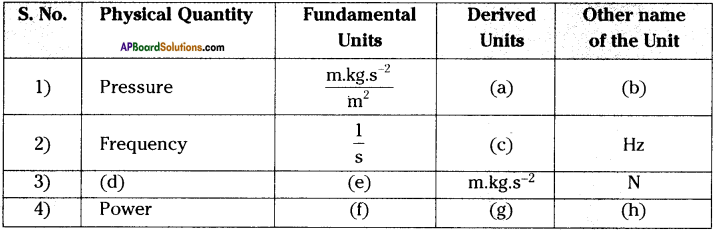
These AP 10th Class Physical Science Chapter Wise Important Questions 9th Lesson Classification of Elements- The Periodic Table will help students prepare well for the exams.
AP State Syllabus 10th Class Chemistry 9th Lesson Important Questions and Answers Classification of Elements- The Periodic Table
10th Class Chemistry 9th Lesson Classification of Elements- The Periodic Table 1 Mark Important Questions and Answers
Question 1.
What is modern periodic law? (AP June 2015)
Answer:
Modern periodic law :
The physical and chemical properties of the elements are periodic functions of their electronic configurations.
Question 2.
Define Moseley’s periodic law. (AP June 2015)
Answer:
Moseley’s periodic law: The physical and chemical properties of elements are periodic functions of their atomic numbers.
Question 3.
Which group elements are called Carbon family? (AP Mareh 2016)
Answer:
14 (or) IVA Group of elements are called Carbon family.

Question 4.
Which atom is bigger in size, Ne or Ar? Why? (AP June 2018)
Answer:
Ar. In groups as we go down number of shells increases due to the formation of new shell.
| “O Group” |
| He |
| Ne |
| Ar |
| Kr |
| Xe |
| Rn |
Question 5.
A and B are two elements. The compound formed with A and B is A2 B. What are the valencies of A and B. (TS March 2018)
Answer:
The valency of A is 1 and B is 2.
Question 6.
A teacher asked to give an example for Dobereiner’s triad. Ramu wrote them as “Li, Na, Mg”. In these three, identify which element does not belongs to this triad? (AP March 2019)
Answer:
Mg or Magnesium do not belongs to this triad.
Question 7.
Write the difference between Mendeleeff’s periodic law and modern periodic law. (AP SCERT: 2019-20)
Answer:
Mendeleeff’s periodic table is prepared based on atomic mass whereas modem periodic table is prepared based on atomic number (electronic configuration).
Question 8.
What is Dobereiner Triad? Give two examples to it.
Answer:
A group of three elements in which atomic weight of middle element is average of first and third element is called Dobereiner triad with similar propertion.
Eg: 1) U, Na, K
2) Cl, Br, I

Question 9.
What is Newlands’ law of octaves?
Answer:
When elements are arranged in the ascending order of their atomic weights, every eighth element starting from a given element resembles in its properties to that of starting element. This is called Newlands’ law of octaves.
Question 10.
What is MendeleefFs periodic law?
Answer:
MendeleefFs periodic law:
The physical and chemical properties of the elements are the periodic functions of their atomic weight.
Question 11.
What is the name given to horizontal rows and vertical columns in MendeleefFs periodic table?
Answer:
Horizontal rows are periods and vertical columns are groups.
Question 12.
What is the property on which MendeleefFs periodic table depends upon?
Answer:
Mendeleeff’s periodic table depends upon atomic weight.
Question 13.
What is the name given to I(A) group elements?
Answer:
Alkali metal family, because aliquili = plant ashes. Na, K, etc. were obtained from plant ash.
Question 14.
Why are VI A group elements called chalcogens?
Answer:
Chalcogeneous = Ore product. As the elements in group 16 (VI A) form ores with metals, they are called chalcogeneous family.
Question 15.
Why are VII A group elements called halogens?
Answer:
Halos – sea salt, genus – produced. So VII A (17) are obtained from nature as sea salt. So they are called halogen family.

Question 16.
What are halogens?
Answer:
Fluorine, Chlorine, Bromine, Iodine, and Astatine of VIIA group elements are called halogens, which are obtained from sea salt.
Question 17.
What are noble gases? What is the general electronic configuration of noble gases?
Answer:
The elements of group VIII A (18) are chemically least reactive so they are called noble gases. Their group electronic configuration is ns²np6 (except) for helium it is 1s².
Question 18.
What are Lanthanides?
Answer:
Elements acquiring same properties are called lanthanides, i.e. 4f elements. They are from 58Ce (Cerium) to 71Lu (Lutetium).
Question 19.
What are Actinides?
Elements acquiring different properties are called actinides, i.e. 5f elements. They are from 90Th (Thorium) to 103Lr (Lawrensium).
Question 20.
What are metals and non-metals?
Answer:
The elements with three or less electrons in the outer shell are considered to be metals and the ore with five or more electrons in the outer shell are considered to be non-metals.

Question 21.
What are metalloids?
Answer:
The properties of elements which are intermediate between the properties of metals and non-metals are called metalloids.
Question 22.
Which will behave like semi-conductors?
Answer:
Metalloids or semi-metals behave like semi-conductors.
Question 23.
What is valency?
Answer:
The combining power of element with respect to hydrogen, oxygen or indirectly any other element through hydrogen and oxygen is called valency.
Question 24.
What is the latest definition of valency?
Answer:
The number of electrons lost or gained or shared during a chemical reaction.

Question 25.
How do we measure atomic radius of solids?
Answer:
It is half of the distance of radius of each atom.
Question 26.
What is covalent radius?
Answer:
Half of the distance between length of covalent bond is called covalent radius.
Question 27.
In which units is atomic radius measured?
Answer:
Atomic radius is measured in pico meter (pm) units.
1 pm = 10-12 m.
Question 28.
What is the method given by Milliken to calculate electronegativity of an element?
Answer:
According to Milliken, electronegativity of element is average value of its ionization energy and electron affinity.

Question 29.
What is electropositive character?
Answer:
The tendency of metals to remain positive ions in compounds is called electropositive character. (OR) The tendency of an atom to lose electrons to form positive ions.
Question 30.
What is screening effect or shielding effect?
Answer:
More the shells with electrons between the nucleus and the valence shell, they act as screens to decrease nuclear attraction over valence electron. This is called screening effect or shielding effect.

