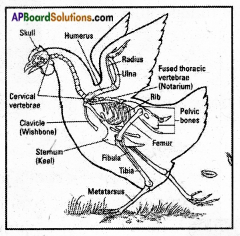
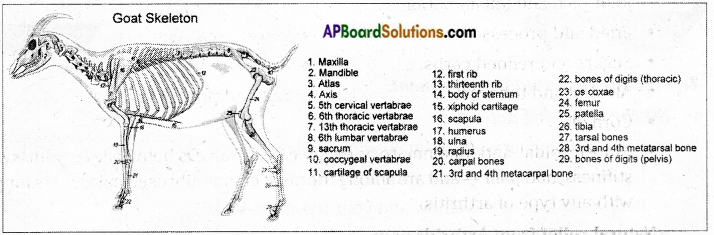
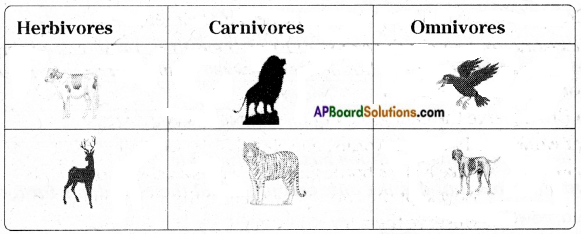
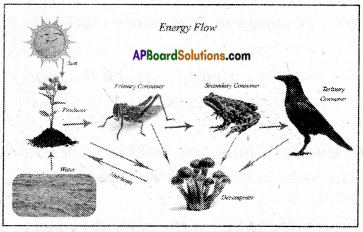
AP State Syllabus AP Board 6th Class Science Solutions Chapter 9 Organisms and Habitat Textbook Questions and Answers.
AP State Syllabus 6th Class Science Solutions 9th Lesson Organisms and Habitat
6th Class Science 9th Lesson Organisms and Habitat Textbook Questions and Answers
Improve Your Learning
Fill in the Blanks.
1. ——– is a dwelling place for plants and animals.
Answer:
Habitat
2. Soil is an ——– component of a habitat.
Answer:
Non-living
Choose the Correct Answer.
1. Which of the following is not a character ofa living thing?
A) Reproduction
B) Growth
C) Breathless
D) Excretion
Answer:
C) Breathless
2. Which of the following is a terrestrial habitat?
A) Pond
B) Garden
C) Lake
D) River
Answer:
B) Garden

Answer the Following Questions.
Question 1.
What are the common characteristics of living things?
Answer:
The living things show different specific characters.
1. Movement: – Most of the living things move from one place to another. They have the organs for movement like legs, wings, fins etc. Certain living things such as plants do not move from one place to another as they are fixed to the soil.
2. Food: – Acquiring food is also a character of living things. They acquire food for getting energy.
3. Growth: – Living things grow from time to time. Growth is a common phenomenon among them.
4. Breathing: – All living organisms inhale and exhale air from their surroundings. Many organisms have specialized organs for it. Plants have specialized organs called stomata for the exchange of gases.
5. Get rid of wastes: – Both plants and animals produce waste materials during life processes. They get rid of it by a process called Excretion.
6. Giving birth to young ones: – All living organisms give birth to young ones. Among them some animals lay eggs called Oviparous and some give birth to young ones called Viviparous. Plants produce seeds.
7. Responding to stimuli: The living things show response to stimulus in their surroundings. A change in the surroundings that make organisms respond to it is called stimulus.
Question 2.
How can you say that a tree is living even though it doesn 7 move?
Answer:
- Tree has got the following characteristics of living beings though it cannot move.
- The plant body shows growth, taking food, breathing, getting rid of wastes, response to stimuli giving birth to young ones through seeds.
- So I can say that tree is living.
Question 3.
What is a habitat? How can you say our house is a habitat?
Answer:
- A habitat is a dwelling place for plants and animals that gives them optimum conditions for life.
- We live in houses that protect us from heat, cold and rain, etc. and are a shelter for us.
- We keep some animals and birds as pets in our houses.
- We also grow some plants which give us fruits and vegetables.
Question 4.
List out the organisms living in various regions of a pond?
Answer:
| Region of the pond |
Organisms living in that region |
| Above the surface |
dragonfly, mayfly and kingfisher, hovering above the pond and then resting over a bamboo pole or a stick jutting out of the surface of the pond. They get food from the surface of the pond. |
| On the surface |
whirling beetle, pond skater, larva of mayfly and dragonfly, Plants like pistia float on the surface completely while those like the lotus have roots going deep under. [Organisms on the surface are easily eaten up by others because there is little protection for them.] However, there is plenty of food and air. Fish usually come to the surface for food. |
| Pond margins |
Several grasses, frogs, cranes, crabs etc. Fish usually lay eggs here. |
| Midwater |
Great water boatman, leech and mosquito larva are found in this region. Fish and crabs also swim around this region. |
| Bottom of the pond |
This region has plants like Hydrilla and animals like mussels, flatworms and some maggots (larvae of some insects). Light is minimum here, but food, in the form of dead and decaying matter is plenty. |

