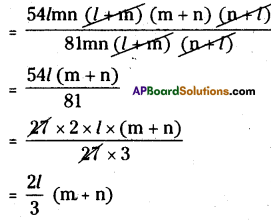
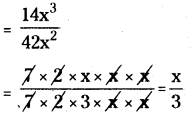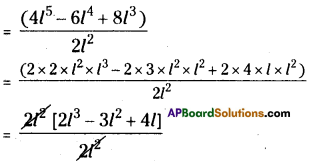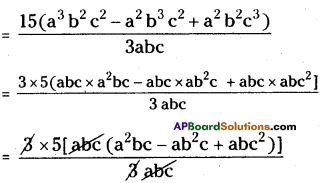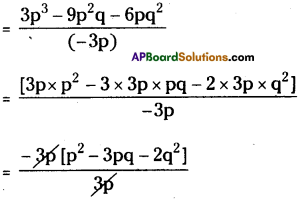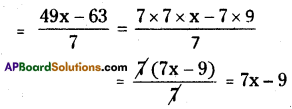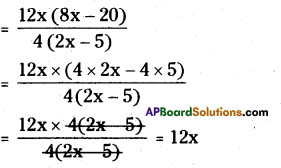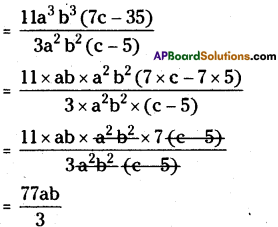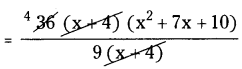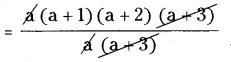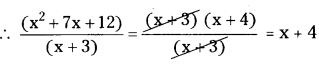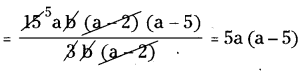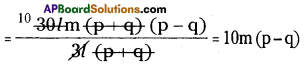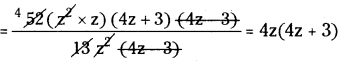AP State Syllabus AP Board 8th Class Maths Solutions Chapter 12 Factorisation Ex 12.4 Textbook Questions and Answers.
AP State Syllabus 8th Class Maths Solutions 12th Lesson Factorisation Exercise 12.4
![]()
Question 1.
Find the errors and correct the following mathematical sentences
(i) 3(x – 9) = 3x – 9
(ii) x(3x+2) = 3x2 + 2
(iii) 2x+3x = 5x2
(iv) 2x + x + 3x = sx
(v) 4p + 3p + 2p + p – 9p = 0
(vi) 3x + 2y = 6xy
(vii) (3x)2 + 4x +7 = 3x2 + 4x +7
(viii) (2x)2 + 5x = 4x + 5x = 9x
(ix) (2a + 3)2 = 2a2 + 6a +9
(x) Substitute x -3 in
(a) x2 + 7x + 12 (- 3)2 + 7(-3) + 12 = 9 + 4 + 12 = 25
(b) x2 – 5x + 6(-3)2 – 5(-3) + 69 – 15 + 6 = 0
(c) x2 +5x = (-3)2 + 5(3) + 6 = -9 – 15 = -24
(xi) (x – 4)2 = x2 – 16
(xii) (x + 7)2 = x2 +49
(xiii) (3a + 4b)(a – b)= 3a2 – 4a2
(xiv) (x + 4) (x + 2) = x2 + 8
(xv) (x – 4) (x – 2) = x2– 8
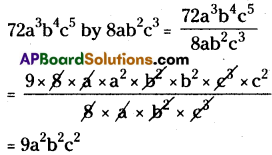
(xvi) 5x3 ÷ 5 x3 = 0
(xvii) 2x3 + 1 ÷ 2x3 = 1
(xviii) 3x + 2 ÷ 3x = \(\frac{2}{3 x}\)
(xix) 3x + 5 ÷ 3 = 5
(xx) \(\frac{4 x+3}{3}\) = x + 1
Solution:
(i) 3(x – 9) = 3x – 9
3(x – 9) = 3x – 9
⇒ 3x – 3 x 9 = 3x – 9
⇒ 3x – 27 = 3x – 9
⇒ – 27 ≠ – 9
∴ The given sentence is wrong. Correct sentence is 3(x – 9) = 3x – 27.
