Students get through AP Inter 1st Year Botany Important Questions 13th Lesson Ecological Adaptation, Succession and Ecological Services which are most likely to be asked in the exam.
AP Inter 1st Year Botany Important Questions 13th Lesson Ecological Adaptation, Succession and Ecological Services
Very Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
Climax stage is achieved quickly in secondary succession as compared to primary succession. Why?
Answer:
- Secondary succession begins in areas where natural biotic communities have been destroyed such as in abandoned farm lands, burned or cut forest, flooded lands.
- Since some soil or sediment is present, secondary succession is faster than primary succession.
Question 2.
Among bryophytes lichens and ferns which one is a pioneer species in a xeric succession?
Answer:
Lichens are pioneer species in a xeric succession.
![]()
Question 3.
Give any two examples of xerarch succession.
Answer:
Newly cooled lava, bare rock, desert
Question 4.
Name the type of land plants that can tolerate the salinities of the sea: [IPE -14]
Answer:
Halophytes. Ex: Rhizophora.
Question 5.
Define heliophytes and sciophytes. Name a plant from your locality that is either heliophyte or sciophyte. [TS M-16]
Answer:
- Heliophytes: Plants which grow in direct sunlight are called heliophytes.Ex:Tridax,Grass plants.
- Sciophytes: Plants which grow in shady places are called sciophytes. Ex: Ferns. Mosses
Question 6.
Define population and community. [APMay-19] [TS Mar, May-17][AP M-15,17,19] [TS M-20,22]
Answer:
- Population is a group of similar individuals, belonging to same species found in an area.
- Community is an assemblage of several populations belonging to different species occuring an area.
Question 7.
Define communities? Who classified plant communities into hydrophytes, mesophytes and xerophytes?
Answer:
- Community is an assemblage of several populations belonging to different species occuring in an area.
- ‘Eugen Warming’ classified plant communities into hydrophytes, mesophytes and xerophytes.
Question 8.
Hydrophytes show reduced xylem. Why? [AP M-15,17,18,20,22] [TS M-15,19,22]
Answer:
- In hydrophytes, absorption of water takes place through all over the surface of the plant body.
- All submerged organs are capable of absorbing water. So, their xylem is reduced.
Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
What are hydrophytes? Briefly discuss the different kinds of hydrophytes with examples.
[AP M-16] [TS M-15, 17, 19]
Answer:
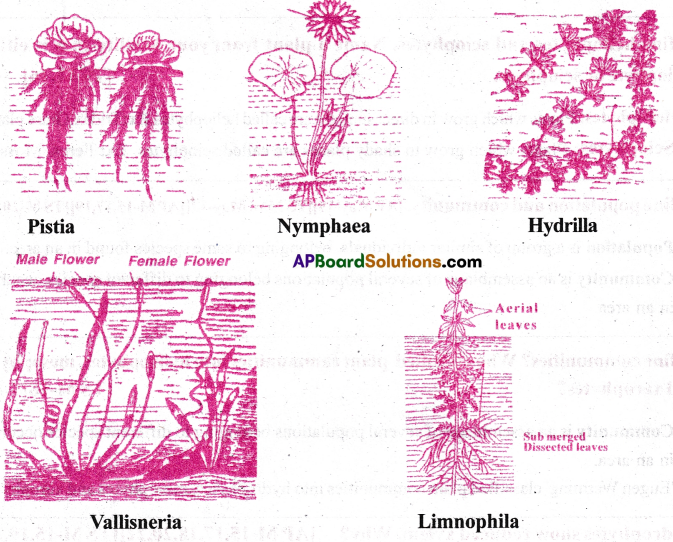
Hydrophytes; Plants that grow in water are called hydrophytes. According to their mode of living in water, these are of five kinds.
1) Free floating hydrophytes: These plants have no contact with soil and thus float freely on water surface. Ex: Pistia, Lemna, Salvinia.
2) Rooted hydrophytes with floating leaves: Roots of these plants are fixed to the substratum, but their long petiolated leaves keep them floating on water surface.
Ex: Nymphaea and Victoria regia.
