Telangana SCERT 8th Class English Guide Telangana State Unit 2A Oliver Asks for More Textbook Questions and Answers.
TS 8th Class English Guide Unit 2A Oliver Asks for More
PRE-READING (Motivotion/Picture Interaction):
Read the saying given below and answer the questions that follow.

Question 1.
What does the sentence mean ?
Answer:
This sentence means that there are many places in the world that can give happiness. Among all the places home is the best. Anyone can be happy at home.
Question 2.
Do you agree/disagree with the view expressed in the saying ? Why?
Answer:
Having a home and a family is a social status. Being in a family gives the feeling of living. Home is the safest and the happiest place in the world. One can feel secure and happy at home among one’s family. So I agree with the view expressed in the above statement.
Question 3.
Do you like your home ? Why ?
Answer:
Yes, I like my home because it is the happiest place for me. It is very pleasant and comfortable to live in. I get love and warmth of members of my family in my home. My parents care for me and do all they can do to make me happy. My mother keeps home always neat and clean. The surroundings of my home are also beautiful.
![]()
ORAL DISCOURSE:
Question.
Talk on – “The feelings of a homeless child.”
Answer:
Homeless children are the kids who are wandering on the streets. They are deprived children. They become homeless because of several reasons. Some of them leave homes to explore the world. Some others leave their homes in short temper. Some others are unlucky fellows. Having lost their parents they become homeless. Poverty is one of the main reasons.
A homeless child suffers from want of love and affection. They miss their near and dear. There is no one who takes care of them. Hence the homeless child strongly wants love and affection from others. The homeless children are left alone on the street. They Eire hungry, thirsty and frightened. They are surrounded by thousands of unknown people. They beg for money on the streets. They want to play like other children they want to go to school and study like other children and they want to grow up in the care of their parents like other children.
They curse themselves why all this has happened only to them. They want someone who can understand them well. They want the company of others. They don’t want sympathy from others but they want to be friends with others. They suffer from problems like anxiety and aggressiveness as they are affected by emotions and dejected from parental love. They suffer from loneliness. They lack smile and starve from hunger for weeks. They want a helping hand which can give them protection.
They aspire that one day they will have a home. They don’t want to be a homeless destitute wandering here and there.
![]()
Comprehension:
Answer the following questions.
Question 1.
How did Oliver feel when he was asked to appear before the live board?
Answer:
Oliver had no clear idea of a live board. He was rather astonished by the information. He was not quite certain whether he- ought to laugh or cry.
Question 2.
Why did Oliver tremble and cry in the white-washed room?
Answer:
In the white-washed room Oliver appeared before the members of the live board. He was frightened on seeing so many gentlemen in the room. The beadle gave Oliver a tap on his back with a cane. So he trembled and cried in the white-washed room.
Question 3.
“What is that, sir?” inquired poor Oliver. What does ‘that’ refer to?
Answer:
‘That’ refers to the word, ‘orphan’. What Oliver means is that he doesn’t know the meaning of the word orphan’.
Question 4.
What kind of people were the members of the board? Justify your opinion.
Answer:
The members of the board were merciless, selfish and cruel. They did not offer adequate food to the children in the workhouse. They used the children for picking oakum. When Oliver asked for more food, they ordered instant punishment. They pasted a notice on the outside of the gate of the workhouse, offering a reward of five pounds to anybody who would take Oliver Twist off the hands of the parish.
![]()
Question 5.
What main differences do you notice between the children and the master? (Observe the physical appearances, dress, behaviour, etc.) What can you infer from these differences?
Answer:
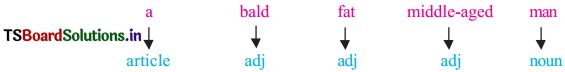
Children were weak and thin. They wore plain clothes. They were afraid of their master. They had a great respect for him. But the master was fat. He wore expensive clothes. He behaved mercilessly and cruelly.
Question 6.
How do you look at Oliver’s request, ‘Please, sir, I want some more!’? What compelled him to say this?
Answer:
He was forced to go and request for more food as he was desperate with hunger and reckless with misery. The situation forced him to go and request his master for more food. It shows the pitiable and helpless condition of the boy.
