Telangana SCERT TS 8th Class Physics Study Material Pdf 9th Lesson Electrical Conductivity of Liquids Textbook Questions and Answers.
TS 8th Class Physics 9th Lesson Questions and Answers – Electrical Conductivity of Liquids
Reflections on concepts
Question 1.
Give examples for good solid conductors and liquid conductors.
Answer:
Examples for good conductors in solids: Metals like copper, aluminium, gold, silver, iron etc.
Examples for good conductors in liquids: Lemon juice, vinegar, dilute sulphuric acid etc.
Question 2.
Give examples for poor solid conductors and liquid conductors.
Answer:
Examples for poor conductors solid: Rubber, plastic, glass, dry wood etc.
Examples for poor conductors liquid: Distilled water, coconut oil, vegetable oil, sugar solution etc.
Question 3.
Give two examples for electrolytes.
Answer:
Electrolyte: Any substance that dissociates into ions when dissolved in a suitable medium or melted and thus forms a conductor of electricity.
Eg:
- CuSO4 (Copper Sulphate)
- AuCl2 (Auric Chloride)
- AgNO3 (Silver Nitrate)
Question 4.
Draw the diagram of Electrolytic cell and explain.
Answer:
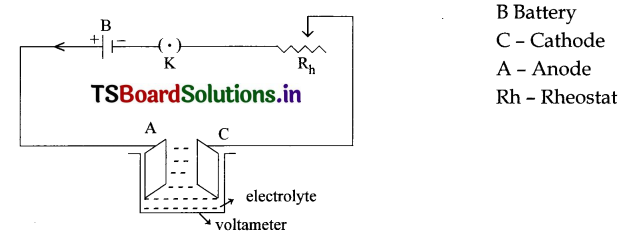
Apparatus: Battery, Key, Rheostat, Voltameter, Electrolyte, Cathode and Anode Explanation:
- Connections are made as per the circuit.
- An electrolyte (CuSO4) is taken in voltameter.
- Two metals electrodes are immersed in the electrolyte.
- The electrode connected to negative of the Battery is known as cathode and the electron connected to positive of the battery in known as anode.
- By pressing the plug key the circuit is closed and current flows in the circuit.
- By adjusting the Rheostat we can increase or decrease the current in the circuit.
- When current flows in electrolyte it dissolve into Cu+ and SO\(\overline{4}\).
- The copper ions are deposited on cathode.
Application of concepts
Question 1.
Which energy is cause for glowing of bulb in electrolytic cell?
Answer:
The chemical energy is converted into electrical energy by electrolysis method. This causes the glowing of bulb.
Question 2.
What do you add to distilled water for making it to conduct electricity?
Answer:
By dissolving materials like acids, bases, salts such as common salt, lemon juice, hydrochloric acid, sulphuric acid, vinegar, caustic soda etc, to distilled water for making it to conduct electricity.
Question 3.
Kavya observed that a discharged dry cell which kept in sunlight by her father for few hours got ability to glow LED. She got many doubts and questions to raise. Can you guess those questions or doubts?
Answer:
- How the discharged dry cell, being charged by sunlight?
- Can we use these dry cells to some more electrical appliances?
- How sunlight is helpful in recharging the dry cell?
- Is it possible to recharge the dry cell in another ways?
- Which material get charged in dry cell, when kept in sunlight?
- What is the mechanism during this process?
Question 4.
Make a battery from four lemons and test It with a LED In the circuit.
Answer:
To make a battery from four lemons.
Required materials: 4 juicy lemons, 4 copper plates, 4 paper clips, 5 alligator clips, 1 red LED, conducting wires.
Procedure: Take 4 lemons and connect each lemon with lemon by clipping one end of an alligator dip to a copper and the other to a paper clip as shown in the circuit Then include one LED into the circuit. Leave the inserted for 20 to 30 minutes. Observation: The LED glows.

Question 5.
Collect the Information and make list of good conductors and bad conductors. How do you use this information in your daily life works?
Answer:
| Good conductors | Bad conductors |
| 1. Copper | 1. Plastic |
| 2. iron | 2. Glass |
| 3. Aluminium | 3. Wood |
| 4. Silver | 4. Rubber |
| 5. Gold | 5. Paper |
Conductors are used in wires to allow electricity to flow. So it can power our appliance insulators like plastic coverings around the wires would stop electricity and prevents electric shock.
