Telangana SCERT TS 8th Class Physics Study Material Pdf 8th Lesson Combustion, Fuels, and Flame Textbook Questions and Answers.
TS 8th Class Physics 8th Lesson Questions and Answers – Combustion, Fuels, and Flame
I. Reflections on Concepts
Question 1.
Give four examples of combustible materials.
Answer:
Some combustible materials are:
- Wood
- Paper
- Kerosene oil
- Straw
- Charcoal
- Match stick etc.
Question 2.
Why should not we store spirit or petrol near our living place’?
Answer:
Spirit or petrol is a ‘highly inflammable’ material. There will always be petrol vapour over the liquid petrol. The vapour is highly inflammable. These vapours can catch any type of flame and burn rapidly. So we should not store spirit or petrol near our living place.
Question 3.
The oil fires should not be sprayed with water. Why?
Answer:
Water is not suitable for fires involving oil and petroleum. :
Reason: Water is heavier than the oil. So water sinks below the oil and oil keeps burning on the top.
Question 4.
Water is not used to control fires involving electrical equipment. Why?
Answer:
If electrical equipment is on fire, water is not used to control fire. Because water may conduct electricity and harm those trying to douse the fire. (Note: ‘Douse’ means to put out the fire, by pouring water.)
Question 5.
List the ways adopted by firefighters to combat fires.
Answer:
To combat fires, firefighters follow one principle, which is the “Principle of elimination of factors which supports the combustion”.
The factors which support the combustion are:
a. Presence of a combustible material or the fuel.
b. Supply of air or oxygen.
c. High temperature.
- The firefighters will put off the electric mains and then start spraying water on the fire.
This water cools the combustible material. This prevents further spreading of the fire. - For fires involving oil and petrol. liquid carbon dioxide fire-extinguisher is used, CO2, gas cools the combustible material. At the same time, it cuts off the
contact between the material and air (oxygen). Then the fire comes under control. This gas does not damage the material. So liquid CO2 is an excellent fire – extinguisher.
Question 6.
Draw the diagram of a candle flame and label all the zones.
Answer:
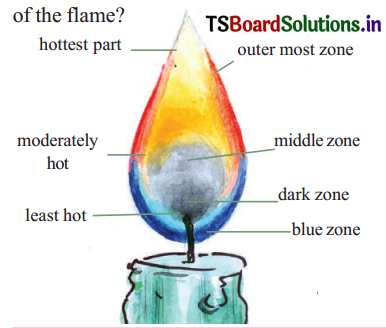
Application of concepts
Question 1.
What precautions are to be taken while pouring water on fire?
Answer:
- Water is not suitable for fires involving oil and petrol.
- If electrical equipment is on fire, water may conduct electricity and harm those trying to douse the fire. So water cannot he used.
Question 2.
Give an example of a good fuel. How do you choose that fuel? Explain.
Answer:
For kitchen, it is LPG and for a motor car, it is CNG. These are some good fuels.
Reasons:
- They are relatively cheap.
- They bum easily in air at a moderate rate (not slow or explosive).
- They produce a large amount of heat.
- They do not leave behind undesirable substances.
- They are easily available.
Question 3.
It is difficult to burn a heap of green leaves but not a heap of dry leaves. Explain why?
Answer:
- It is easy to burn a heap of dry leaves because their ignition temperature is low.
- It is difficult to burn a heap of green leaves because their ignition temperature is high. The green leaves contain water also. So the ignition temperature rises.
Question 4.
Where do you find spontaneous combustion and rapid combustion in your daily life?
Answer:
a) Spontaneous combustion: When we strike the head of a match stick over the side of a matchbox, it catches fire at once and Continues to bum. It is a case of ‘spontaneous combustion’.
b) Rapid combustion: We turn on the knob of the gas stove in the kitchen. Then we bring a lighted matchstick near it. The gas burns rapidly. It is a case of rapid combustion.
Question 5.
Why the fire brigade start the work by putting off the electric mains?
Answer:
- Water conducts electricity. So it harms those trying to douse the fire, using water.
- So the fire brigade starts work after putting off the electric mains.
Question 6.
Explain giving reasons: In which of the following situations water will get heated in a shorter time?
a) Srikar kept water beaker near the wick in the yellow part of a candle flame.
b) Sonu kept water beaker in the outer most part of the flame.
Answer:
Water gets heated in a short time, when the water beaker is kept in the outermost part of the flame.
