These AP 9th Class Social Studies Important Questions 1st Lesson Our Earth will help students prepare well for the exams.
AP State Syllabus 9th Class Social 1st Lesson Important Questions and Answers Our Earth
9th Class Social 1st Lesson Our Earth 1 Mark Important Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Which continent is extended in four hemispheres In the given map. (SA-III : 2015 – 16)
Answer:
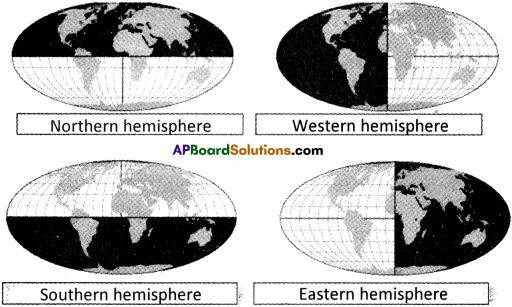
Africa continent.
Question 2.
What do you mean by anti meridian? (SA-III : 2016 – 17)
Answer:
The anti meridian is the meridian of longitude opposite the Prime-Meridian.
9th Class Social 1st Lesson Our Earth 2 Marks Important Questions and Answers
Question 1.
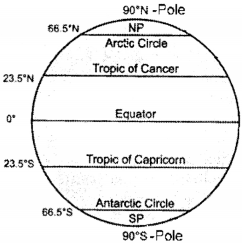
Draw the picture of the Globe and point out all the latitudes that are given special names on it. (SA-III : 2016 – 17)
Answer:
Question 2.
Why is it important to know the latitude and longitude of a place on map? How can it be useful? (SA-II : 2018 – 19)
Answer:
It is very important to know about latitudes and longitudes of a place by the following reasons.
- The particular location of a place on the earth can only be traced precisely with the help of latitude and longitude of that place.
- Latitude also help us in understanding the pattern of wind circulation on the global surface.
- Longitudes are useful to us to define the east-west position of a location on the planet.
- Longitudes are useful to us to know the time of the place.
Question 3.
Wegener hypothesised that the super continents of pangea broke up into two blocks –
1) Laurensia
2) Gondwana. It took millions of years for the continents to reach the present shapes and positions on the globe. (SA-I : 2018 – 19)
1) Laurensia : North America, Greenland, and all of the Eurasia north of Indian sub continent.
2) Gondwana : South America, Africa, Madagascar, India, Arabia, Malaysia, East Indies, Australia and Antartica.
Based on the above information given – answer the following questions.
a) Write any two land masses of present Asian continent which were formed from Gondwana?
b) From which block was the present Europe continent formed?
Answer:
a) India, Arabia, Malaysia, East Indies.
b) The present Europe continent was formed from Laurensia block.

Question 4.
If every state in India follows its local time then what problems will arise? (SA-I : 2019 – 20)
Answer:
If every state follows its local time, the following problems will arise :
- People travelling to different states would have to change their clocks too often.
- There would be confusion and chaos in the timings of railways, airlines, buses etc.
- The schedules of television shows, live shows and games, news etc. would be disrupted.
9th Class Social 1st Lesson Our Earth 4 Marks Important Questions and Answers
Question 1.
What is the difference between local time and standard time ? If every state follows its local time then what problems will rise in India? (SA-III : 2015 – 16)
Answer:
Difference between Local and Standard time:
| Local Time |
Standard Time |
| 1) The time of a place when the mid day sun is over head is called local time. |
1) The local time of the standard meridian of a country is called a standard time. |
| 2) It changes from place to place. |
2) It remains same for that particular country. |
| 3) The place on the same longitude has the same local time. |
3) The place on the same longitude has the different standard time. |
Example:
If the IST is 12.00 noon, the local of Mumbai is 39 minutes – IST = 11.21 minutes a.m. Since Mumbai is on 72°82′ east longitudes, it is 9°45′ behind the 82°30′. Thus the local time of Mumbai is 9.45 x 4 = 38 minutes.
If every state follows its local time, a lot of serious problems would rise. Some of them are being discussed hereunder.
- At the time of national calamities and disasters, it is very difficult for the national government to make necessary emergency announcement.
- At the time of wars and national emergency it is very difficult for the national government to alert all the defensive forces stationed in all the state capitals and the naval forces of all the coastal states.
- It is very difficult for Televisions and Radios to follow a single schedule to broadcast their programmes.
- Railways faces a difficult problem in preparing a timetable for its trains that travel through many states.

