These AP 9th Class Biology Important Questions 2nd Lesson Plant Tissues will help students prepare well for the exams.
AP State Syllabus 9th Class Biology 1st Lesson Important Questions and Answers Plant Tissues
9th Class Biology 2nd Lesson Plant Tissues 1 Mark Important Questions and Answers
Question 1.
What are the functions of stomata?
Answer:
- These are essential for exchange of gases with the atmosphere.
- During transpiration loss of water takes place in the form of water vapour through stomata.
Question 2.
How many types of elements together make up the xylem tissue?
Answer:
Xylem tissue consists of four types of elements. They are trachieds, vessels, xylem parenchyma and xylem fibres.
![]()
Question 3.
What are the constituents of phloem?
Answer:
Phloem is made up of five types of elements. They are sieve tubes, sieve cells, companion cells, phloem fibres and the phloem parenchyma.
Question 4.
How can the plants perform all the life processes?
Answer:
Different parts of the plant having specific tissues perform specific function.
Question 5.
Meristematic tissue present at the tips of root and shoot is called as?
Answer:
Apical meristem.
Question 6.
Which portion of the plant is responsible for transport of water, minerals and food materials?
Answer:
Stele
![]()
Question 7.
What is the other name for stomata?
Answer:
Airpores
Question 8.
Name the cells which divide continuously.
Answer:
Meristematic cells.
Question 9.
Which tissues makes up the husk of coconut?
Answer:
The husk of coconut is made of sclerenchyma tissue.
Question 10.
What is the role of epidermis in plants?
Answer:
Cells of epidermis form a continuous layer without intercellular spaces. It protects all the parts of the plants.
Question 11.
What are guard cells? What is their function?
Answer:
Each stomata is bound by a pair of specialised epidermal cells called guard cells. They control the opening and closing of the stomata.
Question 12.
How many types of elements together make up the xylem tissue? Name them.
Answer:
Xylem is made up of vessels, trachieds, xylem fibres and xylem parenchyma.
Question 13.
What are the constituents of Phloem?
Answer:
Phloem constitutes the sieve tubes, companion cells, phloem parenchyma and phloem fibres.
![]()
Question 14.
What is a vascular tissue?
Answer:
Any tissue which contain vessels through which fluids are passed is called a vascular tissue.
Question 15.
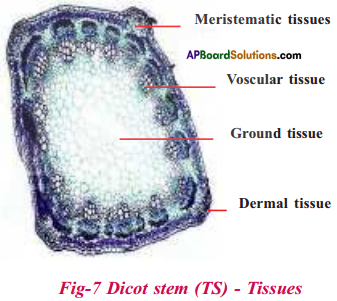
Identify the given tissues.
Answer:
Question 16.
Name the branch of science that deals with the study of tissues.
Answer:
Histology
Question 17.
Name the scientist who coined the term ‘Parenchyma’.
Answer:
Nehamiah Grew
![]()
Question 18.
Name the plants that are possessed with Arenchyma.
Answer:
Water plants like Pistia, Eichornia.
Question 19.
Name the tissue that protects the trees from strong winds.
Answer:
Collenchyma gives flexibility and tensile strengh to the branches of the trees and protect them from strong winds and make them to bend. So, the branches won’t break up when they are exposed to the strong winds.
Question 20.
Where do you find sieve cells? What is their function?
Answer:
Sieve cells found in phloem helps in the transportation of materials.
Question 21.
What are companion cells and state their function?
Answer:
Companion cells are the parts of phloem aiding in transport of materials.
Question 22.
Where do you find vessels? Write their function.
Answer:
Vessels are found in xylem helps in conduction of nutrients. They also give mechanical support to the plant.
Question 23.
Name the tissue that is present in root tips.
Answer:
Meristematic tissue.
![]()
Question 24.
What is meant by differentiation?
Answer:
The process of taking up a permanent shape, size and function is called differentiation.
Question 25.
What happens to the plant if the vascular bundles are destroyed?
Answer:
The transportation of water, nutrients and food in that plant is totally stopped. Hence, the plant will die.
Question 26.
Name the tissue, that brings about overall growth and repair in plants.
Answer:
Meristematic Tissue.
Question 27.
Name the tissue, that form the bulk of the plant body, helping in packing other tissues.
Answer:
Ground Tissue.
![]()
Question 28.
Name the parts of the plant that helps in reproduction.
Answer:
Flowers
9th Class Biology 2nd Lesson Plant Tissues 2 Marks Important Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Name the different elements of xylem. Collect information about the uses of the elements of xylem.