Reason: A flame has three zones (or parts).
- The outermost part of the flame is faintly bluish in colour. Here, the gas undergoes complete combustion. So it is the hottest part of the flame.
- The middle part of the flame is yellow in colour. Here gas undergoes only partial combustion. So this part of the flame is not so hot. It is less hot than the outermost part of the flame.
Higher Order Thinking Questions
Question 1.
Why Phosphorus preserved in water?
Answer:
The inflammable (ignition) temperature of white (or yellow) phosphorus is 45°C. So when it is kept in air it easily catches fire and bursts into flames. So it is preserved in water.
Question 2.
How do you feel about “Fuels have become a part of human life”?
Answer:
- A fuel is a source of energy. When a fuel burns, energy liberates.
- This energy is utilised for various purposes to run automobiles, to operate generators, to run thermal power plants and a variety of industries, to run locomotives, etc.
- All these play an important role in serving the human needs, by providing food, shelter, clothes, transportation and so on. So man depends on fuel, directly or indirectly. Hence it is said, ‘fuels have become a part of human life”.
Question 3.
Is there any other procedure to prove that oxygen is needed for burning?
Answer:
To prove that oxygen ¡s required for burning:
Material required: A pan of water, empty milk bottle, candle, a box of matches.
Instructions: Fix the candle on the pan of water, now light the candle.
Observation: The candle extinguishes and the water rises 1/4 of the milk bottle. We can put off fire by covering with sand or blanket because here we are preventing supply of oxygen from this we can prove that oxygen is needed for burning.
Question 4.
In a few years, the fuels on earth will be exhausted. Think, what would happen to human civilization?
Answer:
Fuel is a source of energy. The common fuels now in use are fossil fuels like coal, petrol, diesel oil, kerosene, natural gas, etc. Apart from these, wood is also used as fuel in some remote parts of rural areas. We know well, how these fuels are serving the man. From these fuels, we derive mainly the heat energy, thermal energy, mechanical energy, light energy etc.
The modern civilization lays its foundation of the applications on these different forms of energy. These fuels are non-renewable. Once exhausted, they cannot be replaced. In the absence of these traditional fuels, human life becomes miserable. Then, we have to go for alternate renewable sources of energy like tidal energy (from sea), wind energy, solar energy, gravitational energy. etc. These serve our purpose only to a very limited extent.
Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
The gas needed for combustion among the following [ ]
a) Argon
b) Oxygen
c) Carbon dioxide
d) Hydrogen
Answer:
b) Oxygen
Question 2.
The lowest temperature at which a substance catches fire is called its [ ]
a) Ignition temperature
b) Maximum temperature
c) Room temperature
d) Normal temperature
Answer:
a) Ignition temperature
Question 3.
The units of calorific value is [ ]
a) Newtons/grams
b) Newtons/Kg
c) Kilojoules/kg
d) Kilojoules/gram
Answer:
c) Kilojoules/kg
Question 4.
Spirit and petroleum turns into gas at [ ]
a) Room temperature
b) Ignition temperature
c) Maximum temperature
d) Normal temperature
Answer:
a) Room temperature
Question 5.
The type of combustion in which material suddenly burns into flames without the application of any external agent is called [ ]
a) Rapid combustion
b) Slow combustion
c) Spontaneous combustion
d) Explosion
Answer:
c) Spontaneous combustion
Suggested Experiments
Question 1.
Conduct an experiment for testing the necessity of air for burning.
Answer:
Experiment:
- A small burning candle is put on a table.
- A glass tumbler is inverted on it.
- The candle continues to burn for a while, then begins to flicker and finally the flame goes off.
- The tumbler is removed and the candle is again lighted. The tumbler is now put back over the candle.
- When the candle flame begins to flicker and seems to be dying out, the tumbler is removed.
- Then the candle continues again to burn.
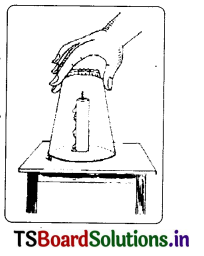
We find that when we put the glass tumbler over the candle, supply of air is cut off. So the flame goes off. When the supply of air restored the candle again continues to burn. The experiment proves that we need air to burn a material.
Question 2.
Conduct an experiment to prove that Oxygen helps in burning.