Higher Order Thinking Questions
Question 1.
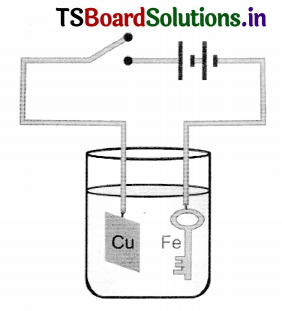
If the key is to be coated with aluminium instead of copper, what changes do we need to make in the experiment of coating on iron key with copper?
Answer:
- Coating on iron key with copper the copper sulphate electrolyte is taken in voltameter.
- When the circuit in closed current flows.
- Here the iron key is taken as cathode.
- Due to the flow of current CuSO4 dissociates into Cu+ and SO–4 ions.
- All the Cu ions goes to the cathode.
- Since we have taken the key as cathode copper gets deposited on the key.
- If the current is passed through few minutes the iron key is changed as copper key.
- It is taken out and dried.
Question 2.
Is plastic coated by the process of electroplating? Why?
(Or)
Is coating on plastics possible like that of metal objects.
Answer:
No. It is not possible.
The plastic is electrically non-conductive and cannot be immersed in a plating solution and coated in the way that metal objects can.
Some method was therefore needed whereby a conductive film could be deposited onto the surface of the plastics to provide the basis for subsequent electrode position.
Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
Which of the following is also used in ornamentation and decoration [ ]
a) Electro typing
b) Electroplating
c) Electro printing
d) Galvanizing
Answer:
b) Electroplating
Question 2.
Pure water is [ ]
a) Electric conductor
b) Semiconductor
c) Insulator
d) Resistor
Answer:
c) Insulator
Question 3.
The material which do not allow electric current to pass through it is known as [ ]
a) Electric conductor
b) Insulator
c) Electric resistance
d) semiconductor
Answer:
b) Insulator
Question 4.
Electroplating is possible through [ ]
a) Electrolysis
b) Chemical process
c) Dissolving
d) Filtration
Answer:
a) Electrolysis
Question 5.
One of the following is not an electrolyte [ ]
a) Sulphuric acid
b) Lemon juice
c) Tamarind juice
d) Detergent solution
Answer:
c) Tamarind juice
Suggested Experiments
Question 1.
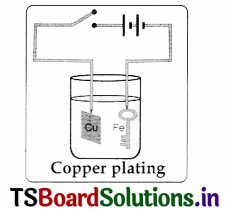
Conduct an experiment for coating on iron key with copper by electroplating method and prepare a report.
Answer:
Aim: Coating copper on iron key by the process of electroplating.
Required materials: Copperplate (2cm X 5 cm), a key made of iron, glass beaker,
battery cell, connecting wires, water, copper sulphate crystals, and sulphuric acid.
Procedure:
- Prepare a concentrated solution of copper sulphate by dissolving copper sulphate crystals in pure water.
- Pour the solution in a beaker and add a few drops of dilute sulphuric acid to increase the conductivity.
- Tie one end of the connecting copper wire to the iron key to be coated with copper. Connect its other end to the negative terminal of a battery and suspend it into the copper sulphate solution.
- Suspend the copper plate into copper sulphate solution from the positive end of the battery through a switch.
- Put the switch on for about 10 minutes, then switch off the circuit and take the iron key out.
Observations: Iron key get coated with copper.
Result: Iron key get coated with copper by the process of electroplating.
Question 2.
Conduct an experiment for testing the electric conductivity of liquids.
Answer:
- Take a LED, dry cell, metal pins, rubber cap of injection bottle and wires for making connections. Set up an electric circuit as shown in the figure
- See that two metal pins, pass through the cap and should have a very small Rubber
gap between them. So that the pins are fairly’ closer but not touching each other. - The LED does not glow when pins are separated by the small distance.
- Now join the force ends of the pins together by pressing them for a moment and make sure that LED glows. If we release the pins they get separated and LED should not glow. This becomes our tester.
- Now fill the rubber cap with different liquids one after another and in each case check whether the LED glows or not. Note your observations in table.