Question 31.
What do you mean by negative or positive electron gain enthalpy?
Answer:
The negative sign indicates that energy is liberated or lost, and the positive sign indicates that the energy is gained or absorbed.
Question 32.
What is a triad?
Answer:
A group of three elements with similar properties in which atomic weight of middle element is average of other two elements.
Question 33.
Chlorine, bromine, iodine are Dobereiner’s triads. How do you justify?
Answer:
Chlorine, bromine and iodine have similar properties and atomic weight of bromine is average of chlorine and iodine.
Question 34.
Why are lanthanides and actinides placed separately at the bottom of the periodic table?
Answer:
Lanthanides and actinides belong to f – block elements with different properties so they are placed at the bottom of periodic table.

Question 35.
Lithium, Sodium, and Potassium were put in one group on the basis of their similar properties.
1) What are those similar properties?
2) What is the common name of this group of family?
Answer:
- They have same number of valence electrons that is 1 and valency 1. So they have similar chemical properties.
- They are called alkali metals.
Question 36.
What are the following groups known as?
1) group VIIA elements
2) Zero group elements.
Answer:
- Group VII A elements are called Halogens.
- Zero group elements are called Noble gases.
Question 37.
An element Barium lies in 2nd group; then answer the following.
1) What is its valency?
2) What will be the formula of its Phosphate?
Answer:
- The element lies in second group. So its valency is 2.
- The formula of Phosphate is Ba3(PO4)2 [since the valency of Phosphate is 3],
Question 38.
A, B, C are three elements having their atomic numbers equal to 2,10 and 5 respectively.
a) Which of these elements belong to same period?
b) Which of these elements belong to same group?
Answer:
The electronic configurations of A, B, C are as follows
A – 2, B – 2, 8, C – 2, 3.
a) So, B and C belong to same period because valence electron enters same orbit.
b) A and C belong to same group because both are noble gases.
Question 39.
Which element of 3rd period will form a chloride of Cl4?
Answer:
It would be Silicon because its electronic configuration is 2, 8, 4. So, it lies in third period and its valency is 4.
Question 40.
Which two elements of 3rd period will form a covalent compound?
Answer:
The two elements are phosporous and chlorine.
Question 41.
An element has atomic number 12. State whether it is metal or non-metal. Why?
Answer:
Its electronic configuration is 2, 8, 2. It lies in 2nd group. The elements towards left of periodic table are generally metals. So the element is metal.

Question 42.
Elements X, Y, and Z belong to IA group of the periodic table. Their atomic radii are as follows.
X → 1.33 Å,
Y → 0.95 Å,
Z → 0.60 Å.
Arrange the elements in the increasing order of atomic number by giving reason.
Answer:
As we move from top to bottom in a group, atomic size increases and atomic number also increases.
So the correct increasing order is Z, Y, X.
Question 43.
An element has an atomic number 16. State
i) period to which it belongs
ii) the number of valence electrons.
Answer:
Its electronic configuration is 2, 8, 6.
i) So it belongs to 3rd period (orbit number).
ii) The number of valence electrons is 6.
Question 44.
Why is energy absorbed when electron is added to uni-negative ion?
Answer:
It is difficult to add an electron to uni-negative ion. In order to overcome the repulsion between the electrons, actually energy should be supplied to add another electron to uni-negative ion.
Question 45.
When do you observe liberation of energy?
Answer:
Atoms of some elements gain electrons while forming ionic compounds. An atom is able to gain electron when the electron is attracted by the nucleus. Attraction involves the liberation of energy.
Question 46.
Why does nitrogen have less electron affinity value compared to oxygen?
Answer:
The electron affinity of nitrogen is less than oxygen because of stable configuration of nitrogen (i.e., 2p³ configuration).

Question 47.
Which one between Na and Na+ would have more size? Why?
Answer:
Na has more size because when one electron is removed from Sodium atom the nucleus attraction over outermost electron increases so atomic size decreases.
Question 48.
Second ionization energy of an element is higher than its first ionization energy. Why?
Answer:
It is difficult to remove an electron from unipositive ion when compared with neutral atom. So second ionization energy is always greater than first ionization energy.
Question 49.
Hydrogen can be placed in group’1 and group 7 periodic table. Why?
Answer:
Hydrogen has both +1 as well as -1 oxidation states. So still there is some ambiguity in position of hydrogen.
Question 50.
Why do inert gases have zero valency value?
Answer:
Inert gases show zero valency because they do not take part in chemical reactions due to stable configuration.
Question 51.
Element ’Z’ belongs to (second) 2nd group in the periodical table. Write the formula of oxide.
Answer:
The formula of oxide of the element is ZO.
Question 52.
Do the atom of an element and its ion have same atomic size?
Answer:
No, generally cation has smaller size and anion has greater size.
Question 53.
The electronegativities of the elements in period 3 of the periodic table are as. follows.

Arrange the elements in which they occur in the periodic table from left to right.
Answer:
Na Mg Al Si P S Cl
10th Class Chemistry 9th Lesson Classification of Elements – The Periodic Table 2 Marks Important Questions and Answers
Question 1.
An element has atomic number 17. Where would you expect this element in the Periodic Table? Why? (AP June 2018)
Answer:
- Electronic configuration of the given element is 1s² 2s² 2p6 3s² 3p5.
- So, it is in 3rd period and 17th group of periodic table.
- Due to the valency electronic configuration of 3s² 3p5 it belongs to 3rd period and 17th group.
Question 2.
How do you appreciate the special nature of inert gases?
Answer:
I appreciate the special nature of inert gases because it helps us in explaining the formation of chemical bonds among the atoms of elements and their stability.

