TS Board Telangana SCERT Class 8 Physics Solutions 3rd Lesson Matter Around Us Textbook Questions and Answers.
TS 8th Class Physics 3rd Lesson Questions and Answers – Matter Around Us
Reflections on concepts
Question 1.
Why do some fibres are called Synthetic? Explain.
Answer:
- Synthetic fibres are not obtained from plant or animal source hut are made by human beings using raw materials obtained from petroleum-based chemicals.
- Petrochemicals are subjected to various chemical processes to obtain synthetic fibres.
- That is the reason why they are called synthetic fibres or simply artificial fibres.
Question 2.
What are thermosetting plastics. Give two examples.
Answer:
The plastics which moulded once can’t be softened by heating are known as thermosetting plastics.
Bakelite and melamine are examples for thermosetting plastics.
Question 3.
Give reasons “for using plastic containers as storing devices.” (AS )
Answer:
- Plastic material will not corrode easily.
- Plastics are non-reactive with other materials or chemicals.
- Plastic is very light, strong, durable and can be moulded into different shapes and sizes.
- Plastics are generally cheaper than metals. Because of the above reasons plastic containers are used as storage devices.
Question 4.
List out the objects made up of Acrylic.
Answer:
The following objects are made up of Acrylic
- Knitted apparels such as fleece, socks, sportswear, and sweaters.
- It is also used in Craft Yarns, upholstery fabrics, carpets, luggage swings and vehicle covers.
- Petrochemicals are subjected to various chemical processes to obtain synthetic fibres.
- That is the reason why they are called synthetic fibres or simply artificial fibres.
![]()
Question 5.
Draw and explain the diagram of Universal recycling symbol.
Answer:
To identify the plastic we look at the recycling icon, the chasing arrows. Inside the arrows, there will he a number that identifies the polymer. When the number is omitted, the symbol is known as the ‘Universal Recycling symbol’, indicating generic recyclable materials.

Application of concepts
Question 1.
How synthetic fibres have changed our daily life?
Answer:
Synthetic fibres changed our daily life, dressing style.
- Production and maintenance of natural fibres are very difficult and time taking. But synthetic fibres are cheaper. They can be dyed in a wide variety of colours.
- We are able to mix the synthetic fibres with other fibres (blending) for better clothing.
- Synthetic fibres absorb less water and dry at a faster rate. Some are even waterproof.
- They are durable, less expensive, readily available, affordable and are easy to maintain.
- They are strong and light in weight.
- Synthetic fibres are not only used for clothing but also for various purposes.
- Today’s life without synthetic fibre cannot be imagined.
- We need to use synthetic fibres in such a manner that we can enjoy their good qualities and at the same time minimise environmental hazards for the living communities.
Question 2.
What would happen, if we make electric switches with thermoplastics.
Answer:
Electric switches are generally made by thermosetting plastic, which will not change its shape on heating and has a stable structure. If electric switches are made by thermoplastics, they will be softened to the heat produced during the passage of current. It is very dangerous to the people. It causes electric shock or short circuit.
Question 3.
What could be the consequences if plastics are not properly disposed?
Answer:
- Plastics take several years to decompose compared to other materials.
- Slow decomposition of plastics causes environmental pollution.
- The burning processes of synthetic material is also very slow and more over they can’t be burnt completely with ease.
- The process of burning releases a lot of poisonous fumes into air causing air pollution.
- So avoid or minimize the use of plastic.
- “Plastic bags are more dangerous than atom bomb for future generations’.
Question 4.
Rani wants to buy clothes to her parents for winter wear.What types of clothes would you suggest? Specify reasons.
Answer:
I suggest Rani to buy clothes which give warmth to our body. Sweaters, shawls and blankets give warmth to our body. These are made up of natural wool or acrylic, a synthetic fibre. Generally wool is very costly and number of sheep would be needed to obtain wool for sweaters. So I suggest to buy sweaters and shawls made up of acrylic, which is relatively cheap.
![]()
Question 4.
Is there any such effort for solid waste management taking place in your Village/Town ? How do you appreciate 4R principle?
Answer:
Yes, In our town solid waste management taking place. The solid wastes are converted into electricity, in our town. Some of the solids wastes are converted into compost.
I appreciate 4R principle. It is for creating an eco-friendly environment, by reducing the use of plastics, reuse of unused plastic items, recycling new articles from the old plastics and recovering the resources like electricity, heat and compost from solid wastes. In these was 4R principle is eco-friendly, Hence I appreciate this 4R principle.