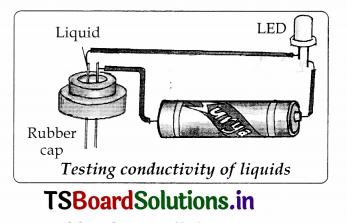
Table (Text. P. No. 122)
| Liquid | LED glows Yes/No | Good conductors/ poor or bad conductors |
| 1. Distilled water | No | had conductor |
| 2. Drinking water | Yes | good conductor |
| 4. Coconut oil | No | bad conductor |
| 5. Lemon juice | Yes | good conductor |
| 6. Vinegar | Yes | good conductor |
| 7. Kerosene | No | bad conductor |
| 8. Vegetable oil | No | bad conductor |
| 9. Sugar solution | No | bad conductor |
| 10. Milk | No | bad conductor |
| 11. Honey | No | bad conductor |
vi. From the above activity we conclude that some liquids are conductors (LED glows) and some liquids are had conductors (LED does not glow)
(a) Why doesn’t the lED glow in all the cases? Or why doesn’t the LED remain off
in all the cases for different liquids?
Answer:
Some liquids such as lemon juice and vinegar are good conductors of electricity. When these liquids are placed between the two pins of the tester allow electric current to pass through. the circuit is closed and the LED glows. Some liquids such as distilled water, coconut oil are had conductors of electricity. When these liquids are placed between the two pins of the tester do not allow electric current to pass through, the circuit is opened and the LED does not glow.
b. List out the good conductors from table.
Answer:
Good conductors:
1. Lemon Juice
2. Vinegar
3. Drinking water.
Question 3.
Conduct an experiment for testing the electric conductivity of electrolytes.
Answer:
Aim: Testing of electric conductivity of electrolyte.
Apparatus: Battery, Tap key, Rheostat, Voltameter, Electrolytes, Electrodes, Electric Bulb.
Circuit:
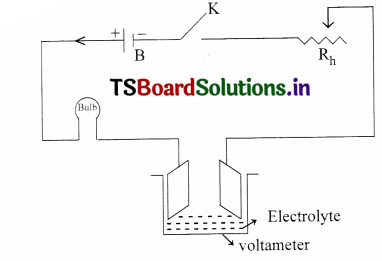
Procedure:
- Connections are made as per the circuit diagram.
- An electric lamp is connected in series in the circuit.
- When the Tap key is pressed current flows in the circuit.
- The copper sulphate solution dissociates.
- As and when plug is closed the bulb glows.
- It indicates that the electric conductivity is taking place in electrolyte.
- This experiment can be done with different electrolytes.
- If electrolyte is charged the brightness in the bulb also changes.
- Hence with this experiment, we can say electric conductivity takes places in electrolytes.
Suggested Projects
Question 1.
Collect the information from various sources on the applications of electroplating in daily life and prepare a report on that.
Answer:
Applications of Electroplating:
- Electroplating is widely used in industry for coating metal objects with thin layer of different metals.
- In electroplating, an inferior metals which are effected by the atmospheric humidity, are coated with superior metal.
- Electroplating is done with view of repairing worn-out parts of machinery.
- Electroplating is also used in ornamentation and decoration.
- Processed food items are preserved in tin-coated iron cans. Tin is less reactive
to the food than iron. So the cans are made by electroplating tin on iron. - Iron is coated with zinc metal, iron becomes more resistant to corrosion and formation rust. So zinc-coated iron is used for bridges and in automobiles.
Question 2.
In many of the activities in this chapter, we have used a tester made up of LED. Can we avoid LED and use something else as a tester? Collect the information and make a model.
Answer:
When current flows in a wire, a compass needle kept nearby gets deflected. Even the current is small, the deflection of the magnetic needle can be seen. To make a tester of magnetic compass needle, take a cardboard tray from inside of a discarded matchbox.
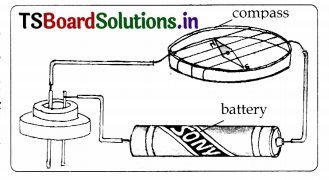
Wrap an electric wire a few times around the cardboard tray. Place a small compass needle inside it. Now connect one free end of the wire to a terminal of a two cell battery. From the other terminal of the battery connect another wire. Now the tester with two free ends of wire is ready.
TS 8th Class Physics 9th Lesson Electrical Conductivity of Liquids Intext Questions
Think and Discuss
Question 1.
