గీత గీసిన పదానికి అర్థం గుర్తించండి.
A) ప్రేమ
B) అభిమానం
C) కోపం
D) ఈర్ష్య
జవాబు:
D) ఈర్ష్య
11. నీ హృదయ కళిక ఎంతో పవిత్రమైనది – గీత గీసిన పదానికి అర్థం గుర్తించండి.
A) పువ్వు
B) దీపం
C) మొగ్గ
D) బంగారం
జవాబు:
C) మొగ్గ
12. కృషి సకల పరిశ్రమలకు మూలము – గీత గీసిన పదానికి అర్థం గుర్తించండి.
A) పశువు
B) వ్యవసాయము
C) పక్షి
D) కష్టం
జవాబు:
B) వ్యవసాయము
13. సంపదయే సుఖాలను పొందడానికి జీవగఱ్ఱ – గీత గీసిన పదానికి అర్థం గుర్తించండి.
A) జీవనౌషధం
B) జీలకట్ట
C) కారణం
D) ఆధారం
జవాబు:
A) జీవనౌషధం
14. నీకు మాత్రం తిండికి, బట్టకు ఎప్పుడూ కఱవె – గీత గీసిన పదానికి అర్థం గుర్తించండి.
A) నిండు
B) సమం
C) క్షామమె
D) ఎక్కువ
జవాబు:
C) క్షామమె
15. పండ్లనిచ్చిన వృక్షమును గూర్చి ఆలోచించరు – గీత గీసిన పదానికి అర్థం గుర్తించండి.
A) కొమ్మ
B ) మొక్క
C) మొగ్గ
D ) చెట్టు
జవాబు:
D ) చెట్టు
16. వ్యవసాయాన్ని చేయడంలో నీ శరీరం అస్థిపంజరంగా మారింది – గీత గీసిన పదానికి అర్థం గుర్తించండి.
A) ఎముక
B) బోను
C) ఎముకల గూడు
D) పుర్రె
జవాబు:
C) ఎముకల గూడు
17. నీకు కొదవ ఏముంది? – గీత గీసిన పదానికి అర్థం గుర్తించండి.
A) లోపం
B) స్థాయి
C) స్థానం
D) హీనం
జవాబు:
A) లోపం
18. బ్రతకడంకోసం స్పర్థ సహజమైన కాలం ఇది – గీత గీసిన పదానికి అర్థం గుర్తించండి.
A) పందెం
B) పోటీ
C) తగాదా
D) యుద్ధం
జవాబు:
B) పోటీ
19. జీవితం అనే సంగ్రామంలో విజయం పొందాలి – గీత గీసిన పదానికి అర్థం గుర్తించండి.
A) పందెం
B) పోటీ
C) యుద్ధం
D) తిట్టు
జవాబు:
C) యుద్ధం
2. పర్యాయపదాలు :
20. ‘వారి సంపదకై యీసు గూరబోవవు’ – గీత గీసిన పదానికి సమానార్థక పదాన్ని గుర్తించండి.
A) ఆశ
B) ఈర్ష్య
C) వాంఛ
D) ప్రేమ
జవాబు:
B) ఈర్ష్య
![]()
21. ఈ ఏడాది నీరు లేక క్షామం వచ్చింది – గీత గీసిన పదానికి పర్యాయపదాలు గుర్తించండి.
A) క్షారం, కాయం
B) కామం, కారం
C) కరవు, అరువు
D) అనావృష్టి, కరవు
జవాబు:
D) అనావృష్టి, కరవు
22. అసూయ మనిషిని రాక్షసుణ్ణి చేస్తుంది – గీత గీసిన పదానికి పర్యాయపదాలు గుర్తించండి.
A) అనసూయ, ఈసు
B) ఈర్ష్య, ఈసు
C) ఈర్ష్య, ద్వేషం
D) కోపం, క్రోధం
జవాబు:
B) ఈర్ష్య, ఈసు
23. శ్రుతిమించి నుతి కూడదు – గీత గీసిన పదానికి పర్యాయపదాలు గుర్తించండి.
A) బావి, నూయి
B) చెరువు, బావి
C) ప్రశంస, పొగడ్త
D) ధర్మం, దానం
జవాబు:
C) ప్రశంస, పొగడ్త
24. కన్నులున్న వారిని సైతం గుడ్డివారిని చేస్తున్నది అంధకారం – గీత గీసిన పదానికి పర్యాయపదాలు గుర్తించండి.
A) అక్షి, కుక్షి
B) నేత్రం, నయనం
C) ఆత్రం, నయనం
D) నేత్రం, నయం
జవాబు:
B) నేత్రం, నయనం
25. మా తాత అంటే మాకెంతో ఇష్టం – గీత గీసిన పదానికి పర్యాయపదాలు గుర్తించండి.
A) తండ్రి తండ్రి, పితామహుడు
B) తల్లి తండ్రి, పితామహి
C) బ్రహ్మ, తండ్రి
D) విధాత, తాత
జవాబు:
A) తండ్రి తండ్రి, పితామహుడు
26. రాయలు గొప్ప క్ష్మా పాలకుడు – గీత గీసిన పదానికి పర్యాయపదాలు గుర్తించండి.