3) Submerged suspended hydrophytes: These plants have contact only with water, being completely submerged and not rooted in the mud.
Ex: Hydrilla and Utricularia.
4) Submerged rooted hydrophytes: These plants are completely submerged in water and
attached to the substratum by their root system. Ex: Vallisneria.
5) Amphibious plants: These plants live partly in water and partly in air.
Ex: Sagittaria, Typha and Limnophila.
Question 2.
Enumerate the morphological adaptations of hydrophytes. [TS M-22] [AP May-19]
Answer:
Morphological adaptations of hydrophytes:
- Roots may be absent or poorly developed. In some plants submerged leaves compensate for roots.
- Root caps are usually absent.
- In amphibious plants, roots are well developed with distinct root caps.
- In some plants, root caps are replaced by root pockets.
- Roots, if present, are generally fibrous, adventitious, reduced in length, unbranched or poorly branched.
- Stem is long, slender and flexible.
- Leaves are thin, long, ribbon shaped or long and linear or finely dissected.
- Floating leaves are large and flat with their upper surfaces coated with wax.
![]()
Question 3.
List out the anatomical adaptations of hydrophytes. [IPE Mar-13]
Answer:
Anatomical adaptations of hy drophytes:
- Cuticle is totally absent in the submerged parts of the plant.
- It may be present in the form of a thin film on the surface of parts exposed to atmosphere.
- The epidermis is composed of thin walled cells and it performs absorption.
- The epidermal cells contain chloroplasts and help in assimilation.
- Stomata are totally absent in submerged hydrophytes.
- Gaseous exchange takes place directly through thin walled cells by diffusion.
- In plants with floating leaves, the leaves are epistomatous.
- All hydrophytes contain aerenchyma that helps in gaseous exchange and buoyancy.
Question 4.
Write a brief account on classification of xerophytes. [AP Mar, May-17] [TS M-16,22]
Answer:
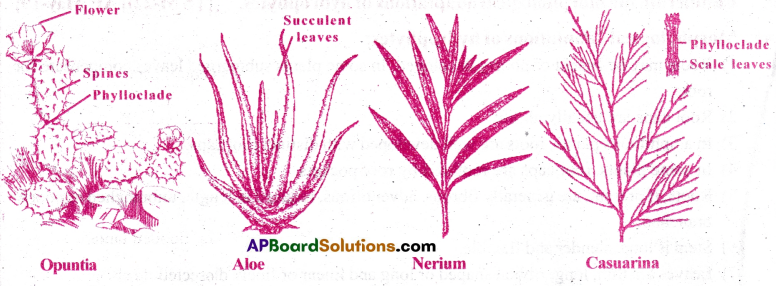
Xerophytes: The plants which grow in habitats deficient of water supply are called xerophytes.
They are classified into three categories. [AP, TS M-20]
Ephemerals:
- These plants are annuals, mostly found in arid (dry) zones.
- They complete their life cycle with in a very short period. Ex: Tribulus.
Succulents:
- These plants absorb large quantities of water during rainy season.
- They store the water in different parts of the plant in the form of mucilage.
- As a result, the plant parts like the stem (Ex: Opuntia), leaf (Ex: Aloe), root (Ex: Asparagus) become succulent.
- The stored water is used during dry periods.
- These are called ‘drought avoiding plants’.
Non-Succulents:
- These are perennial plants which can withstand prolonged periods of drought. Ex:Casuarina, Nerium.
- These are called ‘true xerophytes’.
Question 5.
Enumerate the’hiorphologieal adaptations of xerophytes. [AP M-19, 22]
Answer:
Morphological adaptations of xerophytes:
- Here, the roots are long with extensive branching spread over wide areas.
- Root hairs and root caps are very well developed.
- Stems are stunted, woody, hard and covered with thick bark.
- Stems are usually covered by hairs or waxy coatings.
- Leaves are very much reduced, small and scale like.
- Sometimes leaves are modified into spines to reduce the rate of transpiration.
Question 6.