Why some material allows electric current to pass through them and why some do not? (Text. P. No. 121) (Conceptual understanding)
Answer:
In some materials Like metals, they are good conductors of electricity because the electrons are free to move in a network of metal atom. But in materials such as plastic there will be no free electrons occur. Hence they do not conduct electricity.
Question 2.
If a battery is packed in a box and if only two wires from two terminals are given out, how can we decide the positive and negative terminal of the battery? (Text. P. No. 125) (Information Skills & Projects)
Answer:
Connect a voltmeter probes to the battery terminals, if the voltage is shown as a negative, then switch the voltmeters probes around at the battery end so it shows the voltage as a positive reading in the voltmeter. From this activity, we can decide the positive and negative terminals of the battery.
Question 3.
What is electrolysis? (Conceptual understanding)
Answer:
Electrolysis: The process of decomposition of a chemical compound in a solution, when an electric current passes through it is called electrolysis.
Examples: CuSO4 → Cu+2+SO–4
Question 4.
Discuss with your teacher or collect the information about electrolysis method from your school library books.
Answer:
Student’s Activity
TS 8th Class Physics 9th Lesson Electrical Conductivity of Liquids Activities
Activity – 1: Testing the material to know which allows electric current to pass through it: (Text. P. No. 120)
Question 1.
Conduct an activity to know which materials allow electric current through them and define conductors and bad conductors of electricity.
Answer:
- Take a torch bulb or LED (Light Emitting Diode), a dry cell, a wooden sheet, two drawing pins, a key (safety pin) and pieces of connecting wires.
- Set up the electric circuit as shown in the figure.
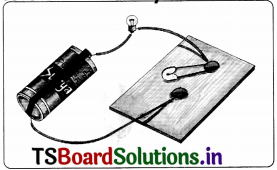
- Place the key in ON position. You may see that the bulb begins to glow.
- Now replace the key by a nail. Observe whether the bulb glows or not.
- Repeat the activity using different types of materials instead of the nail, say a strip of paper, a piece of chalk, a drinking straw, a piece of plastic, a paper clip, a rubber eraser, etc.
Noting in each case whether the bulb glows or not (observations) in a table.
Table (Information Skills & Projects)
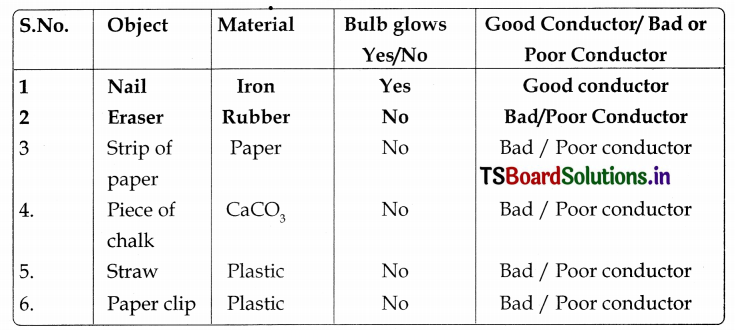
vi. From the above activity we conclude that some materials allow electric current to pass through them. We call them as good conductors of electricity.
vii. Some materials do not allow current to pass’. through them. They are called bad or poor conductors of electricity.
Activity- 2 :
Testing the electric conductivity of liquids (Text. P. No. 122)
Question 2.
Do the liquids allow electric current to pass through them? Test the electric conductivity of liquids through an activity.
Answer:
- Take a LED, dry cell, metal pins, rubber cap of injection bottle and wires for making connections. Set up an electric circuit as shown in the figure
- See that two metal pins, pass through the cap and should have a very small gap between them. So that the pins are fairly closer hut not touching each other.
- The LED does not glow when pins are separated by the small distance.
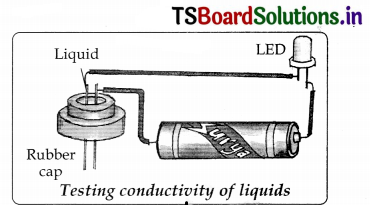
- Now join the force ends of the pins together by pressing them for a moment and make sure that LED glows. If we release the pins they get separated and LED should not glow. This becomes our tester.
- Now fill the rubber cap with different liquids one after another and in each case check whether the LED glows or not. Note your observations in table.