A) భూమి, రాజు
B) నేల, రేడు
C) ధరణీ, మంత్రి
D) వసుధ, పృథ్వి
జవాబు:
D) వసుధ, పృథ్వి
![]()
27. మనదేశం వ్యవసాయం ప్రధాన వృతిగా గల దేశం – గీత గీసిన పదానికి పర్యాయపదాలు గుర్తించండి.
A) సాగు, బాగు
B) సేద్యం, కృషి
C) కరిసనం, కూలీ
D) సేద్యం, మద్యం
జవాబు:
B) సేద్యం, కృషి
28. నీ హలము కన్నను కవి కలము గొప్పదగునె? – గీత గీసిన పదానికి పర్యాయపదాలు గుర్తించండి.
A) అరక, కత్తి
B) పార, ఖడ్గము
C) నాగలి, సీరము
D) గునపము, నాగలి
జవాబు:
C) నాగలి, సీరము
29. ‘నేల నూతులకుగ్గాలు నిలుపువారు’ – గీత గీసిన పదానికి పర్యాయపదాలు ఏవి?
A) బావులు, కూపములు
B) గోతులు, పాతరలు
C) తాళ్ళు, నూతులు
D) చేలు, పొలములు
జవాబు:
A) బావులు, కూపములు
30. ‘కావున కృషీవలా నీవె కారణమవు’ – గీత గీసిన పదానికి పర్యాయపదాలు ఏవి?
A) రైతు, కార్మికుడు
B) కర్షకుడు, సైరికుడు
C) రైతు, పనివాడు
D) శ్రామికుడు, కార్మికుడు
జవాబు:
B) కర్షకుడు, సైరికుడు
31. వృక్షములు మానవుల పాలిటి ప్రత్యక్ష దైవాలు – గీత గీసిన పదానికి పర్యాయపదాలేవి?
A) చెట్టు, గుట్టు
B) పైరు, పచ్చ
C) తరువు, చెట్టు
D) తీగ, పాదు
జవాబు:
C) తరువు, చెట్టు
![]()
32. ‘జీవన సంగ్రామం అనే పోరాటంలో శ్రామికుడికే విజయం ‘ – గీత గీసిన పదాలకు పర్యాయపదం గుర్తించండి.
A) పరిశ్రమ
B) కృషి
C) రణము
D) ప్రయత్నం
జవాబు:
C) రణము
3. వ్యుత్పత్యర్థాలు :
33. ‘కావ్యం’ వ్యుత్పత్తి గుర్తించండి.
A) కవికర్త
B) కవి కర్మము
C) కవి క్రియ
D) కవి హేతువు
జవాబు:
B) కవి కర్మము
34. తిథి, వార, నక్షత్ర, నియమం లేక భోజనానికి వచ్చేవాడు – వ్యుత్పత్త్యర్థం గుర్తించండి.
A) చుట్టం
B) మిత్రుడు
C) అతిథి
D) హరిదాసు
జవాబు:
C) అతిథి
35. చేసిన మేలు మఱచువాడు నరకానికి పోతాడు – గీత గీసిన వానికి వ్యుత్పత్త్యర్థం గుర్తించండి.
A) ధన్యుడు
B) ధర్మాత్ముడు
C) పుణ్యశీలి
D) కృతఘ్నుడు
జవాబు:
D) కృతఘ్నుడు
36. సత్పురుషులయందు పుట్టు మాటలు శిరోధార్యాలు – గీత గీసిన వానికి వ్యుత్పత్త్యర్థం గుర్తించండి.
A) సత్యం
B) ప్రాణం
C) జీవితం
D) గుండె
జవాబు:
A) సత్యం
37. ‘పున్నామ నరకం నుండి కాపాడువాడు’ – దీని వ్యుత్పత్త్యర్థం గుర్తించండి.
A) అల్లుడు
B) తమ్ముడు
C) పుత్రుడు
D) మిత్రుడు
జవాబు:
C) పుత్రుడు
![]()
38. ‘భారమును వహించుట యందు క్షమ కలది’ – వ్యుత్పత్యర్థం గుర్తించండి.
A) క్షా
B) క్యా
C) క్ష్వా
D) క్ష్మా
జవాబు:
D) క్ష్మా
39. ‘కృషీవలుడు’ పదానికి వ్యుత్పత్తిని గుర్తించండి.
A) కృషి చేసేవాడు
B) భూమిని దున్ని బ్రతికేవాడు
C) పొలంపని చేసేవాడు
D) కార్మికుడు
జవాబు:
B) భూమిని దున్ని బ్రతికేవాడు
4. నానార్థాలు :
40. మానవుడు కాల మాన పరిస్థితులకు అనుగుణంగా ఉండాలి – గీత గీసిన పదానికి నానార్థాలు గుర్తించండి.
A) సమయం, నలుపు
B) చావు, మరణం
C) నలుపు, తెలుపు
D) సమయం, సాయం
జవాబు:
A) సమయం, నలుపు
41. ఆత్మ, పరమాత్మ వేరని ద్వైత సిద్ధాంతం చెబుతుంది – గీత గీసిన పదానికి నానార్థాలు గుర్తించండి.