Answer:
- Xylem consists of trachieds, vessels, xylem parenchyma and xylem fibres.
- Trachieds and vessels are tubular structures. This allows them to transport water and minerals vertically.
- The parenchyma stores food and helps in the sideways conduction of water.
- Fibres are mainly supportive in function give mechanical support to vascular bundles.
Question 2.
What are the differences between the plant tissues and animal tissues?
Answer:
| Plant Tissues | Animal Tissues |
| 1. Most of the tissues are dead. | 1. Most of the tissues are living. |
| 2. Plants need less maintenance energy. | 2. Animals need more maintenance energy. |
| 3. Tissues organisation is to support fix habitat. | 3. Tissues organisation help the organism for locomotion. |
Question 3.
What are the differences between simple tissue and complex tissue?
Answer:
- Simple tissues are composed of one type of cells which are structurally and functionally similar.
e.g. : Parenchyma, Collenchyma and Sclerenchyma. - Complex tissues consists of more than one type of cells which perform a common function.
e.g.: Xylem and phloem.
Question 4.
What are the characteristic features of cells in meristematic tissue?
Answer:
Cells in the meristematic tissue are
- Small and having thin cell wall.
- Living with prominent nucleus and abundant cytoplasm.
- Compactly arranged without intercellular spaces.
- Continuously dividing cells.
![]()
Question 5.
Differentiate between Parenchyma, Collenchyma and Sclerenchyma on the basis of their cell walls.
Answer:
| Parenchyma | Collenchyma | Sclerenchyma |
| The cell walls are thin and made of cellulose. | The cell walls are thick due to cellulose and pectin formation in some places on the walls. | Due to lignin deposition cell walls are thick. |
Question 6.
Complete the following flow chart.
Answer:
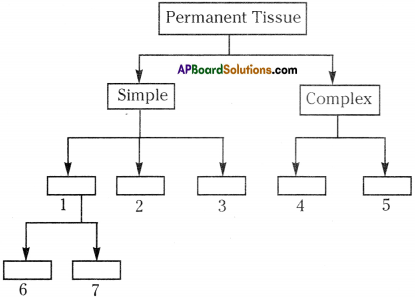
- Parenchyma
- Sclerenchyma
- Collenchyma
- Xylem
- Phloem
- Chlorenchyma
- Arenchyma
Question 7.
Write down the arrangement of cells in the given table :
Answer:
| Arrangement of the cells (Tissues) | Shoot tip | Root tip |
| 1. At the tip | Apical meristems are present. | Meristems below the root cap are present. |
| 2. At the lateral side | Lateral meristems are present. | Lateral meristems are present. |
| 3. At the point of branching | Intercalary meristems are present. | Meristems are absent |
Now answer the following questions.
1) Where do you find meristems in the root tip?
Answer:
Below the root cap.
2) Where do you find intercalary meristems in the shoot tip?
Answer:
At the point of branching
![]()
Question 8.
Draw a neat and labelled diagram of stomata.
Answer:
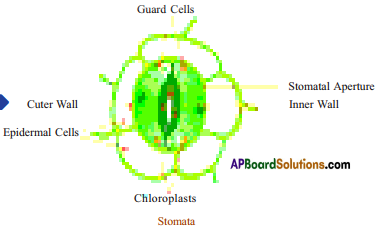
Question 9.
a) Identify the given structures.
b) State the role performed by the two structures.
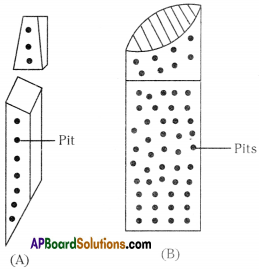
Answer:
a) A is trachied
B) B is vessel
Both help in transporting water and minerals vertically.
Question 10.
Observe the diagram of location of meristematic tissue in plant body. Identify the types of meristematic tissue found in the labelled regions and write their functions.
Answer:
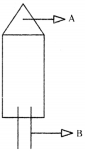
- Apical meristems are found in the A region
- Lateral meristems are found in the B region.
- Apical meristem increases the length of the stem and the root.
- Lateral meristem (cambium) increases the growth of the stem and root.
Question 11.
How does the cork act as protective tissue?
Answer:
- Cork has dead cells and compactly arranged without intercellular spaces.
- They have deposition of suberin on the walls that make them impervious to gases and water.
![]()
Question 12.
How do you appreciate the functions of vascular tissue in plants?