Question 5.
Where do we use the process of recycling? How is it useful? Give examples.
Answer:
- Generally, we might have noticed our mother selling old plastic articles which are broken and not useful to the local vendor.
- They collect all plastics from the households and send it for recycling.
- From this recycled plastic new products are prepared after giving it a proper treatment.
- Recycling can be used to obtain materials from which the original products were made.
Higher Order Thinking Questions
Question 1.
What made the human beings to search for the alternative for natural fibres?
Answer:
Natural fibres like cotton, wool and silk are very costly. it is not even accessible to all. Production and maintenance of natural clothes are also very difficult and time taking jobs. On the other hand synthetic fibre is cheap, absorbs less water and dry at a faster rate. Some are even waterproof. They are durable, less expensive, readily available, affordable and are easy to maintain.
Question 2.
Imagine what would happen if we do not discover plastics?
Answer:
- If we do not discover plastics, we depends on metals for many purposes in our daily life.
- If we use iron pipes they will rusted and they are not easily mouldable like plastic pipes.
- Metals will not be converted into any shape as plastics.
- We may be got electric shock if we are not discovered plastics which are used as covering for electric wires in houses.
- Plastics have also replaced glass items.
- Nowadays it is impossible to imagine our life without plastics.
Question 3.
indiscriminate usage of plastic is a serious threat to biodiversity. What are the efforts of Government and Non-government organizations in this regard?
Answer:
Indiscriminate usage of plastic is a serious threat to biodiversity. We need to use synthetic fibres and plastics in such a manner that we can enjoy their good qualities and at the same time minimize the environmental hazards for the living communities.
The government banned the usage of low-density carry bags which are not recyclable. We have to follow the ways and means of ‘solid waste management order given by supreme court.
N.G.Os, Government and the people follow the 4R principle. The solid waste should be converted into resources such as electricity, heat, compost and fuel through thermal and biological means.
![]()
Question 4.
Thermoplastics are eco-friendly than thermosetting plastics? Do you agree with statement?
Answer:
- Thermoplastics are more eco-friendly than thermosetting plastics because these plastics are easily recyclable.
- These are softened and remoulded on heating.
- Thermosetting plastics become hard and can not be remoulded on heating. They are not recycled. Hence thermoplastics are more eco-friendly than thermosetting plastics.
Question 5.
The introduction of synthetic fibres in the textile industry brought revolutionary change across the world in the dressing patterns irrespective of culture and customs. How do you appreciate this?
Answer:
I appreciate the introduction of synthetic fibres because they possess unique characteristics which make them popular dress materials. They dry up soon, are durable, less expensive, readily available and easy to maintain. Thus the introduction of synthetic fibres in the textiles industry brought revolutionary change across the world in the dressing patterns irrespective of culture and customs.
Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
Rayon is prepared by [ ]
a) Coal
b) Oxygen
c) Fibre
d) Cellulose
Answer:
d) Cellulose
Question 2.
Necessity of labels on clothes [ ]
a) Required by law
b) To identify fabric content
c) Both A and B
d) They do not decompose
Answer:
b) To identify fabric content
Question 3.
The material which is not decomposed by natural process is called [ ]
a) Non bio-degradable material
b) Bio-degradable material
c) Polyester
d) Nylon
Answer:
a) Non bio-degradable material
Question 4.
The symbol ![]() represents [ ]
represents [ ]
a) PET
b) HDPE
c) LDPE
d) Others
Answer:
b) HDPE
![]()
Question 5.
Which is a Natural fibre among the following? [ ]
a) Rayon
b) Nylon
c) Polyster
d) Silk
Answer:
d) Silk
Suggested Experiments
Question 1.
Conduct a flame test to identify Thermoplastics and Thermosetting plastics.
Answer:
Aim: Identifying thermoplastic and thermosetting plastics by flame test.
Materials required: Tong, spirit lamp, samples of plastics (Collect small pieces of plastics from the objects like comb, toothbrush handle, plastic bucket, handle of utensil, and electric switch, piece of melamine of meals plate and coffee mug)
Procedure:
- Take a spirit lamp and light it.
- Clamp one piece of plastic sample say piece of toothbrush with tong.
- Place the sample on spirit lamp flame.
- Observe the changes during the burning of sample.
- Note your observations like whether sample are being softened or burnt with smell or become hard etc.
- Repeat procedure with other samples.
- Record your observations sample-wise in the following table.
Question 2.
