These TS 7th Class English Important Questions 8th lesson Snakes in India will help the students to improve their time and approach.
TS 7th Class English Important Questions 8th Lesson Snakes in India
Section – A: Reading Comprehension (25 Marks)
Questions : 1 – 10, Marks : 15
Passage No. 1:
Read the following passage.
Of the death-dealing quartet, the Russell’s viper is found from the paddy fields and river valleys of north India to the densely forested hills of Tamil Nadu, Kerala, and Karnataka in the south. Tan or brownish, thick-bodied, and reaching a length of one metre, it has long, movable fangs that inject a large amount of venom, making it even more dangerous than the Indian cobra.
The Indian cobra, a relative of some killer snakes of Asia, Africa and Australia, is readily recognized by the ‘spectacle’ (picture on the right) and ‘monocle’ (picture on the left) marks on its back. However, the black cobra has no distinguishing marks.
About one and a half to two metres long, the cobra spends much of its time underground or beneath dead logs or stones, feeding mainly on frogs and rats. The cobra’s bite is shallow and delivers a smaller dose of venom. But the venom is three times as toxic as that of the Russell’s viper.
Now, answer the following questions. Each question has four choices. Choose the correct answer and write (A), (B), (C) or (D) in your answer booklet. 5 × 1 = 5
Question 1.
What does the word ‘toxic’ mean ?
A) non-poisonous
B) poisonous
C) conscious
D) painful
Answer:
B) poisonous
Question 2.
Which of the following is a relative of some killer snakes of Asia, Africa and Australia?
A) Common krait
B) Russell’s viper
C) Saw-scaled viper
D) Indian cobra
Answer:
D) Indian cobra
Question 3.
Spectacle or Monocle is not seen on the back of _________
A) Black cobra.
B) Indian cobra.
C) Saw-scaled viper.
D) Russell’s viper
Answer:
A) Black cobra.
Question 4.
Death-dealing quartet means _________ venomous and rather dangerous snakes.
A) three
B) two
C) four
D) five
Answer:
C) four
Question 5.
What does the cobra feed on ?
A) cats
B) rats
C) buffaloes
D) cows
Answer:
B) rats

Answer the following questions in two or three sentences, each. 5 × 2 = 10
Question 6.
Where is the Russell’s viper found ?
Answer:
The Russell’s viper is found from the paddy fields and river valleys of north India to the densely’forested hills of Tamil Nadu, Kerala and Karnataka in the south.
Question 7.
How is the Russell’s viper ?
Answer:
The Russell’s viper is tan or brownish, thick-bodied, and reaching a length of one metre. It has long, movable fangs.
Question 8.
What makes the Russell’s’viper even more dangerous than the Indian cobra ?
Answer:
The long, movable fangs of the Russell’s viper inject a large amount of venom. That makes the Russell’s viper even more dangerous than the Indian cobra.
Question 9.
How is the Indian cobra recognised ? Which cobra has no distinguishing marks ?
Answer:
The Indian cobra is recognised by the ‘spectacle’ or ‘monocle’ marks on its back.
The black cobra has no such distinguishing marks.
Question 10.
What does the cobra’s bite deliver ? How powerful is its venom ?
Answer:
The cobra’s bite delivers a smaller dose of venom. But its venom is three times as toxic as that of the Russell’s viper.

Passage No. 2:
Read the following passage.
Kamal examined his foot and saw two tiny marks near the ankle. Convinced it was a snakebite, he hastily tied a rope just above his knee, and called out to a relative working nearby, who immediately took him by taxi to a local doctor’s dispensary. Unfortunately, the doctor was not a fully qualified allopathic practitioner and did not know about antivenin serum (anti-snake venom) or how to administer it. He gave Kamal a pain- killing injection and antibiotic tablets. He told him.to rest at home until the pain subsides.
But during the next few hours, Kamal felt increasingly giddy and vomited continually. His right foot and lower leg swelled alarmingly and the pain was unbearable. Kamal’s relatives rushed him to a large public hospital in central Mumbai.
Now, answer the following questions. Each question has four choices. Choose the
correct answer and write (A), (B), (C) or (D) in your answer book. 5 × 1 = 5
Question 1.
Which of the following gives the meaning ‘completely sure about’?
A) toxic
B) giddy
C) convinced
D) nocturnal
Answer:
C) convinced
Question 2.
The local doctor did not know about _________
A) how to administer anti-venin serum.
B) antibiotic tablets.
C) a pain-killing injection.
D) what medicine he should prescribe.
Answer:
A) how to administer anti-venin serum.
Question 3.
Kamal felt increasingly _________
A) toxic.
B) giddy.
C) fat.
D) nervous.
Answer:
B) giddy.
Question 4.
Where was the large public hospital?
A) in central Mumbai
B) in central Chennal
C) in Bengaluru
D) in Delhi
Answer:
A) in central Mumbai
Question 5.
How many tiny marks did Kamal see near his ankle ?
A) three
B) four
C) many
D) two
Answer:
D) two

Answer the following questions in two or three sentences, each. 5 × 2 = 10
Question 6.
What did Kainal do, when he convinced himself that it was a snakebite ?
Answer:
When convinced that it was a snakebite, Kamal hastily tied a rope just above his knee. Then he called out to a relative working nearby.
Question 7.
How did the local doctor treat Kamal ?
Answer:
The local doctor gave Kamal a pain-killing injection and antibiotic tablets. He told him to rest at home until the pain subsided.
Question 8.
Did the local doctor give Kamal an injection of antivenin ? Why or why not ?
Answer:
No, the local doctor did not give an injection of antivenin to Kamal because he was not a fully qualified allopathic practitioner and did not know about antivenin serum.
Question 9.
What happened to Kamal during the next few hours ?
Answer:
During the next few hours, Kamal felt increasingly giddy and vomited continually. His right foot and lower leg swelled alarmingly and the pain was unbearable.
Question 10.
If you were in Kamal’s position, what would you do ?
Answer:
If I were in Kamal’s position, I would at once tie a rope just above my knee and go to an allopathic doctor who knows about antivenin serum, by taking the help of some people.

