AP State Syllabus AP Board 6th Class Science Solutions Chapter 5 Materials: Separating Methods Textbook Questions and Answers.
AP State Syllabus 6th Class Science Solutions 5th Lesson Materials: Separating Methods
6th Class Science 5th Lesson Materials: Separating Methods Textbook Questions and Answers
Improve Your Learning
Fill in the Blanks.
1. Combination of more than one substance forms a ——–.
Answer:
Mixture
2. The method used to separate stones from rice is ——–.
Answer:
handpicking
3. The process in which a substance changes directly from solid to gaseous form and vice-versa is called ——–.
Answer:
Sublimation
![]()
Choose the Correct Answer.
1. Which of the following does not change its shape?
A) Solid
B) Liquid
C) Gas
D) None of these
Answer:
D) None of these
2. This method is useful for the separation of dissolved substances from a liquid
A) Sedimentation
B) Chromatography
C) Crystallization
D) Filtration
Answer:
C) Crystallization
3. Chromatography is the method used to separate
A) Mud from Water
B) Colours
C) Impurities from water
D) Husk from grains
Answer:
B) Colours
Answer the Following Questions.
Question 1.
List five things that we can make using each of the following materials:
a) glass b) metal c) plastic d) wood
Answer:
A) Five things made of glass:
- Drinking a glass
- Glass bowl
- Glass paperweight
- Glass jar
- Glass beaker
- Round bottomed glass flask
B) Five things made of metal:
- Metal metre scale
- Metal box
- Metal sheet
- Metal cauldron
- Metal pan
C) Five things made of plastic:
- Plastic chair
- Plastic comb
- Plastic bottle
- Plastic cup
- Plastic bags
- Plastic dish
D) Five things made of wood:
- Wooden chairs
- Wooden doors
- Wooden tables
- Wooden almirah
- Wooden sheet
- Wooden cot
- Wooden cup-board
![]()
Question 2.
Why is handpicking necessary after winnowing?
Answer:
- During winnowing, only husk and light particles can be separated from grains.
- But small stones and clay pieces will remain in the grains heap as they are heavy.
- To remove these stones and other particles, we have to pick them by hand and separate them.
- Hence handpicking is necessary after winnowing.
Question 3.
Which separation process is used when one component is in a mixture,
a. Heavier than the other?
b. Bigger than the other?
c. Different shape and colour from the other?
d. One is soluble in water and the other is not?
e. One floats and the other sinks in water?
Answer:
a) Winnowing
b) Sieving
c) Handpicking
d) Filteration
e) Decantation
Question 4.
Siri saw a ship travelling on a sea. She knows that iron nail sinks in water. She has many doubts. What are her doubts? Write them.
Answer:
- Why is the ship not sinking in water though it is made up of iron?
- Does iron float in salty water?
- Why did such a huge body like ship not sink in sea?
- What is the secret of ships floating in the sea?
- What is the science behind this floating?
Question 5.
We use so many wooden items in our daily life. Is it good to use wood? What happens by excessive use of it? What is the reason? Is there any alternative for this?
Answer:
- In fact it is good to use wooden items then the plastic items as it is biodegradable.
- But excessive use of it may lead to deforestation as we have to cut more trees for making wooden items.
- It may lead to several consequences such as
i) disturbance in the water cycle,
ii) decrease in rainfall,
iii) decrease in the amount of oxygen in the atmosphere,
iv) increase in carbon dioxide and pollution,
v) imbalance in nature etc, - We can use items made up of bamboo instead of wood as bamboo is a type of grass and grow quickly when compared to woody trees.
- We can also use items made up of metals as they lost longer and can be recycled.
Question 6.
How can you get your own distilled water in the laboratory?
Answer:
Aim: To get distilled water from normal water.
What do you need? (Materials required):
1. Water, 2 conical flasks, 2 one holed rubber cork, delivery tube, bunsen burner, stand.
What to do? (Procedure):
- Fill a conical flask with water, close it with a cork having a hole.
- Take another conical flask with a cork having a hole.
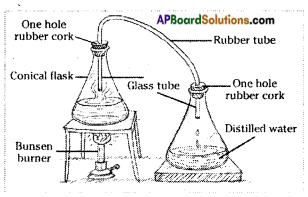
- Connect both flasks with a delivery tube.
- Now heat the flask containing water using a burner.
What do you see? (Observation): After some time, water vapour goes into the second conical flask through the delivery tube. The water vapour will slowly turn to water.
What do you learn? (Result) : This water is called a distilled water. It is free from impurities.