Question 3.
The atomic number of an element is 35. Where would you expect the position of this element in the periodic table? Why? (TS June 2015)
Answer:
- The Electronic configuration of element with atomic number 35 is 2, 8, 18, 7.
- So it has seven valence electrons.
- That’s why it is present in 17th group or VII A group and 4th period.
- The element is Bromine.
Question 4.
Why were Dobereiner, Newlands and Mendeleeff not 100% successful in their classification of elements? Why is the modern table relatively a better classification? (TS March 2016)
Predict the reason.
Answer:
- All the known elements at the time of Dobereiner could not be arranged in the form of triads.
- Newlands’ periodic table was restricted only for 56 elements.
- As Mendeleeffs classification is based on atomic weight, his classification led to two defects like anomalous pair of elements and dissimilar elements placed together.
- Modern periodic table was prepared on the basis of atomic number. So the periods and groups are clearly defined.
Hence Dobereiner, Newlands, and Mendeleeffs classifications were not 100% successful, but modern classification is successful.
Question 5.
Observe the electronic configurations given below and write the group and period numbers of those elements. (TS March 2016)

Answer:
a) The period number is 3 and group number is 1.
b) The period number is 3 and group number is 15.
Question 6.
Observe the information provided in the table and answer the questions given below it. (TS June 2017)
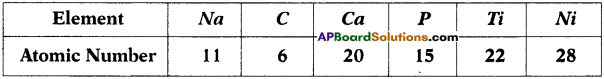
i) What are the s-block elements in the table?
ii) What are the ‘p’ block and ‘d’ block elements in the table?
Answer:
i) s-block elements : Na, Ca
ii) p-block elements : C, P
d-block elements : Ti, Ni.
Question 7.
Imagine, which one in each of the following pairs is large in size relatively with other? Explain. (AP March 2019)
(X) Na, Al (Y) Na, Mg+2
Answer:
(X) 1. Na is large in size than Al.
2. Atomic size gradually decreases from left to right in a period.
(Y) 1. Na is large in size than Mg2+.
2. Na is larger than Mg and Mg is larger than Mg2+.

Question 8.
What are the limitations of Dobereiner triad?
Answer:
- All the known elements could not be arranged in the form of triads.
- The law failed for very low mass or for very high mass elements.
Eg : In case of F, Cl, Br the atomic mass of Cl is not an arithmetic mean of atomic masses of F and Br.
- As the techniques improved for measuring atomic masses accurately, the law was unable to remain strictly valid.
Question 9.
Distinguish between electron affinity and electronegativity.
Answer:
| Electron affinity |
Electronegativity |
| 1. It is the property of an isolated gaseous atom. |
1. It is the property of a bonded atom. |
| 2. It is the energy released and is measured in ev/atom or kJ/mole. |
2. It is relative quantity and has no units. |
| 3. It is the attraction of an atom for a single electron. |
3. It is the attraction of an atom for a pair of electrons. |
Question 10.
What is electronegativity? What are the various methods used to determine electronegativity? Explain.
Answer:
Electronegativity :
The electronegativity of an element is defined as the relative tendency of its atom to attract electrons towards itself when it is bounded to the atom of another elements.
Various methods to calculate Electronegativity :
1) Milliken Scale :
According to Milliken, the electronegativity of an element is the average value of its ionization energy and electron affinity.
2) Pauling Scale :
Pauling scale is based on bond energies. The electronegativity of hydrogen is assumed as 2.20. Electronegativity of other elements is calculated with respect to hydrogen.
Question 11.
Give the electronic configurations of following elements. What do say about these elements by writing their electronic configurations?
a) Na
b) Al
c) Sc
d) Ce
Answer:
a) Na : 1s² 2s² 2p6 3s¹
b) M : 1s² 2s²2 2p6 3s² 3p¹
c) Sc : 1s² 2s² 2p6 3s² 3p6 4s² 3d¹
d) Ce : 1s² 2s² 2p6 3s² 3p6 3d10 4s² 4p6 4d10 5s² 5p6 6s² 4f²
Inference :
The valence electron enters different orbitals. So these elements belong to different blocks in modern periodic table, i.e. s, p, d, and f respectively.

Question 12.
Do you think that Newlands’ law of octaves is correct? Justify.
Answer:
No, Newlands’ law of octaves was restricted to only 56 elements and did not leave any room for new elements. Elements that were discovered later could not be filled into Newlands’ table in accordance with properties.
Question 13.
Why did Mendeleeff have to leave certine blank spaces in his periodic table?
Answer:
Mendeleeff predicted that some elements were missing in the table so he left blank spaces at the appropriate places in the table.
Question 14.
Give reason for the need of classification of elements.
Answer:
Classification is necessary because it is difficult to remember the properties of all the elements separately. It is easy to identify the properties of elements by making them groups with similar properties.
Question 15.
x, y, and z are the elements of a Dobereiner’s triad. If the atomic mass of ‘x’ is 7 and that of ‘z’ is 39, what should be the atomic mass of ‘y’?
Answer:
The atomic mass of x = 7 ;
The atomic mass of z = 39
x, y, z form Dobereiner triad
∴ Atomic mass oi y = average of x and z = \(\frac{7+39}{2}\) = \(\frac{46}{2}\) = 23
Question 16.
Name the two elements that would expect to have chemical properties similar to element with atomic number 11. What is the base for your choice?
Answer:
The element with atomic number 11 is sodium and its electronic configuration is 1s² 2s² 2p6 3s¹ or 2, 8, 1.
So it has one valence electron, i.e. present in I group. We know that the elements present in same group have same valence electrons. So they show similar properties.
Therefore the other two elements are Lithium and Potassium.
Question 17.
An element X belongs to 3rd period and group 14 of the periodic table. State
a) the number of valence electrons
b) the valency
c) the name of the element.
Answer:
a) The number of valence electrons are 4.
b) Its valency = 8 – 4 = 4.
c) The electronic configuration of element is 2, 8, 4.
(Because 3rd period means third orbit, group 14 has 4 valence electrons). So, the element with atomic number 14 is Silicon.

Question 18.
Why is it easier to remove 4f electron than 4s?
Answer:
Orbitals belonging to the same main shell have different penetration power towards the nucleus. In fourth main shell the order of penetration is like this 4s > 4p > 4d > 4f. So, it is easier to remove 4f electron than 4s.
Question 19.
How is screening effect responsible for low ionization of cesium?
Answer:
- More the shells with electrons between the nuclear and the valence shell, they act as screens and decrease nuclear attraction over valence electron. This is called the screening effect.
- More the screening effect, less is the ionization energy.
- Cesium with more inner shells has less ionization energy.
Question 20.
Why does Boron have less ionization energy when compared with Beryllium?
Answer:
- The electronic configuration of Be and B are 1s² 2s² and 1s² 2p² 2p¹.
- The element Boron has less ionization energy due to less penetration power of 2p compared to 2s.
Question 21.
We know that as we move from left to right ionization energy increases. But ionization energy Nitrogen is more than Oxygen. Why?
Answer:
- It is easier to remove an electron from Oxygen when compared to Nitrogen.
- This is because Nitrogen has stable 1s² 2s² 2p³ electronic configuration which contains half filled 2p orbitals whereas Oxygen has 1s² 2s² 2p4 configuration.
Question 22.
Why is it difficult to remove an electron from Mg+ when compared with Mg?
Answer:
- The energy required to remove the first electron outermost orbit of a neutral gaseous atom of the element is called first ionization energy.
- The energy required to remove from unipositive ion of the element is called second ionization energy.
- Second ionization energy is always more than first ionization energy because it is difficult to move electron from unipositive ion due to greater nuclear attraction.
- So it is difficult to remove an electron from Mg+ when compared with Mg.