A) మనస్సు, మనసు
B) బుద్ధి, పరమాత్మ
C) దేహం, శరీరం
D) బుద్ధి, బుద్ధుడు
జవాబు:
A) మనస్సు, మనసు
42. రసములు తొమ్మిది – గీత గీసిన పదానికి నానార్థాలు గుర్తించండి.
A) చారు, సాంబారు
B) పాదరసం, హసరసం
C) రుచి, కోరిక
D) శృంగారాది, హాస్యం
జవాబు:
C) రుచి, కోరిక
![]()
43. నేడు ధరకు విపరీతంగా ధర పెరిగింది – గీత గీసిన పదాలకు నానార్థాలు రాయండి.
A) ఖరీదు, ప్రియము
B) నేల, నెల
C) ధరణి, వెల
D) రేటు, గోటు
జవాబు:
C) ధరణి, వెల
44. సరియైన వర్షం లేక పంటలు పండలేదు – గీత గీసిన పదం నానార్థాలు ఏవి?
A) వాన, సంవత్సరం
B) వర్షం, హర్షం
C) వాన, నాన
D) ఏడు, పంట
జవాబు:
A) వాన, సంవత్సరం
5. ప్రకృతి – వికృతులు :
45. పూల కాంక్ష చెట్టు తల్లి పాదాల చెంత రాలిపోవాలని – గీత గీసిన పదానికి వికృతిని గుర్తించండి.
A) కచ్చు
B) కోరిక
C) ఇచ్చ
D) వాంఛ
జవాబు:
A) కచ్చు
46. కష్టము చేసినవాడు ఫలితం తప్పక పొందుతాడు – గీత గీసిన పదానికి వికృతి పదం గుర్తించండి.
A) కసము
B) కసుట
C) కసట
D) కసటము
జవాబు:
B) కసుట
![]()
47. ఆత్మవిశ్వాసం ఎప్పుడు విడిచిపెట్టకూడదు – గీత గీసిన పదానికి వికృతి పదం గుర్తించండి.
A) నమ్మకం
B) విశవాసం,
C) విసువాసం
D) విసాసం
జవాబు:
C) విసువాసం
48. స్పర్థా వర్తతే విద్యా – గీత గీసిన పదానికి వికృతి పదం గుర్తించండి.
A) పోటీ
B) పందెం
C) యుద్ధం
D) పంతం
జవాబు:
D) పంతం
49. మట్టి పిసుక్కొనే వారిని హీనంగా చూడకు – గీత గీసిన పదానికి ప్రకృతి పదం గుర్తించండి.
A) మర్యం
B) మృత్తిక
C) నేల
D) భూమి
జవాబు:
B) మృత్తిక
50. పుత్రుడు లేనివారికి మోక్షపదం రాదా? – గీత గీసిన పదానికి వికృతి పదం గుర్తించండి.
A) పుతుడు
B) సుతుడు
C) బొట్టె
D) కొడుకు
జవాబు:
C) బొట్టె
51. వారి సంపదకై ఈసు గూరబోవు – గీత గీసిన పదానికి ప్రకృతి పదం ఏది?
A) ఈస
B) ఈర్ష్య
C) అసూయ
D) ద్వేషం
జవాబు:
B) ఈర్ష్య
52. అఖిల వాణిజ్యములు సిరి కాటపట్టు – గీత గీసిన పదానికి ప్రకృతిని గుర్తించండి.
A) సిరీ
B) హరీ
C) శ్రీ
D) హరి
జవాబు:
C) శ్రీ
53. ఎంత నిర్మలమోయి నీ హృదయ కళిక – గీత గీసిన పదానికి వికృతిని గుర్తించండి.
A) ఎద
B) డెందము
C) చిత్తము
D) గుండె
జవాబు:
A) ఎద
6. సంధులు :
54. ‘కషార్జితం’ – పదాన్ని విడదీయుము.
A) కష్ట + ఆర్జితం
B) కష్ట + అర్జితం
C) కష్టా + ఆర్జితం
D) కష్టా + అర్జితం
జవాబు:
A) కష్ట + ఆర్జితం
55. ‘తో దోపు’ పదాన్ని విడదీయుము.
A) తో + తోపు
B) తోపు + తోపు
C) తో + దోపు
D) తోపు + దోపు
జవాబు:
B) తోపు + తోపు
56. ‘కన్ను + ఎత్తి’ – సంధి పేరేమిటి?
A) ఇత్వసంధి
B) అత్వసంధి
C) ఉత్యసంధి
D) గుణసంధి
జవాబు:
C) ఉత్యసంధి
![]()
57. కింది వానిలో గసడదవాదేశ సంధికి ఉదాహరణను గుర్తించండి.
A) వస్తున్న
B) దుర్భరావస్థ
C) హితార్థ
D) ప్రొద్దు గ్రుంకు
జవాబు:
D) ప్రొద్దు గ్రుంకు
58. ‘ద్రుత ప్రకృతికము మీది పరుషములకు సరళములగు’ – ఈ సూత్రానికి సంబంధించిన ఉదాహరణను కింది వానిలో గుర్తించండి.