Passage No. 3:
Read the following passage.
Even more toxic is the venom of the secretive and timid common krait. One to one and a half metres in length, it is found throughout India. The common krait is usually glistening, bluish-black, with thin, often indistinct, white cross-bands.
Contrary to what many people believe, most snakes are timid, nocturnal creatures, feeding mostly on rats, mice, frogs, toads, lizards or birds. They attack humans only when actually stepped upon, or provoked in some way. Precautions, such as wearing shoes and long trousers when walking through high grassand undergrowth, will lessen the risk of being bitten, for most snake – bites in India occur as people walk barefoot. Carry a lantern or a torch when you venture out at night.
Beat the ground ahead with a long stick as you walk – snakes will perceive the vibrations and slither away. The snakes move around as long as they have rats to feed on. Hence, keep your home and its surroundings rat-free. One should be alert during the monsoon season when snakes are most active.
Now answer the following questions. Each question has four choices. Choose the correct answer and write (A), (B), (C) or (D) in your answer booklet. 5 × 1 = 5
Question 1.
What does the word ‘nocturnal’ mean ?
A) Active during the day time
B) Active during the night time
C) Venomous
D) Poisonous
Answer:
B) Active during the night time
Question 2.
Most snakebites occur as people walk _________
A) with long sticks.
B) with lantern.
C) barefoot.
D) wearing shoes.
Answer:
C) barefoot.
Question 3.
Snakes are most active during _________
A) monsoon season
B) summer season
C) winter season.
D) spring season.
Answer:
A) monsoon season
Question 4.
Most snakes are _________
A) timid.
B) nocturnal.
C) nocturnal and brave.
D) timid and nocturnal.
Answer:
D) timid and nocturnal.
Question 5.
Which among the death-dealing quartet, is glistening?
A) Common krait
B) Russell’s viper
C) Saw-scaled viper.
D) Indian cobra
Answer:
A) Common krait

Answer the following questions In two or three sentences each. 5 × 2 = 10
Question 6.
What precautions are to be taken to lessen the risk of being bitten by a snake ?
Answer:
To lessen the risk of being bitten by a snake, we should wear shoes, and long trousers when walking through grass and undergrowth. While venturing out at night, we should carry a lantern or a torch. While walking, we should beat the ground ahead with a long stick.
Question 7.
What kind of animals are snakes ?
Answer:
A majority of snakes are non-poisonous. Besides, most snakes are timid and nocturnal creatures.
Question 8.
On which do snakes feed mostly ?
Answer:
Snakes feed mostly on rats, mice„ frogs, toads, lizards or birds.
Question 9.
Why should we keep our home and its surroundings rat-free ? In which season are snakes most active ?
Answer:
We should keep our home and its surroundings rat-free because snakes move around as long as they have rats to feed on. During the monsoon season, snakes are most active.
Question 10.
How is the common krait ? Where is it found ?
Answer:
The common krait is usually glistening, bluish-black, with thin, often indistinct, white cross-bands. It is found throughout India.

Passage No. 4:
Read the following passage.
What are the most dangerous animals on the Indian subcontinent? They are not lions, tigers or wolves but poisonous snakes. They attack far more frequently than most people suspect. Over 20,000 humans are bitten by venomous snakes in India each year. Unfortunately, the death-rate from snake bites is high largely because of widespread ignorance about snakes and snakebite prevention.
Also, proper medical treatment is often delayed or unobtainable. According to an estimate made by the World Health Organization, about 15,000 deaths from snakebites occur annually in India—nearly half the world total of such deaths. Even for those who survive, it is a dreadful experience, usually resulting in days or weeks of agony.
Take what happened to Tengal Kamal on a rainy evening in August 1981. Kamal, a 25-year-old farmer living near Goregaon, a suburb of Mumbai, was working barefoot in his fields when he suddenly felt a sharp sting on his right foot.
Now answer the following questions. Each question has four choices. Choose the correct answer and write (A), (B), (C) or (D) in your answer booklet. 5 × 1 = 5
Question 1.
What are the most dangerous animals on the Indian subcontinent?
A) Snakes
B) Lions
C) Tigers
D) Wolves
Answer:
A) Snakes
Question 2.
What happened to Tengal Kamal in August 1981 ?
A) He was bitten by a snake.
B) He was bitten by a mad dog.
C) He was bitten by a stray dog.
D) His hut was set on fire.
Answer:
A) He was bitten by a snake.
Question 3.
The percentage of the world total of snakebite deaths occurs annually in India is _________
A) 40%.
B) 33%.
C) 60%.
D) 50%.
Answer:
D) 50%.
Question 4.
Goregaon is _________
A) a district in Maharashtra.
B) a suburb of Mumbai.
C) a suburb of Kolkata.
D) a village near Nasik.
Answer:
B) a suburb of Mumbai.
Question 5.
How many humans in India are bitten by venomous snakes, each year ?
A) 20,000
B) 2,000
C) 200,000
D) 200
Answer:
A) 20,000

Answer the following questions in two or three sentences each. 5 × 2 = 10
Question 6.
Who was Tengal Kamal ? Where did he live ?
Answer:
Tengal Kamal was a 25-year-old farmer. He lived near Goregaon, a suburb of Mumbai.
Question 7.
What happened to Tengal Kamal ? When did it happen ?
Answer:
Tengal Kamal was bitten by a snake. It happened on a rainy evening in August 1981 when he was working barefoot in his fields.
Question 8.
Mention two reasons to say why the death-rate from snakebites is high ?
Answer:
Two reasons to say why the death-rate from snakebites is high are:
- The widespread ignorance about snakes and snakebite prevention and
- Proper medical treatment is often delayed or unobtainable.
Question 9.
What is the estimate made by the World Health Organization with regard to snake-bite deaths ?
Answer:
The estimate made by the World Health Organization with regard to the snakebite deaths is about 15,000 deaths from snakebites occur annually in India – nearly half the world total of such deaths.
Question 10.
For whom is snake – bite a dreadful experience ? What does it usually result in ?
Answer:
Snakebite is a dreadful experience for those who survive from snakebites. This dreadful experience results in days or weeks of agony.