Thus Impurities can be removed from water by distillation get our own distilled water.
![]()
Question 7.
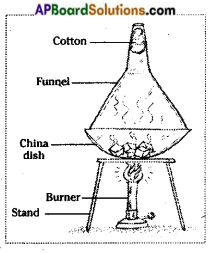
Draw a labelled diagram showing the experimental setup required for the sublimation of camphor?
Answer:
Question 8.
We know that a ship, even though it is made up of tonnes of iron, floats on water. How do you feel about the scientists who found the scientific principles and efforts in making a ship?
Answer:
- The ship is so constructed that it is full of air which keeps it a float.
- Air makes the ship lighter than the surrounding water.
- The displaced water of the ship pushes back up against the ship holding it up.
- The observation of the scientists who felt that the shape of the ship can hold more air to make it light made them to construct this.
- Observation of scientists as well as putting it to practical use is very much appreciable on the part of the scientists.
Activities and Projects
6th Class Science Textbook Page No. 58
Question 1.
Drop an egg in a beaker of water. Now drop the same egg in another beaker of water in which excessive salt is added. Write your observation.
Answer:
- When the egg is droped in a beaker of water the egg sinks in the water.
- When the egg is droped in the beaker of water in which excessive salt is added, the egg floats in that water.
- In the first case the density of water is less so no upward force act on the egg to float.
- But in the later case salt water density is more then normal water, so it exerts upward force on the egg as a result egg floats.
Question 2.
Do the following activities. Write down your observations. What do you conclude.
a. Mix chalk powder in water.
b. Place a piece of candle in water.
c. Add some oil drops to a beaker of water.
Answer:
a) Chalk powder is insoluble in water and is precipitated in water.
b) The candle floats in water. The density of the candle is less than the density of water.
c) The oil drop spreads as a thin film on the water surface. The density of oil is less than the density of water.
Question 3.
Make a list of items from your kitchen like utensils, food ingredients etc. Classify them as sinks /floats and soluble/insoluble.
Answer:
| S. No. | Item | Sink/Float in water | Soluble / Insoluble in water |
| 1. | Plastic glass | float | insoluble |
| 2. | Steel glass | sink | insoluble |
| 3. | Sugar | sink | soluble |
| 4. | Oil | float | insoluble |
| 5. | Salt | sink | soluble |
| 6. | Pan | sink | insoluble |
| 7. | Rice | sink | insoluble |
| 8. | Green chilli | float | insoluble |
![]()
Question 4.
Is it possible to separate sugar mixed with wheat flour? If yes, how will you do it? If powdered sugar is mixed with wheat flour, how do you separate them?
Answer:
- Yes. This can be done through the process of sieving.
- The mixture of sugar and wheat flour is allowed to pass through a sieve.
- The fine wheat flour passes through the sieve while sugar remains on the sieve.
- To separate powdered sugar from wheat flour, first we have to add excess water to the mixture of powdered sugar with wheat flour.
- As sugar is soluble in water it get dissolves in water.
- Wheat flour is insoluble in water so it settles down.
- Now wheat flour can be separated from sugar solution by decantation or filtration.
- Now sugar can be obtained from sugar solution by crystallization (heating till the water evaporates leaving behind the sugar in crystalized form).
6th Class Science 5th Lesson Materials: Separating Methods Activities
Activity – 1
Finding the materials used to make different objects. (Page No. 46)
1. A list of things in a house are given in table. Name the materials from which each object is may possibly be made of:
| S.No. | Object | Material |
| 1. | t) oor | Wood, metal, rubber, paint. |
| 2. | Towel | |
| 3. | Eraser | |
| 4. | Knife | |
| 5. | Mirror | |
| 6. | Shoes | |
| 7. | Water bottle | |
| 8. | Pot |
Answer:
| S.No. | Object | Material |
| 1. | Door | Wood, metal, rubber, paint. |
| 2. | Towel | Cotton, dye. |
| 3. | Eraser | Synthetic rubber, synthetic soy based gum, vinyl |
| 4. | Knife | Wood, stainless steel. |
| 5. | Mirror | Glass, metal or wooden or plastic frame. |
| 6. | Shoes | Leather or cotton or rubber |
| 7. | Water bottle | Plastic or glass or fibre |
| 8. | Pot | Clay |
i) Which objects are made of one material?
Answer:
- Pot
- Towel (if not dyed)
- Shoes
- Water bottle.
ii) Which objects are made of more than one material?