Give in detail the anatomical adaptations shown by xerophytes. [AP M-15]
Answer:
Anatomical adaptations of Xerophytes: [TS M-17]
- In Xerophytes, epidermis is covered with thick cuticle to reduce the rate of transpiration.
- Epidermal cells may have silica crystals.
- Epidermis may be multilayered. Ex: Leaves of Nerium.
- Stomata may be confined to lower epidermis of leaves (hypo-stomatous)
- In some leaves the stomata are present in pits (sunken) Ex: Nerium
- Mechanical tissues are relatively well developed.
- Vascular tissues are relatively well developed.
Question 7.
Define plant succession. Differentiate primary and secondary successions.
Answer:
Riant succession: The gradual and fairly predictable change in the species composition of all communities in response to the changing environment till it reaches equilibrium is called plant succession.
| Primary Succession | Secondary Succession |
| 1) Primary succession occurs in a bare area where no living organisms ever existed. Ex: Bare rocks. 2) It occurs in a biologically sterile area. 3) It is a slow process. 4) It takes long time to reacth the climax stage. |
1) Secondary succession occurs in an area where all living organisms that existed are lost. Ex: Burned forests, flooded lands. 2) It occurs in a biologically fertile area. 3) It occurs faster than primary succession. 4) It takes short time to reach the climax stage. |
Question 8.
Define ecosystem/ ecological services. Explain in brief with regard to pollination.
Answer:
Ecosystem/ Ecological services: The processes by which the environment produces resources that we often take for granted such as clean water, timber and habitat for fisheries and pollination of natiye and agricultural plants.
![]()
Pollination Transfer of pollen grains from anther to stigma of a flower is called pollination. Ecosystem with regard to Pollination:
- Pollination is to fertilize the ovaries of flowers.
- It is an essential part of a healthy ecosystem.
- Most flowering plants require pollinators to produce fruits and seeds.
- Pollinators play a significant role in the production of more food crops in the world.
- The most important pollinator for agricultural puiposes is the honey bee.
- Bees, moths, butterflies, beetles and flies serve as pollinators world wide.
- Predicting the effects of the loss of a particular pollinator is extremely difficult.
- Evidence reveal that some populations of pollinators are diminishing.
- Continued decline in pollinator activity results in (i) rising costs of pollinator dependent fruits and vegetables (ii) disruption of entire ecological systems.
Question 9.
Write about the measures to be taken to sustain ecological functions.
Answer:
Measures to be taken to sustain ecological functions:
- Choose products produced with methods that conserve resources.
- Minimise waste and reduce environmental damage
- Prefer products made with methods that reduce the use of pesticides
- Reduce consumption and waste production.
- Support usage of renewable energy alternatives.
- Use public transit, cycle or walk to conserve natural resources.
- Reduce the pollution and enjoy health benefits.
- Participate in developing community garden and tree plantation programmes.
- Avoid the usage of pesticides and follow methods of natural pest control.
- Use native plants in the garden and provide habitat for wild life.
Question 10.
What measures do you suggest to protect the pollinators?
Answer:
Measures to protect the Pollinators:
- Creating a own pollinator -friendly garden using a variety of native flowering plants.
- Encouraging the planting of native flowers in open spaces and outside public buildings.
- Reducing the level of pesticides used in and around your home.
- Encouraging local clubs to build artificial habitats like butterfly gardens, bee boards and bee boxes.
- Supporting agriculture enterprises with pollinator – friendly practices such as farms that avoid pesticides use.
- Encouraging government agencies to take into account that full economic benefits of wild pollinators when formulating policies for agriculture.
- Stress the need to develop techniques for cultivating native pollinator species for crop pollination.
Long Answer Questions
Question 1.
Give an account of ecosystem services with reference to carbon fixation and oxygen release.
Answer:
I) Ecosystem services-Carbon fixation:
- Trees are essential for carbon fixation.
- Trees absorb excess carbon from entering the atmosphere.
- The chemical flow between forests and atmosphere is the exchange of CO2 and O2 by photosynthesis.
- Forests provide a vast bank for CO2 and a huge amount of CO2 is deposited in its timber.