A) తోదోపు
B) కన్నెత్తియుం జూతురే
C) జీవగడ్డ
D) ప్రొద్దువొడిచిన
జవాబు:
B) కన్నెత్తియుం జూతురే
59. ‘దుర్భరావస్థ’ అనే పదాన్ని విడదీయండి.
A) దుర్భ + రావస్థ
B) దుర్భరా + వస్థ
C) దుర్భరము + అవస్థ
D) దుర్భర + అవస్థ
జవాబు:
D) దుర్భర + అవస్థ
60. ‘భోగోపలబ్ది’ – ఈ పదంలో గల సంధి ఏది?
A) ఉత్వ సంధి
B) గుణ సంధి
C) సవర్ణదీర్ఘ సంధి
D) వృద్ధి సంధి
జవాబు:
B) గుణ సంధి
61. ‘ఉత్కటము + దుర్బరావస్థ’ – సంధి జరిగిన పిమ్మట ఏర్పడిన పదం ఏది?
A) ఉత్కటపు దుర్భరావస్థ
B) ఉత్కటంపు అవస్థ
C) ఉత్కట దుర్భరావస్థ
D) ఉత్కటావస్థ
జవాబు:
A) ఉత్కటపు దుర్భరావస్థ
62. “సిరి కాటపట్టు’ – విడదీసి, సంధిని గుర్తించండి.
A) సిరి + కాటపట్టు (ఇత్వ సంధి)
B) సిరిక + ఆటపట్టు (సవర్ణదీర్ఘ సంధి)
C) సిరికిన్ + ఆటపట్టు (ఇత్వ సంధి)
D) సిరికాట + పట్టు (అత్వ సంధి)
జవాబు:
C) సిరికిన్ + ఆటపట్టు (ఇత్వ సంధి)
7. సమాసాలు :
63. భూమి పుత్రుడు’ లోని విగ్రహవాక్య విభక్తిని గుర్తించండి.
A) చేత
B) వలస
C) యొక్క
D) అందు
జవాబు:
C) యొక్క
64. “జీవన సంగ్రామం’ సమాసం పేరేమిటి?
A) రూపకం
B) షష్టి
C) ద్వంద్వం
D) బహువ్రీహి
జవాబు:
A) రూపకం
![]()
65. ‘హృదయకళిక’ లోని విభక్తిని గుర్తించండి.
A) మైన
B) అనెడి
C) లో
D) అందు
జవాబు:
B) అనెడి
66. ‘శూరులందు శ్రేషుడు’ – సమాసం పేరేమిటి?
A) షష్టీ
B) తృతీయా
C) బహువ్రీహీ
D) సప్తమీ
జవాబు:
D) సప్తమీ
67. విశేషణ పూర్వపద కర్మధారయ సమాసానికి ఉదాహరణను గుర్తించండి.
A) జీవన స్పర్థ
B ) పవిత్రమూర్తి
C) ధరణీపతి
D) హాలిక వర్య
జవాబు:
B ) పవిత్రమూర్తి
68. ‘జీవన సంగ్రామము’ పదానికి విగ్రహవాక్యం గుర్తించండి.
A) జీవనము చేత సంగ్రామం
B) జీవనం కొఱకు సంగ్రామం
C) జీవనము అనే సంగ్రామం
D) జీవనము, సంగ్రామము
జవాబు:
C) జీవనము అనే సంగ్రామం
69. ‘హృదయ కళిక‘ వికసించినది – గీత గీసిన పదం ఏ సమాసం?
A) రూపక సమాసం
B) ద్విగు సమాసం
C) ద్వంద్వము
D) ఉపమాన ఉత్తరపద కర్మధారయం
జవాబు:
A) రూపక సమాసం
![]()
70. ‘చిటికెలతో పందిళ్ళు’ – సమాస పదంగా కూర్చండి.
A) చిటికెల పందిళ్ళు
B) చిటికె పందిళ్ళు
C) పందిరి చిటికెలు
D) చిటిక పందిళ్ళు
జవాబు:
A) చిటికెల పందిళ్ళు
8. గణాలు:
71. ‘హితార’ గురులఘువులు గుర్తించండి.
A) III
B) IIU
C) IUI
D) UII
జవాబు:
C) IUI
72. ‘గౌరవం’ అనేది ఏ గణం?
A) మ గణం
B) ర గణం
C) న గణం
D) భ గణం
జవాబు:
B) ర గణం
73. ‘శ్రమలు’ గురులఘువులు గుర్తించండి.
A) III
B) UII
C) IUI
D) IIU
జవాబు:
A) III
74. ‘న, జ, భ, జ, జ, జి, ర’ గణాలు ఏ వృత్తానికి చెందినవి?
A) ఉత్పలమాల
B) మత్తేభం
C) శార్దూలం
D) చంపకమాల
జవాబు:
D) చంపకమాల
75. ‘1 సూర్యగణం, 2 ఇంద్రగణాలు, 2 సూర్యగణాలు’ – ఇవి ఏ పద్యానికి చెందిన గణాలు (S.A. II – 2017-18)
A) ఆటవెలది
B) తేటగీతి
C) కందం
D) సీసం
జవాబు:
B) తేటగీతి
76. మత్తేభ వృత్తంలోని యతి స్థానం
A) 11
B) 10
C) 14
D) 13
జవాబు:
C) 14
77. ‘భ,ర,న,భ,భ,ర,వ’ గణాలు ఏ వృత్తానికి చెందినవి?