Answer:
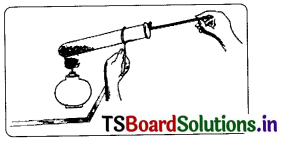
Aim: To prove that oxygen helps in burning.
Material required: Test tube, test tube holder, spirit lamp, matchbox, boom stick (agarbatti), potassium permanganate (KMnO4)
Procedure:
1. A few crystals of potassium permanganate are taken in a test tube.
2. The test tube is heated carefully.
3. Potassium permanganate decomposes, liberating oxygen gas. The chemical decomposition is:

4. Insert the agarbatti with the burning stub into the test tube.
5. We will observe that stick will burn with a flame.
Question 3.
Can you heat water in a paper vessel’? How is it possible? Conduct an experiment to understand the Ignition temperature.
Answer:
Yes. We can heat water in a paper vessel.
Reason:
- The heat supplied to the paper vessel gets transferred to water, by conduction of heat.
- So, in the presence of water, the ignition temperature of the paper is not reached. Hence it does not burn. We can even boil water (say, 50 ml) if we take it in a small paper cup and heat with a candle.
Suggested Projects
Question 1.
List out the different fuels that are used in your daily life and classify them into solids, liquids, and gases.
Answer:
Domestic use: Wood, coal, coke, charcoal, kerosene, LPG, biogas. Automobiles! Aircraft! Trains/Rockets: Diesel oil, petrol, ethyl alcohol
Industry: Coal, charcoal, natural gas, biogas, diesel oil, coal gas, water gas, producer gas, oil gas, and semi-water gas.
Classification of fuels above fuels into solid, liquid, gases:
| Solid | Liquid | Gases |
| Wood, coal, coke, charcoal, lignite |
Kerosene, LPG, diesel oil, petrol, ethanol (Ethyl alcohol) |
Biogas, natural gas coal gas, water gas, semi-water gas, producer gas, oil gas. |
Question 2.
Collect information available on different fuels. Find out the cost per kg. Compare the cost with calorific value. Prepare report on that.
Answer:
It is observed that, as the calorific value of a fuel increased, its cost per kg also increased simultaneously.
Among the solid fuels, wood is cheaper than coal. Their calorific values are:
Wood (nearly 20,000 KJ / Kg)
Coal (nearly 29,000 KJ / Kg)
Among the liquid fuels, petrol, kerosene and diesel have almost the same
calorific values (45,000 KJ / Kg).
Among gaseous fuels, [PG has slightly more calorific value, than CNG.
(LPG = 55,000 KJ / Kg and CNG = 50,000 KJ / Kg)
Question 3.
Collect the information about annual fuel consumption in different parts of the world. How many years more the fossil fuels last? Make a poster with this information and
issue an appeal to save fuel.
Answer:
From a study of the statistical survey reports about the annual fuel consumption in different parts of the world, we arrive at the following conclusions.
- There is the highest consumption of fossil fuels in developed countries like America, Russia, Europe etc.
- The consumption of fossil fuel is comparatively less in underdeveloped countries like India, Pakistan, etc.,
- The consumption of fossil fuel by the undeveloped countries like South Africa is least.
If the consumption of fossil fuels continues at the present rate, all the natural sources of the fuel get exhausted very soon. It may hardly take fifty or seventy years for the natural sources to drain.
TS 8th Class Physics 8th Lesson Combustion, Fuels and Flame Intext Questions
Think & Discuss
Question 1.
Why some materials burn and why some do not? Give reasons. (Text Page No: 109)
Answer:
- Substances that vapourise on heating, burn.
- Substances that do not vapourise on heating, do not burn.
Reason: it is the vapours of the substance that catch fire and burn, The solid or the liquid form of the substance does not catch fire.
Question 2.
Why some materials which do not burn at normal temperaturess burn at higher temperatures? (Text Page No: 109)
Answer:
- Every material has an ignition temperature.
- If the ignition temperature is low, the material burns at normal temperature.
- If the ignition temperature is high, the material burns at a higher temperature.
Question 3.
If you lift the glass tumbler (Which Is placed over a burning candle) to 1cm height what happens? Why? (Text Page No :110)
Answer:
When we lift the glass tumbler to a certain height, air enters the tumbler from below. Then the candle continues to burn.
Reason: There is supply of air. So the candle continues to hum.
Question 4.
How do you say that the gas released in burning of KMnO4 experiment is oxygen for burning? (Text Page No: 111)
Answer:
- We know that oxygen is essential for combustion.