Take a wool, silk, cotton thread, bandage, piece of umbrella cloth, thread of sweater, piece of rope and carefully conduct a flame test. Based on smell and type of melting Classify them as natural and artificial fibres.
Answer:
| Type of Thread Fibre | Flame Test result | Natural/ Artificial Fibre |
| 1. Wool | Smells like burning hair | Natural fibre |
| 2. Silk | Smells like burning hair | Natural |
| 3. Cotton thread | Smells like burning paper | Natural |
| 4. Bandage | Smells like burning paper | Natural |
| 5. Piece of plastic | Melts in the flame | Artificial |
| 6. Thread of sweater | Melts in the flame | Artificial |
| 7. Piece of rope | Smells like burning hair. | Natural |
Question 3.
Collect small pieces of plastic from some objects and conduct a flame test. Record the observations and classify them into Thermoplastic/Thermosetting plastics.
Answer:
| Name of the plastic sample | Softened/become hard on heating | Thermoplastic/ Thermosetting plastic |
| 1. Toothbrush handle | Softened | Thermoplastic |
| 2. Comb | Softened | Thermoplastic |
| 3. Piece of bucket | Softened | Thermoplastic |
| 4. Handle of utensil | become hard | Thermosetting plastic |
| 5. Electric switch | become hard | Thermosetting plastic |
| 6. Meals plate | become hard | Thermosetting plastic |
| 7. Coffee mug | become hard | Thermosetting plastic |
![]()
Suggested Projects
Question 1.
Prepare a table of various synthetic fibres which are used to make household articles from them.
Answer:
| Type of Synthetic Fibre | Source Material | Articles made from it |
| 1. Nylon | Coal, water and air | Ropes, tents, sarees, toothbrush, bristles fishing nets, etc. |
| 2. Rayon | Wood pulp, some chemicals | Clothes, bed sheets, carpets, sanitary products, diapers and bandages. |
| 3. Acrylic | Coal, air, water, oil and limestone | Fleece, socks, sportswear, sweaters, carpets, vehicle covers |
| 4. Polyester | Chemicals mainly dicarboxylic acid and dihydric alcohol | Bottles, utensils, films, wires |
Question 2.
Collect the figures made up of thermosetting, thermoplastics used in your daily life and make a poster.
Answer:
Articles made up of thermoplastics:
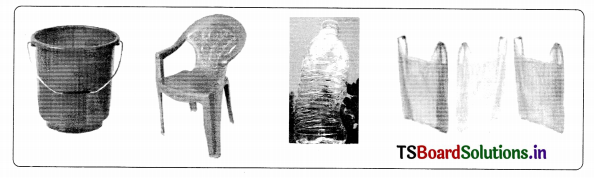
Articles made up of thermosetting plastics:

Question 3.
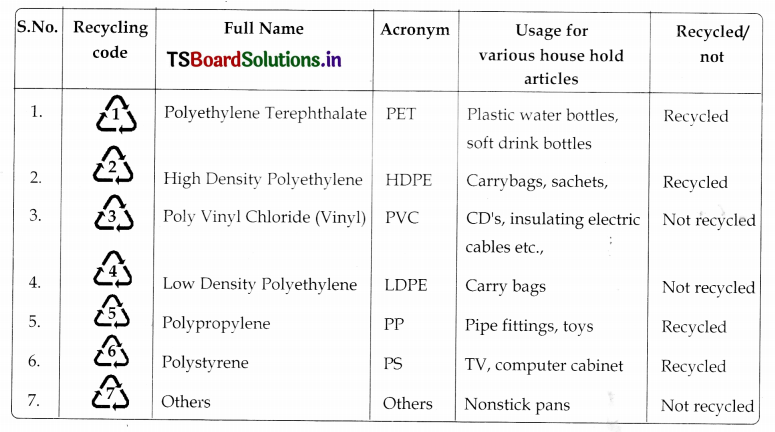
Prepare a chart which can explain recycling codes, full names and acronyms of plastic and its usage for various household articles, recycled or not, if recycled what will be made from that.
Answer:
TS 8th Class Physics 3rd Lesson Matter Around Us Intext Questions
Think & Discuss
Question 1.
Which fibre source material Is not exhaustible? Why? (Text. P. No. 33) (Making hypothesis)
Answer:
Synthetic fibres sources are not exhaustible. Because synthetic fibres are man-made. They are prepared from petroleum-based substances or petrochemicals. The sources of synthetic fibres are cheap and made from different man-made processes. So they are not exhaustible.