A) తేటగీతి
B) ఆటవెలది
C) కందము
D) ఉత్పలమాల
జవాబు:
D) ఉత్పలమాల
![]()
78. తేటగీతి పద్యపాదంలో ఉండే గణాలు ఏవో గుర్తించండి.
A) 3 సూర్య, 2 ఇంద్ర గణాలు
B) 1 సూర్య, 2 ఇంద్ర, 2 సూర్య గణాలు
C) 5 సూర్య గణాలు
D) భరనభభరవ
జవాబు:
B) 1 సూర్య, 2 ఇంద్ర, 2 సూర్య గణాలు
79. ‘సంగ్రామం’ అనేది ఏ గణం?
A) భ గణం
B) ర గణం
C) త గణం
D) మ గణం
జవాబు:
D) మ గణం
9. అలంకారాలు :
80. ‘జీవన సంగ్రామం’ రూపకాలంకారానికి చెందిన ఉదాహరణ – దీనిలో ఉపమానం గుర్తించండి.
A) జీవనం
B) సంగ్రామం
C) రెండూ
D) ఏదీకాదు
జవాబు:
B) సంగ్రామం
81. ‘హృదయ కళిక’ దీనిలోని అలంకారం గుర్తించండి.
A) ఉపమా
B) అతిశయోక్తి
C) రూపకం
D) శ్లేష
జవాబు:
C) రూపకం
82. ‘జింకలు బిత్తరి చూపులు చూస్తూ చెవులు నిగిడ్చి చెంగు చెంగున దూకుతున్నాయి’ – ఈ వాక్యంలో గల అలంకారమును గుర్తించండి.
A) ఛేకానుప్రాస
B) స్వభావోక్తి
C) అతిశయోక్తి
D) శ్లేష
జవాబు:
B) స్వభావోక్తి
![]()
83. వాక్యాలకు బింబ ప్రతిబింబత్వం ఉన్నట్లయితే అది ఏ అలంకారం?
A) స్వభావోక్తి
B) దృష్టాంతం
C) ఉపమా
D) అర్థాంతరన్యాస
జవాబు:
B) దృష్టాంతం
10. ఆధునిక వచనాన్ని గుర్తించడం:
84. ‘శ్రమలు లేకయె ఫలములు దుముకబోవు’ – దీనికి ఆధునిక వాక్యం ఏది?
A) శ్రమ పడకుండా ఫలితాలు దుముకవు.
B) శ్రమలు లేకుండా ఫలాలు రావు
C) శ్రమ లేనిదే ఫలితాలు అవే రావు
D) శ్రమే లేకపోతే ఫలాలు ఎక్కడివి
జవాబు:
A) శ్రమ పడకుండా ఫలితాలు దుముకవు.
85. ‘సిరియె భోగోపలబ్ధికి జీవగట్టి’ – ఆధునిక వాక్యం గుర్తించండి.
A) సిరి సుఖాలను పొందడానికి మందు
B) సిరి భోగోపలబ్దికి జీవగట్టు
C) సంపదయే సుఖాలన్నిచ్చే మందు
D) సిరియె సుభాలనిచ్చే జీవనౌషధం
జవాబు:
B) సిరి భోగోపలబ్దికి జీవగట్టు
11. కర్తరి, కర్మణి వాక్యాలను గుర్తించడం :
86. రైతు పంట పండించాడు – కర్మణి వాక్యము గుర్తించండి.
A) రైతు పంట పండించబడింది
B) రైతు చేత పంట పండించాడు
C) రైతుచే పంట పండించబడింది
D) రైతు పంటచేత పండించాడు
జవాబు:
C) రైతుచే పంట పండించబడింది
![]()
87. ‘నీవు చెప్పిన విషయం పరిశీలించబడుతుంది’ – ఈ కర్మణి వాక్యానికి కర్తరి వాక్యం గుర్తించండి.
A) నీవు చెప్పిన విషయాన్ని పరిశీలిస్తారు.
B) నీవు చెప్పిన విషయం పరిశీలిస్తాము.
C) నీవు చెప్పినది పరిశీలించరు.
D) నీ చేత చెప్పిన విషయం పరిశీలిస్తారు.
జవాబు:
A) నీవు చెప్పిన విషయాన్ని పరిశీలిస్తారు.
12. ప్రత్యక్ష, పరోక్ష కథనాలను గుర్తించడం:
88. “నీకు సుఖం ఉందా” అని రైతును కవి అడిగాడు – పరోక్ష కథనం గుర్తించండి.
A) సుఖం ఉందాని రైతును కవి అడిగాడు
B) సుఖంగా ఉన్నావాయని రైతును కవి అడిగాడు
C) సుఖం ఉందాయని కవితో రైతు అడిగాడు
D) రైతుతో సుఖం ఉందాని అన్నాడు కవి.
జవాబు:
A) సుఖం ఉందాని రైతును కవి అడిగాడు
89. వాని చేతిలోని నాగలి గొప్పదని దువ్వూరి అన్నారు – ప్రత్యక్ష కథనం గుర్తించండి.