Passage No. 5:
Read the following passage.
By then it was more than five hours since Kamal had been bitten and blood had begun to ooze from the snakebite marks. His gums were also bleeding and a soft thin tube put through Kamal’s nose into his stomach revealed a large amount of blood. Fearing that it might already be too late, the doctor gave Kamal an injection
of antivenin, and began ah emergency blood transfusion.
Over the next three days, Kamal was given 15 such transfusions as well as a repeat shot of antivenin. It was only after the fifth day that he was declared out of danger. After about a fortnight he was finally discharged from hospital.
Only about 50 of the more than 200 species of snakes in India are venomous. Of these, only four – Russell’s viper, saw-scaled viper, Indian cobra and common krait – are really dangerous. They are found across the country, from desert to fertile plains. While all the four are most common in rural India, Indian cobras and common kraits can be found in and around any human dwelling, posing danger even in the suburbs of major cities like Mumbai, Kolkata, and New Delhi.
Now answer the following questions. Each question has four choices. Choose the correct answer and write (A), (B), (C) or (D) in your answer book. 5 × 1 = 5
Question 1.
How many blood transfusions were Kamal given?
A) 5
B) 10
C) 20
D) 15
Answer:
Question 2.
Kamal was declared out of danger only after _________
A) a week.
B) the fifth day
C) the 3rd day
D) 4th day.
Answer:
Question 3.
Which poisonous snakes are found in and around human dwellings ?
A) Indian cobras and Russell’s viper
B) Saw-scaled viper and Russell’s viper
C) Indian cobras and common kraits
D) Indian cobras and saw-scaled viper
Answer:
C) Indian cobras and common kraits
Question 4.
Among the options given below, choose the word that gives the meaning of ‘producing poisonous liquid’.
A) Venomous
B) Anti-venomous
C) Transfusions
D) Antivenin
Answer:
A) Venomous
Question 5.
Through which a soft thin tube was put into Kamal’s stomach ?
A) the mouth
B) the belly
C) the nose
D) the shoulder
Answer:
C) the nose

Answer the following questions in two or three sentences each. 5 × 2 = 10
Question 6.
How many species of snakes in India are venomous ? Of them, mention the four snakes that are really dangerous.
Answer:
50 species of snakes in India are venomous. Of them, Russell’s viper, saw-scaled viper, Indian cobra and common krait are really dangerous.
Question 7.
When was Kamal declared out of danger ? When was he discharged from hospital?
Answer:
It was only after the fifth day, Kamal was declared out of danger. After about a fortnight he was discharged from hospital.
Question 8.
Where can Indian cobras and common kraits be found ? Even in which areas do they pose danger ?
Answer:
Indian cobras and common kraits can be found in and around human dwellings. They pose danger even in the suburbs of major cities like Mumbai, Kolkata and New Delhi.
Question 9.
What did the doctor do to Kamal when he feared that it might already be too late ?
Answer:
When the doctor feared that it might already be too late, he gave Kamal an injection of antivenin and began an emergency blood transfusion.
Question 10.
How was Kama! saved ?
Answer:
When Kamal was taken to a large public hospital in Mumbai, the doctor noted that his condition was critical and so he gave him antivenin injections and 15 blood ‘ transfusions for about three days. Thus Kamal was saved.

Questions : 11 – 16, Marks : 10
Passage No. 1:
Read the following passage.
All of you are bright children. You know me well. For centuries, poets and great thinkers have written in praise of me. They call me Mother Earth with love and affection. That is because, for hundreds of years, I have taken good care of people, just as mother takes care of her children.
Do you know how old I am? I am 4.6 billion years old, much older than your father, your grandfather and any of your great grandfathers.
I give you food to eat, like rice, wheat, and fruits. You also wear clothes made of cotton and live in houses made of leaves, wood, and bricks; all of which come from me. Long ago, humans used to worship me as a goddess and they used to care for me. But now they have big axes to cut my trees down; and cars and buses to pollute my air with smoke and fumes.
They don’t respect me any more.
Fill in the blanks in the following. 2 × 1 = 2
Question 11.
The earth is _________ years old.
Answer:
4.6 billion
Question 12.
_________ are made of cotton.
Answer:
Clothes
Answer the questions in complete sentences. 4 × 2 = 8
Question 13.
Who have written in praise of Mother Earth ? How did they call her ?
Answer:
Poets and great thinkers have written in praise of Mother Earth. They called her Mother Earth’ with love and affection.
Question 14.
What are clothes made of and what are houses made of ? From which do these come?
Answer:
Clothes are made of cotton and houses are made of leaves, wood and bricks. All these come from Mother Earth.
Question 15.
‘You know me well.’ .
Who does ‘You’ refer to and who does ‘me’ refer to ? Does it take good care of us?
Answer:
‘You’ refers to children and ‘me’ refers to ‘Mother Earth’. Yes, Mother Earth takes good care of us.
Question 16.
What did people long ago do ? What do people now do ?
Answer:
Long ago people worshipped Mother Earth as a goddess. But now people cut her trees down with big axes and use cars and buses to pollute her air with smoke and fumes.

Passage No. 2:
Read the following poem.
Trees are the kindest Things I know,
They’do no harm, they simply grow,
And spread a shade for sleepy cows,
And gather birds among their boughs…
They give us fruit in leaves above.
And wood to make our houses of.
And leaves to burn on Halloween
And in the Spring new buds of green.
They are the first when day’s begun
To touch the beams of morning sun,
They are the last to hold the light
When evening changes into night.
And when a moon floats on the sky
They hum a drowsy lullaby
Of sleepy children long ago…
Trees are the kindest things I know -Harry Behn
Now, answer the following questions. Each question has four choices. Choose the correct answer and write (A), (B), (C) or (D) in your answer booklet. 2 × 1 = 2
Question 11.
What does the word ‘boughs’ mean ?
A) wings
B) branches
C) rays
D) leaves
Answer:
B) branches
Question 12.
In which season, do new buds of green appear ?
A) Spring
B) Summer
C) Autumn
D) Winter
Answer:
A) Spring
Answer the following questions in complete sentences. 4 × 2 = 8
Question 13.
Who hum a drowsy lullaby ?
When do they hum ?
Answer:
Trees hum a drowsy lullaby. Trees hum when a moon floats on the sky.
Question 14.
What are the kindest things ? Why !
Answer:
Trees are the kindest things. They never do harm to any living being.
Question 15.
What do trees give us ?
Answer:
Trees give us fruit to eat, wood to make our houses, leaves to burn on Halloween and new buds of green in the spring.
Question 16.
What are the trees first to ? What are the last to ?
Answer:
Trees are the first to touch the beams of morning Sun. They are the last to hold the light when evening changes into night.