Question 2.
Describe the internal structure of the earth. (SA-III : 2016 – 17) (SA-I : 2018 – 19)
Answer:
The earth is made up of three main layers.
A) Crust:
- The outer part of the earth on which we live is called the crust.
- While the earth was boiling in a molten form the lighter particles cooled at the top and formed the layer of crust.
- The curst mostly consists of various kinds of rocks.
- This layer goes up to a depth of 30 to 100 kms.
B) Mantle:
- While the earth was boiling in a molten form the less heavier particles settled in the middle and formed the mantle.
- The upper part of the mantle is a pliable layer over which the crust floats.
- This layer consists mainly of chemicals called silicates.
- It exists at the depths from 100 kms to 2900 kms.
C) Core:
- While the earth was boiling in a molten form the heaviest substances formed core.
- It is composed of dense and heavy substances like Iron and Nickel.
- It exists at the depths from 2,900 kms to 6,376 kms.
- It can be divided into two sub-layers.
a) Outer core :
This layer is composed of liquid metallic material like nickel and iron. It is 2,900 – 5,100 kms in thickness.
b) Inner core :
The solid inner core is made up of iron compounds and heavy substances like gold. It is 5,100 – 6,376 kms in thickness.
9th Class Social 1st Lesson Our Earth Important Questions and Answers
Question 1.
How can you say the man himself is responsible for environmental crises?
Answer:
- More than any other animal human beings have been trying to make the earth a better place to live in.
- Trying to change ourselves and our surroundings we have entered into conflict with other inhabitants of the earth.
- For long we’ve been exploiting the earth for its resources.
- The reckless exploitation of the earth resulted in environmental crises such as global warming and poisoning of our soils, water and air.
- Thus we can say man himself is responsible for environmental crises.

Question 2.
What were the initial ideas of people about the earth, the sun the moon and other astronomical bodies?
Answer:
- For thousands of years humans have been looking into the sky trying to understand objects that shine there.
- Initially, people thought that earth was firm and stationary and all others went round it.
- They also thought that the earth, the stars and the sun have been like this forever and will be like this forever without any change.
Question 3.
Write about the phases of evolution of facts, about the astronomical bodies their birth and growth.
Answer:
- Initially, people were of the view that the earth was firm and stationary and all the other bodies went round it.
- About five hundred years ago scientists concluded that the earth is not in the middle of everything.
- The earth actually moves round the sun and that the sun itself is also moving.
- The countless stars in the sky are actually so many suns.
- During the last hundred years or so people learnt the stars are born, they grow old and even die.
- Scientists even came to know that the stars are actually part of larger groups called galaxies.
- There are millions of galaxies in the universe.
- Now scientists are of the view that the universe itself started some 13.7 billion years ago with a Big Bang and it may end several billion years later.
Question 4.
How dkl the universe come into existence?
Answer:
- The universe itself started some 13.7 billion years ago with a Big Bang.
- From this Big Bang, several galaxies were formed.
- Within these galaxies, stars were formed.
- Planets were formed around stars and went around them.
However these astronomical changes take place over thousands and even millions of years.
Question 5.
Describe the process of evolution of the Earth.
(OR)
How did the earth come into existence and get its present form?
Answer:
- The earth began to form around four and a half billion years ago.
- It began as a ball of swirling dust and clouds and passed through a molten age.
- Gradually it grew in size.
- It was very hot and was in molten stage.
- The lighter particles cooled at the top and formed a layer of crust.
- Heavier particles formed the part of the molten core.
- As the earth’s interior cooled and contracted, the outer crust wrinkled, forming ridges and basins.
- The rain filled the basins and thus oceans formed.
- Slowly atmosphere developed and slowly life appeared on the earth.
Question 6.
How and when did the life appear on earth?
Answer:
- Different kinds of gases including water vapour formed the atmosphere on earth.
- Most of these gases were such that life as we know it today could not survive on it.
- Because it did not have oxygen necessary for life to survive.
- It took a long time for the air to develop.
- Then life appeared on oceans first.
It slowly evolved into diverse forms – plants, animals and human beings.
Question 7.
Are the shapes and positions of the continents fixed and permanent as they appear on the globe?
Answer:
The shapes and positions of the continents may seem fixed at the time scale of human experience. But on old earth continents have moved, collided, merged and then been torn apart again.
Mountains have risen and been razed to the ground, oceans have formed and dried up. Valleys have been carved and so during the course of earth’s eventful history. Alfred Wegener’s theory of Continental drift proves the same idea.
Thus the shapes and positions of the continents are not fixed and permanent.