A) నా చేతిలోని నాగలి గొప్పది అని దువ్వూరి అన్నారు.
B) నీ చేతిలోని నాగలి గొప్పది” అని దువ్వూరి అన్నారు.
C) అతని చేతిలోని నాగలి గొప్పది అని దువ్వూరి అన్నారు.
D) నీ చేతిలోని నాగలి గొప్పదే కదా అని దువ్వూరి అన్నారు.
జవాబు:
B) “నీ చేతిలోని నాగలి గొప్పది” అని దువ్వూరి అన్నారు.
90. “చిన్నప్పటి నుండి నాకు బోటనీ అభిమాన విషయం” అన్నాడు రచయిత-దీనిని పరోక్ష వాక్యాన్ని గుర్తించండి.
A) చిన్నప్పటి నుండి నీకు బోటనీ అభిమాన విషయ మని రచయిత అన్నాడు.
B) చిన్నప్పటి నుండి తనకు బోటనీ అభిమాన విషయ మని రచయిత అన్నాడు.
C) చిన్నప్పటి నుండి ఆమెకు బోటనీ అభిమాన విషయ మని రచయిత అన్నాడు.
D) చిన్నప్పటి నుండి ఆయనకు బోటనీ అభిమాన విషయమని రచయిత అన్నాడు.
జవాబు:
B) చిన్నప్పటి నుండి తనకు బోటనీ అభిమాన విషయ మని రచయిత అన్నాడు.
13. వ్యతిరేకార్థక వాక్యాన్ని గుర్తించడం :
91. రైతుకు తిండి లేదు – వ్యతిరేక వాక్యం గుర్తించండి. చెందినదో గుర్తించండి?
A) తిండి ఉంది
B) రైతుకు తిండి ఉంది
C) రైతుకు తిండి పెట్టు
D) రైతుకు ఆకలి లేదు
జవాబు:
B) రైతుకు తిండి ఉంది
![]()
92. పళ్ళు తినేవారు చెట్టును చూడరు – వ్యతిరేక వాక్యం గుర్తించండి.
A) పళ్ళు లేనివారు చెట్టును చూస్తారు
B) చూస్తారు
C) పళ్ళు తినేవారు చెట్టును చూస్తారు
D) చూడరు
జవాబు:
C) పళ్ళు తినేవారు చెట్టును చూస్తారు
![]()
93. ‘ఒకే ఒక్క ఆవు తిరిగి రాలేదు’ – వ్యతిరేకార్థక వాక్యాన్ని గుర్తించండి.
A) ఒకే ఒక్క ఆవు తిరిగి వచ్చింది.
B) ఆవులన్నీ తిరిగి వచ్చాయి.
C) ఒకే ఒక్క ఆవు తిరిగి రాదు.
D) ఒక్క ఆవు మాత్రం వచ్చింది.
జవాబు:
A) ఒకే ఒక్క ఆవు తిరిగి వచ్చింది.
14. వాక్యరకాలను గుర్తించడం:
94. రైతు మనస్సు స్వచ్ఛమైంది. రైతు మనస్సు అసూయలేనిది – సంయుక్త వాక్యం గుర్తించండి.
A) రైతు మనస్సు స్వచ్చమైంది, అసూయలేనిది.
B) రైతు మనస్సు స్వచ్ఛమైంది, అనసూయలేనిది
C) స్వచ్చమైంది మనస్సు, అసూయలేనిది రైతు
D) స్వచ్ఛమైంది, అసూయ ఉంది రైతు మనస్సు
జవాబు:
A) రైతు మనస్సు స్వచ్చమైంది, అసూయలేనిది.
95. బుద్దుడు వటవృక్ష చ్ఛాయకు వచ్చాడు. అష్టాంగ ధర్మ ప్రవచనం ప్రారంభమైంది – ఈ వాక్యాలలో సంయుక్త వాక్యాన్ని గుర్తించండి.
A) బుద్ధదేవుడు వటవృక్ష చ్ఛా యకు వచ్చి అష్టాంగ ధర్మ ప్రవచనం ప్రారంభం చేశాడు.
B) బుద్ధదేవుడు వటవృక్ష చ్ఛాయకు రాగానే అష్టాంగ ధర్మ ప్రవచనం ప్రారంభమైంది.
C) బుద్ధదేవుడు వటవృక్ష చ్ఛాయకు వచ్చాడు వెంటనే అష్టాంగ ధర్మ ప్రవచనం ప్రారంభమైంది.
D) బుద్ధదేవుడు వచ్చిన వెంటనే అష్టాంగ ధర్మ ప్రవచనం ప్రారంభం అయ్యింది.
జవాబు:
C) బుద్ధదేవుడు వటవృక్ష చ్ఛాయకు వచ్చాడు వెంటనే అష్టాంగ ధర్మ ప్రవచనం ప్రారంభమైంది.