Passage No. 3:
Read the following passage.
Your teacher must have told you how my forests and mountains help to make rain and keep life on earth going. But nowadays, even my mountains and forests are being destroyed. You humans are yourselves destroying my bountiful forests and making my lands barren. Don’t you understand that I need them to give you enough rain? Without rain, you will not have any food to survive.
I am very sad about what is being done to me. That is why I am talking to you. You will all grow up and become good citizens and I want you to take care of me. Plant more trees in your house, in your school, and in your towns and villages.
Think now, after all you have just one Mother Earth.
I trust you will take care of me well.
Fill in the blanks in the following, with suitable answers. 2 × 1 = 2
Question 11.
‘You humans are yourselves destroying my bountiful forests ………………..
In the above statement, the word ‘bountiful’ means ………………
Answer:
available in large quantities.
Question 12.
The earth needs _________ to give enough rain.
Answer:
bountiful forests.
Answer the following questions in complete sentences. 4 × 2 = 8
Question 13.
What should children do to take care of Mother Earth ?
Answer:
Children in order to take care of Mother Earth should plant more trees in their houses, in their school, and in their towns and villages.
Question 14.
I trust you ………………
Who do the words ‘I’ and ’you’ refer to ?
What does the word ’trust’ mean ?
Answer:
‘I’ refers to Mother Earth.
‘You’ refers to children.
The word ‘trust’ means believe / rely on / depend on.
Question 15.
What help to make rain ?
Which bears them ?
Answer:
Forests and mountains help to make rain. Mother Earth bears forests and mountains.
Question 16.
Why is Mother Earth sad ?
Answer:
Mother Earth is sad because people are cutting down the trees and destroying the forests indiscriminately. They are polluting the air with smoke and fumes.

Passage No. 4:
Read the following passage.
At the far end of the village lived a poor farmer. He lived in a small hut, in the middle of a small piece of land. Years before, when he had come to live in the village, people had tried to be friendly. But the farmer was a strange man. He did not talk much to the people. Soon they went about doing their own work and left him to himself.
Near the farmer’s hut was an old tree. The tree had a hole, and in the hole lived a cobra. When the days were hot, the cobra would come out of its hole and coil itself up in the shade of the tree. The farmer sat on the ground nearby until the sun had set and he would then return to his house.
One day, the man who owned the place came to the farmer and said to him, “I must have firewood for my home. I want you to cut down the tree. Tomorrow I will ask a man to come and help you with the cutting.” And then the land owner left. The farmer watched him as he disappeared down the road.
The farmer stood there thinking. His tree was to go – his tree which gave him shade and comfort! And the cobra? Yes, what about the cobra? If the tree were cut down, he would lose more than shade. He would lose the cobra too, his friend of the summer days.
The farmer sat on the ground thinking. Near the hole the cobra lay coiled. Both remained in complete stillness. The sun set, but the man did not return to his house. The cobra sank into its coils as if it understood the great trouble of its friend. The man slept there that night. Next morning, when he woke up, he his heart sank. In front of its hole lay the cobra, cold and dead.
Now, answer the following questions. Each question has four choices. Choose the correct answer and write (A), (B), (C) or (D) in your answer booklet. 2 × 1 = 2
Question 11.
What kind of man was the farmer?
A) st range
B) cunning
C) proud
D) harmful.
Answer:
A) st range
Question 12.
Who tried to be friendly?
A) The farmer
B) The land owner
C) People in the village
D) The man sent by the land owner
Answer:
C) People in the village
Answer the following questions in complete sentences. 4× 2 = 8
Question 13.
Where did the farmer live ? Was he rich ?
Answer:
The farmer lived in a small hut, in the middle of a. small piece of land, No, he was not rich.
Question 14.
What would the cobra do when the days were hot ?
Answer:
When the days were hot, the cobra would come out of its hole and coil itself up in the shade of the tree.
Question 15.
Why was the farmer sad ?
Answer:
The farmer was sad because the tree which gave him shade and comfort was going to be cut down and his friend, the cobra would die.
Question 16.
What should we learn from this story ?
Answer:
One should not cut down trees which are always helpful and never do any harm.