Question 7.
What happened to Oliver at the end of the story?
Answer:
At the end of the story he was given instant punishment. Next morning a bill was pasted on the outside of the gate, offering a reward of five pounds to anybody who would take Oliver Twist off the hands of the parish. In other words, five pounds and Oliver Twist were offered to any man or woman who wanted an apprentice to any trade, business, or calling.
Question 8.
Do you find children like Oliver around you? How would you help them to live better?
Answer:
Yes. I find a few children like Oliver in some places. I would help them by giving my used clothes. I request my parents to give them good food. I would admit them in a good orphanage for food and education with the help of my teachers and parents.
![]()
Vocabulary:
I. Look at the underlined part in the following sentence.
Answer:
“You have come here to be educated…”, said the red-faced gentleman.
The word ‘red-faced’ is called a Compound Adjective.
The phrase red-faced gentleman’ is a short form of ‘a gentleman with a red face’.
Exercise – 1:
Question 1.
Pick out the phrases with Compound Adjectives from the story or elsewhere and write how they can be rewritten to express the same meaning.
Answer:
Phrases with compound Adjectives and their rewritten form with the same meaning :
(a) white-washed room : a room with white wash
(b) well-educated man : a man with well education
(c) old-aged people : people in old age
(d) narrow-minded person : a person with narrow mind
(e) short-tempered teacher : a teacher with short temper
(f) well-behaved student : a student with well behaviour
(g) cold-hearted person : a person with a cold heart
(h) quick-drying glue : the glue that dries quickly
(j) high-priced car : car with high price
(j) man-made mistake : a mistake made by man
Exercise – 2:
Question 2.
Change the underlined parts in the following paragraph into Compound adjectives. Rewrite the paragraph in your, notebook.
Sachin Tendulkar is a cricketer who is famous all over the world. He is a batsman playing with right hand. He has many world records to his credit which are mind blowing. Besides all these, he is a person with a kind heart. He works with an NGO (Non-Governmental Organization) based in Mumbai to help more than 200 orphans every year.
Answer:
Sachin Tendulkar is a world-famous cricketer. He is a right-handed batsman. He has many mind-blowing world records to his credit. Besides all these, he is a kind-hearted person. He works with a Mumbai-based NGO (Non-Governmental Organization) to help more than 200 orphans every year.
![]()
Exercise – 3:
Question 3.
Fill in the blanks with appropriate compound adjectives from the box given below.
deep-rooted, old-fashioned, well-mannered, soft-spoken, brand-new
Latha is a ________ girl. She speaks kindly with her classmates. Look at her, she is wearing an ________ dress. She does not like to wear ________ dresses. Don’t you think Latha is a ________ girl?
Answer:
Latha is a soft-spoken girl. She speaks kindly with her classmates. Look at her, she is wearing an old-fashioned dress. She does not like to wear brand-new dresses. Don’t you think Latha is a well-mannered girl?
Grammar:
I. Look at the following sentence taken from the story.
‘The boy is a fool.’ said the gentleman in the white waistcoat.
As you know, the above underlined expression, can be changed into a question.
How do we change the above statement into a question? By putting the auxiliary verb before the subject ‘the boy’.

Look at some more sentences.
1. ‘I understand that he asked for more.’
‘Do I understand that he asked for more?’
2. ‘Oliver asks for more’
Does Oliver ask for more?
3. ‘The boys took their places.’
Did the boys take their places?
These sentences are changed into a question by placing ‘do/does/did at the beginning, such questions are called Yes / No questions.
![]()
Exercise:
Change the following statements into Yes/ No questions.
Question 1.
Oliver was frightened at the sight of so many gentlemen.
Answer:
Was Oliver frightened at the sight of so many gentlemen?
Question 2.
You are an orphan.
Answer:
Are you an orphan?
Question 3.
You say your prayers every night.
Answer:
Do you say your prayers every night?
Question 4.
You will pick oakum tomorrow morning.
Answer:
Will you pick oakum tomorrow morning?
Question 5.
Mr. Bumble rushed into the room.
Answer:
Did Mr. Bumble rush into the room?
Question 6.