- The burning stub of the agarbatti catches fire when inserted into the test tube. So there must be oxygen present in the test tube.
Question 5.
Can we replace KMnO4 with any other substance to release oxygen?
Answer:
Yes, Oxygen can also be obtained by the following methods.
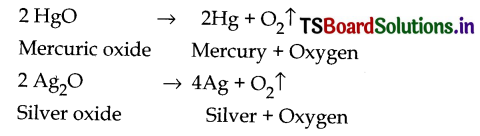
1. By hearing chlorates:
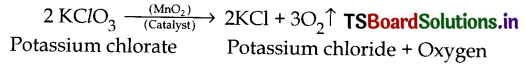
2. By heating metal oxides, Some metal oxides decompose on heating into the respective metal and oxygen.
Question 6.
Is there any other procedure to prove that oxygen ¡s needed for burning?
Answer:
To prove that oxygen is required for burning:
Material required: A pan of water, empty milk bottle, candle, a box of matches.
Instructions: Fix the candle on the pan of water, now light the candle.
Observation: The candle extinguishes and the water rises 1/4 of the milk bottle. We can put off fire by covering with sand or blanket because here we are preventing supply of oxygen from this we can prove that oxygen is needed for burning.
Question 7.
Why is phosphorus preserved in water? (Hint: Think about the role of Ignition temperature in combustion) (Text Page No: 113)
Answer:
The inflammable temperature of white (or yellow) phosphorus is 45’C So when it is kept in air it easily catches fire and bursts into flames. So it is preserved in water.
Question 8.
Why Kerosene stoves and Bunsen burners in your lab have small holes in them? (Hint: Think about the role of air) (Text Page No: 113)
Answer:
- Air is required for the fuel to bum.
- Air enters the stove or the burner through these small holes.
- This air mixes with the fuel.
- Then the fuel bums, if ignited.
Question 9.
A wax candle burns with a yellow flame. The domestic gas burns when lighted burns with a blue flame. Why? (Text Page No: 116)
Answer:
- Yellow flame is produced due to the incomplete (or partial) combustion of wax.
- Domestic gas (say, LPG) burns with a blue flame, due to the complete combustion of the petroleum gas.
TS 8th Class Physics 8th Lesson Combustion, Fuels, and Flame Activities
Activity – 1 :
(Do all materials burn?) (Text Page No: 108)
Question 1.
Describe an activity for testing different types of materials to determine whether they burn or not. What can we conclude from this activity?
Answer:
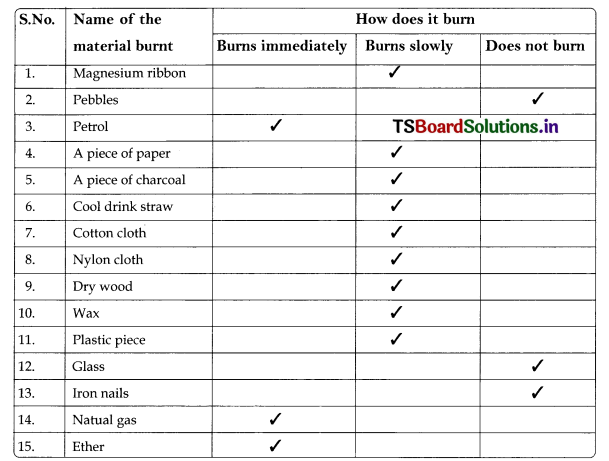
Using tongs, pick up a small piece of paper and bring it near to the lighted candle and keep it on flame as shown in the figure. Record your observations ma table.

Observations testing different types of materials to determine whether they burn or not.
Questions based on the above Activity -1
a. What do you observe in your attempt of burning water? (TexL P. No. 109)
Answer:
Water does not burn
b. Is there any difference in flame of lighted stick?
Answer:
From the above activity we can conclude that some materials burn and others dont. From the above activity we also observe that when we hum materials in air, heat and light are produced.
c. What happened to the lighted stick when it Is brought closer to water in the plate?
Answer:
The flame is put out.
d. What can we conclude from this activity?
Answer:
In the above activity -1 we observe that how the materials hum. Whether they burns immediately, slowly does not bum. In the above activity, we observed that when we burn material in air, heat and light are produced.
e. Which of the materials in the above activity are combustible?