![]()
(ii) x(3x+2) = 3x2 + 2
x(3x + 2) = 3x2 + 2
⇒ x × 3x + x × 2 = 3x2 + 2
⇒ 3x2 + 2x ≠ 3x2 + 2
∴ The given sentence is wrong.
Correct sentence is x(3x + 2) = 3x2 + 2x.
(iii) 2x+3x = 5x2
2x + 3x = 5x2
⇒ 5x = 5x2
⇒ x ≠ x2
∴ The given sentence is wrong. Correct sentence is 2x + 3x = 5x.
(iv) 2x + x + 3x = 5x
2x + x + 3x = 5x
⇒ 6x = 5x
⇒ 6 ≠ 5
∴ The given sentence is wrong. Correct sentence is 2x + 3x = 5x.
(v) 4p + 3p + 2p + p – 9p = 0
4p + 3p + 2p + p – 9p = 0
⇒ 10p – 9p = 0
⇒ p = 0
It is not possible
∴ The given sentence is wrong. Correct sentence is
4p + 3p + 2p + p – 9p – p = 0
![]()
(vi) 3x + 2y = 6xy
3x + 2y = 6xy
a + b ≠ ab
∴ The given sentence is wrong.
Correct sentence is 3x x 2y = 6xy.
(vii) (3x)2 + 4x +7 = 3x2 + 4x +7
(3x)2 + 4x +7 = 3x2 + 4x +7
⇒ (3x)2 = 3x2
⇒ 9x2 = 3x2
⇒ 9 = 3
It is not possible
∴ The given sentence is wrong. Correct sentence is
(3x)2+ 4x + 7 = 9x2 + 4x + 7.
(viii) (2x)2 + 5x = 4x + 5x = 9x
(2x)2 + 5x = 4x + 5x = 9x
⇒ 4x2 + 5x = 4x + 5x
⇒ 4x2 = 4x
⇒ x2 = x
⇒ x ≠ √x
∴ The given sentence is wrong. Correct sentence is (2x)2 + 5x = 4x2 + 5x.
(ix) (2a + 3)2 = 2a2 + 6a +9
(2a + 3)2 = 2a2 + 6a +9
⇒ (2a)2 + 2 × 2a × 3 + 32 = 2a2 + 6a + 9
⇒ 4a2 + 12a + 9 = 2a2+ 6a + 9
⇒ 4a2 – 2a2 = 6a – 12a
⇒ 2a2 = – 6a
⇒ 2a ≠ 6
∴ The given sentence is wrong.
Correct sentence is
(2a + 3)2 = 4a2 + 12a + 9.
![]()
(x) Substitute x -3 in
(a) x2 + 7x + 12 (- 3)2 + 7(-3) + 12 = 9 + 4 + 12 = 25
x2 + 7x + 12 = (- 3)2 + 7 (- 3) + 12
= 9 – 21 + 12
= 21 – 21
= 0 25 (False)
(b) x2 – 5x + 6(-3)2 – 5(-3) + 69 – 15 + 6 = 0
x2 – 5x + 6 = (-3)2 – 5 (- 3) + 6
= 9 + 15 + 6
= 30 ≠ 0 (False)
(c) x2 +5x = (-3)2 + 5(3) + 6 = -9 – 15 = -24
x2 + 5x = (- 3)2 + 5 (- 3)
= 9 – 15 = – 6 ≠ 24 (False)
(xi) (x – 4)2 = x2 – 16
(x – 4)2 = x2 – 16 = (x)2 – (4)2
(a – b)2 ≠ a2 – b2
∴ (x-4)2 ≠ (x)2 – (4)2
∴ The given sentence is wrong.
Correct sentence is (x – 4)2 = x2 – 8x + 16.