They can devour the big bowl.
Answer:
Can they devour the big bowl?
Question 7.
Boys have generally excellent appetites.
Answer:
Have boys generally excellent appetite?
![]()
Detailed Rules for Framing Yes/No Questions:
1. If there is one verb in the statement and the verb is a helping verb, simply switch the positions of the subject and verb.
Statement – Question
Raju is a singer. – Is Raju a singer?
Children will come here. – Will children come here?
2. If there are two or more verbs, simply switch the positions of the subject and the first verb.
Statement-Question
Sindhu is eating biscuits. – Is Sindhu eating biscuits?
Aparna has bought a car. – Has Aparna bought a car?
Manju has been sleeping since 8 a.m. – Has Manju been sleeping since 8 a.m.?
3. If there is one verb, and the verb is not a helping verb, the process is more complex.
(a) Add ‘Do’ at the beginning of the sentence.
Statement – Question
They live in that house.-Do they live in that house?
(b) If the main verb carries a third person singular ‘s’, move that ‘s’ to Do, making it Does.
Statement – Question
Balaji drives a car. – Does Balaji drive a car?
(c) If the main verb carries past tense, move the past tense to Do, making it Did.
Statement – Question
Keerthana played tennis yesterday. – Did Keerthana play tennis yesterday?
4. In American English, the helping verb ‘have’ functions like a main verb in questions. This is not common in British English.
Statement – Question
You have a bad cold. – Do you have a bad cold? (American English) (or) Have you a bad cold? (British English)
II. Read the following sentence taken from the story.
“You were brought up by the parish, weren’t you?”
In this sentence ‘weren’t you?’ at the end is called a question tag. Question tags are used to get information or confirmation. The question tags are positive if the statements are negative. And if the statements are positive, question tags are negative. These tags are short / contracted form of questions. If the statement has an auxiliary, the tag begins with an auxiliary. In case it does not have an auxiliary, it will begin with do/does/did.
Read the following dialogue to understand the usage of question tags.
Ramu : The weather is good today, isn’t it?
Vijay : Indeed, Ramu.
Ramu : How about going out now? Hope you’ll join me, won’t you?
Vijay : I’ve got some important work now, I am afraid.
![]()
Exercise:
Read the following dialogue that took place at a party. Add suitable question tags to complete it.
Rohit : Hi, I’ve met you before, ________
Suma : No, I don’t think so.
Rohit : But your name is Vani, ________
Suma : No, it’s Suma! Anyway, glad to meet you.
Rohit : Me too. This is Rohit. The party seems to be really lively, ________
Suma : Yes, definitely. We enjoy ourselves a lot on such occasions, ________
Rohit : Yeah, we do.
Answer:
Rohit : Hi, I’ve met you before, haven’t I?
Suma : No, I don’t think so.
Rohit : But your name is Vani, isn’t it?
Suma : No, it’s Suma! Anyway, glad to meet you.
Rohit : Me too. This is Rohit. The party seems to be really lively doesn’t it?
Suma : Yes, definitely. We enjoy ourselves a lot on such occasions, don’t we?
Rohit : Yeah, we do.
Detailed information on Question Tags:
A tag question consists of two parts: a statement and a shortened yes/no question that refers to it and asks if the first statement is true. The two parts are separated by a comma.
- When the main sentence is positive, the tag is negative. When the main sentence is negative, the tag is positive.
- The noun in the first part becomes a pronoun in the tag.
- The second part (the tag) consists of a verb and pronoun only. A question tag repeats the helping verb of the main sentence.
Examples:
- You don’t like me, do you?
- You won’t tell him my secret, will you?
- He doesn’t speak German, does he?
- You’re coming to my party, aren’t you?
- She’s really good at chess, isn’t she?
- You haven’t done your homework, have you?
Note:
The tense of the tag is determined by the tense of the auxiliary/modal verb of the statement that precedes it. If the statement does not use an auxiliary/modal (i.e., it is in the present or past simple tense), then the auxiliary to do must be used.
- She comes from Korea, doesn’t she?
- You like heavy metal music, don’t you? –
- He got top grade in the maths test, didn’t he?
- I really messed up, didn’t I?