Answer:
- Door
- Rubber
- Knife
- Mirror
iii) How many materials can be used for making chairs? List them.
Answer:

- Wood
- Iron nails
- Plywood
![]()
Activity – 2
Finding the objects made from different materials: (Page No. 47)
2. Name as many things/objects as you can, made using the materials given in the table shown.
| S. No. | Material | Things/Objects |
| 1. | Metal | Utensils………. |
| 2. | Plastic | Bag,…….. |
| 3. | Glass | Mirror,………. |
| 4. | Wood | Table,…….. |
| 5. | Cotton | Cloth,……… |
| 6. | Leather | Shoes,…….. |
| 7. | Ceramic | Cup………. |
| 8. | Rock | Idols,………. |
Answer:
| S. No. | Material | Things/Objects |
| 1. | Metal | Utensils, chairs, cots, crowbar, pans |
| 2. | Plastic | Bag, chairs, combs, tubs, buckets, covers |
| 3. | Glass | Mirror, window pans, spectacles, paper weight, jars |
| 4. | Wood | Table, chair, windows, doors, rafters |
| 5. | Cotton | Cloth, sarees, covers, dress, shoes |
| 6. | Leather | Shoes, purses, belts, suitcases, bags |
| 7. | Ceramic | Cup, saucers, plates, plugs, tails |
| 8. | Rock | Idols, statues, walls, paper weights, buildings |
Activity – 3
Light a candle (Page No. 48)
3. You may have lit a candle with a matchstick many times, holding the burning matchstick to touch the wick of the candle until the wick catches fire. But, can you light the candle without touching the wick with a burning matchstick? Do you think this is impossible? Let us see how it can be done.
Answer:
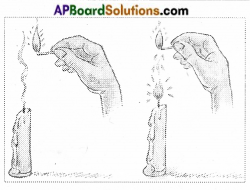
- A candle is taken and is lighted. The candle is lit only when the burning match stick touched its wick.
- When the candle is burning at the bottom of the wick liquid wax can be observed.
- White smoke is observed over the flame of the candle, when the flame is put off. This is the vapour state of wax.
- If a burning match stick is brought near this smoke, the candle catches fire though match stick does not touch the wick.
i) Did the candle catch fire from a distance?
Answer:
Yes, It catches fire from a distance.
ii) Discuss with your friends how and why the candle got lit from a distance.
Answer:
The candle got lit from a distance because the white smoke rising from the wick is flammable. It catches fire as a result candle got lit.
iii) Does the white smoke represent candle wax in the state of gas?
Answer:
Yes, that white smoke is nothing but the wax in the gaseous state.
![]()
Activity – 4
Classification of Materials: (Page No. 49)
4. Think of different solids, liquids and gases around you and group them in the table.
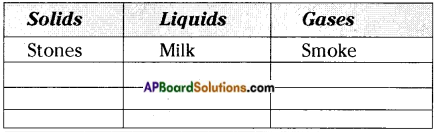
Answer:
| Solids | Liquids | Gases |
| 1. Stone | Milk | Smoke |
| 2. Ice | Water | Steam |
| 3. Wood | Kerosene | Butane |
| 4. Pen | Ink | Carbon dioxide |
| 5. Coal | Oil | Coal gas |
| 6. Salt | Sea water | Chlorine |
| 7. Rubber | Gum paste | Iodine vapours |
Discuss with your friends and find out who had the longest list. Can you list their properties? For example, liquids take the shape of the container they are put into. Write all possible properties of solids, liquids and gases in your notebook. Discuss them with your friends and teachers.
Answer:
A) Solids:
- Solids have a definite shape.
- Solids are incompressible.
- Solids do not flow.
B) Liquids
- Liquids occupy the shape of the container.
- Liquids are incompressible.
- Liquids can flow.
C) Gases:
- Gases have no fixed shape.
- Gases can be compressible.
- Gases flow and diffuse.
![]()
Activity – 5
Sinking or Floating in Water (Page No. 50)
Let us assume that a tomato, brinjal, potato, iron nail, sponge, wood, stone, leaf, piece of chalk and paper are given to you. Predict which of them will sink or float in water. Record your predictions in table.
| Prediction | Objects |
| Sinks | Stone … |
| Floats |
Answer:
| Prediction | Objects |
| Sinks | Stone, Iron nail, piece of chalk, potato. |
| Floats | Sponge, wood, leaf, paper, tomato, brinjal. |
i) Now try to test whether your predictions are correct or wrong by dropping the above objects in a beaker of water one by one. What do you find? Record your observations in the following table.