Question 2.
How synthetic fibres evolved to the present position? (Text. P. No. 34 (Daily life application/Appreciation)
Answer:
Synthetic fibres dry up quickly. They are durable; less expensive. They are readily available and easy to maintain. Some cotton fabrics Like rayon, absorb moisture or sweat, hence keep light weight.
Most of them are elastic, due to which they retain their original shape when compressed or stretched. They do not wrinkle easily, retain their original shape. They can handle heavy loads without breaking.
![]()
Question 3.
If we use cotton cloth and cotton ropes in preparing a parachute what will happen? (Text. P. No. 36) (Making hypothesis/Daily life application)
Answer:
Nylon is much stronger than other threads, nylon thread is stronger than steel wire of same thickness. So we use nylon fibre to prepare parachutes. If you use cotton ropes in preparing a parachute the rope may be cut easily because it is not as strong as nylon. Cotton also absorbs water easily. Absorbing water makes cotton weak and cause the fibre to break.
Question 4.
Traditionally fishermen used cotton nets. Now they are using nylon nets. What could be the advantage of nylon nets? (Text. P. No. 36) (Application in daily life/Rio diversity)
Answer:
Cotton absorbs water easily. Absorbing water makes cotton weak and causes the net to break. And it increases the weight o the net. Nylon fibre is strong, elastic and light in weight. It does not absorb water and easy to wash, So fishermen are using nylon nets.
Question 5.
Nylon sarees are much better than the cotton sarees. Is it better to use only nylon sarees? Do you agree with this? (Text. P. No. 36) (Application to daily life/Appreciation)
Answer:
Nylon sarees are much better than the cotton sarees. I also agree with that. Because nylon Is cheaper, light weight does not absorb water and easy to wash.
![]()
Question 6.
What characteristics make artificial rayon better than natural silk? (Text. P. No. 37) (Conceptual Understanding/Making hypothesis/Aesthetic sense)
Answer:
Rayon is not perfect, because it is made from plant cellulose. It absorbs water easily. Absorbing water makes rayon weak and causes the fibre to break.
Question 7.
If you want to purchase a doormat made of synthetic fibre. Which synthetic fibre door mat will you select? Why? (Text. P. No. 37) (Applications in daily life)
Answer:
If I want to purchase a door mat made of synthetic fibre, 1 select door mat made of rayon mixed with wool. Because it is cheaper and also be dyed in wide variety of colours. It also absorbs water, as natural wool and cotton.
Question 8.
If sanitary diapers and bandages are made of nylon, what happens? (Text. P. No. .37) (Making hypothesis/Field investigation/Conceptual understanding)
Answer:
Generally, sanitary diapers and bandages are made by rayon because it absorbs water and wet. If sanitary diapers and bandages are made by nylon, nylon does not absorb water and wet. So the purpose of diapers and bandages are not fulfilled.
Question 9.
Which type of blended fabrics do you find more comfortable in winter? Why? (Text. P. No. 38) (Application in daily life/Making hypothesis)
Answer:
In winter acrylic fabrics are more comfortable. Because acrylic gives warmth to our body. Acrylic looks like natural wool. The wool obtained from natural sources is quite expensive, where as clothes made from acrylic are relatively cheap.
Question 10.
The fabrics namely natural, synthetic and blended are available for garments. Which fabrics will you prefer to wear for rare occasions like functions and in routine? Why? (Text. P. No. 38)(Daily life applications/Concern to bio-diversity)
Answer:
For functions prefer natural garments because they look very rich and comfortable. I also prefer blended garments because they have the best qualities of both fibres. For routine, I prefer synthetic garments. Because they are cheap, long-lasting, durable, readily available, affordable and are easy on maintenance.
Question 11.
Which fabrics do you prefer? Natural or Synthetic? Why? Discuss comparatively. (Text. P. No. 39) (Conceptual understanding/Daily life application)
Answer:
For routine, I prefer synthetic garments because they are cheap, long-lasting, durable, readily available and are easy on maintenance.
Question 12.
What is the difference between washing of clothes at home and washing by dry cleaning at laundry? (Text. P. N’o. 39) (Conceptual understanding/Making hypothesis/Daily life applications)
Answer:
In our home the washing method is same for all types of clothes. We use same type of detergent and washing powder for washing various types of clothes irrespective of laundry label codes.
But in laundry different washing methods are used for different kinds of clothes. Basing the laundry label codes on clothes, they use different detergents, and chemicals for washing different types of clothes.