Question 5.
I am a living being. I have four legs. I live in water and also on land. “Who am I? And who are there in my habitat along with me?
Answer:
- The four-legged organism which lives in water and also on land is a frog.
- Turtles will also be in the habitat of frogs.
Question 6.
What questions do you ask to know more about microorganisms?
Answer:
- What are microorganisms?
- What is the smallest microorganism?
- Can we see microorganisms with the naked eye?
- What is the instrument using for observing microorganisms?
- Are all microorganisms harmful to us?
Question 7.
How do you prove that earthworms respond to stimulus?
Answer:
Response to light by earthworm:
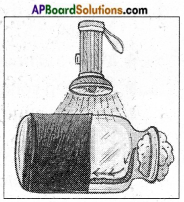
Aim: To observe the response of earthworm to light.
What we need: – Glass jar, Black Paper, Torch, Moist soil, Earthworm.
How to do:
- Get an earthworm from a nearby moist soil.
- Take a glass jar.
- Cover half of the glass jar with black paper, pour the moist oil in the jar and put the earthworm in the uncovered portion of the jar.
- Close the jar with a lid that contains small holes.
- Shed some light on the jar.
What do we see: – The earthworm moves to the dark portion of the jar
What do we learn: – The earthworm shows a response to the light (Stimulus).

Question 8.
Draw the diagram showing different regions of a pond.
Answer:
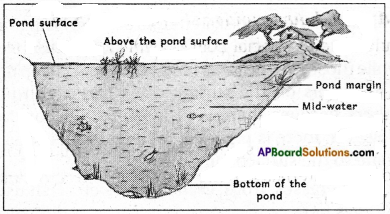
Question 9.
What steps do you take to keep a habitat good?
Answer:
- We should not dump the wastes in nearby ponds, lakes, rivers, and ground.
- We should not cut down the forest.
- The industries should not release wastes into air.
- We should not dump polythene covers on the soil.
- We should not burn the plastic, tires, and polythene covers.
- We should not dig bore wells indiscriminately.
Activities and Projects
6th Class Science Textbook Page No. 106
Question 1.
Collect sweet potato, bottle, salt, and water. Take a bottle full of water and add salt, then put the sweet potato inside the bottle. Observe for a few days. What happens? Note your observations. How can you prove that sweet potato is also a living thing?
Answer:
- The sweet potato bulges by absorbing saltwater.

- The metabolic changes continue in the potato, though removed from the parent plant.
- It forms roots and stem.
- This proves that sweet potato is also a living thing.