Answer:
A piece of paper a piece of charcoal, magnesium ribbon, cool drink straw, cotton cloth, nylon cloth, dry wood, wax, plastic piece. petrol, natural gas and ether are combustible materials.
f. What is needed for the process of combustion?
Answer:
We need a matchstick or a lighter to hum a material.
Activity – 2: Testln the necessity of air for bimini (Text Page No: 110)
Question 2.
How will you prove that air is needed to a burn a material (or) Write an experiment for testing the necessity of air for burning.
Answer:
Experiment:
- A small burning candle is put on a table. . .
- A glass tumbler is Inverted on it.
- The candle continues to burn for a while, then begins to flicker and finally, the flame goes off.
- The tumbler is removed and the candle is again Lighted. The tumbler is now put back over the candle.
- When the candle flame begins to flicker and seems to be dying out, the tumbler is removed.
- 6. Then the candle continues again to hum. We find that when we put the glass tumbler over the candle, supply of air is cut off. So the flame goes off.
When the supply of air restored the candle again continues to burn, The experiment proves that we need air to burn a material.
Questions based on the above Activity – 2
a. Can we burn a material in the absence of air?
Answer:
No, we cant burn a material in the absence of air. Actually the oxygen that present in air supports the combustion of burning.
Activity – 3; Burning a paper with sun rays (Text Page No: 111)
Question 3.
Write how you can bum a paper with sun rays using a hand lens. (Magnifying lens)
Answer:
- On a sunny day, if we focus the sun’s rays as a spot on a piece of paper using a hand lens, the paper first gets heated up at that spot.
- After some time, smoke comes out and then the paper catches fire.
- In this way we can burn a paper with sun rays.
Questions based on the above Activity – 3
a. Does a matchstick burn by itself? (Text Page No: Ill)
Answer:
No, a matchstick does not hum by itself.
b. Why do you rub the match stick on the side of the matchbox to burn it?
Answer:
A matchbox contains safety matches.
- The sides of the matchbox (rubbing surfaces) contain a mixture of powdered glass and a little red phosphorus.
- The head of the match stick contains a mixture of antimony trisulphide, Head of the safety (Sb2S3) and potassium chlorate (KClO3).
- When the match stick is struck against the rubbing surface, some red phosphorus converts into white phosphorus.
- This reacts immediately with potassium chlorate in the matchstick head. Then heat is produced.
- This heat ignites antimony trisulphide. Then combustion starts and it produces flame. The stick then catches fire and continues to burn.
c. Can you burn a piece of wood by bringing it near to a lighted matchstick?
Answer:
No. The lighted match stick does not produce sufficient heat, required to ignite the wood.
d. Why do we use paper or kerosene oil to start fire in wood or coal?
Answer:
- The materials wood and coal are not easily combustible materials, They require high heat to catch fire. Their ignition temperatures are high.
- Heat produced by a lighted match is not sufficient to ignite these materials.
- A burning paper or kerosene produces the required heat, to ignite these materials.
- So we use paper pieces or kerosene oil to start fire in wood or coal.
e. Can you make a list of some more inflammable substances? (Text P. No: 112)
Answer:
Some of the inflammable substances are:
- Liquids: Petrol, alcohol, spirit, Liquified Petroleum Gas (LPG) and many organic liquids like benzene.
- Gases: Compressed Natural Gas (CNG), Natural gas.
Activity -4:
Understandinf i2nitlon temoerature. (Text Page No: 112)
Question 4.
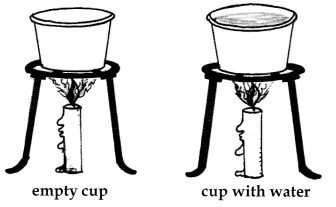
Take two small paper cups. Pour water in one of the cups. Put the two cups on different tripod stands and heat both of them using a candle.
Answer:

Questions based on the above Activity-4 (Text Page No: 112)
a. Which cup burns first?
Answer:
The empty cup burns first.
b. Does the water in the cup become hot? Why?
Answer:
Yes, The water in the cup becomes hot.
Reason: In this cup, heat is transferred to water, by conduction.
c. When does the second cup start burning?
Answer:
As long as there is water in the cup, the cup does not catch fire. So when all the water boils and vapourises away the graph cup catches fire.
Activity – 5: Observing the behaviour of different solid fuels: (Text PagNo; 115)
Question 5.
Explain an activity to observe the “Ignition Temperature.
