Telangana SCERT TS 6th Class Social Study Material Pdf Lesson 3A Land Forms Textbook Questions and Answers.
TS 6th Class Social Lesson 3A Questions and Answers -Land Forms
Intext Questions
Text Book Page No. 16
Question 1.
Look at the pictures of mountains, plain and plateau and try to find out which of them is similar to your region.
Answer:
I live in Karimnagar district of Telangana State. I have seen several hills in this region such as Kandikal and Rakhi hills.
Question 2.
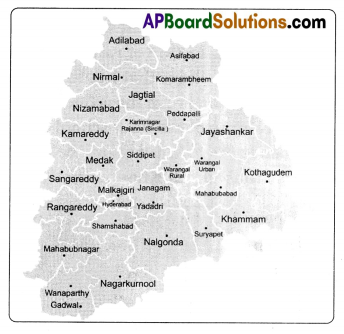
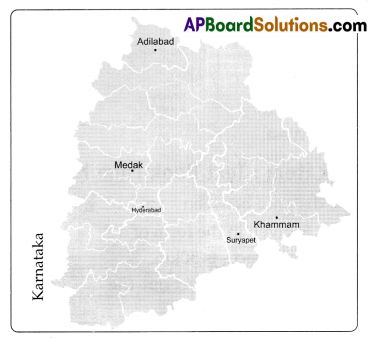
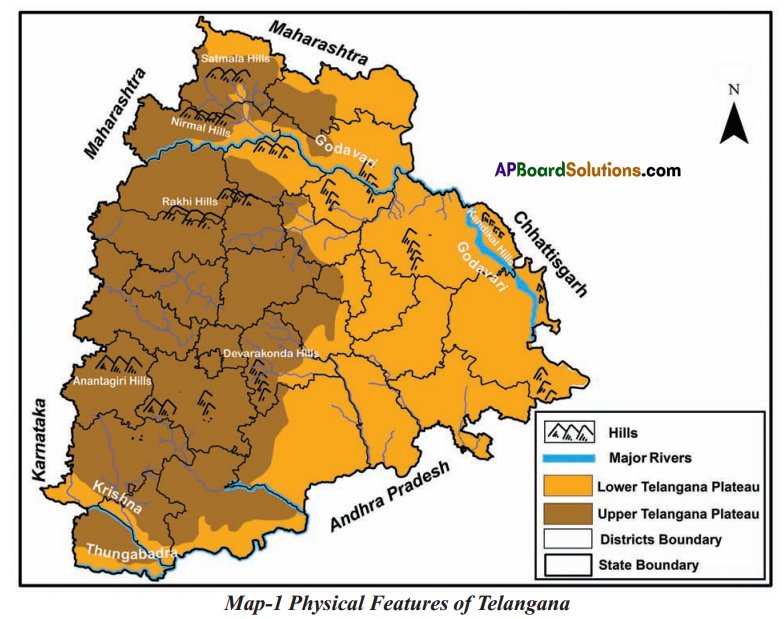
Look at the map of Telangana and find out which of these towns are on the upper and
lower Telangana plateau- Bhongiri. Bhadiachalam, Siddipet, Manthani, Manchiryala, Shadnagar, Sircilla, Chennur, Kamareddy, Vikarabad.
Answer:
As per the map of Telangana. I found the following towns are on the upper and lower Telangana plateau.
| Upper Telangana Plateau | Lower Telangana Plateau |
| Siddipet | Bhadrachalam |
| Shadnagar | Manthani |
| Vikarabad | Manchiryala |
| Siricilla | Chennur |
| Bhongiri, | Kamareddy |
Question 3.
In which districts are the Anantha giri hills, Devarakondahills, Nirmal hills, Sirnapally hills situated?
Answer:
| Name of the hill | District |
| 1. Ananathagiri hills | Ranaga Reddy |
| 2. Devara Konda | Nalgonda |
| 3. Nirmal hills | Adilabad |
| 4. Sirnapally hills | Nizamabad |
Text Book Page No. 18
Question 4.
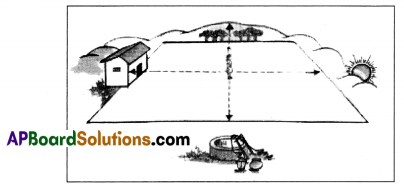
How do you think will the dams across the rivers affect the delta soils?
Answer:
The dams store water and regulate the water supply for agricultural purposes.
![]()
Question 5.
Find out the names of some other deltas In India.