Question 2.
Identify the habitat in which the following live. More than one organism may be present in one habitat (use information given in the help box).
Our intestine, pond margin, kitchen, garden, tree, underground, grass,
Answer:
- Our intestine: Bacteria, Roundworms, Hookworms
- Pond margin: Several green types of grass, frogs, cranes, crabs, snails etc.
- Kitchen: Cockroach, lizards, rats, ants, flies, etc.
- Garden: Rats, bees, butterfly, ants, earthworms, garden lizard, beetles etc.
- Tree: Birds, bees, squirrels, mosquitoes, insect larvas, ants, termites etc.
- Underground: Snakes, rats, earthworms, snails, crabs, Termites, ants, etc.
- Grass: Crickets, grasshopper, ants, insects, larvas, etc.
Question 3.
Observe a spider in its web and write how a spider shares its habitat.
Answer:
- The web of the spiders is made up of a special protein that solidifies to form silken threads.
- The spider spins a web to trap insects.
- When an insect accidentally flies over the web it gets stuck in the web.
- The vibrations in the web are received by the spider and it attacks on the insect.
- The spider releases some poisonous materials into the body of an insect to paralyzes it and makes the prey into liquid form.
- This liquid form of food is absorbed by the spider.
- This is how a spider shares its habitat.
Question 4.
Collect a hydrilla plant. Put it in a glass of water and observe for a week, how it grows.
Answer:
- Hydrilla is a submerged plant.
- It does not contain specialized roots.
- The leaves are very small and strap-shaped with pointed tips.
- The leaves have a distinct midrib.
- The leaves are directly attached to the stem without a petiole.
- When we put this Hydrilla in a glass of water it grows an inch in a day.
- The plant gets it food from sunlight by a process called photosynthesis.
Question 5.
Take a map of Andhra Pradesh and color the areas where mangroves grow.
Answer:
Student Activity. Ex :

Question 6.
Write your experiences with your pet dog/cat/cow etc, that shows its affection on you.
Answer:
- The animals like dogs/cat/cow are called as pet animals.
- Man domesticated these organisms in earlier days to fulfill his needs.
- He domesticated these for protection and food.
- So we should take care of our pet animals.
- In this process we clean them, we supply food and fodder to them.
- If we show concern on these organisms, they become more affectionate to us.
- So sometimes we can see the dogs licks our feet and wags its tails and sit near us. This is the way they show their affection on us.
- Our motto should be “Live and Let Live”.
Question 7.
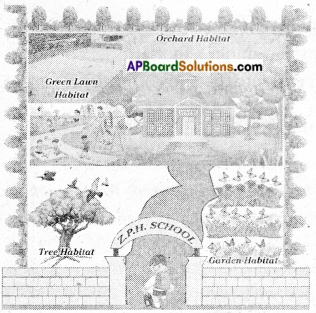
Prepare a map that represents different habitats that exist in your school.
Answer:
Question 8.
Prepare an article to deliver a speech in Literary Association meeting on “Animals also have right to live. ”
Answer:
“Animals also have the right to live”,
- In this beautiful world, animals have as much right to live as human beings.
- In totality, the entire earth is a common property of all of us.
- It is our world and it is their world. People often ask if animals should have rights, and quite simply, the answer is “Yes !”
- Animals surely deserve to live their lives free from suffering and exploitation. Just because we are at the top of the food chain.
- Life is life and it should be valued, no matter what you are.
- Animals cannot speak for themselves and for that reason we need to protect them.
- Protecting them is something we should take pride in, it is our responsibility.
- By respecting animal rights and having consideration for animal welfare, we also support ecological balance.