Question 23.
Using the periodic table predict formula of compound formed between an element ‘X’ of group 2 and another element of group 17.
Answer:
- The element X belongs to group 2. So, the number of valence electrons are 2 and its valency is 2.
- The element Y belongs to group 17 or VII. So, the number of valence electrons are 7 and its valency = 8 – 7= 1.
During formation compound elements exchange their valencies.
∴ The formula of compound is XY2.
Question 24.
How do electronegativity values vary in period and group?
Answer:
Period :
When we move from left to right in period, the electronegativity increases due to decrease in atomic size.
Group:
When we move from top to bottom in a group, the electronegativity decreases due to increase in atomic size.
Question 25.
How does metallic and non-metallic characters vary in a period and group?
Answer:
Period:
When we move from left to right in a period, the metallic character decreases and non-metallic character increases.
Group :
When we move form top to bottom in a group, non-metallic character decreases and metallic character increases.
Question 26.
How do valency vary in period and group?
Answer:
Period :
When we move from left to right in a period, the valency does not follow a regular trend. For example, in second period the valency starts from 1 and increases to 4, then thereafter decreases to ‘O’.
Group :
When we move top to bottom in a group, the valency remains the same because in a group the valence electrons are same.
Question 27.
How does electron affinity vary in a period and group?
Answer:
Period :
When we move from left to right in period, electron affinity increases due to greater nuclear attraction over electron.

Group :
When we move from top to bottom, the electron affinity decreases in atomic size. As the size of the atom increases, the nuclear attraction over outermost electron decreases. So electron affinity decreases.
Question 28.
An element has atomic number 19. Where would you expect this element in the periodic table anti why?
Answer:
The electronic configuration of element is 1s²2s²2p63s²3p64s¹. So the element is in 4th period and I group.
Question 29.
The electronic configuration of the element X, Y, and Z are given below,
a) X = 2, 5
b) Y = 2, 8, 1
c) Z = 2, 8
i) Which element belongs to 18th group?
ii) Which element belongs to 15th or V group?
iii) Which element belongs to third period?
Answer:
i) Z belongs to 18th group because it is a noble gase (i.e. Ne).
ii) X belongs to 15th or V group because it has 5 valence electrons.
iii) Y belongs to 3rd period because the valence electron is present in 3rd orbit.
Question 30.
Referring the part of periodic table given below answer the questions that follow.

1) What happens to the atomic size if moved from left to right? Support your answer.
2) What changes do you observe in the metallic properties of the elements when moved from left to right?
Answer:
1) When we move from left to right in a periodic table atomic radii of elements decrease, as a result the size of the,atom decreases,
2) When we move from left to right in a periodic table electronegativity values of elements increase, as a result the metallic properties of the elements decrease.
Question 31.
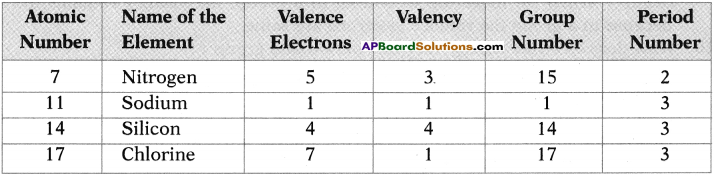
State the name of element, number of valence electrons, valency, the group number and the period number of each element given in the following table.
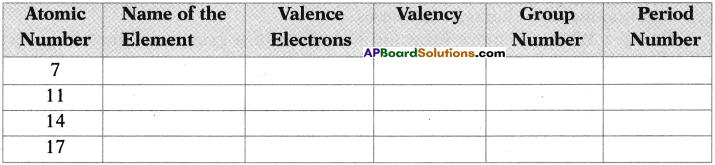
Answer:
10th Class Chemistry 9th Lesson Classification of Elements- The Periodic Table 4 Marks Important Questions and Answers
Question 1.
What is Ionization Energy? Explain the factors that effect Ionization Energy. (AP June 2017)
(OR)
What is ionization energy? What are the factors which influence ionization energy? Explain.
(OR)
Write the factors that influence ionization energy and explain any three of them. (TS March 2019)
Answer:
Ionization energy :
The energy required to remove an electron from the outermost orbit or shell of a neutral gaseous atom is called ionization energy.
Factors influencing ionization energy :
1) Nuclear charge :
As nuclear charge increases, ionization energy increases.
2) Screening effect or shielding effect:
More the screening effect, less is the ionization energy.
3) Penetrating power of the orbitals :
If the orbitals have less penetrating power, then the ionisation energy is less. Generally, the penetrating power of orbits are like this : s > p > d > f.
4) Stable configuration :
The elements having half-filled or completely filled orbitals have more stability. So the ionization energy is more when the element has stable configuration.
5) Atomic size :
As the atomic size increases, the nucleus attraction over outermost electron decreases. So ionization energy decreases.