Table (Text. P. No. 122)
| Liquid | LED glows Yes/No | Good conductors/ poor or bad conductors |
| 1. Distilled water | No | bad conductor |
| 2. Drinking water | Yes | good conductor |
| 4. Coconut oil | No | bad conductor |
| 5. Lemon juice | Yes | good conductor |
| 6. Vinegar | Yes | good conductor |
| 7. Kerosene | No | bad conductor |
| 8. Vegetable oil | No | bad conductor |
| 9. Sugar solution | No | bad conductor |
| 10. Milk | No | bad conductor |
| 11. Honey | No | bad conductor |
vi. From the above activity we conclude that some liquids are conductors (LED glows) and some liquids are had conductors (LED does not glow)
(a) Why doesn’t the LED glow in all the cases? Or why doesn’t the LED remain off
in all the cases for different liquids? (Conceptual understanding)
Answer:
Some liquids such as lemon juice and vinegar are good conductors of electricity. When these liquids are placed between the two pins of the tester allow electric current to pass through. the circuit is closed and the LED glows.
Sonic liquids such as distilled water, coconut oil are bad conductors of electricity. When these liquids are placed between the two pins of the tester do not allow electric current to pass through, the circuit is opened and the LED does not glow.
b. List out the good conductors from table.
Answer:
Good conductors:
- Lemon juice
- Vinegar
- Drinking water.
Activity – 3:
Transforming a poor electric conductor into a Lood conductor.’ (Text. P. No. 124)
Question 3.
How do you convert a poor electric conductor into a good conductor?
(or)
Can we make poor conductors like distilled water to conduct electricity? Explain with an activity.
Answer:
- Take same amount of distilled water in three different containers.
- Dissolve small quantity of common salt in the water of first container.
- Dissolve the Copper Sulphate (Mylatuttam), lemon juice in 2nd and 3rd containers respectively.
- Take LED, dry cell, metal pins, rubber cap of injection bottle and wires for making connections. Set up an electric circuit as shown in figure.

- See that two metal pins, pass through the cap and should have a very small gap between them. So that the pins are fairly closer but not touching each other.
- Now fill the rubber cap with distilled water and the solutions of above three containers one after another and check whether the LED glows are not.
- Note your observations in table.
Table
| Material | Does the LED glow? Yes/No | Good conductor/bad or poor conductor |
| 1. Distilled water | No | Bad conductor |
| 2. Dist. water + salt | Yes | Good conductor |
| 3. Dist. water + CuSO4 | Yes | Good conductor |
| 4. Dist. water + lemon juice | Yes | Good conductor |
- From the above table we conclude that pure distilled water is a bad conductor of electricity, but water with salt is a good conductor of electricity.
- In this way distilled water is converted into conductor by adding salts.
(a) Why you are advised not to touch electric appliances with wet hands? (Applications to daily lift’)
Answer:
Water with salts is a good conductor of electricity and the current flowing through household electric appliances is vers’ high. Therefore, we should never touch the electrical appliances with wet hands.
Activity -4:
Testing the effect of electric current on potato : (Text. P. No. 125)
Question 4.
How do you test the effect of electric current on potato? (If solutions of different salts and acids conduct electricity, what do vegetables and fruits do? Let us try to find that out.) (Experimentation & F.I.)
Answer:
- Take a potato. Cut in into two halves and take LED one hail of it.
- Construct tester with LED bulb.
- Insert two copper wires of the tester into the potato leaving some distance (around 1 cm) between them.
- LED would glow. Leave the inserted wires for 20 – 30 minutes.
- A greenish-blue spot is seen on the potato around the wire connected to the positive terminal of the hatter’ But no such spot is seen around the other wire connected to the negative terminal.
- This greenish-blue spot on the potato around the wire connected to the positive terminal of the battery is due to chemical change in the potato.
- From this we conclude that there is chemical change in some fruits and vegetables due to the passage of current through them.

Questions based on the above Activity – 4
a. Does the LED glow?
Answer:
Yes, LED would glow.
b. What do you observe the surface of the potato after leaving the inserted wires for 20-30 minutes?
Answer:
A greenish-blue spot is seen on the potato around the wire connected to the positive
terminal of the battery. But no such spot is seen around the other wire connected to the negative terminal.
c. What could be the cause behind this change?
Answer:
This greenish-blue Spot on the potato around the wire connected to the positive terminal of the batter’ is due to a chemical change in the potato.
d. Will other vegetables also show electric conductivity?