6th Class Science 9th Lesson Organisms and Habitat Activities
Activity – 1
Living things & Non-living things. (Page No. 93)
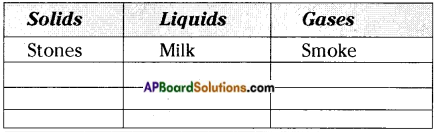
1. List some living things. Don’t forget to give reasons for why you think something is living.
Answer:
Dog – it takes a breath
Tree – it has growth
Buffalo – moves with legs
i) Chairs and tables also have four legs like buffalo. But they can’t move, why?
Answer:
Chairs and tables are non-living things. So they can’t move.
ii) Trees cannot move but they can produce seeds that give birth to new plants. Are they living things?
Answer:
Yes, trees are living things, but they can’t move. Except for this (movement), it has all living characters.
iii) How do we know whether some things are living and some others are nonliving?
Answer:
Living things have some special characters like growth and breath. By these charac¬ters we find living things.
iv) Will you notice that there are many characteristics of living things?
Answer:
Yes, living things have many characters.
v) Do all living things have common characteristics that make them different from non-living things?
Answer:
Yes, all living things have common characteristics that make them different from non-living things.
vi) Do you know that you are a living being? How can you say that?
Answer:
Yes, human beings are living things, they have living characters like growth, breath, and reproduction.
Activity – 2
Compare the characteristics. (Page No. 94)
2. Some characteristics are listed in table. Compare these characteristics with plants, animals and rocks.
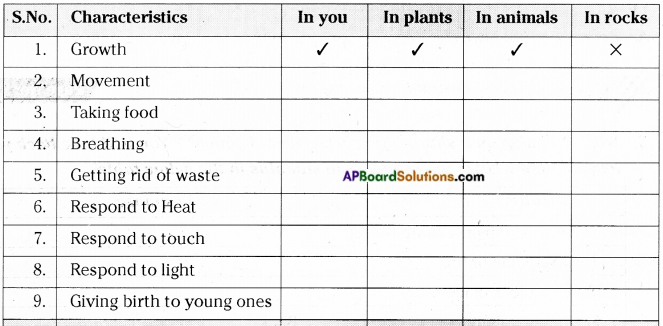
Answer:
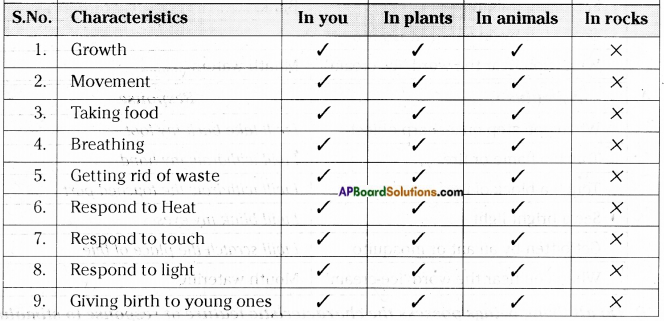
i) Do plants and animals possess the same characteristics as you do?
Answer:
Yes, mostly plants and animals possess the same characteristics as me, but plants can’t move.

ii) In which way do the characteristics of plants differ from you or from other animals?
Answer:
Plants can’t move.
iii) What characteristics are the same in plants and animals?
Answer:
- Growth
- Movement
- Taking food
- Breathing
- Getting rid of waste
- Respond to heat
- Respond to touch
- Respond to light
- Giving birth to young ones
iv) Do you agree that you are the same as other animals?
Answer:
Yes, I agree that living characters are the same as animals, but human beings are more intellectual and cultural.
v) What characteristics do you observe in rocks?
Answer:
Rocks do not have any living characters, so they are non-living things.
Activity – 3
Response to stimulus. (Page No. 95)
3. When you step on a sharp object what would you do? You will take back your feet. Is it not? Fill your responses to the stimulus in the below table.
| Stimulus |
Response |
| When you step on a sharp object |
|
| Touch a flame or fire |
|
| Touch a block of ice |
|
| See a bright light |
Blink………. |
| Get bitten by an ant or mosquito |
|
| When you hear the word ‘ice-cream’ |
Mouth waters……….. |
Answer:
| Stimulus |
Response |
| When you step on a sharp object |
I will take back my foot |
| Touch a flame or fire |
I will withdraw my hand |
| Touch a block of ice |
I will withdraw the touched part |
| See a bright light |
I will blink my eyes |
| Get bitten by an ant or mosquito |
I will scratch the place of bite |
| When you hear the word ‘ice-cream’ |
Mouth watering |
i) Do all living beings possess the characteristic feature of response to stimulus.
Answer:
Yes, all living beings possess the characteristic feature of response to stimulus
ii) Do other animals also respond to stimuli like us?
Answer:
Yes, all other animals also respond to stimuli like us.
iii) Do plants respond to stimuli like animals?
Answer:
Yes, plants respond to stimuli like animals.