Note: If the subject + verb combination is ‘I am’ , the tag of that statement is aren’t I?
Example: I am a student, aren’t I?
Note: If the subject is ‘this /that’, it becomes it in question tag. If the subject is these / those, it becomes they in question tag.
Examples :
This is your dog, isn’t it?
That wasn’t your mom, was it?
These movies are wonderful, aren’t they?
![]()
III. Editing:
Read the following passage. Every numbered sentence has an error. Identify and edit it.
(1) When Rohit was nine, his family lived for a small town. (2) His father Rajarao were a clerk in Rao & Rao Company. (3) Janaki, Rohit’s mother, was an housewife. She used to be alone in the daytime when Rohit was at school, and Rajarao, in his office. (4) She wanted to has a pet. (5) She asked Rohit’s father several time for a pet.
Answer:
(1) When Rohit was nine, his family lived in a small town. (2) His father Rajarao was a clerk in Rao & Rao Company. (3) Janaki, Rohit’s mother, was a housewife. She used to he alone in the daytime when Rohit was at school, and Rajarao, in his office. (4) She wanted to have a pet. (5) She asked Rohit’s father several times for a pet.
Writing:
I. Anne Frank was a little girl of thirteen. She was as lonely as Oliver Twist. When the German army invaded her country, she had to hide in a smart building with her family. She suffered a lot. She recorded her feelings and thoughts in her diary.
Friday, 1st October, 1942.
Just for fun, I am going to tell you each person’s first wish, when we are allowed to go out again. Mrs. Van says, ‘If I go out, I’ll eat cream cakes.’ Dussel says, ‘If I am let free, I’ll run to see my wife Lotje.” Mummy says, ‘I will have a cup of coffee.’ Peter says, ‘I will go to the cinema.’ I long for so many things. But Hong for a home of our own.
1. What did Anne write in her diary?
personal feelings/thoughts/reflections
events other than routine
future plans
2. Did you notice any variety in the sentences?
3. Are all the sentences connected with each other properly?
After facing the live board, Oliver returned to his bed crying. He sat up to write his diary. Now, imagine you are Oliver Twist. Attempt a diary entry with the above features in mind.
Answer:
Diary Entry
27 August.
O! God, I am afraid of the live board. They seem to be very cruel. I know they don’t show mercy on children like me. I wish I had my mother and father. I don’t know-what happened to my parents. I feel like going out of this workhouse. But I know there is no way to escape from this place. They asked me to pick oakum from tomorrow. If my parents were alive, they wouldn’t send me for picking oakum. May God give the members of the board good and kind heart!
![]()
Oliver Asks for More Summary in English
(This is an extract from the novel ‘Oliver Twist’ written,by a British novelist, Charles Dickens (1812-70). It is the story of an orphan boy named Oliver, who is brought to a children’s home.)
In the workhouse of an unidentified place, on an unspecified date, a child is bom. As the infant struggles for survival, the pretty young mother’s life is ebbing. An old pauper, Mrs. Thingummy, who has assisted the attending surgeon, explains to the doctor that the young woman was unknown and had been brought in the night before, after being found lying in the street.
At the sound of her child’s voice, the mother murmurs faintly, “Let me see the child and die.” Both wishes are granted. After giving him one kiss, she dies. The new born child is Oliver Twist.
Young Oliver is kept in the workhouse for eight or ten months, but the accommodations there not being suited to the care of infants, he is transferred to a private asylum. This haven for juveniles is run by Mrs. Mann, an entrepreneur who earns money by starving the children and pocketing most of the allowance dispensed for their sustenance. The youngsters perish with regularity, but investigation always sustains the report that death was due to natural causes or “accident.”
Under this gentle system of charity, Oliver Twist spends his first nine years. His birthday is celebrated with a beating and confinement in the coal cellar with two other malefactors for “atrociously presuming to be hungry.”
![]()
While Oliver is thus disposed of, Mr. Bumble, a minor church official, suddenly appears at the garden gate. Mrs. Mann keeps him waiting until the prisoners are released. After Bumble is admitted, he demonstrates his sense of importance by rebuking Mrs. Mann before they then join in a demonstration of mutual hypocrisy as he partakes of her gin.