Question 8.
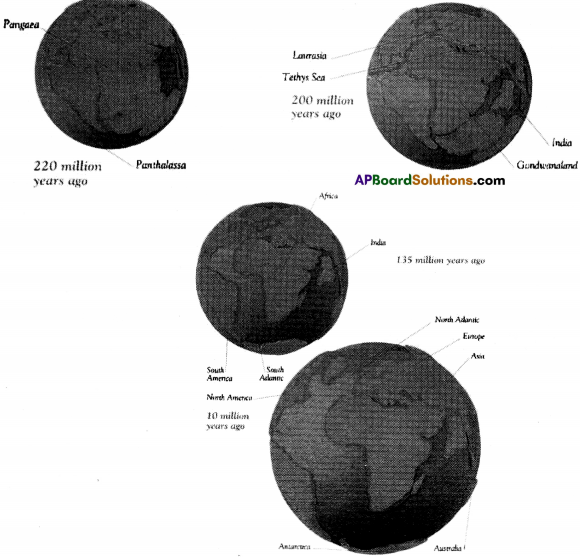
Describe the theory of continental drift.
Answer:
- In 1912 Alfred Wegener propounded the theory of continental drift to describe the present arrangement of continents and ocean basins.
- He postulated a massive super continent Pangaea that existed 220 million years ago.
- Pangaea, the hypothetical continent, from which present continents originated by the drift from Mesozoic era to the present.
- Wegener hypothesized that the super continent of Pangaea broke up to from :
a) Laurensia – consisting of present North America, Greenland and all of Eurasia north of Indian subcontinent and
b) Gondwana land – consisting of present South America, Africa, Madagascar, Arabia, India, Malaysia, East Indies, Australia and Antarctica.
- These two blocks were separated by a long shallow inland sea called Tethys sea.
- It took millions of years for the continents to reach the present shapes and positions on the globe.
- Even today many of the continents are moving very slowly pushing each other.
Question 9.
What do you know about latitudes?
Answer:
- Latitudes are imaginary lines drawn around the earth.
- The word ‘latitude’ comes to us from the Latin word ‘iatitudo’ meaning width.
- Latitudes are also called parallels because they are parallel to each other.
- Latitudes are circles.
- Latitudes are expressed in degrees (°), minutes (‘) and seconds (“).
- Latitude values range from 0° t* 90° North (the North Pole) and 90° South (the South Pole).
- Thus there are 180° main latitudes (not counting the equator)
- Equator, the 0° latitude is the largest among all the latitudes.
- Latitudes are used together with the longitudes to locate a place on the earth.
- Latitudes are used to locate the climatic zones on the earth.
Question 10.
What do you know about longitudes?
Answer:
- Longitudes are imaginary lines connecting North and South’Poles.
- Longitudes are semi-circles.
- Longitudes are also called meridians because when the sun is overhead on a longitude at the time on that longitude it is noon (meridianus).
- There are 360 longitudes in total.
- The longitudes from 0° to 180° to the east are called eastern longitudes.
- The longitudes from 0° to 180° to the west are called western longitudes.
- 0° meridian is called the Prime meridian or Greenwich meridian.
- Longitudes are also expressed in degrees (°), minutes (‘) and seconds (“).
Question 11.
How are the time zones formed and why are they formed?
Answer:
- It takes 4 minutes for the sun’s position to move 1° of longitude.
- This means that the time is different for each degree of longitude.
- This can cause a lot of confusion.
- Therefore to end up this confusion the world is divided into 24 time zones.
- The width of each time zone is 15° of longitude.
- This means the difference between one time zone and the next is 1 hour.
- As you go from Greenwich meridian, you add time; as you go west of the Greenwich meridian you subtract time.
Question 12.
Why does every country have its own standard time?
Answer:
- The world is divided into 24 time zones.
- The width of each time zone is 15° of longitude.
- This means that the difference between one time zone and the next is one hour.
- Some countries would have more than one time zone with less than one hour division.
- This is considered too complicated to be useful.
- That is why some countries choose the time along one of the meridians that pass throught their territory and follow the time of that meridian for the whole country.
- This time is called standard time.