Activity – 4
Mimosa (Atti-Patti) (Page No. 96)
4. It is very interesting to observe a touch-me-not (Attipatti or mimosa) plant Touch it. Record your observations.
Answer:
i) How does this plant respond when you touch it?
Answer:
When we touch the mimosa, it closes its leaves.
ii) How much time does it take to return to its previous position?
Answer:
It takes nearly 15 to 20 minutes.
Activity – 5
Seeds – Living or not: (Page No. 96)
5. Seeds are produced from plants. We know that plant is a living being. Can we say that seeds are also living things? Let us discuss the characteristics of living seeds?
Answer:
i) Does a seed take in food? From where?
Answer:
Seed has stored food in it. So it does not take in food. The food store is in the endosperm, and/or in the cotyledons.
ii) Will it die if stored for a long time?
Answer:
Yes, if we preserve it carefully we can store the food for a long time.
iii) What happens when a seed is sown in soil?
Answer:
When a seed is sown in the soil it will germinate.
Activity – 6
Microorganisms in water. (Page No. 98)
6. Collect water samples from a pond, well, bore well. Keep them separately. Put a drop of water on a slide. Keep a coverslip on it. Observe under the microscope.
Draw what you have observed. Describe the shapes of the micro-organisms.
i) What type of micro-organisms do you see in water samples?
Answer:
I found different types of microorganisms some are thread-like structures and some are round.
ii) Do all water samples have the same type of microorganisms?
Answer:
No.different water samples have different types of microorganisms.
iii) Is there any water without micro-organisms?
Answer:
No all water samples have microorganisms, but few in topwater.
iv) Which water contains a larger number of micro-organisms? Why?
Answer:
Pond water has more microorganisms because it is an open-source to grow micro¬organisms.
v) What kind of micro-organisms do you find in the water from a pond and borewell?
Answer:
Pond water has more greenish microorganisms and the bore well has moving organisms.

Activity – 7
Who lives where. (Page No. 98)
7. Write the names of organisms in the box below according to where they are found. Some examples are filled to help you.
| Under the ground |
On the ground |
In/On water |
Some other place |
| Snake |
Snake |
Snake |
|
| Earthworm |
|
|
|
|
Cat |
Lotus |
|
|
|
|
Sparrow (in homes) |
Answer:
| Under the ground |
On the ground |
In/On water |
Some other place |
| Snake |
Snake |
Snake |
Birds (tree) |
| Earthworm |
Frog |
Frog |
Eagle (rocks) |
| Rabit |
Cat |
Lotus |
squirrel (tree holes) |
| Ant |
Ant |
Dragon fly |
Sparrow (in homes) |
| Rat |
Squirrel |
Leech |
Honey bees (trees and rocks |
| Crab |
Snail |
Crab, snail |
– |
i) Which organisms are found mostly in your area often?
Answer:
Crows and cows are found mostly in my area often.
ii) How many organisms are present in more than one column?
Answer:
Two organisms are present in more than one column.
iii) Why did you place them there?
Answer:
They live in more than one place.
iv) In which column will you put a frog?
Answer:
I will put the frog in the second and third columns.
Activity – 8
8. Read the table and answer the following questions. (Page No. 100)
| S.No. |
Region of the pond |
Organisms living in that region |
| 1. |
Above the surface |
dragonfly, mayfly and kingfisher, hovering above the pond and then resting over a bamboo pole or a stick jutting out of the surface of the pond. They get food from the surface of the pond. |
| 2. |
On the surface |
whirling beetle, pond skater, larva of mayfly and dragonfly, Plants like pistia float on the surface completely while those like the lotus have roots going deep under. [Organisms on the surface are easily eaten up by others because there is little protection for them.] However, there is plenty of food and air. Fish usually come to the surface for food. |
| 3. |
Pond margins |
Several grasses, frogs, cranes, crabs etc. Fish usually lay eggs here. |
| 4. |
Midwater |
Great water boatman, leech and mosquito larva are found in this region. Fish and crabs also swim around this region. |
| 5. |
Bottom of the pond |
This region has plants like Hydrilla and animals like mussels, flatworms and some maggots (larvae of some insects). Light is minimum here, but food, in the form of dead and decaying matter is plenty. |
i) Name some organisms in the pond that can stay in different regions in the same pond?
Answer:
Frogs, cranes, crabs.
ii) What makes them stay in different regions in the pond?
Answer:
Their food habits and body structure makes them stay in different regions in the pond.
iii) Can different places in the pond also be called as habitat? Why? or why not?
Answer:
Yes, particular organisms are live in different places in the pond. So it be called as habitat.