Answer:
- Vascular tissues carry water to a great heights in the plant body.
- It is upto nearly 200ft in Eucalyptus plants and upto nearly 330ft in the Redwood trees.
- It is an amazing factor of nature. I appreciate the functions of vascular tissue which carry water up to a greater heights.
Question 13.
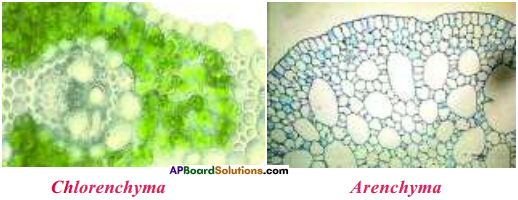
Write a note on Arenchyma.
Answer:
- Air spaces are present in this type of Parenchyma.
- This type of Parenchyma is seen in plants which float on water, such plants are called hydrophytes.
Ex : Pistia, Eichornia, Hydrilla.
9th Class Biology 2nd Lesson Plant Tissues 4 Marks Important Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Draw a flow chart for plant tissues.
Answer:
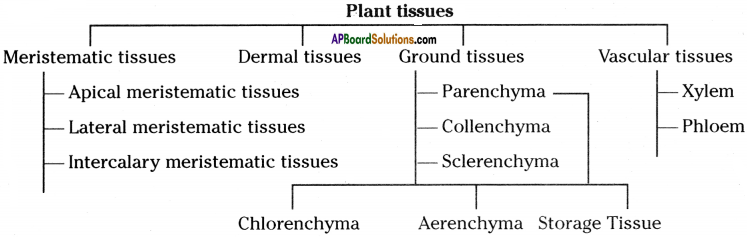
Question 2.
What are meristems? Write the types of meristems.
Answer:
1. Tissues that bring about overall growth and repair are called meristems.
2. Meristems are of three types.
- Apical meristems
- Intercalary meristems
- Lateral meristems.
3. Meristems at the growing tip that bring about growth in length are apical meristems.
e.g. : Stem and Root tips.
4. Meristems present around the edges in a lateral manner and giving rise to growth in diameter or girth of the stem are called lateral meristems.
5. Meristems present at the branching takes place or a leaf or a flower stalk grows are known as intercalary meristems.
![]()
Question 3.
Describe the structure of parenchyma, collenchyma and sclerenchyma with the help of a diagram.
Answer:
1) Structure of Parenchyma :
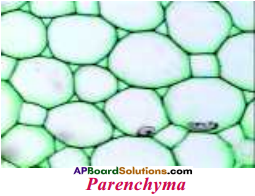
- The cells of parenchyma are soft thin walled and loosely packed.
- The parenchyma which contains chloroplasts is chlorenchyma, parenchyma which contains air spaces is arenchyma and the parenchyma which stores food or water is storage tissue.
2) Structure of Collenchyma :
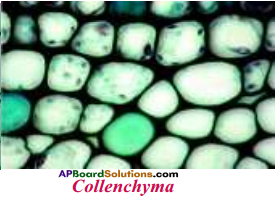
- Collenchyma tissues have thicker walled longer cells.
- They give mechanical support to plant.
- Intercellular spaces are present.
3) Structure of Sclerenchyma :
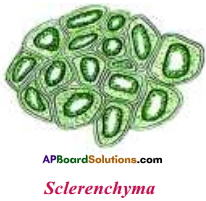
- In the sclerenchyma the cells are thick walled and compactly arranged withtiearly no spaces between them.
- They give mechanical strength to the plant.
Question 4.
Draw the diagram showing different types of ground tissue in plants.
Answer:
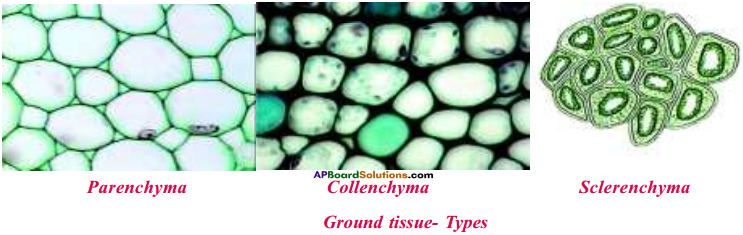
Question 5.
Draw the diagram showing different cells of xylem and phloem.
Answer:
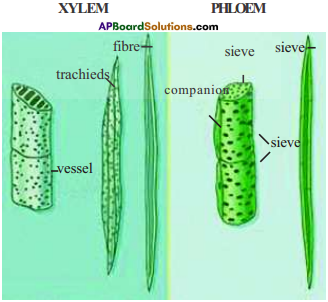
Question 6.