Question 2.
Elements of one short period of the Periodic Table are given below in the order from left to right. (AP March 2017)
Li, Be, B, C, N, F, Ne
Answer the following:
(i) To which period, do these elements belong?
(ii) One element of this period is missing. Which is the missing element and where it should be placed?
(iii) Which of the above elements belong to the family of halogens? What is its electronegativity value?
(iv) How does the metallic character varies in the Period?
Answer:
(i) 2nd period.
(ii) Oxygen.
It should be placed between Nitrogen and Flourine.
(iii) Flourine
Electro negativity 4.0
(iv) Decreases from left to right.
Question 3.
In the table given below, names of some elements of families are given. Based on this, fill the information in the empty boxes. (TS June 2015)
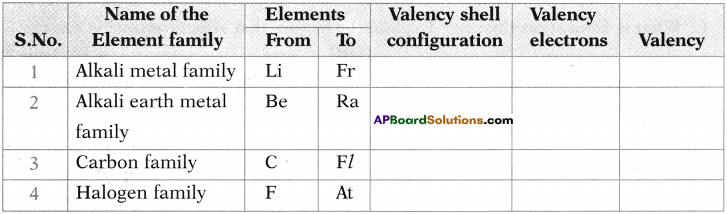
Answer:
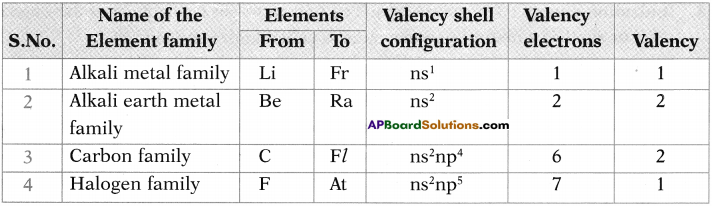
Question 4.
Two elements X and Y belong to Groups 1 and 2 respectively in the same period of the Periodic Table. Compare these elements with respect to : (TS March 2015)
i) number of electrons in their outermost orbit.
Answer:
The number of electrons in the outermost orbit of element X = 1
The number of electrons in the outermost orbit of element Y = 2
ii) their atomic size and their valencies.
Answer:
The atomic size of the Y is lesser than X
Valence of X = 1 ; Valence of Y = 2
iii) their ionisation energy and metallic character.
Answer:
The ionization energy of Y is greater than X, X has higher metallic character than Y.
iv) formulae of their chlorides and sulphates.
Answer:
Chloride of X …. XCl
Chloride of Y …. YCl2
Sulphate of X …. X2SO4
Sulphate of Y …. YSO4
Question 5.
How are the elements arranged into groups and periods in the Modern Periodic Table? Elements in a group possess similar properties, but elements in a period do not show similarities in their properties. Why? (TS June 2017)
Answer:
- The Modern periodic table is arranged in groups and periods based on the electronic configuration of the atoms of elements.
- Physical and Chemical Properties of elements are related to their electronic con-figurations particularly the outershell configurations.
- The atoms of the elements in a group posses similar electronic configurations.
- The elements in a group should have similar chemical properties and there should be regular gradation in their physical properties from top to bottom.
- Across the table from left to right in any period, elements gets an increase in the atomic number by 1 unit between any two successive elements.
- Therefore the electronic configuration of valence shell of any two elements in a given period is not same.
- Due to this reason elements along a period posses different chemical properties with regular gradation in their physical properties from left to right.
Question 6.
Explain any four factors which influence the electron affinity (Electron Gain Enthalpy). (TS March 2017)
Answer:
Factors effecting of electron affinity
1. Nuclear Charge :
If nuclear charge increases electron affinity increases, similarly it decreases if nuclear charge decreases.
2. Screening effect:
If screening effect value increases electron affinity increases, if it decreases electron affinity decreases.
3. Penetration power of the orbitals :
If penetration power of the orbitals increases electron affinity increases. If it decreases electron affinity decreases.
4. Stable configuration :
If an atom has stable electron configuration electron affinity will decreases.
5. Atomic radius :
If atomic radius increases electronic affinity will be increases. If atomic radius decreases electron affinity decreases.
6. Metallic property :
If metallic property increases electron affinity decreases.
7. Non-Metallic property :
Non-Metallic property increases electron affinity value increases.

Question 7.
Observe the information and answer the following questions. (TS June 2018)
| Name of the Element |
Atomic Number |
Electronic Configuration |
| Sodium |
11 |
[Ne] 3s1 |
| Magnesium |
12 |
[Ne] 3s2 |
| Potassium |
19 |
[Ar] 4s1 |
| Calcium |
20 |
[Ar] 4s2 |
1) What is valency of Magnesium?
Answer:
Valency of magnesium is two.
2) Which element has more electro-positivity?
Answer:
Potassium (K) has more electro-positivity.
3) Write the elements which belongs to (third) 3rd Period.
Answer:
The elements which belongs to 3rd period are Sodium (Na), Magnesium (Mg).
4) Write the elements which belongs to 1st Group.
Answer:
Sodium (Na), Potassium (K) belong to 1st Group.
Question 8.
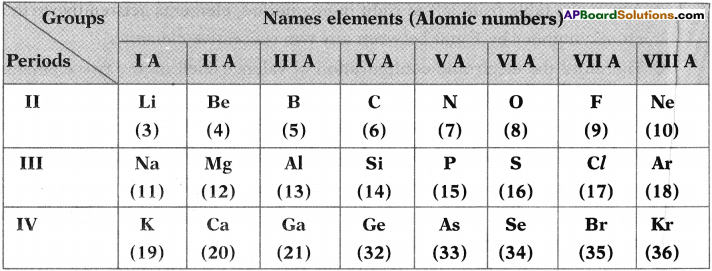
Answer the following from the above in brmation. (TS March 2018)
i) Which element posses the higher atomic radius in the above table?
Answer:
The element having higher atomic radius is ‘K’ (Potassium)
ii) Mention two plair of element which forms ionic bond.
Answer:
Na, Cl Mg, CL
iii) Name the two elements having valency 2.
Answer:
Elements having valency 2 are Be, Mg, Ca, 0, S, Se.
iv) Which element has electronic configuration of 1s² 2s² 2p4.
Answer:
Oxygen.
Question 9.
Explain the significance of three quantum numbers in predicting the position of an electron in an atom. (AP SCERT: 2019-20)
Answer:
Each electron in an atom is described by a set of three quantum numbers n, 1 and ml.
1. Principal quantum number (n):
The principal quantum number is used to describe the size and energy of the main shell. It is denoted by ‘n’. ‘n’ has positive integer values of 1, 2, 3, It is used to know the number of orbitals (n²) and electrons in an orbit. (2n²).
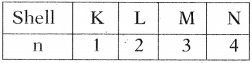
As ‘n’ increases the shells becomes larger and the electrons in those shells are farther from the nucleus and their energies increases.
2. The angular – momentum quantum number (l) :
‘l’ has integer values from O’ to n – 1, for each value of ‘n’. Each ‘l’ value represents one sub-shell. It is used to describe the shape of an orbit.