![]()
Question 13.
Certain try pans are said to be non-stick. What made them as non-stick? (Text. P. No. 44) (Conceptual understanding/Applications in daily life)
Answer:
Certain Fry pans are made up of Teflon. Teflon is a non-stick plastic. Teflon is used as a non-stick coating in cookware, So they ate said to be non-stick.
Question 14.
Firemen wear dress which does not catch fire. What type of fabric is it made of?
(or)
Why is it advised not to wear synthetic clothes while working in a laboratory or working with fire. (Making hypothesis is/Daily life applications)
Answer:
Firemen wear dress made with fireproof plastic%. The synthetic fibre melts on heating. If the cloth catches fire it can be very disastrous. The fabric melts and sticks to the body of the person wearing it. So it is therefore advised not to wear synthetic clothes while working in a laboratory or working with fire. For these reasons, human beings prefer for the alternative for natural fibres.
TS 8th Class Physics 2nd Lesson Friction Activities
Activity -1:
Identify household articles made up of natural and synthetic fibre: (Text. P. No. 32)
Question 1.
Look around you and prepare a table with articles made up of natural and synthetic fibre. (Project work/Conceptual understanding)
Answer:
| Source | Articles |
| Natural fibres from plants | Chair, table, cotton dress, jute bag, pencil, paper. |
| Natural fibres from animals | Woollen clothes. |
| Synthetic fibres | Plastic containers carry bags, pen, polyester clothes, electric switches, combs, toys, kitchen wares |
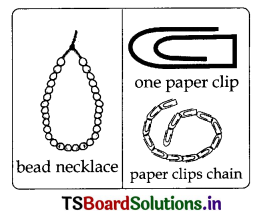
Activity -2: Beads and paper clips Dattern: (Text. P. No. 33)
Question 2.
How do you explain the structure of Polymer’ with the help of bead or paper clips? (Experimentation)
Answer:
Take some bead or paper clips and Join them together. Observe the structure formed.
Single units of beads or paper clips can be joined together to form a long chain-like structure. Each bead or dip is a separate unit but when many such units are joined, they form a new, different structure.
Similarly, synthetic fibres are also chains of small units joined together. Many small identical units combine to form a large unit called polymer. The small units are called monomers. Synthetic fibres are made of polymers.
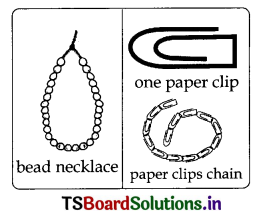
Questions based on the above Activity – 2
a. What does polymer mean? (Conceptual understanding)
Answer:
‘Poly’ means many and ‘Per means part or unit. The word is derived from Greek. So polymer is a structure made up of many small repeating units.
![]()
Activity -3: identifying fibres – burning test: (Text. P. No. 34)
Question 3.
How do you Identify the fibres with burning test or flame test? (Experinientation/ Project work)
Answer:
I will identify the libres, by conducting burning test to different arts and conduce that
- If it smells like burning hair, the yarn is wool or silk.
- If it smells like burning paper, the yarn may be cotton or rayon.
- If the yarn melts in the flame, it is a synthetic Fibre such as nylon and acrylic.
Activity -4: How strong Is nylon: (Text. P. No. 35)
Question 4.
How do you find the strength of a fibre? Explain an activity and find out which Is the strongest fibre. (Experimentation/Project work)
Answer:
- Take an iron stand with a clamp.
- Take cotton, wool, nylon and silk thread about 50cm in length. Note that all the threads should be of the same length and almost of the same thickness.
- Tie a cotton thread to stand, and at the free end suspend a pan so that weight can be placed on it.
- Add weight one by one till the thread breaks. Note down the total weight required to break the thread.
- Repeat the same activity with threads of wool, silk and nylon. Find out the total weight required to break each thread.
| Type of thread | Total weight fibre required to break |
| 1. Cotton | |
| 2. Wool | |
| 3. Silk. | |
| 4. Nylon. |
vi. From the above activity, you find the nylon thread is stronger than others.
Activity -5: (Text. P, No. 37)
Question 5.
Why we combine fibres?
Answer:
- Visit a nearby garment shop and look at the labels on the clothes (figure).
- Record the percentage of different fibres mentioned on labels.
- You may find rayon mixed with wool and cotton, polyester is mixed with cotton and wool. Even Nylon is mixed with polyester.
- Natural and synthetic fibres are often blended for preparing better fabric.