Passage No. 5:
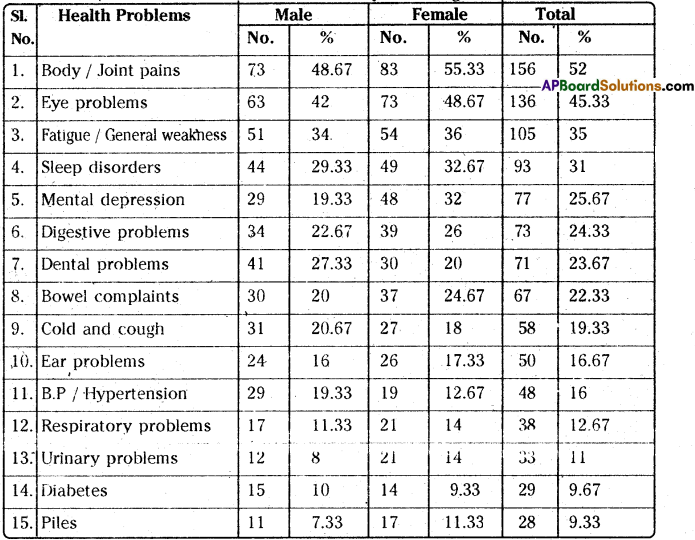
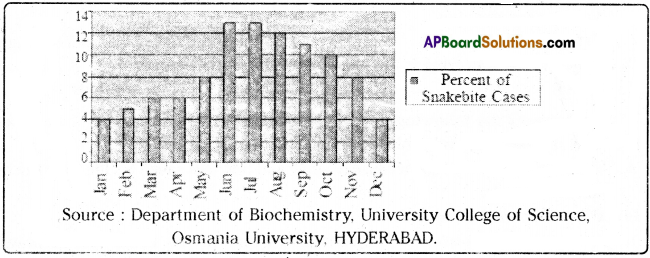
Study the bar-chart and answer the questions that follow.
Monthwise distribution of 1379 snakebite incidences during the period 1999 – 2003.
Fill in the blanks in the following with suitable answers. 2 × 1 = 2
Question 11.
_________ months record the highest number of snakebite cases.
Answer:
June and July months
Question 12.
In which months did 8% of snakebite cases occur ?
Answer:
May and November
Answer following the questions in complete sentences. 4 × 2 = 8
Question 13.
What is this bar-chart about ?
Answer:
This bar-chart is about the month-wise distribution of snakebite incidences during the period 1999 – 2003.
Question 14.
What did January and December months record ?
Answer:
January and December months recorded the lowest percent of snakebite cases.
Question 15.
What was the average percentage of snakebite cases in T.S. per month ?
Answer:
The average percentage of snakebite cases in T.S. was 8.3%.
Question 16.
What other inferences tan you draw from this chart ? Support your answer.
Answer:
Snakebites occurred more during rainy season. Snakes are active during rainy season.

Passage No. 6:
Read the following passage.
Once it was the summer season. A stag was grazing in the forest. Suddenly a hunter came there. He set his hounds after the stag. The stag ran for his life. He ran as fast as he could. Soon he was out of the reach of the hunter and his hounds. Thus his ugly and thin legs saved his life.
But unluckily, his big horns were caught in a bush. He tried hard to make himself free but in vain. Now the stag realised his folly. He began to praise his legs that had saved him. At the same time he was attacked by the hounds. The hounds injured the stag severely. But he began to curse his horns that were going to become cause of his death.
Choose the correct answer from the four choices given below the question. 2 × 1 = 2
Question 11.
The stag was very proud of his horns because _________
A) they were very big.
B) they were beautiful.
C) they were very sharp.
D) they help to escape from the danger.
Answer:
A) they were very big.
Question 12.
Which of the following is the meaning of the word ‘hounds’ ?
A) bow and arrows
B) nets
C) foxes
D) dogs
Answer:
D) dogs
Now answer the following questions in complete sentences. 4 × 2 = 8
Question 13.
Why did the stag praise his legs ?
Answer:
The stag praised his legs because his ugly and thin legs saved his life from the hunter and his hounds.
Question 14.
What happened at once ?
Answer:
At once, his big horns were caught in a bush and the stag could not run away, then.
Question 15.
How did the stag realise his folly ?
Answer:
When his horns were caught in a bush, he tried hard to make himself free but in vain. Then he realised his folly.
Question 16.
What was unlucky for the stag ?
Answer:
The stag with its thin legs ran so fast that he went out of the reach of the hunter and his hounds. But the unlucky thing for the stag was his big horns were caught in a bush and he could not free himself.

Section – B : Vocabulary and Grammar (20 Marks)
Questions : 17 – 21, Marks : 5
Passage No. 1:
Read the following passage taken from your textbook.
I am very (17) sad about what is being (18) did to me. That is why I am talking to you. You will all grow up and become good citizens and I want you to take care of me. Plant more (19) trees in your house, in your school, and in your towns and villages.
Think now, after all you have just one Mother Earth.
I (20) trust you will take care of me well.
Yours (21) lovingly,
Mother Earth
Now, answer the following questions in complete sentences. 5 × 1 = 5
Question 17.
What is the antonym of the underlined word ?
Answer:
The antonym of ‘sad’ is happy.
Question 18.
Write the correct form of the word.
Answer:
The correct form of the underlined word is done.
Question 19.
Give the singular form of the’word underlined.
Answer:
The singular form of ‘trees’ is tree.
Question 20.
What is the synonym of the underlined word ?
Answer:
Synonym of ‘trust’ is ‘believe’ or ‘rely on’.
Question 21.
Write the suffix of the word underlined.
Answer:
The suffix part in the word ‘lovingly’ is ‘-ly’.

Passage No. 2:
In (17) give you food to eat, like rice, wheat, and fruits. You also (18) wear clothes (19) made of cotton and live in houses made of leaves, wood, and bricks; all of which come from me: Long ago, (20) humans used to worship me as a goddess and they used to care for me. But now they have big axes to cut my trees down and cars and buses to pollute my air (21) with smoke and fumes.
Now answer the following questions. Each question has four choices. Choose the correct answer and write (A), (B), (C) or (D) in your answer book. 5 × 1 = 5
Question 17.
Choose the antonym of the underlined word.
A) send
B) take
C) issue
D) offer
Answer:
B) take
Question 18.
What is the synonym of the underlined word ?
A) Put on
B) Put off
C) Put out
D) Keep out
Answer:
A) Put on
Question 19.
Choose the appropriate verb form in the present simple tense (V1) form.
A) making
B) make
C) has made
D) maked
Answer:
B) make
Question 20.
Choose the suitable meaning to the underlined word.
A) trees
B) immortals
C) animals and birds
D) people
Answer:
D) people
Question 21.
Identify the part of speech of the underlined word.
A) Preposition
B) Adverb
C) Adjective
D) Noun
Answer:
A) Preposition

Passage No. 3:
Kamal examined his foot and saw two (17) tiny marks near the ankle. (18) Convinced it was a snake-bite, he hastily tied a rope just above his knee, and called out to a relative working nearby, (19) who immediately took him by taxi to a local doctor’s dispensary. (20) Unfortunately, the doctor was not a fully qualified allopathic practitioner and did not (21) know about antivenin serum (anti-snake venom) or how to administer it.
Now answer the following questions.
Question 17.
Write the antonym of the word underlined.
Answer:
Big
Question 18.
Give a synonym of the underlined word.
Answer:
Completely sure about
Question 19.
What is the part of speech of the word underlined?
Answer:
The underlined word is a pronoun.
Question 20.
What is the prefix in the underlined word ?
Answer:
Un-
Question 21.
There is a word in the given passage, that, sounds same as ‘No’. Identify it and write it.
Answer:
Know