- This cuts down the CO2 concentration in the atmosphere.
- It plays an essential role in maintaining a balance between CO2 and O2 in atmosphere.
- So CO2 fixation has an indirect economic value.
- It can be estimated by taking account alternate methods of fixing CO2.
- According to the equation of photosynthesis, to produce 180gms of glucose and 193 gms of plants will absorb 264 gms of CO2, 180 gms of water and consume 677.2 K.cal of solar energy.
- Then 180 gms glucose can be transformed to 162 gm of polysaccharide ihsfae the plant.
- Therefore, when plant produces 162 gms of dry organic matter, 264 gms of CO2 Will be fixed.
- That is production of every 1 gm dry organic matter can fix 1.63 gms of CO2.
- The economic value of CO2 fixation can be estimated by the total fixed amount multiplied by a standard opportunity cost for per unit CO2 fixation.
- Natural ecosystems helped to stabilize climate and prevent over heating of the earth by removing more of the green house gas, CO2 from the atmosphere.
II) Ecosystem services – Oxygen release:
- The leaves of the green trees perform photosynthesis and liberate O2 as a bye product.
- The amount of O2 produced by a tree depends on the species of tree, its age and its health.
- According to recent research findings a mature leafy tree produces as much oxygen in a season as 10 people inhale in a year.
- A single mature tree can inhale 48 lbs of CO2/yr and release enough oxygen to support 2 human beings.
- One acre of trees annual produce oxygen for 18 people to breath for a year.
- Submerged macrophytes release oxygen and enrich dissolved oxygen in water.
- The plants and planktons are sometimes described as “the lungs of the World”.
- Some microbes, especially cyanobacteria release the oxygen directly.
- Some bacteria degrade cellulose organic compounds and can make compounds used as a source of food by another organisms.
- This subsequent utilisation can both consume and produce oxygen at various stages of digestive process.
Exercise
Question 1.
Categorise the following plants into hydrophytes, halophytes, mesophytes and xerophytes and give reasons.
a) Salvinia
b) Opuntia
c) Rhizophora
d) Mangifera
Answer:
a) Salvinia is a hydrophyte which floats freely on water surface.
b) Opuntia is a xerophyte, grows in habitats where water supply is deficient in the soil.
c) Rhizophora is a halophyte, which can tolerate marshy, saline conditions of sea water.
d) Mangifera is a mesophyte, grows in soils where there is plenty of water.
Question 2.
In a pond, we see plants which are free-floating; rooted-submerged; rooted emergent; rooted w ith floating leaves. Write the type of plants against each of them.
Plant Name
a) f hydrilla
b) Tvpha
c) Nymphaea
d) Lenina
e) Vallisncria
Answer:
a) Hydrilla – Submerged suspended hydrophyte
b) Typha – Amphibious, rooted emergent hydrophyte
c) Nymphaea – Amphibious, rooted emergent hydrophyte
d) Lemna – Free floating hydrophyte Submerged
e) Vallisneria – rooted hydrophyte
![]()
Question 3.
Undertake the following as a part of learning process: _
a) Identify and assess ecological services found in your area
b) Think of measures or means to sustain such ecological services
c) Observe the type ofplants or crops grown in your area ’
d) Enumerate ecological services of your area
e) Find out the ecological goods of natural forests commonly used in your area
f) Observe the biotic agents of pollination for ornamental flowering plants and / or agricultural crops in your locality.
Answer:
a) Ecological services:
- Purification of air and water
- Decomposition of wastes.
b) Measures to sustain ecological services:
- Reduce consupmtion and waste production.
- Avoid the usage of pesticides
c) Crops grown in our area:
- Paddy
- Maize
- Sugar cane
- Black gram
d) Ecological services:
- Purification of water
- Decomposition and recycling of solid wastes.
e) Ecological goods:
- Cotton
- Jute
- Fossil fuels
- Petro crops
- Timber
f) Biotic agents of pollination:
- Insects
- Birds
- Snails
- Bats
- Snakes
Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
A biome can be understood as a
1. Group of different populations
2. Group of different communities
3. Group of different ecosystems
4. Group of similar organisms
Answer:
3. Group of different ecosystems
Question 2.