iv) Is there any animal with legs in the pond?
Answer:
Yes, the frog has legs.
v) Do all animals in the pond have tails?
Answer:
No, all the animals in the pond does not have tail.
vi) Do all animals in the pond swim?
Answer:
No, crane can’t swim.
vii) What are the animals that share the surface of the pond as habitat?
Answer:
Whirling beetle, pond skater, larva of mayfly and dragonfly.
viii) Are the leaves of all plants growing in a pond, similar?
Answer:
No, the leaves of all plants growing in a pond are not similar. They are of different types. Ex : Hydrilla, Lotus.
ix) What is the difference between the leaves of a plant growing at the bottom (hydrilla) and that floating on the surface (lotus)? Try to think and write why we find such differences.
Answer:
a) The leaves of a plant growing at the bottom (hydrilla) have small tubular leaves to pass water flow.
b) Floating on the surface (lotus) plants have large leaves to grasp sunlight.
Activity – 9
Now, in the same way, let us study a plant or a tree as habitat. Birds, monkeys, squirrels, snakes, ants, spiders, caterpillars, moths, bees, wasps, small plants (mosses), mosquitoes are some organisms that you may find on a tree. Try to classify them in table based on where you find them. Add some more examples that you know. (Page No. 101)
| At the base of the tree |
ants, …….. |
| On the trunk |
|
| Between the branches |
monkeys, ……… |
| On or within the leaves |
|
Answer:
| At the base of the tree |
ants, snakes, caterpillars, moths, small plants, mosquitoes. |
| On the trunk |
ants, caterpillars, moths, mosquitoes, squirrels, bees, wasps, spiders. |
| Between the branches |
monkeys, birds, caterpillars, squirrels, mosquitoes, bees, wasps, snakes, ants, spiders. |
| On or within the leaves |
birds, monkeys, squirrels, snakes, ants, spiders, caterpillars, bees, small plants. |
Activity – 10
10. i) Can animals that are our pets live in other places as well? (Page No. 101)
Answer:
Yes, our pets live in other places.
ii) Name the animals and also write the places where they can live.
Answer:
Dog – it lives in the streets.
Cat – it lives in the forest.
Parrots – lives on the tree.

iii) Why do only certain types of animals and plants live along with us?
Answer:
For food and shelter, some animals live along with us
For our food and needs, we cultivate some plants.
Activity – 11
11. Compare water (Aquatic) plants with land (Terrestrial) plants. (Page No. 103)
i) Collect an aquatic plant like Hydrilla or Vallisneria, also collect any terrestrial plant. Now compare the two and write your observations in the below table.
| Parts |
Terrestrial plant (Tulsi) |
Aquatic plant (Valisneria / Hydrilla) |
| Stem |
|
|
| Leaf |
|
|
| Root |
|
|
| Others |
|
|
Answer:
| Parts |
Terrestrial plant (Tulsi) |
Aquatic plant (Valisneria / Hydrilla) |
| Stem |
Woody, grows towards the sunlight. |
Weak, less availability of sunlight. |
| Leaf |
Grows on stem with petiole and veins |
No petiole and simple leaf. |
| Root |
Tap root is present. |
Fibrous roots are present. |
| Others |
Grown on land, terrestrial plant. |
Grown in water. aquatic plant. |
ii) Good Habit – Good Life:
Which habitat do you like more? Habitat – A or Habitat – B. Why?

Answer:
Habitat – A: I like more which is clean and tidy. Whereas in Habitat B there is environmental degradation which causes danger to plants and animals life.
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()


![]()
![]()
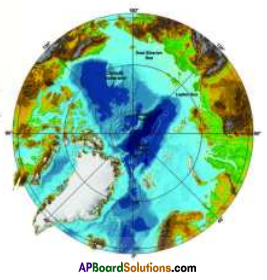
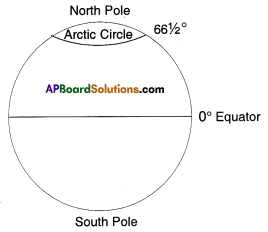
 You have seen the north pole and south pole on the globe. The region which lies near the poles is called the “polar region”. Look at Map. It shows the north pole and its surrounding regions. The entire polar region has been shaded lightly. Notice the boundary of this region. This is known as the ‘Arctic Circle’.
You have seen the north pole and south pole on the globe. The region which lies near the poles is called the “polar region”. Look at Map. It shows the north pole and its surrounding regions. The entire polar region has been shaded lightly. Notice the boundary of this region. This is known as the ‘Arctic Circle’.![]()
![]()
![]()