![]()
(xii) (x + 7)2 = x2 +49
(x + 7)2 = x2 + 49 = (x)2 + (7)2
(a + b)2 ≠ a2 + b2
∴ (x+7)2 ≠ (x)2 – (7)2
∴ The given sentence is wrong.
Correct sentence is (x + 7)2 = x2 + 14x + 49.
(xiii) (3a + 4b)(a – b)= 3a2 – 4a2
3a(a – b) + 4b(a – b) = 3a2 – 42
3a2 – 3ab + 4ab – 4b2 = – a2
3a2 + ab – 4b2 ≠ a2
∴ The given sentence is wrong. Correct sentence is
(3a + 4b) (a – b) = 3a2 + ab – 4b2
(xiv) (x + 4) (x + 2) = x2 + 8
(x + 4) (x + 2) = x2 + 8
⇒ x2 + 6x + 8 = x2 + 8
⇒ 6x ≠ 0
Here ’6x’ term is missing in R.H.S.
∴ The given sentence is wrong. Correct sentence is
(x + 4)(x + 2) = x2 + 6x + 8.
(xv) (x – 4) (x – 2) = x2– 8
(x – 4) (x – 2) = x2 – 8
⇒ x2 – 6x + 8 ≠ x2 – 8
∴ The given sentence is wrong. Correct sentence is
(x – 4) (x – 2) = x2 – 6x + 8
![]()
(xvi) 5x3 ÷ 5 x3 = 0
5x3 ÷ 5 x3 = 0
⇒ x3-3 = 0
⇒ x0 = 0
∴ 1 ≠ 0 (∵ but x° = 1)
∴ The given sentence is wrong. Correct sentence is 5x3 ÷ 5x3 = 1.
In the denominator the term T is missing. .•. The given sentence is wrong. Correct sentence is
(xvii) 2x3 + 1 ÷ 2x3 = 1
2x3 + 1 ÷ 2x3 = 1
⇒ \(\frac{2 x^{3}+1}{2 x^{3}}\) = 1
In the denominator the term T is missing.
∴ The given sentence is wrong. Correct sentence is
2x3 + 1 ÷ 2x3 = 1 + \(\frac{1}{2 \mathrm{x}^{3}}\)
(xviii) 3x + 2 ÷ 3x = \(\frac{2}{3 x}\)
3x + 2 ÷ 3x = \(\frac{2}{3 x}\)
⇒ \(\frac{3 x+2}{3 x}=\frac{2}{3 x}\)
⇒ 1 + \(\frac{2}{3 x}=\frac{2}{3 x}\) ⇒ 1 ≠ 0
∴ The given sentence is wrong. Correct sentence is 3x + 2 ÷ 3x = 1 + \(\frac{2}{3 x}\)
(xix) 3x + 5 ÷ 3 = 5
⇒ \(\frac{3 x+5}{3}\) = 5
⇒ \(\frac{3 x}{3}+\frac{5}{3}\) = 5 ⇒ x + \(\frac{5}{3}\) ≠ 5
∴ It is a wrong sentence.
Correct sentence is 3x + 5 ÷ 3 = x + \(\frac{5}{3}\)
![]()
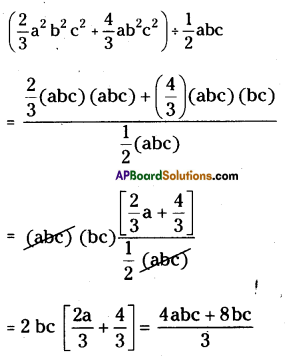
(xx) \(\frac{4 x+3}{3}\) = x + 1
\(\frac{4 x+3}{3}\) = x + 1
⇒ \(\frac{4 \mathrm{x}}{3}+\frac{3}{3}\) = x + 1
⇒ \(\frac{4 \mathrm{x}}{3}\) + 1 ≠ x + 1
∴ It is a wrong sentence.
Correct sentence is \(\frac{4 x+3}{3}=\frac{4 x}{3}+1\)