Answer:
Ignition temperature:
The lowest temperature at which a substance catches fire is called its ignition temperature.
Activity:
- Take two small paper cups. Pour water in one of the cups.
- Put the two cups on different tripod stands and heat both of them using a candle.
- The empty cups burns quickly. So its ignition temperature is less.
- Though we supply head to both paper cups, but the heat in the second cup is transferred to water.
- The presence of water in the second cup prevents the paper to reach its ignition temperature and hence it does not burn.
a. Describe the activity to observe the behaviour of different solid fuels.
Answer:
- Collect some fuels like candle, coat, charcoal, magnesium ribbon, wood. cakes of cow during. camphor, wick of the oil lamp, wick of kerosene stove, etc.
- Burn each of them one by one with the help of spirit lamp and note the time they take to catch fire.
- All of them do not burn in the same manner.
- Coal, charcoal, wood and cakes of cow-dung catch fire after a long time. They burn with slow fire. They do not produce flames.
- Magnesium ribbon catches fire slowly hut bums quickly with a dazzling light.
- Camphor, kerosene stove, wick of oil lamp and candle catch fire soon and burn producing a flame.
b. Do all they burn in same manner? If not what difference do you notice? (Text Page No: 115)
Answer:
1. All of them do not burn in the same manner.
2.
- Coal, charcoal, wood and cakes of cow-dung catch fire after a long time. They burn with slow fire. They do not produce flames.
- Magnesium ribbon catches fire slowly hut burns quickly with a dazzling light.
- Camphor. kerosene stove, wick of oil lamp and candle catch fire soon and burn producing a flame.
c. Do all of them form a flame while they are burning? (Text Page No: 115)
Answer:
No. Only some of the solid fuels form a flame and some do not form flame while they are burning.
d. Prepare a table, with fuels which form flame and which do not form flame on burning.
Answer:
Questions based on the above Activity (Text Page No: 112)
a. Which cup burns first?
Answer:
The empty cup burns first.
b. Does the water in the cup become hot? Why?
Answer:
Yes, the water in the cup becomes hot.
Reason: In this cup, heat is transferred to water, by conduction.
c. When does the second cup start burning?
Answer:
As long as there is water in the cup. the cup does not catch fire. So when all the water boils and vapourises away the empty cup catches fire.
Activity – 5 :
Observing the behaviour of different solid fuels: (Text Page No: 115)
Question 5.
Explain an activity to observe the “Ignition Temperature”.
Answer:
Ignition temperature:
The lowest temperature at which a substance catches fire is called its ignition temperature.
Activity:
- Take two small paper cups. Pour water in one of the cups.
- Put the two cups on different tripod stands and heat both of them using a candle.
- The empty cups burns quickly. So its ignition temperature is less.
- Though we supply head to both paper cups, but the heat in the second cup is transferred to water.
- The presence of water in the second cup prevents the paper to reach its ignition
temperature and hence it does not burn.
a. Describe the activity to observe the behaviour of different solid fuels.
Answer:
- Collect some fuels like candle, coat, charcoal, magnesium ribbon, wood. cakes of cow dung, camphor, wick of the oil lamp, wick of kerosene stove, etc.
- Burn each of them one by one with the help of a spirit lamp and note the time they take to catch fire.
- All of them do not burn in the same manner.
- Coal, charcoal, wood and cakes of cow-dung catch fire after a long time. They burn with slow fire. They do not produce flames.
- Magnesium ribbon catches fire slowly but bums quickly with a dazzling light.
- Camphor, kerosene stove, wick of oil lamp and candle catch fire soon and burn producing a flame.
b. Do all they burn in same manner? If not what difference do you notice? (Text Page No:115)
Answer:
- All of them do not burn in the same manner,
- a) Coal, charcoal, wood and cakes of cow-dung catch fire after a long time. They burn with slow fire. They do not produce flames.
b) Magnesium ribbon catches fire slowly but bums quickly with a dazzling light.
c) Camphor. kerosene stove, wick of oil lamp and candle catch fire soon and burn producing a flame.
c. Do all of them form a flame while they are burning? (Text Page No: 115)
Answer:
No. Only some of the solid fuels form a flame and some do not form flame while they are burning.
d. Prepare a table, with fuels which form flame and which do not form flame on burning.
Answer:

Activity – 6:
Observing the structure of the flame: (Text Page No: 116)
Question 6.
a. How many colours are there in a flame? “
Answer:
There are three zones in a candle flame.