Question 13.
What is a Grid?
Answer:
A grid is a square or a rectangle that is formed between when two latitudes and longitudes out across each other. In other words, the network of latitudes and longitudes drawn on the globe is called a ‘grid’.
Question 14.
When it is 12 noon in Greenwich (0°), what is the local time at Mumbai (73° E)?
Answer:
Mumbai (73° E) : Local time at Mumbai is : 73 x 4 = 292 minutes, i.e. 4 hours 52 minutes. That means the local time at Mumbai is 4 hours 52 minutes after 12 noon i.e., 12.00 + 4.52 = 4.52 p.m.
Question 15.
When it is 12 noon in Greenwich (0°), what is the local time at Chicago (87°30′ W) ? Chicago (87°30‘ W) : Local time at Chicago is : 87°30‘ x 4 = 350 minutes, i.e. 6 hours 50 minutes. That means the local time at Chicago is 6 hours 50 minutes less than 12.00 noon at Greenwich.
i.e. 12.00-6.50 = 5.10 a.m.
Question 16.
When it is 12 noon in Greenwich (0°), what is the local time at Sydney (151° E)?
Answer:
Sydney (151° E): Local time at Sydney is 151° x4 = 604 minutes, i.e. 10 hours 4 minutes before Greenwich time.
That means the local time at Sydney is 12.00 + 10.04 = 10.04 p.m
Question 17.
a) What are called ‘parallels’?
b) What are called ‘meridians’?
Answer:
а) Latitudes are called ‘parallels’,
b) Longitudes are called ‘meridians’.
Question 18.
What is the standard meridian of India?
Answer:
82°30′ Eastern longitude is the standard meridian of India.
Question 19.
If you were to travel from India to Japan. How would be the change in time?
Answer:
- Japan is located in East to India.
- If we travel to East, then we gain time as per East Gain Add (EGA).
- India is in 5Vi hours time zone and Japan in 9 hours time zone.
- Both are in eastern hemisphere. Thus we gain nearly 3% hours time.
Question 20.
How do you think human greed led to exploitation of the earth?
Answer:
- Human life on earth dates back to one lakh years, whereas formation of the earth was four and a half billion years ago.
- Man has constantly trying to change our surrounding to make it a better place to live in.
- He looked on earth as a storehouse of resources and making use of it, at will.
- Thus his greed led to exploitation of the earth.

Question 21.
Why do you think, it took so long time to understand the interior of the earth?
Answer:
- It is difficult for man to know directly about the Earth’s interior.
- So far man could dig a 3 km interior of the earth.
- He could send pipes upto a depth of 6K km.
- But, the radius of the earth is 6,440 km.
- Apart from this, if we go deep the earth-temperature raises at a rate of 1°C for every 32 meters.
- An estimated temperature at the centre of the interior of the earth is 6000°C.
- Thus man was unable to get direct information.
- So he need to rely on indirect sources like seismic waves etc.
- Thus it took so long time to understand the interior of the earth.
Question 22.
Describe the earth’s interior.
Answer:
- The earth has a radius of 6440 km.
- The temperature increases at a rate of 1°C for every 32 mts. of depth.
- The temperature at the centre of the earth would be 6000° C.
- As such the rocks will be in molten stage.
- Pressure also increases when one goes deeper into the earth.
- The earth is made up of three layers. They are : 1) Crust, 2) Mantle, 3) Core.
- These layers differ from one another in thickness and also in their physical and chemical compositions.
Question 23.
What is “continental drift theory”? Explain.
(OR)
What is the “theory of continental drift”?
Answer:
- Alfred Wagener postulated the theory of continental drift.
- It explains the present arrangement of continents and ocean basins.
- He postulated a massive super continent called “Pangaea” which existed 220 million years ago.
- Present continents originated, by the drift from this “Pangaea”.
- Wagener hypothesised that the supercontinent of Pangaea broke up into two blocks
1) Laurensia,
2) Gondwana land.
- The two blocks were separated by a long shallow inland ocean called “Tethys”.
- It took millions of years for the continents to reach the present shape and position.
Question 24.
Differenciate between latitudes and longitudes.
Answer:
| Latitudes |
Longitudes |
| 1. Latitude comes from a Latin word “Latitudo”, meaning width. |
1. Longitude is derived from a Latin word “Longitudo”, meaning height. |
| 2. The circles drawn parallel to the equator at 1° interval are known as latitudes. |
2. The semicircles drawn connecting pole to pole are known as longitudes. |
| 3. There are 180 latitudes excluding the equator. |
3. There are 360 longitudes. |
| 4. Every latitude must be designated with either “N” or “S” direction. |
4. Every longitude must be designated with either “E” or “W” direction. |
| 5. They are also known as “Parallels”. |
5. They are also known as “Meridians”. |
| 6. The climate of a place can be identified with the help of latitudes. |
6. The differences in time can be calculated with the help of longitudes. |
Question 25.
How many blocks did the Pangaea brake up into? What are they?
Answer:
The super continent of Pangaea was broke up into two blocks.
1) Laurensia:
Present N.America, Greenland and all of Eurasia, north of Indian subcontinent formed from it.
2) Gondwana land :
Present S.America, Africa, Madagascar, India, Arabia, Malaysia, East Indies, Australia and Antarctica formed from it.