3. The magnetic quantum number (ml) :
The magnetic quantum number (ml) has integer values between -l and +l including zero.
If l = 0, the possible ml value is 1.
l = 1, the possible ml value is -1, 0 and 1.
Thus for a certain value of 1, there are (2l + 1) integer values of ml.
These values describe the orientation of the orbital in space relative to the other orbitals in the atom.
Ex: When l = 1, (2l + 1) = 3, that means ml has 3 values namely -1, 0, 1 or three p orbitals, with different orientations along x, y, z axes, labelled as px, py and pz orbitals.
Predicting the position of an electron in an atom :
If the values of n, l, and ml are 2, 1,-1 respectively the electron is present in 2px orbital in L – shell.

Question 10.
Answer the following question based on the values of the atomic radii of the elements of one of the periods in modern periodic table (AP SCERT: 2019-20)
Li (152), Be (111), B (88), C (77), N (74), O (66) and F (64)
a) What is the trend of atomic radii of given elements?
b) In the numerical listing of periods in the modern periodic table, what number was given to above elements?
c) Mention the unit of atomic radius.
d) Why the values of atomic radius varied along the period?
Answer:
a) Atomic radii of elements decrease while going left to right in the periodic table.
b) Period – 2
c) Unit of atomic radius is ‘pm’ (picometer).
d) There should be no change in distance between nucleus and outer most shell for the elements in one period.
But, nuclear charge increases because of the increase in the atomic number of elements in a period.
Hence, the nuclear attraction on the outer shell electrons increases.
As a result the size of the atoms decreases while going left to right in a period.
Question 10.
Mendeleeff classified the then known 63 elements in the form of a periodic table. Mention any two things that benefitted study of chemistry, to support the above statement.
Answer:
- Mendeleeff accepted minor inversions in the order of increasing atomic weights as these inversions resulted in elements being placed in the correct group.
- It was the extraordinary thinking of Mendeleeff that made the chemists to accept the periodic table and recognise Mendeleeff more than anyone else as the originator of the periodic law.
- At the time when Mendeleeff introduced his periodic table even electrons were not discovered.
- Even then the periodic table was prepared to provide a scientific base for the study of chemistry of elements.
- In his honour the 101 element was named “Mendelevium”.
Question 11.
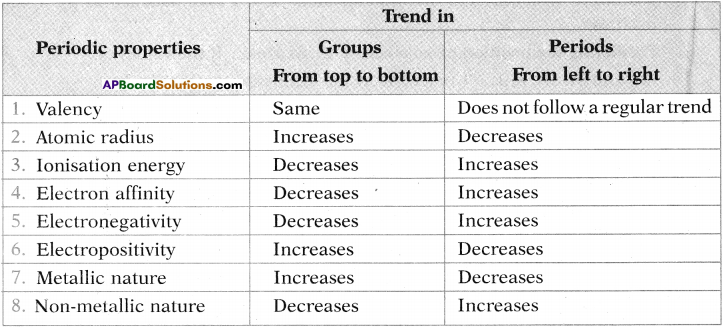
How do these properties vary in period and group?
1) Valency
2) Atomic radius
3) Ionisation energy
4) Electron affinity
5) Electronegativity
6) Electropositivity
7) Metallic nature
8) Non-Metallic nature.
Answer:
Question 12.
Explain the salient features and achievements of the Mendeleeffs periodic table.
Answer:
Mendeleeffs periodic table is based on atomic weight.
1) Periodic law:
The physical and chemical properties of the elements are the periodic functions of their atomic weights.
2) Groups and sub-groups :
The vertical columns in Mendeleeffs periodic table are called groups. There are eight groups and elements in each group have similar properties. Each group is divided into sub-groups A and B.
3) Periods :
The horizontal rows are called periods. There are ‘seven’ periods in Mendeleeffs periodic table.
4) Predicting the properties of missing elements :
Based on the arrangement of elements in table, Mendeleeff predicted that some elements were missing and left blank spaces at appropriate places in the table. Later they were discovered.
5) Correction of atomic weight :
It is useful in correcting atomic weights of elements.
6) Anomalous series :
More atomic weight element like Tellurium (Ti) is placed before the less atomic weight element like Iodine in order to place these elements in the correct group.