The self-important Bumble has come on business. His efforts to discover the identity of Oliver’s father or the origin of his mother have failed. The authorities have ruled that the orphan is to be returned to his birthplace — the workhouse. In the meantime, Oliver has been removed from the coal bin and has been made presentable. He is now brought forth and delivered to Mr. Bumble, who escorts him to his new home.
That very evening, the board in control of workhouse affairs is meeting, and Oliver is s promptly summoned to face that august body. After being admonished to persevere in gratitude for the blessings given him so far, the boy is told that he is to be further favoured by being taught a trade – picking oakum, (a tar-soaked fibre used as a caulking in ships) starting the next morning.
Following this scene the author discloses that the authorities have just devised a new food menu for the workhouse. The paupers are restricted to a pitifully small portion of food, and other callous measures are put into practice. The policy succeeds in reducing the workhouse population, although many depart for the graveyard.
After several months of the most meagre meals, the boys are desperate with hunger. One night at dinner, one child tells the others that if he does not have another bowl of gruel he might eat one among them who sleeps next to him in the workhouse. Terrified, the workhouse boys hold a council meeting to select one among them as the member to go and request the authorities for more to eat. The children at the workhouse cast lots (a game of choice by chance), determining that whoever loses shall be required to ask for more food for the boy.
Oliver loses, and after dinner, the other children insist that Oliver should ask for more food at supper. That evening after the skimpy ration of thin gruel has been consumed; Oliver approaches the fat workhouse master and asks for more. The master is overwhelmed with astonishment. In a state of agitation, Bumble rushes to inform the board, which is in session. The members are horrified; a gentleman in a white waistcoat is satisfied beyond all doubt that the culprit will end up on the gallows.
Oliver is instantly ordered to confinement. The next morning, a notice is posted on the gate offering five pounds to anyone who will accept Oliver Twist as an apprentice to any trade or – business.
![]()
About the Author:
Charles Dickens (1812-1870) is a well known English novelist. Due to his father’s imprisonment Charles left school and worked in a shoe factory. While he was working as an office boy he launched his writing career. His novels Oliver Twist, Great Expectations, Pickwick Papers, Bleak House, A Tale of two Cities and David Copperfield brought him name all over the world. He went on lecture tours to America and got literary reputation. He focussed on social issues and human ailments in his works.
Glossary:
extract (n) : passage that has been taken
orphan (n) : a child whose parents are dead
strides (n) : long steps
grasping (v) : taking a firm hold
trotted (v) : ran and walked fast taking short quick steps
board (n) : a group of people who have power to make decisions and control an organisation
appear (v) : to be seen
forthwith (adv) : immediately/at once
defined notion : clear idea
live board : board with life
astonished (adj) : very surprised
bow (v) : move one’s head or the top half of one’s body forwards and downwards as a sign of respect
brushed away : dropped
lingering (v) : exist somewhere
frightened (adj) : afraid/feeling fear
tremble (v) shake in a way you cannot control because you are very nervous
beadle (n) : a minor church official
tap (n) : hit somebody quickly and lightly
parish (n) : a church committee
gruff (adj) : unfriendly ; deep and rough
stammered (v) : spoke with difficulty, repeating sounds or words often stopping
oakum (n) : loose fibre obtained by untwisting and picking apart old ropes
surly (adj) : serious or angry
gruel (n) : a thin liquid food of oats, rice, etc.
devoured (v) : ate hungrily or quickly
stray (adj) : separated
![]()
splashes (n) : small amounts of liquid that falls onto
appetite (n) : the desire to eat; hunger
voracious (adj) : wanting great quantities of food
lots (n) : using a method of choosing somebody to do something
cast (v) : through something
ranged (v) : moved around
desperate (adj) : worried/distressed
nudged (v) : pushed
advancing (v) : moving/walking forward
stupefied (adj) : shocked
paralyzed (v) : became motionless
ladle (n) : a long handled spoon used to serve liquids
countenance (n) : a person’s face or facial expression
confinement (n) : putting in a prison or a closed room
apprentice (n) : one who works under a skilled person
calling (n) : a profession or career