Question 26.
How do you find a place in an atlas?
Answer:
- We can find the information about a place in an atlas with the help of latitudes and longitudes.
- Places are listed alphabetically at the back of the atlas.
Ex : To locate “Visakhapatnam”.

Question 27.
What are longitudes? How many are there? Name some important longitudes.
Answer:
- The semicircles connecting pole to pole are called longitudes.
- They are 360 in number.
- Some important longitudes are :
a) Prime Meridian – 0° longitude
b) International Date Line – 180° longitude
Question 28.
“For long we have looked at the Earth as a store house of resources, which we can exploit and use at will. Gradually we are realizing the fallacy of this view point” – Interpret the above statement.
Answer:
For long we have looked at the earth as a store house of resources. With this view we recklessly exploited the earth and are responsible to the destruction of forests, rivers, hills, fellow animals and even fellow humans. This resulted in the environmental crises such as global warming and poisoning of our soils, water and air.
But gradually we understand that the earthly resources are not infinite but finite and the environmental system is a closed one. So we should not use the natural resources indiscriminately.
If a man has to survive, he must derive something from the nature. The exploitation of minimum resources from the natural environment to fulfil the basic needs of human society would cause disequilibrium of some sort in the ecological balance resulting into environmental degradation and pollution. We should always use the natural resources in such a way that they are always at available in a desired quantity and quality.
Question 29.
“Today more than any other time we need to build a new understanding of the Earth, how it works and what we do on it and what we do with each other” – Interpret the above statement.
Answer:
In the decades of 1970s there emerged a concern about the fear of depletion of natural resources because of irrational and rapacious utilization of natural resources. This serious concern arises from the fact-rapid rate of rapacious exploitation of natural resources and modern production processes and advanced technologies. Thus the exploitation of natural resources has threatened the stability and survival of natural ecosystems and existence of several plant and animal species.
Hence today more than any other time we need to build a new understanding of the earth, how it works and what we do on it and what we do with each other.
Question 30.
Read the following para and answer the questions.
Scientists have figured out that the stars are actually part of larger groups called galaxies and that there are millions of such galaxies in the universe. Now, they are of the view that the universe itself started some 13.7 billion years ago with a ‘Big Bang’ and that it may end several billion years later.
1) What is a galaxy?
Answer:
A larger group of stars is called a galaxy.
2) When was the ‘Big Bang’ happened?
Answer:
‘Big bang’ was happened some IB.7 billion years ago.
3) How many galaxies are contemplated by scientists?
Answer:
Scientists contemplated that there are millions of galaxies in the universe.
4) When would be the end of the universe?
Answer:
The end of the universe would be after several billions of years.