Answer:
Yes, vegetables like tomatoes, onions also conduct electricity, since they have the highest acidity level, citrus fruits like apples, grapes, oranges, lemons are also excellent conductors due, to the high acidity level.
Activity -5 :
Make your own cell: (Text. R No. 127)
Question 5.
How do you make your own cell?
Answer:
Collect two injection bottles. Cut two 5 cm-long hits of thick copper wire. Use sandpaper to scrape about 1 cm of the coating off both ends of the wires. Break open a exhausted dry cell and remove its outer metal covering (made of zinc). Cut two 2 mm wide and 5 cm long strips from this zinc plate. Insert the copper wires and zinc strips into the rubber caps of the injection bottles as shown in figure. Ensure that the copper wire and zinc strips do not touch each other.

Now take a wire and connect the copper wire of one bottle with the zinc plate of the other bottle. Fill both bottles with dilute sulphuric acid. Carefully close the bottles with the caps in which the copper wires and zinc strips are inserted.
Your cell is ready. Take a LED. Attach two wires to its two terminals. Touch the wire from one terminal to the zinc plate and the wire from the other terminal to the copper wire. Did the LED light up? If not, change the connections vice-versa.
Questions based on the have Activity-5;
a. What other liquids can be used to make the cell? (info a lion Skills & Projects)
Answer:
Lemon juice, tamarind juice, tomato juice, and vinegar-like solutions which are acidic in nature can be used to make the cell.
b. Will the detergent solution be useful? Find it out for yourself.
Answer:
Detergents contain caustic soda which is a strong base. So detergent solution be useful.
c. How does the above cell function?
Answer:
The cell works on the process of electrolysis. Here the chemical energy is converted into electrical energy.
d. Can you compare sulphuric acid cell with dry cell? Which is good one? Why? (Conceptual understanding)
Answer:
Sulphuric acid cell contains liquid electrolyte dilute sulphuric acid and voltage of the cell is low. But dry cell contains solid electrolyte and voltage is comparatively high.
Lab Activity
Question 1.
How do you coat an iron key with copper by electroplating method. (Text. P. No. 128)
Answer:
Aim: Coating an iron key with copper by electroplating method.
Required material: Copperplate of size 2 cm x 5 cm, crystals of copper sulphate (blue vitriol), a key made by iron, glass beaker, water, sulphuric acid, battery and some connecting copper wires.
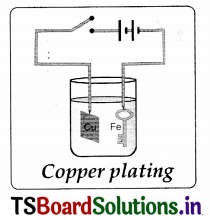
Procedure:
- Dissolve crystals of copper sulphate in pure water to prepare concentrated solution (deep blue in colour).
- Pour the solution in a beaker and add a few drops of dilute sulphuric acid to it.
- Tie one end of a connecting copper wire to the iron object (key) to be coated with copper.
- Connect its other end to the negative terminal of a battery.
- Suspend the tied iron object into the copper sulphate solution.
- Suspend the copper plate into copper sulphate from positive end of the battery through a switch as shown.
- Plate and key do not touch each other and are a little away from one another. Put the switch on for about lO minutes.
- When electric current is passed through the copper sulphate solution, the copper sulphate dissociates into copper and sulphate ions.

- Gets drawn to electrode connected to the negative terminal of the battery key and gets deposited on it.
- Thus one metal is coated with another material. This process is known electroplating.
- In this way we coat a iron key with copper by electroplating method.
Questions based on the above Lab Activity (Tert. P. No. 128)
a. Does the iron key get coated with a shiny, brown colour?
Answer:
Yes, the iron key get coated with a shiny, brown colour of copper metal. In this process of electrolysis cu2’ ions are liberated from CuSO4 (electrolyte) and deposited as copper metal iron key (cathode)
b. What is the colour due to?
Answer:
The shiny brown colour is due to the deposition of copper metal on iron key by the process of electroplating.
c. What will happen if you interchange the battery terminals?
Answer:
If we interchange the battery terminals electrolysis does not take place. This is because of the external battery supplies the electrons. They enter through cathode and come out through anode.
d. Why does copper get deposited on the iron key?
Answer:
When electric current is passed through the copper sulphate solution, the copper sulphate dissociate into copper and sulphate ions. The free copper gets drawn to
the electrode connected to the negative terminal of the battery arid gets deposited
on it.