Passage No. 4:
Every child is born with some (17) inherited characteristics, into a specific (18) socio – economic and emotional environment, and trained in certain ways by figures of authority. Mr. Tirupathi Venkata Guruvardhan inherited (19) honesty and self – discipline from his father; from his mother, Sitarama Kalyani, he inherited faith in goodness and deep kindness and so did his sister, Nagalakshmi. In his childhood, he had three close – friends – Guravaiah, Hanuman and Chennakesava Sarma. We all were from (20) orthodox Hindu Brahmin families. Last year, my friend Guravaiah arranged transport for visiting (21) pilgrims.
Now answer the following questions. Each question has four choices. Choose the correct answer and write (A), (B), (C) or (D) in your answer book. 5 × 1 = 5
Question 17.
Choose the noun form of the underlined word.
A) inheritance
B) inherit
C) inherits
D) inheritably
Answer:
A) inheritance
Question 18.
Socio-economic’ is a _________
A compound noun.
B) compound adjective.
C) phrasai verb.
D) phrase.
Answer:
B) compound adjective.
Question 19.
Choose the appropriate antonym of the word underlined.
A) inhonesty
B) unhonesty
C) non-honesty
D) dishonesty
Answer:
D) dishonesty
Question 20.
Choose the appropriate synonym of the underlined word from the given choices.
A) classical
B) rich
C) conventional
D) courageons
Answer:
C) conventional
Question 21.
‘Pilgrims’ are _________
A) animals which go round the villages.
B) people who journey to sacred places for religious reasons.
C) people who make pillows.
D) books read by religious people.
Answer:
B) people who journey to sacred places for religious reasons.

Passage No. 5:
There was once a town in the heart. of America where all life seemed to live in harmony with its surroundings …………….. Even in winter, the roadsides were places of beauty, where countless birds carne to feed on the berries and on the seed heads of the (17) dried weeds rising above the snow ……………..
Then a strange blight crept over the area and everything began to (18) change. Some evil spell had settled on the community: (19) mysterious maladies swept the flocks of chickens; the (20) cattle and sheep sickened and died. Everywhere was a shadow of death ……………. there had been (21) several sudden and unexpected deaths.
Now answer the following, as directed. 5 × 1 = 5
Question 17.
The simple present tense (V1) form of the underlined is
Answer:
The simple present tense of ’dried’ is ‘dry‘.
Question 18.
Write a synonym for the underlined word.
Answer:
The synonym of ‘change’ is ‘alter‘.
Question 19.
What is the suffix in the underlined word ?
Answer:
The suffix in ‘mysterious’ is ‘ous‘.
Question 20.
What is the underlined noun ?
Answer:
‘Cattle’ is a collective noun.
Question 21.
Write the opposite of the underlined word.
Answer:
Opposite of ‘several’ is ‘a few‘.

Questions : 22 – 26, Marks : 5
Complete the passage choosing the right word from those given below it. Each blank is numbered and for each blank has four choices (A), (B), (C) and (D). given. Choose the correct answer and write (A), (B), (C) or (D) in your answer book. 5 × 1 = 5
Passage No. 1:
Your teacher must _________ (22) told you how many forests and mountains help to _________ (23) rain and keep life _________ (24) earth going. But, nowadays, even mountains and forests are being destroyed. You humans are yourselves _________ (25) my beautiful forests and making my lands barren. Don’t you understand that I need them _________ (26) give you enough rain ? Without rain, you will not have any food to survive.
Question 22.
A) had
B) have
C) will
D) was
Answer:
B) have
Question 23.
A) made
B) make
C) making
D) makes
Answer:
B) make
Question 24.
A) in
B) under
C) upon
D) on
Answer:
D) on
Question 25.
A) destroyed
B) destroys
C) destroying
D) destroy
Answer:
C) destroying
Question 26.
A) to
B) for
C) of
D) about
Answer:
A) to

Passage No. 2:
Venkata Guru was _________ (22) naughty boy who lived in the village of Parnasala _________ (23) mother did not know what to do with him as he refused to study or _________ (24) any work. One day, she took him to school _________ (25) told the teacher to take care of him. The teacher _________ (26) him to come to school regularly.
Question 22.
A) an
B) the
C) a
D) one
Answer:
C) a
Question 23.
A) His
B) Her
C) Him
D) Their
Answer:
A) His
Question 24.
A) doing
B) did
C) do
D) done
Answer:
C) do
Question 25.
A) but
B) and
C) yet
D) also
Answer:
B) and
Question 26.
A) tell
B) tells
C) telling
D) told
Answer:
D) told

Passage No. 3:
Near the farmer’s hut was _________ (22) old tree. The tree had a hole, and in the hole _________ (23) a cobra. When the days were hot, the cobra would come out _________ (24) its hole and coil itself up in the shade of the tree. The farmer sat on the ground nearby until the sun had set and _________ (25) would _________ (26) return to his house.
Question 22.
A) the
B) any
C) an
D) a
Answer:
C) an
Question 23.
A) lived
B) live
C) lives
D) living
Answer:
A) lived
Question 24.
A) into
B) of
C) off
D) in
Answer:
B) of
Question 25.
A) they
B) it
C) he
D) she
Answer:
C) he
Question 26.
A) than
B) then
C) now
D) when
Answer:
B) then

Passage No. 4:
One day, Tirupathi Hanumayamma was walking _________ (22) a forest _________ (23) suddenly she _________ (24) someone crying out for help. She _________ (25) in the direction of the sound and _________ (26) upon a well that was dried up.
Question 22.
A) by
B) through
C) in
D) from
Answer:
B) through
Question 23.
A) or
B) though
C) when
D) but
Answer:
C) when
Question 24.
A) heard
B) hear
C) hears
D) hearing
Answer:
A) heard
Question 25.
A) go
B) went
C) goes
D) going
Answer:
B) went
Question 26.
A) came
B) come
C) coming
D) comes
Answer:
A) came