15. ప్రక్రియలను గుర్తించడం :
96. ‘శ్రమ చేయకుండా ఫలితాలు రావు’ – ఇది ఏ ప్రక్రియకు –
A) చేదర్థకం
B) ప్రశ్నార్థకం
C) శత్రర్థకం
D) క్యార్ధకం
జవాబు:
A) చేదర్థకం
97. ‘రైతు ఉదయం నుండి సాయంత్రం వరకు కష్టపడతాడు” -ఏ ప్రక్రియ?
A) ఆశ్చర్యార్థకం
B) సామర్థ్యార్థకం
C) నిషేధార్థకం
D) హేత్వర్ణకం
జవాబు:
B) సామర్థ్యార్థకం
98. పండ్లు ఇచ్చిన చెట్టు గూర్చి ఎప్పుడైనా ఆలోచిస్తారా? -ఏ ప్రక్రియ?
A) సందేహార్థక
B) విధ్యర్థకం
C) ప్రశ్నార్ధకం
D) అనుమత్యర్థకం
జవాబు:
C) ప్రశ్నార్ధకం
![]()
99. నీ గొప్పతనాన్ని నీవు తెలుసుకో – ఏ ప్రక్రియ?
A) ప్రార్ధనార్థకం
B) ఆశీర్వాద్యర్థకం
C) సామర్థ్యార్థకం
D) ప్రేరణార్థకం
జవాబు:
D) ప్రేరణార్థకం
100. ఈ కింది వాక్యంలోని అసమాపక క్రియ ఏదో గుర్తించండి. ‘కాపలా కాస్తూ హాయిగా తిని కూర్చో’.
A) చేదర్థకం
B) శత్రర్థకం
C) తద్ధర్మార్థకం
D) ప్రశ్నార్థకం
జవాబు:
B) శత్రర్థకం







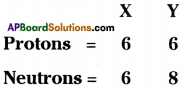
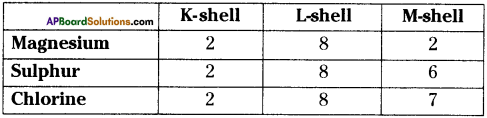

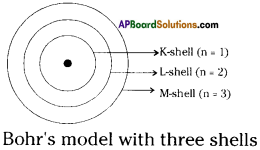
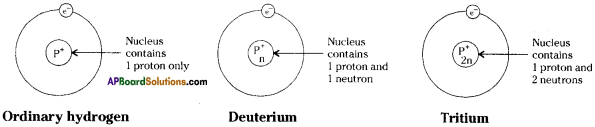


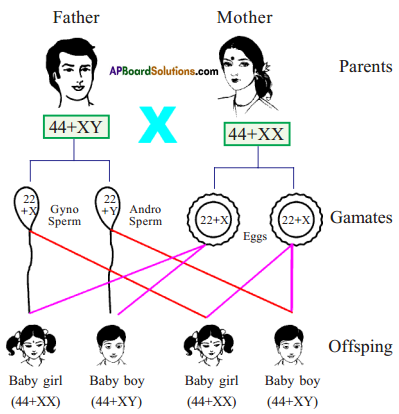
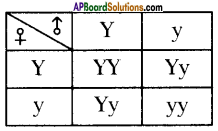
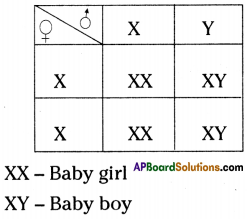
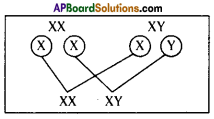 Who decides the sex of the baby – mother or father? How?
Who decides the sex of the baby – mother or father? How?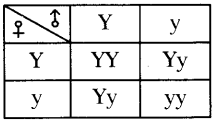 (OR)
(OR)

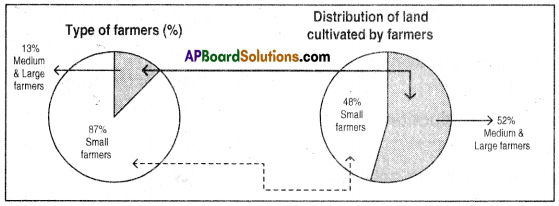
 i) Write phenotypic ratio of monohybrid cross.
i) Write phenotypic ratio of monohybrid cross.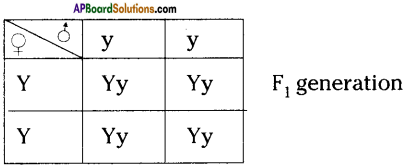 All pea plants are yellow in F1 generation on self pollination in F1 generation.
All pea plants are yellow in F1 generation on self pollination in F1 generation.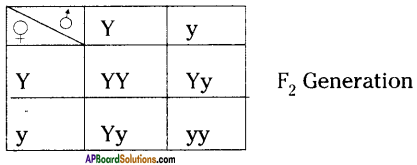 In F2 generation, we can observe that 75% are yellow seed producing pea plants and 25% are green ones.