Answer:
| Object | Prediction | Finding |
| Stone | Sinks | Sunk |
| Iron nail | Sinks | Sunk |
| Piece of chalk | Sinks | Sunk |
| Tomato | Floats | Floated |
| Brinjal | Floats | Floated |
| Potato | Sinks | Sunk |
| Sponge | Floats | Floated |
| Wood | Floats | Floated |
| Leaf | Floats | Floated |
| Paper | Floats | Floated |
ii) For which of these objects your prediction is wrong? Why?
Answer:
1) All my predictions proved correct.
2) I have taken good quality tomato, brinjal and potato.
Now, add a lot of salt to the water in the beaker. Try this same activity with water which is excessively salty..
iii) What do you observe?
Answer:
Some of the objects which sinks previously now began to float.
iv) Do you get the same result? Discuss.
Answer:
No, some of the objects which sink previously now began to float. This is because the density of salt water is more than that of freshwater. As the density of water increases objects with less density than this water will float.
![]()
Activity – 6
Do Iron Objects of boat (Page No. 50)
6. i) Take some water in a wide-mouthed bowl. Put an iron nail in it. What do you observe?
Answer:
The wooden nail will sink to the bottom.
ii) Put an empty iron tin in that bowl. What do you observe?
Answer:
The iron tin float on the water.
iii) Also try to observe whether a wooden piece floats on water. What happens when a wooden bowl is dipped in water?
Answer:
When a wooden bowl is dipped in water, it again floats.
iv) What do you conclude from this activity?
Answer:
Some materials in one shape will sink in water but float on water when they are in another shape. The materials that can sink can be made to float, but all the materials that float cannot be made to sink.
Activity – 7
Soluble or Insoluble in Water: (Page No. 51)
7. i) Take five beakers with water. Take small quantities of sugar, salt, chalk powder, sand and sawdust. Add each material to separate beakers and stir- Observe the changes and record your observations in the table.
| S.No. | Material added | Dissolves (Yes /No) |
| 1. | Sugar | |
| 2. | Salt | |
| 3. | Sand | |
| 4. | Saw dust | |
| 5. | Chalk powder |
Answer:
| S.No. | Material added | Dissolves (Yes / No) |
| 1. | Sugar | Yes |
| 2. | Salt | Yes |
| 3. | Sand | No |
| 4. | Saw dust | No. |
| 5. | Chalk powder | No |
![]()
ii) Repeat the above activity with different liquids like vinegar; lemon juice, coconut oil and kerosene and add them to water. What do you observe? Discuss.
Answer:
| S. No. | Liquid added to water | Dissolves (Yes /No) | Soluble/Insoluble |
| 1. | vinegar | Yes | Soluble |
| 2. | lemon juice | Yes | Soluble |
| 3. | coconut oil | No | Insoluble |
| 4. | kerosene | No | Insoluble |
iii) List out the different substances that are used to make the items given in table.
| Item | Substances |
| Tea | Milk………. |
| Laddu | |
| Lemon Juice | |
| Concrete | |
| Soil |
Answer:
| Item | Substances |
| Tea | Milk, Tea powder, Sugar, Elachi |
| Laddu | Sugar, Boondi, Elachi, Ghee |
| Lemon Juice | Lemon Juice, Sugar, Water |
| Concrete | Sand, Cement, Water, Gravel Iron |
| Soil | Find Sand, Humus, Gravel, Clay, Coarse Sand |
iv) Complete the following table.

Answer:
| Mixture | Components | Natural / Man made |
| Lemon water | Lemon juice, water, sugar | Man-made |
| Laddu | Sugar, boodi, elachi, ghee | Man-made |
| Concrete | Sand, cement, water, gravel | Man-made |
| Soil | Fine sand, humus, gravel, clay, coarse sande | Natural |
| Rock salt | Salt – soil – sand | Natural |
Activity – 8
Sedimentation and Decantation: (Page No. 53)
8. How do you separate mud and sand from muddy water? What is sedimentation and decantation?
Answer:
- Take a mixture of soil and water in a glass tumbler and keep it undisturbed for some time.
- You will find that the sand and the mud particles in the soil settle down at the bottom of the glass tumbler.
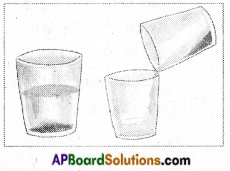
- These are called sediments and this process of sepa¬ration of mud and sand is called sedimentation.
- After sedimentation, the tumbler is gently lifted.