1. Outermost zone of flame: Blue
2. Middle zone of flame: ‘Yellow
3. Innermost zone : Black

b. Starting from the base of the flame, how many flame zones do you observe?
Answer:
Starting from the case of the t lame, we observe two large zones – the yellow and the blue zones of the flame,
c. What is the colour of the outermost zone of flame?
Answer:
The outermost zone of the flame is blue in colour. It is the hottest part of the flame.
d. Observe the innermost zone of flame is dark. What do you observe?
Answer:
The innermost zone lying near the hase of the flame is dark.
Reason: Air cannot enter this region. So the wax vapours here, do not burn. Hence there is no light here. It is dark.
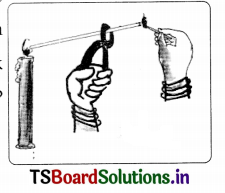
Activity -7:
Observing what happens in different zones of candle flame: (Text Page No:116)
Light a candle. Hold a glass tube with a pair of tongs and introduce its one end in the dark zone ola non, flickering candle flame. Keep lightened match stick nearby other ends of the glass tube. What do you observe?
a. Do you see a flame? :
Answer:
I do not see a flame.
b. If so what is it that produces a flame?
Answer:
When vapours of wax bum in air (oxygen), flame is produced. It is called, combustion.
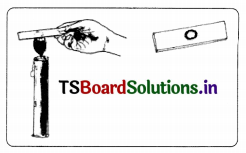
c. Introduce a clean glass slide into the luminous zone of the flame when The candle’s flame is steady for 10 seconds. What do you observe?
Answer:
A blackish circular ring is observed on the glass slide.
d. A blackish circular ring is formed on the glass slide. What is it?
Answer:
It indicates the deposition of unburnt carbon particles present in the luminous zone of the flame. Incomplete combustion of wax takes place in this zone.
e. Hold a thin long copper wire just inside the flame for about half a minute. What do you observe?
Answer:
- The copper wire just outside the flame gets red hot.
- It indicates that the non-luminous zone of the flame has high temperature.
f. Why flames produce light?
Answer:
Light of a flame conìes from a process, called fluorescence or from incandescence’ of some particles.
Incandescence: When some substances are heated strongly to a very high temperature, the’ emit light. The process is called. incandescence. Eg: The tungsten filament in a filament bulb.
g. Why is fire hot?
Answer:
- Fire is produced due to combustion of fuel.
- Combustion is an oxidation reaction.
- Oxidation reaction liberates heat. exothermic reaction). So fire (or flame) is hot.
h. Why caWt we fry food with water but of with oil?
Answer:
- All food materials contain water. So to remove this water, food is to he heated beyond the boiling point of water (100°C).
- If we use water to fry food, all this water vapourises away at 100°C. So water cannot be used to remove water present in the food material.
- However, oil can be heated to more than 15OE’C, without charring the food (making it black). Oil is not vapourised at this temperature. So the food can he fried now.
Lab Activity – 1
Question 1.
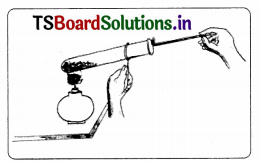
How do you prove that oxygen helps for combustion? (Text Page No: 110 (Application to daily life, concern fo biodiversity)
Answer:
Aim: To prove that oxygen helps in burning.
Material required: Test tube, test Lube holder, spirit Lamp, matchbox, boom stick (agarbatti), potassium permanganate (KMnO4)
Procedure:
1. A few crystals of potassium permanganate are taken in a test tube.
2. The test tube is heated carefully.
3. Potassium permanganate decomposes. liberating oxygen gas. The chemical decomposition is:

4. Insert the agarbatti with the burning stub into the test tube.
5. We will observe that stick will burn with a flame.
Question 2.
How does scented stick started burning?
Answer:
There is sufficient quantity of oxygen and heat in the test tube, to rekindle the burning stub of the agarbatti. So the agarbatti got fire.
Question 3.
Why does not it catch again fire when agarbatti (scented stick) is kept aside in air after putting its flame off?
Answer:
Though air contains oxygen.
- The available oxygen is not sufficient to rekindle the burning stub of the scented stick.
- The required temperature also is not available in air, to rekindle the burning stub.
- The ‘ignition temperature is not reached’.
- So the agarbatti does not catch again fire when it is kept aside in air after putting its flame off.