Question 31.
What factors determine the number of standard times of countries?
Answer:
Countries which have much east-west extension will have a number of standard times.
Ex: Russia.
Question 32.
Identify other names of “Earth”.
Answer:
Bhoomi, Prudhvi, Dharithri, Dharani, Pudami, etc.
Question 33.
| Layer of Earth |
Depth |
Composition |
| 1. Crust |
30 – 100 km |
Various kinds of rocks |
| 2. Mantle |
100 – 2900 kms |
Chemicals & Silicates |
| 3. Outer core |
2900-5100 kms |
Nickel & Iron |
| 4. Inner core |
5100 – 6376 kms |
Iron compounds & Gold |
Observe the table and answer the following questions.
1) Which is uppermost layer of the interior of the earth?
Answer:
Crust is the uppermost layer of the interior of the earth.
2) What is the thickness of the core?
Answer:
The thickness of the core is 3476 kms.
3) Which layer is supposed to have more gold?
Answer:
The inner core is supposed to have more gold.
4) What is the radius of the earth?
Answer:
The radius of the earth is 6376 km.
Question 34.
Observe the following table and answer the questions given below.
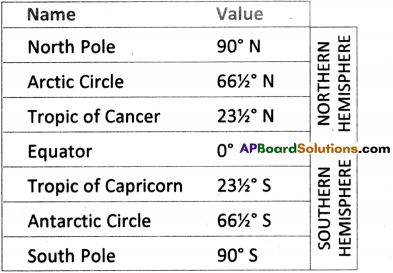
What is the latitudinal value of “Equator”?
Answer:
The latitudinal value of Equator is “0°”.
2) What is the name given to 90° N and 90° S latitudes?
Answer:
90° N is called North pole and 90° S is called South pole.
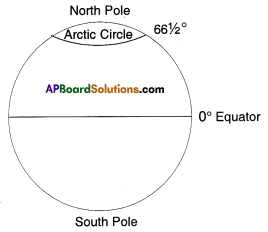
3) What are the values of Arctic and Antarctic circles ?
Answer:
The value of Arctic circle is 6634° N.
The value of Antarctic circle is 6634° S.
4) In which hemisphere is the Arctic circle situated ?
Answer:
Arctic circle is in Northern hemisphere.
5) Which latitude does not have any direction?
Answer:
The Equator does not possess any direction.

Question 35.
One among our ‘environment crises’ is the poisoning of air. in light of this, how would you assess the Government of Delhi, deciding to allow vehicles with odd and even number plates on alternate days?
Answer:
- Air pollution is one among the environmental crises we face.
- Government of Delhi decided to allow the odd number plate vehicles to ply on the Delhi roads the other day.
- This alternate day journey provision definitely reduces the traffic congestion.
- It also promises in reduction of pollution.
- Already petrol vehicles ply on Delhi roads was banned.
- Compressed Natural Gas is the need of the hour.
- However, care must be taken to disallow everyone to have a vehicle with odd number and another with even.
Question 36.
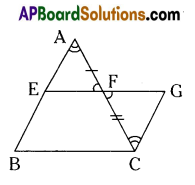
Observe the following pictures.

a) What do the above pictures represent?
Answer:
The above pictures represent the stages of continental drift.
b) Look at the above picture “2” and identify the following.
1) India,
2) Africa,
3) Tethys sea

c) Identify.
i) South America in picture “3”.
ii) Antarctica in picture “4”.
Answer:

Question 37.
How can you say the Earth’s orbit is nearly circular but not exactly circular or an elongated oval path?
Answer:
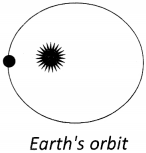
- The orbit is the path of the Earth around the sun.
- The difference between earth’s farthest point (about 152 million km from the sun and the closest point 147 million km) is very small.
- Thus we can say the earth’s orbit is nearly circular but not exactly circular or an elongated oval path.

Question 38.
Prepare a palmphet on environmental crises.
Environment Crises
Answer:
For longtime man looked on earth as a store house of resources and tried to exploit at will. His reckless exploitation of earth has meant distruction of forests, rivers, hills, fellow animals and even fellow human beings.
Global warming, which is caused by the increased presence of green house gases like carbon dioxide, methane etc. It is resulting in melting of ice and submerging of low lands and coasts.
Soil pollution is caused by excessive use of chemicals, fertilizers and pesticides in agriculture and industrial waste deposition. Soil erosion is caused by excessive falling of trees and lack of pastures.
Water pollution is caused by routing of industrial wastes into water, usage of chemicals and pesticides etc. Air pollution is caused by the emissions from vehicles, air conditions etc.
Question 39.
Create visual representation to understand the time as described in the earth’s origin to your birth.
Answer:
![]()

![]()