Answer:
Names of some other deltas in India.
- Ganges delta
- Mahanadi delta
- Kaveri delta
- Sunderban delta.
Question 6.
Find out the names of at least two rivers that join in the Krishna and Godavari.
Answer:
| Rivers join in Krishna | Ehima, Dindi, Peddavagu, Halia, Musi, Paleru, Munneru, Venna, Koyna, Thungabhadra, Panchaganga, Budha Ganga, Ghataprabha, Malaprabha. |
| Rivers join in Godavari | Puma, Pranahitha, lndravathi, Sabari. Taliperu, Wanganaga. Penganaga, Wardha, Budhana. Pvavara, Manjira, Peddavagu, Mandir, Kinnerasani. |
Question 7.
Find out the location of a large dam on the Godavari river.
Answer:
- The Godavari is the second-largest river in India.
- The ‘jayakwadi dam near pathan Is one of the large dam on Godavari River, It is in Maharashtra
Question 8.
Why is it not possible to construct a large dam In Medak district?
Answer:
It is not possible to construct a large dam in Medak district because It is in Upper Telanagana plateau region.
Additional Questions
Question 1.
How many kinds of landforms are there? What are they?
Answer:
There are three kinds of bnd forms – mountain, plain and plateau.
Question 2.
What do you mean by a mountain? Give examples.
Answer:
Mountain is a very high place and has steep slope with a very little flat land on it. Eg. : Seshachalam hills, Papikondalu Hills, Velikorida Hills, Nallamala Hills.
Question 3.
What do you mean by a ‘river valley’? How are they formed? Give examples.
Answer:
An elongated lowland between ranges of mountains, hills, or uplands is known as a ‘valley’. River valleys are formed due to the erosional activity of a river or glacier. Eg. : Krishna river valley, Godavari river valley.
![]()
Question 4.
Define a ‘plateau’. How is the Deccan plateau formed?
Answer:
Plateaus are landforms with some unevenness but relatively level surfaces with a steep slope only on one side. Generally, plateaus are high above the sea level. Large portions of Telangana and Ravalaseema fall in plateau region which is called the Deccan plateau.
Question 5.
What is a ‘plain’? How is the plain useful?
Answer:
A plain is a level land with very gentle slope. Andhra Pradesh has several districts in East coastal plain. Plain is, in general, fertile and more habitable.
(MAPPING SKILLS)
a) Map Reading:
i)

Q. Can you tell what kind of landscape is the above picture?
Answer:
Hills.
ii)

Q. (Can you tell what Kind of a landscape is me above picture?
Answer:
Plain
iii)

Q. Can you tell what kind of landscape is the above picture?
Answer:
Plateau landscape.
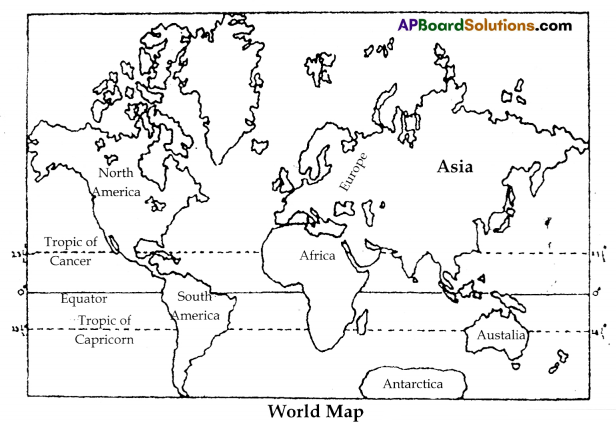
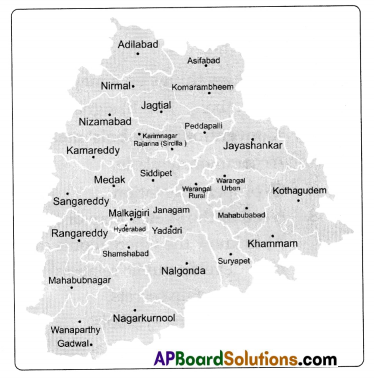
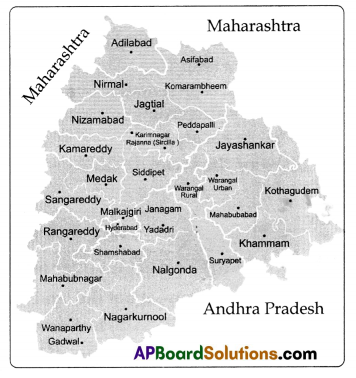
b) Locate the rivers and hills in Telangana state in the following map.