Secondary succession is faster due to the presence of
1. Soil
2.Water
3. Buds
4. Air
Answer:
1. Soil
Question 3.
Community is an assemblage of
1. similar species of an area
2. different species of an area
3. all populations of an area
4. only one population of an area
Answer:
3. all populations of an area
Question 4.
Green house gases are
1. Sulphur dioxide and Nitrous oxide
2. Carbon dioxide and Carbon monoxide
3. Oxygen and hydrogen
4. Nitrogen and ammonia
Answer:
2. Carbon dioxide and Carbon monoxide
Question 5.
Global warming can be minimised by
1. Afforestation
2. Deforestation
3. Promoting high rainfall conditions
4. Reducing soil erosion
Answer:
1. Afforestation
Question 6.
Ephemeral plants
1. store water
2. have long slender stem
3. live for very short period
4. grow in saline soils
Answer:
3. live for very short period
Question 7.
Ephemerals are drought
1) loving plants
2) enduring plants
3) escaping plants
4) resistant plants
Answer:
3) escaping plants
![]()
Question 8.
In CAM plants, the stomata
1. are non functional
2. open at night time
3. open at day time
4. are totally absent
Answer:
2. open at night time
Question 9.
In hydrophytes, the mechanical tissues and xylem are
1. highly developed
2. poorly developed
3. totally absent
4. found in stem parts only
Answer:
2. poorly developed
Question 10.
Pioneer plants of hydrarch succession are
1. Lichens
2. Phytoplankton
3. Algae
4. Fungi
Answer:
2. Phytoplankton
Question 11.
One of the following is not a character of Hydrilla
1. Presence of aerenchyma
2. Xylem not well developed
3. Waxy coating on the epidermis
4. Presence of stomata
Answer:
4. Presence of stomata
Question 12.
The lungs of the world are
1. Biotic factors of ecosystem
2. Atmosphere and its gases
3. Plants and phytoplankton
4. Animals and zooplankton
Answer:
3. Plants and phytoplankton
Question 13.
Water medium is enriched with dissolved oxygen by
1. Floating hydrophytes
2. Amphibious plants
3. Submerged macrophytes
4. Phytoplankton
Answer:
3. Submerged macrophytes
Question 14.
Sciophytes grow in
1. Salt water
2. Sandysoil
3. Shade of big trees
4. 0pen sunlight
Answer:
3. Shade of big trees
Question 15.
Leaves are finely dissected in
1. Utricularia
2. Vallisneria
3. Hydrilla
4. Salvinia
Answer:
1. Utricularia
Question 16.
Long ribbon like leaves are present in
1. Hydrilla
2. Vallisneria
3. Pistia
4. Lemna
Answer:
2. Vallisneria
Question 17.
Pollination in Zostera is
1. Anemophily
2. Epihydrophily
3. Entomophily
4. Hypohydrophily
Answer:
4. Hypohydrophily
Question 18.
Greatest threat to pollinators is
1. Destruction of habitat
2. Environmental pollution
3. 0ver use of pesticides
4. 0ver use of artificial fertilisers
Answer:
1. Destruction of habitat
![]()
Question 19.
Tundras are inhabited by all of the following except
1. Lichens
2. Trees
3. Grasses
4. Sedges
Answer:
2. Trees
Question 20.
The term Ecosystem was coined by
1. Ramdeo Mishra
2. W.H.Pearsall
3. Answer:G. Tansley
4. Eugen Warming
Answer:
3. Answer:G. Tansley
Question 21.
The functional unit of nature is
1. Population
2. Ecosystem
3. Heliophytes
4. Biosphere
Answer:
2. Ecosystem
Question 22.
Plants that grow in shady places are called
1. Sciophytes
2. Epiphytes
3. Biome S.Heliophytes
4. Halophytes
Answer:
1. Sciophytes
Question 23.