Passage No. 5:
Trees are the _________ (22) things. They _________ (23) no harm, they simply grow. They spread _________ (24) shade for sleepy cows _________ (25) give us fruit to eat and wood to make _________ (26) houses of.
Question 22.
A) kind
B) kindly
C) kinder
D) kindest
Answer:
D) kindest
Question 23.
A) did
B) do
C) does
D) doing
Answer:
B) do
Question 24.
A) a
B) the
C) some
D) an
Answer:
A) a
Question 25.
A) It
B) They
C) Their
D) Its
Answer:
B) They
Question 26.
A) their
B) your
C) our
D) his
Answer:
C) our

Passage No. 6:
Kanadibhatla Ramalakshmamma and Kallem Bhramaramba are friends. Bhramaramba’s daughter, Kalyani was _________ (22) to Venkateswarlu and Ramalakshmamma’s daughter, Hanumayamma was married _________ (23) Tirupathi Guravaiah. Kalyan _________ (24) two children _________ (25) Hanumayamma has five children. Kalyani’s younger brother marriecl Parameswari. Hanumayamma’s eldest daughter, Venkata Narasamma _________ (26) married to Chandramouli.
Question 22.
A) marry
B) marrying
C) will marry
D) married
Answer:
D) married
Question 23.
A) to
B) for
C) on
D) with
Answer:
A) to
Question 24.
A) have
B) having
C) has
D) had
Answer:
C) has
Question 25.
A) whereas
B) which as
C) when as
D) why as
Answer:
A) whereas
Question 26.
A) were
B) was
C) are
D) being
Answer:
B) was

Questions : 27 – 31, Marks : 10
Rewrite the following passage given below. Five sentences in the passage are numbered (27 – 31) at the beginning. Each of the five sentences has an error. Correct and rewrite them in the answer booklet. 5 × 2 = 10
1. (27) Only about 50 of the more than 200 spices of snakes in India are venomous. Of these, only four-Russell’s viper, saw-scaled viper, Indian cobra and common krait—are really dangerous. (28) They are found across the country, from desert and.fertile plains. (29) While all the four are most common in rural India, Indian cobras can be find in and around human dwelling, posing danger even in the suburbs of major cities like Mumbai, Kolkata, and New Delhi. (30) Contrary to what money people believe, most snakes are timid and nocturnal. (31) It attack humans only when they are stepped upon or provoked.
Answer:
27) Only about 50 of the more than 200 species of snakes in India are venomous.
28) They are found across the country, from desert to fertile plains.
29) While all the four are most common in rural India, Indian cobras can be found in and around any human dwelling, posing danger even in the suburbs of major cities like Mumbai, Kolkata, and New Delhi.
30) Contrary to what many people believe, most snakes are timid and nocturnal.
31) They attack humans only when they are stepped upon or provoked.
2. (27) Beat the ground ahead on a long stick as you walk. (28) Snakes will perceive the vibrations but slither away. (29) The snakes move around as long as they have rats to food on. (30) Hence, keep your home and it surroundings rat-free. (31) One should be alert during the monsoon season where snakes are most active.
Answer:
27) Beat the ground ahead with a long stick as you walk.
28) Snakes will perceive the vibrations and slither away.
29) The snakes move around as long as they have rat’s to feed on.
30) Hence, keep your home and its surroundings rat-free.
31) One should be alert during the monsoon season when snakes are most active.

3. Dear children,
All of you are bright children. You know me well. (27) For centuries, poets and great thinkers has written in praise of me. (28) They call me Mother Earth with lovely and affection. (29) I have took good care of people. (30) Do you no how old I am ? (31) I was 4.6 billion years old.
Answer:
27) For centuries, poets and great thinkers have written in praise of me.
28) They call,me Mother Earth with love and affection.
29) I have taken good care of people.
30) Do you know how old I am ?
31) I am 4.6 billion years old.
4. It was cold and wind night. (27) Varalakshmi and Nagalakshmi met after a long time and are chatting for hours. (28) They did not noticed that time flew away and it was close to ten. (29) They decided to take a auto-rickshaw to go to their room.
It started raining. They hurried to get into an auto-rickshaw and reach their place. (30) None of the auto-rickshaws stopped for them expect one. (31) The driver asked them if where they wanted to go and they told him the place.
Answer:
27) Varalakshmi and Nagalakshmi met after a long time and were chatting for hours.
28) They did not notice that time flew away and it was close to ten.
29) They decided to take an auto-rickshaw to go to their room.
30) None of the auto-rickshaws stopped for them except one.
31) The driver asked them where they wanted to go and they told him the place.
5. (27) Once upon a time there was a hungry fox that is looking for something to eat. He was very hungry. (28) No matter how hard he tried, he could not found food. Finally he went to the edge of the forest and searched there for food. (29) Suddenly, he caught the cite of a big tree with a hole in it.
Inside the hole, there was a package. (30) The hungry fox thought that their might be food in it. He became very happy. (31) He jumped in the hole. He opened the package and saw a lot of food, bread and meat in it.
Answer:
27) Once upon a time there was a hungry fox that was looking for something to eat.
28) No matter how hard he tried, he could not find food.
29) Suddenly, he caught the sight of a big tree with a hole in it.
30) The hungry fox thought that there might be food in it.
31) He jumped into the hole.

Section – C : Conventions of Writing (5 Marks)
Question : 32, Marks : 5
Read the following passage taken from your text book and rewrite it with proper punctuation. 5 Marks
Question 1.
of these only four Russell’s viper saw scaled viper indian cobra and common krait are really dangerous they are found across the country from desert to fertile plains.
Answer:
Of these, only four – Russell’s viper, saw – scaled viper, Indian cobra and common krait – are really dangerous. They are found across the country, from desert to fertile plains.
Question 2.
the king asked tell me oh poor brahmin how could you withstand the extreme temperature all through the night the innocent brahmin replied I could see a faintly glowing light a kilometer away and I withstood with that ray of light
Answer:
The King asked, “Tell me, oh poor Brahmin How could you withstand the extreme temperature all through the night ?” The innocent Brahmin replied, “I could see a faintly glowing light a kilometer away and I withstood with that ray of light.”
Question 3.
did you see the snake the next day doctor I asked
The doctor laughed and said I have never seen it since, it was a snake which was taken with its own beauty
Answer:
“Did you see the snake the next day, doctor ?” I asked.
The doctor laughed and said, ”I have never seen it since. It was a snake which was taken with its own beauty!”