Activity -6: How can you say a bottle is PET bottle: (Text. P. No. 40)
Question 6.
How can you say a bottle is PET bottle? (Field investigation/Making hypothesis/ Conceptual understanding)
Answer:
collect different kinds of water bottles and look at them carefully, You observe a triangle-shaped symbol at the bottom of the bottle or on the brand label slicker.
If ‘1’ number is in the centre of the triangle, then it is a PET bottle.
a. Draw the different Resin Identification codes and Explain the symbols. (Drawing/Daily life application/Comment the diagrams)
Answer:
- Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET, PETE)
- High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE)
- Vinyl (Poly Vinyl Chlonde or PVC)
- Low-Density Polyethylene (LDPE)
- Polypropylene (PP)
- Polystyrene (PS)

other (The category of “other” includes any resin not specifically numbered 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, or 6, or combinations of one or more of these resins.)
![]()
Activity-7 (Text. P.No. 40)
Question 7.
Identification of various articles with recycling codes.
Answer:
1. Collect bottles of soft drinks (500 ml or more), bottles of juice, and containers of fruit jam, Ketchup, shampoo, Boost or Bournvita and try to look for the triangle.
2. First look at the soft drinks and juices. You may observe that irrespective of the brand name, the number 1 is marked in the middle of the triangle.
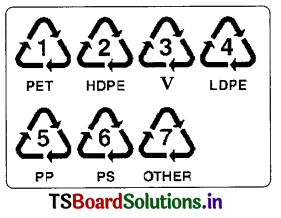
3. It indicates that it is a PET bottle.
4. In the same way other objects are also identified by recycling codes given below.
Activity -8: (Text. P. No. 42)
Question 8.
How do you identify the thermoplastic and thermosetting plastics? (Experimentation/Field Investigation/Making hypothesis)
Answer:
- Take two bottles made up of plastic. One is Tupperware and another ordinary.
- Pour some hot water in both the bottles. Observe what will happen?
- Plastics which get deformed easily on heating are known as thermoplastics.
- Some plastics, which moulded once cant be softened by heating are called as thermosetting plastics.
Activity – 9: Biodegradable – Non-biodegradable (Text. P. No. 46)
Question 9.
How do you know whether the substance Is biodegradable or non-biodegradable? (Project/Experimentation)
Answer:
- Take peels of fruits and vegetables, leftover foodstuff, waste paper, cotton cloth and plastic bag.
- Keep this material in a pit. List the material which remains for a long time and those that disappear quickly.
- By observing the time taken for the decomposition of the substances, classify them into bio-degradable and non -biodegradable.
| Type of waste | Approximate time | Degradable/ non degradable |
| Peels of fruits and vegetables | 1 to 2 weeks | Degradable |
| Leftover foodstuff | 1 to 2 weeks | Degradable |
| Waste paper | 10 to 30 days | Degradable |
| Cotton cloth | 2 to 5 months | Degradable |
| Plastic bag | Several years | Non – degradable |
Lab Activity
Question 1.
How do you identify the thermoplastic and thermosetting plastic? (Text. P. No. 42)
Answer:
Aim: Identifying thermoplastic and thermosetting plastics by flame test.
Materials Required: Tong.. spirit lamp, samples of plastics (Collect small pieces of plastics from the objects like comb, toothbrush handle, plastic bucket, handle of utensil, and electric switch, piece of melamine of meals plate and coffee mug)
Procedure:
- Take a spirit lamp and light it
- Clamp one piece of plastic sample say piece of toothbrush with tong.
- Made the sample on spirit lamp flame.
- Observe the changes during the burning of sample.
- Note your observations like whether sample are being softened or burnt with smell or become hard etc.
- Repeat procedure with other samples.
- Record your observations sample wist in the following table.
a. Collect small pieces of plastic from some object and conduct a flame test. Record the observations and classify them into Thermoplastic/Thermosetting plastics. (Project work/Expethnentation)
Answer:
| Name of the Plastic sample | softened/become on heating | Thermoplastic/Thermosetting plastic |
| 1. Toothbrush handle | Softened | Thermoplastic |
| 2. Comb | Softened | Thermoplastic |
| 3. Piece of bucket | Softened | Thermoplastic |
| 4. Handle of utensil | become hard | Thermosetting plastic |
| 5. Electric switch | become hard | Thermosetting plastic |
| 6. Meals plate | become hard | Thermosetting plastic |
| 7. Coffee mug | become hard | Thermosetting plastic |