- The tip of the tumbler is inclined on the edge of another tumbler without disturbing the sediments.
- The water gets separated from the sediment(mud).
- This process is called decantation.
i) Why did mud particle settle at the bottom of the tumbler?
Answer:
Mud particles settle at the bottom of the tumbler as they are insoluble in water and heavier in weight.
Sedimentation and decantation are used in your home while cleaning rice and pulses for cooking.
![]()
ii) Think of other examples where we use this method of separation and list them.
Answer:
Example of sedimentation are: Tea leaves settling down on cup of tea, soil settling in pond water.
Example of decantation: Oil and vinegar mixture decanting in the experiment, water is poured out from cooked peas etc.
Activity – 9
9. Why can’t we filter salt from salt water? (Page No. 54)
Answer:
Take water in a beaker. Dissolve some salt in it. Filter this mixture with a filter paper.
i) Are you able to separate the salt from the salt water with a niter paper?
Answer:
We cannot separate the salt from the salt water with a filter paper.
ii) Why could you not niter the salt from salt water?
- The pores in a filter paper are so minute that we cannot see them with naked eyes.
- The dissolved salt particles are very minute and they pass through the filter paper.
- So we cannot filter the salt from salt water with a filter paper.
Activity – 10
Crystallization. (Page No. 54)
10. Explain the process of Crystallization.
Answer:
Aim: To separate salt from salt water.
What you need? Salt, water, beaker, glass rod, tripod Stand, Bunsen burner, wire guage.
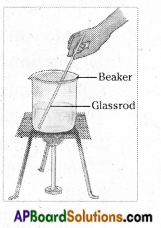
What to do?
- Heat some salt water in a beaker, over a flame.
- Stir the solution with a glass rod.
- Continue heating till all the water in the beaker has evaporated.
What do you see? Crystals of salt remain in the beaker.
What do you learn? Salt can be separated from salt water by heating (Crystallization). Some dissolved substances can be separated from the liquids by heating. On heating water evaporates and dissolved substances will form their crystals. This method of separation is called Crystallization.
![]()
Activity – 11
Get your own Distilled Water (Page No. 55)
11. How do you prepare distilled water ? (Or) Explain the process of distilling water.
Answer:
Aim To get distilled water from normal water.
What you need?:
1. Water, 2 conical flasks, 2 one holed rubber cork, delivery tube, bunsen burner, stand.
What to do?:
- Fill a conical flask with water, close it with a cork having a hole.
- Take another conical flask with a cork having a hole.

- Connect both flasks with a delivery tube.
- Now heat the flask containing water using a burner.
What do you see? After some time, water vapour goes into the second conical flask through the delivery tube. The water vapour will slowly turn to water. This water is called a distilled water. It is free from impurities.
What do you learn? Impurities can be removed from water by distillation.
Activity – 12
Sublimation of camphor (Page No. 55)
12. How do you demonstrate the sublimation of camphor?
Answer:
Aim To understand the process of sublimation.
What you need? Mixture of camphor and powdered salt, china dish, funnel, cotton, stand burner.
What to do?
- Take a mixture of camphor and powdered salt in a china dish and cover it with a funnel.
- Close the tube of the funnel with cotton.

- Place the dish on a stand and heat it with a burner.
What do you see? When camphor is heated, it transforms to gaseous form without changing into liquid leaving the salt powder in the dish. On reaching the cotton it cools, the gaseous form of camphor changes directly into a solid without going to the liquid state.
What do you learn? The process in which a substance changes directly from solid to gaseous form and vice-versa is called sublimation.
![]()
Activity – 13
A Chalk with different colours (Page No. 56)
13. How do you separate colour from a miture of colours?
Answer:
Aim : To separate colours from a mixture of colours (ink).
What you need?: stick of white chalk, ink, plate, water
What to do?:
- Take a whole stick of white chalk.
- Around the curved surface of the chalk put an ink mark with blue or black ink.
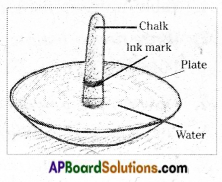
- Now pour some water in a plate and keep the piece of chalk in the water.
- Ensure that the water in the plate is very little and does not touch the ink mark.
- Observe the colour patterns that form on the piece of chalk after some time.
- Remove the chalk before the water reaches its top.
What do you see?: Different colours are formed around the chalk from the bottom to top.
What do you learn?: The ink appears to be made of a single colour but it is actually a mixture of many colours hidden in it. Those colours are separated by this method. It is an example of chromatography.