In F2 generation, we can observe that 75% are yellow seed producing pea plants and 25% are green ones.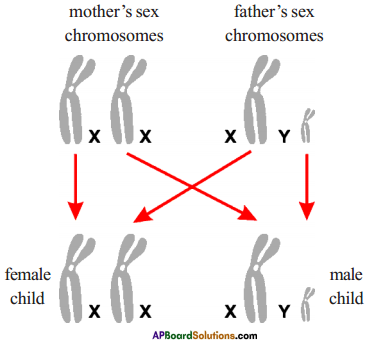 Answer:
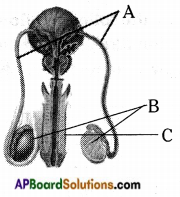
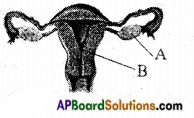
Answer: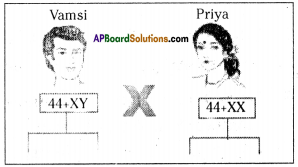 a) Draw a probable diagram showing transfer of chromosomes from parents to give birth to male child.
a) Draw a probable diagram showing transfer of chromosomes from parents to give birth to male child.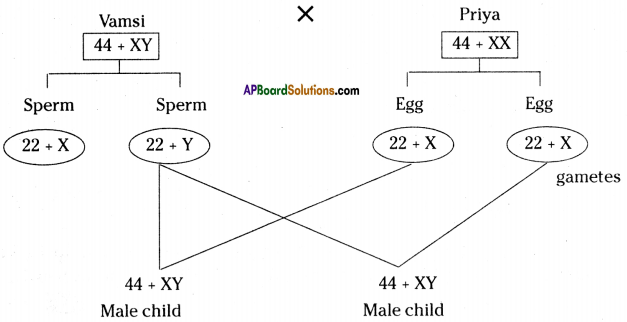 b) Who determines the sex of the baby? How can you say ?
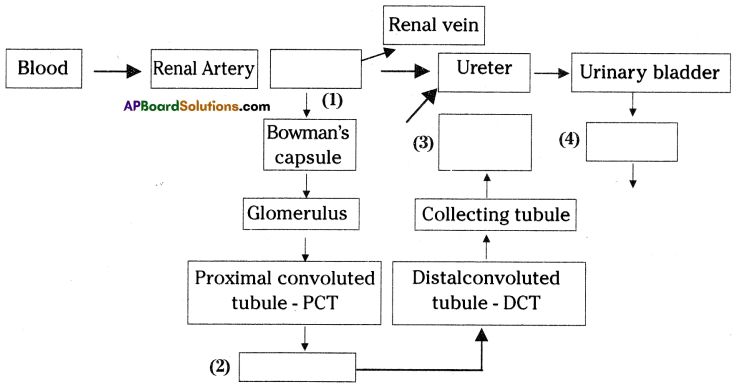
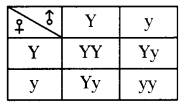
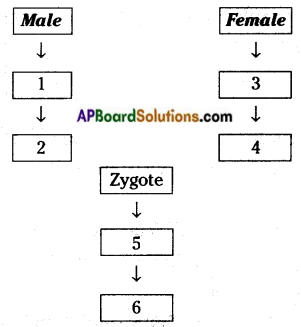
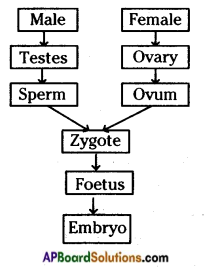
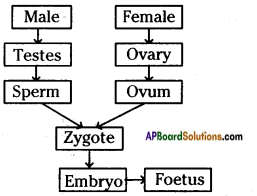
b) Who determines the sex of the baby? How can you say ?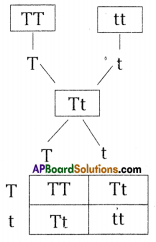 i) What does the flow – chart represent?
i) What does the flow – chart represent?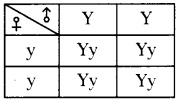



















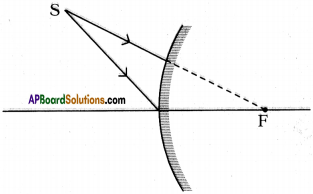
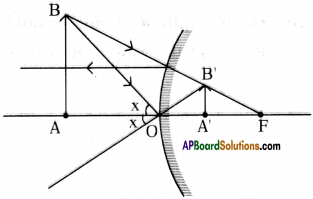


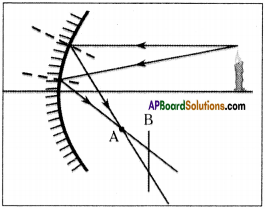

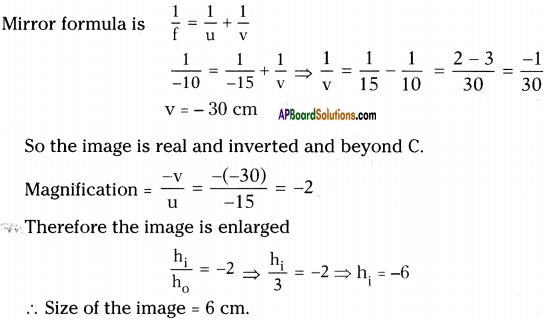


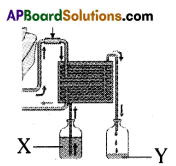 The above is a procedure of haemodialysis in a hospital.
The above is a procedure of haemodialysis in a hospital.