Draw and label the diagram of L.S. of shoot tip.
Answer:
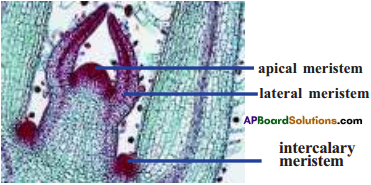
Question 7.
If you want to know more about Xylem and phloem, what questions will you ask?
Answer:
I will ask the following questions to know more about xylem and phloem.
- What is the economic importance of xylem and phloem?
- What are the factors that are helpful to vascular tissue in conducting water?
- How do plants get water in the higher mountains?
- What is the commercial importance of bast fibres?
9th Class Biology 2nd Lesson Plant Tissues Important Questions and Answers
Question 1.
What will happen if stomata are absent in the leaves of the plant
Answer:
- Gaseous exchange will not takes place in leaves.
- Transpiration does not take place.
Question 2.
What are the different types of ground tissues in plants
Answer:
- Parenchyma
- Collenchyma
- Sclerenchyma
![]()
Question 3.
Give reasons.
a) Xylem is a conductive tissue.
b) Adipose tissue acts as an insulator of heat.
c) Cardiac muscle works without rest.
d) Epidermis provides protection to plants.
Answer:
a) Xylem acts as conducting tissue as it transports water and minerals from the roots to the top of tree.
b) Fat in our body is stored in adipose tissue. It is found below the skin and between internal organs. They act as insulators.
c) i) The muscles present in the heart are responsible for pumping of blood.
ii) The cells are long, branched and have nuclei.
iii) Cardiac muscles have striations. Though they have striations, they are involuntary muscles.
d) i) Dermal tissue (Dermis) usually consists of a single layer of tissues showing variations in the types of cells on the basis of their functions and location.
ii) The dermal tissue protects the plants from loss of water, mechanical damage like breaking and cleaning of branches and invasion of parasites and disease causing organisms.
Question 4.
Read the following paragraph and answer the following questions :
| The cells of the parenchyma are soft, thin walled and loosely packed. The parenchyma which contains chloroplast is called Chlorenchyma. The parenchyma which contains large air spaces are called Aerenchyma and which store water or food is called storage tissue. Collenchyma have thicker walls and longer when compared to Parenchyma. In the sclerenchyma the cells are thick walled and compactly arranged with nearly no spaces between them. |
a) What does the paragraph denote?
b) What function does chlorenchyma perform and why?
c) In which plants do you find Aerenchyma abundantly and why?
d) Give some examples of plants where storage tissue is commonly seen.
Answer:
a) Ground tissue in plants.
b) Chlorenchyma has chloroplasts, which are capable of trapping solar energy. Hence, they perform photosynthesis.
c) Aerenchyma is found in water plants [Hydrophytes], Aerenchyma enables the water plant to float on water.
d) Potato, Carrot, Raddish.
![]()
Question 5.
a) Kshitija selected a plant and took out a thin section of its stem. She observed it under powerful compound microscope. Draw a diagram of what she observed and label it.
b) Add a note on Vascular bundle.
Answer:
a)
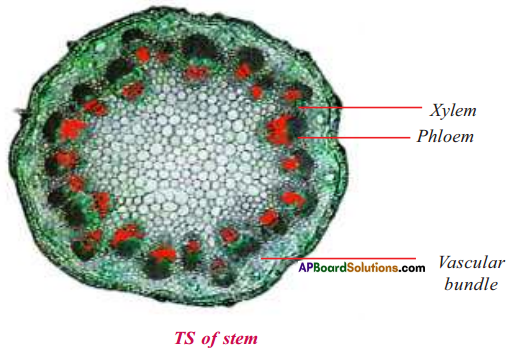
b)
- Xylem and phloem are collectively called as Vascular bundle.
- They are called as conducting tissue or vascular tissue.
- Xylem is responsible for transportation of water and salts.
- Phloem is responsible for transportation of food materials prepared by photosynthesis in other parts of the plants.
WorkBook Part
1. Take permanent slides of chlorenchyma, arenchyma, storage tissue in your labora-tory. Observe them under microscope and write their characters and differences.
2. Draw and label the diagram of the T.S. of stem.
3. How many basic types of tissues are there in plants? What are they?
4. Write the name of the following picture and write its parts.