Question 4.
i am looking at the house he said why do you want to buy it asked the girl is it your house asked the man it’s my father’s replied the girl. .
Answer:
“I am looking at the house,” he said. “Why ? Do you want to buy it ?” asked the girl.
“Is it your house ?” asked the man. “It’s my father’s,” replied the girl.
Question 5.
this is because for hundreds of years i have taken good care of people just as mother takes care of her children
do you know how old i am i am 4.6 billion years old much older than your father your grandfather and any of your grandfathers
i give you food to eat like rice wheat and fruits
Answer:
This is because, for hundreds of years, I have taken good care of people, just as mother takes care of her children.
Do you know how old I am ? I am 4.6 billion years old, much older than your father, your grandfather and any of your great grandfathers.
I give you food to eat, like rice, wheat, and fruits.
Question 6.
What are the most dangerous animals on the indian subcontinent they are not lions tigers or wolves but poisonous snakes according to an estimate made by the world health organization about 15000 deaths from snakebites occur annually in india nearly half the world total of such deaths even for those who survive it is a dreadful experience usually resulting in days or weeks of agony.
Answer:
What are the most dangerous animals on the Indian subcontinent ? They are not lions, tigers or wolves but poisonous snakes. According to an estimate made by the World Health Organization, about 15000 deaths from snakebites occur annually in India – nearly half the world total of such deaths. Even for those who survive, it is a dreadful experience, usually resulting in days or weeks of agony.

Section – D : Creative Writings (20 Marks )
Question : 33, Marks : 12
1. You have read the letter from Mother Earth. In her letter, she urges you to protect her. She has explained the need of protecting her. You are moved after reading the letter.
Now, write a letter to your friend saying about Mother Earth, her importance and the steps to be taken to protect her.
Answer:
4-23-5/1,
Near Poleramma temple,
Farooq Nagar,
4 July, 20xx.
My dear Venkata Guruvardhan,
I am fine and pink in health. Hope you are also fine and healthy, doing your part well. In this letter, I want to write to you about something very important for each and every human being.
It’s about Mother Earth. Yes, we ought to call ‘Mother Earth’ as she takes full care of all the living things just as our mother does for us. Without Mother Earth, can we exist ? You know it has mountains and forests to give us rainfall with which we are able to survive. Knowing her importance, people in olden days praised her as ‘Mother Earth’ and worshipped her as the Goddess ‘Bhudevi’. But it is rather unfortunate to note that the people nowadays, even the educated, ignore her importance and the service she is doing for us. instead, they are destroying mountains and forests for their selfish deeds and needs, giving the future generation a threat to live on. Deforestation is the cause of global warming which affects the lives rather badly.
It’s time we became strongly determined to protect Mother Earth and took all the steps needed to protect her. Let trees be not cut down. We all should see that more and more Plants / trees are planted every year.
‘Pachani Chetlu Pragathiki MeNu’
Chetkinti Natithe Kshemam
Chetlanu Narikithe Kshamam.
Hope my words go deep into your heart..
Please convey my regards to your parents.
Yours lovingly,
xxxxx
Address on the Envelope:
To
Tirupathi Venkata Guruvardhan,
S/o T. Venkateswarlu,
Near Gandhi Bomma Centre,
Huzur Nagar (Post),
Suryapet district.
Telangana state.

2. You have read about a snakebite death case in the newspaper. You were moved. Write a letter saying about the Dos and Don’ts when a snake bites.
Answer:
Beside Andhra Bank,
Kazipet.
10 October, 20xx.
Hai, Nagalakshmi !
How are you ? Hope this letter finds in happy and healthy mood. Here I am fine. It’s really long since I received a letter from you.
Yesterday I read a snakebite death case in the newspaper. I was shocked and deeply moved. Hence I am writing this letter to make you aware of snakes. Most snakes are non-poisonous. Only a few like the cobra and the common krait are poisonous and dangerous. Snakes are timid and nocturnal. They attack human beings only when they are stepped upon or provoked. Yet we should know the Dos and Don’ts when a snake bites. Given below are the Dos and Don’ts when a snake bites.
Dos:
- Keep the person (victim) calm.
- Keep the affected area below the heart well.
- Tie up the leg upto the knee, when the bite is on the ankle or the foot.
- Let antivenin serum be injucted.
- Treat it straight way.
- Let blood-transfusion be taken.
Don’ts :
- Don’t wait to see if the bite causes any problems.
- Don’t lose heart.
- Don’t be over frightened.
- Don’t cut, wash or suck the bite.
- Don’t frighten the victim.
- Don’t delay in giving the victim to antivenin serum.
- Don’t delay in taking the victim to hospital.
I hope you would keep these things in your mind well and tell your friends / neighbours about this.
Convey my regards to your parents. No more to my pen, now.
Ever yours,
xxxxx
Address on the Envelope :
To
Tirupathi Nagalakshmi,
D/o Venkateswarlu,
Behind Sivalayam,
4th line,
Sampath Nagar,
Hanamkonda,
Warangal Urban (Dt.)

Question : 34, Marks : 8
1. Prepare a poster, using the information given below.
Answer:


2. You are Arijaneyulu, a student of class VII of ZPH School, Armur. You have found a wrist-watch in the school playground.
Draft a notice to be put up on the school notice-board announcing the find and inviting the owner to claim it from you.
Answer:
Z.P.H SCHOOL, Armur
Nizamabad District
NOTICE
4th August, 20xx.
WRIST WATCH FOUND
A wrist watch was found in the school playground, yesterday. You are requested to collect it from the undermentioned person, if it belongs to you, after giving proper details.
T. Anjaneyulu
Class VII
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()

![]()
![]()
 indicates
indicates indicates
indicates