Khizophora is an example for
1) Halophytes
2) Sciophytes
3) Heliophytes
4) Fungi
Answer:
1) Halophytes
Question 24.
The special photosynthetic pathway shown by desert plants is
1) CAM pathway
2) TCA cycle
3) C3 pathway
4) C4 pathway
Answer:
1) CAM pathway
Question 25.
Which of the Xerophytes face external and internal dry ness?
1) Ephetnerals
2) Succulents
3) Non succulent
4) 1 and 2
Answer:
3) Non succulent
Question 26.
Pair of follow ing hydrophytes that are neither contact with soil nor with air
1) Vallisneria, Hydrilla
2) Hydrilla, Utricularia
3) Salvinia, Pistia
4) Limnophila, Typha
Answer:
2) Hydrilla, Utricularia
Question 27.
Abundant aerenchyma and xylem cavity are found in
1) Roots of Cicer
2) Stem of Opuntia
3) Stem of Hydrilla
4) Roots of Asparagus
Answer:
3) Stem of Hydrilla
Question 28.
Suspended hydrophyte leading insectivorus life is
1) Ceratophyllum
2) Utricularia
3) Dionaea
4) Nepenthes
Answer:
2) Utricularia
Question 29.
Submerged hydrophytes have
1) Stomata on both surfaces
2) Stomata on upper surface
3) Stomata on lower surface
4) No stomata
Answer:
4) No stomata
![]()
Question 30.
Select a pair of plants that show contact with water and air
1) Potamogeton, Vallisneria
2) Hydrilla, Ceratophyllum
3) Wolffia, Pistia
4) Typa, Limnophila
Answer:
3) Wolffia, Pistia
Question 31.
In submerged hydrophytes, gaseous exchange occurs through
1) Hydathodes
2) Stomata
3) General body surface
4) Injured parts
Answer:
3) General body surface
Question 32.
Which one not suffers from both external and internal dryness
1) Opuntia
2) Zizipphus
3) TribuIus
4) Aloe
Answer:
3) TribuIus
Question 33.
The correct pair of plants which can withstand prolonged period of drought
1) Casuarina, Tribulus
2) Nerium, Tribulus
3) Ziziphus, Tribulus
4) Casuarina, Calotropis
Answer:
4) Casuarina, Calotropis
Question 34.
Sunken stomates and multiple epidermis occur in ……….
1) Hydrilla
2) Mangifera
3) Nerium
4) Vallisneria
Answer:
3) Nerium
Question 35.
In floating leaved hydrophytes, stomata
1) occurs on both the surface of leaf
2) present on only the lower surface
3) present on only the upper surface
4) absent
Answer:
3) present on only the upper surface
Question 36.
Primary succession takes much longer time than secondary succession because it involves .
1) Colanization by organisms
2) Development of soil
3) Development of seed banks
4) All
Answer:
2) Development of soil
Question 37.
Identify the correct statement
1) Cost of the soil formation accounts for about 10 percent
2) Food, fibre are regulating services
3) Recreation and nutrient cycling accounts for less than 10%
4) Water pruification & food production are supporting services.
Answer:
3) Recreation and nutrient cycling accounts for less than 10%
![]()
Question 38.
Oxygen produced by the plants in one acre area sufficient to breath how many people?
1) 10
2) 18
3) 20
4) 36
Answer:
2) 18
Question 39.
In U.S. how much percentage of food production is required for pollination by bees?
1) 30-60%
2) 5-15%
3) 15-30%
4) 0.15-0.30%
Answer:
3) 15-30%
Question 40.
Stability of climax community depends on the …………..
1) type of species in it
2) Changes in the environment
3) Stability of environment
4) Reproduction method of biotic factors
Answer:
2) Changes in the environment
Question 41.
Select the true combination
1) Soil formation-Cultural service
2) Supply of fuel-Supporting service
3) Flood control-Regulating service
4) Development of parks & gardens-Provisioning sendee
Answer:
3) Flood control-Regulating service
![]()
Question 42.
Number of vertebrate species which help in pollination
1) 100,000
2) 18,000
3) 1,035
4) 25
Answer:
3) 1,035