Question 13.
How does atomic radius vary la period and group? Explain.
Answer:
Period :
- As we move from left to right the atomic radius decreases because the electrons enter the same main shell.
- The nuclear charge increases because of increase in atomic number of elements in period.
- Hence, the nuclear attraction on the outer shell electron increases. As a result, the size of atom decreases.
Group:
- Atomic radius increases from top to bottom in a group of the periodic table.
- As we go down in a group, the atomic number of element increases. In order to accommodate more number of electrons, there are more additional shells.
- As a result, the distance between the nucleus and the outer shell of atom increases.
- So atomic size increases.
Question 14.
What is electron affinity? What are the factors which influence electron affinity?
Answer:
Electron affinity :
- The electron affinity of an element is defined as the energy liberated when an electron is added to its neutral gaseous atom.
- Electron affinity of an element is also called electron gain enthalpy of that element.
- M(g) + e– → M–(g) + EA1 (M = Atom of element, EA1 = First Electron affinity)
M–(g) + e– → M-2(g) + EA2 (EA2 = Second Electron affinity)
Factors influencing Electron affinity :
1) Nuclear charge :
Greater the nuclear charge, greater the electron affinity value because of greater attraction for incoming electron.
2) Atomic size :
As the atomic size increases, the attractive force of the nucleus on the electron decreases. So electron affinity decreases.
3) Electronic configuration :
The elements having stable electronic configurations of half filled or completely filled valence sub-shells show very small tendency to accept additional electron. So the electron affinity is low or almost zero for these elements.
4) Penetrating power of the orbitals :
As the penetrating power of the orbitals increases, the electron affinity increases.
5) Screening effect or shielding effect:
More the screening effect of orbitals, less is the electron affinity value.
Question 15.
How did Mendeleeff correct atomic weights of various elements?
Answer:
- Atomic weight = Equivalent weight x Valency
- By using the formula, the atomic weight of Beryllium was calculated as 13.5 (Equivalent weight of Be = 4.5, valency = 3)
- With this atomic weight the element should be placed in wrong group.
- So Mendeleeff predicted its valency is only 2. From that he calculated the atomic weight of Beryllium as 9.
- Now it fitted into correct group.
- Similarly, Mendeleeff corrected atomic weights of Indium and Gold.
Question 16.
Answer the following questions if atomic number of element is 15.
1) What is the name of the element?
2) What is the electronic configuration of element?
3) Which period and group does it belong to?
4) How many valence electrons are there in the element?
5) What is the valency of the element?
Answer:
- The element is phosporous,
- The electronic configuration of element is 1s² 2s² 2p6 3s² 3p³ or 2, 8, 5.
- It belongs to 3rd period (orbit number is 3) and V or 15 group (Number of electrons in valence orbit is 5.)
- Number of valence electrons are 5.
- Its valency is 8 – 5 = 3.
Question 17.
If an element belongs to 3rd period and 17th group, then answer the following questions.
1) What is its electronic configuration?
2) How many valence electrons are there in the element?
3) What is the valency of element?
4) What is atomic number of element?
5) What is the name of the element?
6) Give two more elements which have similar properties as this element?
Answer:
- The element belongs to 3rd period and 17th group. So the valence orbit is 3rd and number of valence electrons in that orbit is 7. So its electron configuration is 2, 8, 7.
- The number of valence electrons are 7.
- The valency of element = 8 – 7 = 1.
- The atomic number of element is 17.
- Name of the element is chlorine.
- Chlorine belongs to Halogen family. So Fluorine, Bromine, Iodine, and Astatine have similar properties as chlorine.
Question 18.
The elements of a periodic table are given below in the order from left to right.
Li Be B C O F Ne
1) To which period do these elements belong?
2) One element of this period is missing. Which is the missing element and where should it be placed?
3) Which one of the elements in this period shows the property of catenation?
4) Place the three elements fluorine, beryllium, and oxygen in the order of increasing electronegativity.
5) Which one of the above elements belongs to halogen series?
Answer:
- The elements belong to 2nd period.
- The element which is missing is Nitrogen which is placed in between carbon and oxygen.
- Carbon shows the property of catenation.
- The ascending order of electronegativity for these element is Beryllium < Oxygen < Fluorine.
- Fluorine belongs to halogen family.

Question 19.
A group of elements in periodic table is given below.
Boron, Aluminium, Gallium, Indium, and Thallium.
(Boron is the first element and Thallium is the last element)
Answer the following questions in relation to the above group of elements.
1) Which element has the most metallic character?
2) Which element would be expected to have the highest electronegativity?
3) If the electronic configuration of Aluminium is 2, 8, 3, how many electrons are there in outer shell of thallium?
4) The atomic number of Boron is 5. Write the chemical formula of the compound formed when Boron reacts with Chlorine.
5) Do the elements in the group to the right of this Boron group have more metallic or less metallic character? Justify your answer.
Answer:
1) Thallium has the most metallic character because as we move from top to bottom in a group the metallic character increases.
2) Boron has the highest electronegativity because as we move from top to bottom in a group electronegativity decreases.
3) Thallium is in the same group as Boron. So, the number of electrons in outermost shell of Thallium is 3.
4) The atomic number of Boron is 5. So, its electronic configuration is 2, 3. Therefore its valency is 3.
Whereas the atomic number of Chlorine is 17. So, its electronic configuration is 2, 8, 7. Therefore its valency is 1.
The formula of compound formed between Boron and Chlorine is BCl3.
5) The elements in the group right to Boron group have lesser metallic character because as we move from left to right in a period metallic character decreases.
Question 20.
The following questions refer to the periodic table.
1) Name the first and the last element in period 2.
2) What happens to the atomic size of elements moving from top to bottom of a group?
3) Which of the elements has the highest electron affinity among the halogens?
4) What is common feature of the electronic configurations of the elements in group 16?
Answer:
1) The first and the last elements of 2nd period or Lithium and Neon.
2) The atomic size decreases as we move from top to bottom in a group because there is an addition of shell each time as we move down the group.
3) Chlorine has the highest electron affinity. We know as move from top to bottom the electron affinity values decrease. But due to small size of fluorine there would be more electron-electron repulsions, if we add electron. So Chlorine has more electron affinity.
4) All these have same general outermost electronic configuration that is ns² np4.

Question 21.
Answer the following.
1) Elements of which groups have low ionization energy?
2) What is your guess about atomic size of an element with seven electrons among all the elements in the same period?
3) Which element has the highest electronegativity? Why?
4) Which element has the highest electropositivity? Why?
Answer:
1) Group IA, IIA elements have lower ionization energy values because they have metallic character.
2) As we move from left to right in a period atomic size decreases. So element with seven outermost electrons has least size among all the elements in the same period.
3) Fluorine has the highest electronegativity because when we move from left to right in a period atomic size decreases and electronegativity values increase. So Fluorine has the highest electronegativity.
4) Cesium has the highest electropositivity or positive character because when we move from top to bottom in a group atomic size decreases. So electropositive character increases. Therefore Cesium has the highest electropositive character.
Question 22.
Given below is the electronic configuration of A, B, C, D.
| A) 1s2 2s2 2p¹ |
a) Which are the elements coming within the same period? |
| B) 1s2 2s2 2p6 |
b) Which are the elements coming within the same group? |
| C) 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 |
c) Which are the noble gas elements? |
| D) 1s2 |
d) Which group and period does the element C belong to? |
Answer:
a) A and B belong to same period because the valence electrons of both the elements lie in the same orbit.
b) Elements A and C and elements B and D.
c) B and D are noble gas elements.
d) C belongs to 3rd period (orbit number) and III group (Number of valence electrons).
Question 23.
Write down the characteristics of the element having atomic number 16.
i) Electronic configuration
ii) Period number
iii) Group number
iv) Element family
v) Number of valence electrons
vi) Valency
vii) Metal or non-metal
viii) Name of the element
Answer:
i) Electronic configuration of element is 1s² 2s² 2p6 3s² 3p4 or 2, 8, 6.
ii) Period number is 3 because valence electron lies in 3rd orbit.
iii) Group number is 6 because the number of valence electrons are 6.
iv) Element belongs to chalcogen family.
v) Number of valence electrons are 6.
vi) Valency = 8 – 6 = 2.
vii) It is a non-metal because in a period when we move from left to right non-metallic character increases.
viii) Name of the element is sulphur.

Question 24.
The second period element ‘F has electron gain enthalpy than the third period elements of same group ‘Cl’. Why?
Answer:
- In a group of elements, the electron gain enthalpy decreases from top to bottom.
- But in general the second element in a group, i.e. 3rd period element has greater electron gain enthalpy than the first element, i.e. 2nd period element.
Ex : E.A of F < E.A of Cl.
- This is because Fluorine atom is smaller in size than Chlorine atom.
- F2 also has strong inter electronic repulsions.
- In the addition of an electron to fluorine atom, the electronic repulsions overcome at the expense of a part of the energy liberated.
Hence the overall energy liberated is less than that of Chlorine atom.
Question 25.
Differentiate the metals and non-metals.
Answer:
| Metals |
Non-Metals |
| 1. Metals have lustrous surface. |
1. Non-metals do not have lustrous surface. |
| 2. They show malleability. |
2. They do not show malleability. |
| 3. They show ductility. |
3. They do not show ductility. |
| 4. They produce sonorous sound. |
4. They do not produce sonorous sound. |
| 5. Generally they are hard. |
5. Generally they are soft. |
| 6. They are good conductors of electricity. |
6. They are bad conductors of electricity. |
| 7. Generally they liberate hydrogen gas when they are treated with acids. |
7. They do not liberate hydrogen gas. |
Question 26.
The electronic configuration of atom A is 2, 8, 6.
a) What is the atomic number of element A?
b) State whether the atomic size of element A is bigger or smaller than the atom having atomic number 14. Why?
c) Which of the elements exhibits similarity in chemical properties as element A 0(8), C(6), N(7), AV(18). Why?
d) How does the element form inert gas configuration?
Answer:
The electronic configuration of atom – A is 2, 8, 6.
a) Atomic number of element ‘A’ is 16, i.e. Sulphur.
b) The atom which has atomic number – 14 is Silicon (Si).
Atomic size of element decreases across period from left to right. So the atomic size of element ‘A’ is smaller than the atom having atomic number 14.
c) Element oxygen O8 – exhibits similarity in chemical properties as element A, because they belong to the same group.
d) Given element – A becomes inert gas, i.e. Argon configuration by gaining ‘2’ electrons.

Question 27.
Select the correct answers from the choices A, B, C, D which are given with reference to the variation of properties in the periodic table. Which of the following is generally true?
A : Atomic size increases from left to right across a period.
B : Ionisation energy increases from left to right across a period.
C : Electropositive character increases going down a group.
D : Electronegativity increases going down a group.
Answer:
1) A is wrong because when we move from left to right the atomic number increases. So, the nuclear attraction over outermost orbital increases. Therefore the atomic size decreases.
2) B is correct but it does not follow a regular trend in a period.
3) C is correct. As move from top to bottom in a group atomic size increases. Therefore it is easy to lose electrons. So electropositive character increases.
4) D is wrong because as we move from top to bottom in a group atomic size increases. So electronegativity decreases.
Question 28.
Some elements belonging to second period of periodic table, and their atomic radii are given below. Observe them and write answers.

1) Write the elements in the ascending order of their atomic radii.
2) Which of the 2nd period elements closer to the configuration of inert gas?
3) Which is the outermost orbit of all these elements?
4) Which element’s atomic size is bigger, Beryllium or Carbon? Why?
Answer:
- The ascending order of atomic sizes is O, N, C, B, Be and Li.
- Lithium has closest inert gas configuration, i.e. 1s² 2s¹. Its nearest inert gas is Helium.
- The outermost orbit for all these elements is second orbit.
- Beryllium has more atomic size than Carbon. Because when we move across a period the atomic number increases. So nuclear attraction over outermost orbit increases and atomic size decreases. So carbon has lesser size than Beryllium.
Question 29.
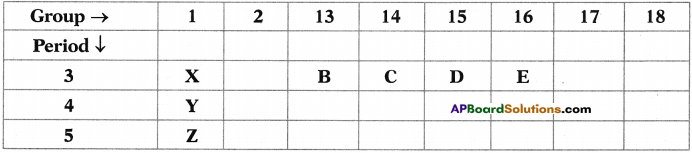
Refer the above part of periodic table and answer the following questions.
a) Element with the least atomic size.
b) Write the electronic configuration of the elements B and E.
c) Identify the elements that have similar physical and chemical properties as the element Y.
d) Arranged elements increasing order of their electronegativity values.
Answer:
a) The element with least atomic size is E. Because when we move from left to right in a period the atomic size decreases,
b) Electronic configuration of B is 1s² 2s² 2p6 3s² 3p¹ Because the element belongs to 13th group its general configuration is ns² np¹ and the element belongs to third period and its atomic number is 13. Similarly electronic configuration of E is 1s² 2s² 2p6 3s² 3p¹. Because the element belongs to 16th group. Its general configuration is ns2np4 and it is in third period. So its atomic number is 16.
c) The elements which have similar physical and chemical properties with Y are X and Z. Because they lie in a single group, i.e. 1st group. In a group, elements are having similar physical and chemical properties.
d) Z < Y < X < B < C < D < E.
Question 30.
Consider the section of the periodic table given below.
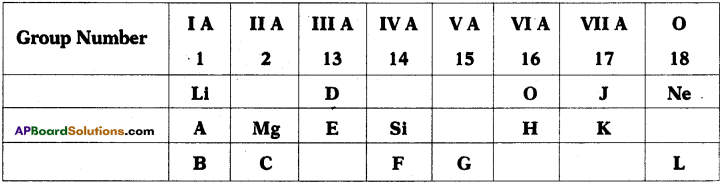
1) Which is the most electronegative?
2) How many valence electrons are present in G?
3) Write the formula of the compound between B and H.
4) Which element has similar properties as J?
5) Which element has greater size-either D or E?
Answer:
- J is the most electronegative. In a period electronegative values increase.
- G is present in V group. So the number of valence electrons is 5.
- B is present in first group. So its valency is 1 and hydrogen also has valency 1. Therefore the compound is BH.
- K lies in same group as J. Elements belonging to same group have similar properties. So, K has similar properties as J.
- E has greater size because as we move from top to bottom the atomic size increases.
![]()
![]()

![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()