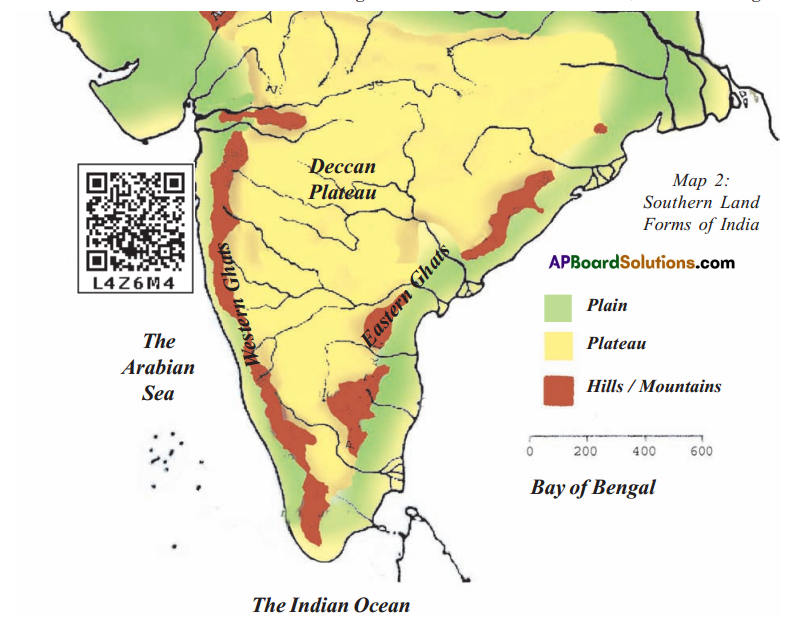
C) Mark the southern plateau region of India.
Two marks Questions
Question 1.
What is a Mountain?
Answer:
A mountain is a very high and it has steep slopes with very little flat land on it.
Question 2.
What are the mountain ranges in our country?
Answer:
Himalayas, Aravallis, Vindhyas and Satpura.
Question 3.
What is a Plateau?
Answer:
A plateau is a flat land with somi hill. in the middle of them.
Question 4.
Which is the biggest plateau in India?
Answer:
Deccan plateau.
![]()
Question 5.
Where do we find Satmala range of hills?
Answer:
Adilabad district in TeLangana.
Question 6.
Which districts are found in lower Telangana plateau?
Answer:
Khammam, Karimnagar. Warangal
Question 7.
Which districts are found in upper Telangana plateau?
Answer:
Rangareddy, Hyderabad, Medak. Nizamabad.
Question 8.
What is the shape of Delta’?
Answer:
Triangle.
Question 9.
What are the two main rivers in Telangana?
Answer:
Godavari and Krishna.
(Appreciation And Sensitivity)
Question 1.
Write about the importance of the river Godavari and the river Krishna.
Answer:
- The Krishna and the Godavari form deltas which are very fertile.
- Pruiects are constructed over the rivers which produce electricity and supply water to our lands.
- So many cities are developed on the banks of these rivers.
(Objective Type Questions)
Question 1.
How many kinds of landforms are there? ( )
A) One
B) Two
C) Three
Answer:
C) Three
Question 2.
These are very highlands ( )
A) Mountains
B) Hills
C) Plateaus
Answer:
A) Mountains
Question 3.
The district that has a hilly terrain region ( )
A) Adilabad
B) Warangal
C) Nizamabad
Answer:
A) Adilabad
Question 4.
The famous Ananthagiri hills are located in ( )
A) Rangareddy
B) Karimnagar
C) Mahabubnagar
Answer:
A) Rangareddy
Question 5.
This is the biggest among the rivers In Telangana ( )
A) The Krishna
B) The Penna
C) The Godavari
Answer:
C) The Godavari
![]()
Question 6.
Large portions of Telangana fall in this relief ( )
A) Mountains
B) Plateaus
C) Plains
Answer:
B) Plateaus
Question 7.
Hyderabad and Secunderabad are located in this region ( )
A) Mountain
B) Plateau
C) Plain
Answer:
B) Plateau
Question 8.
These are very fertile soils ( )
A) The plains
B) The hills
C) The tributaries
Answer:
A) The plains
Question 9.
Rivers Krishna and Godavari are originated from ( )
A) Eastern Ghats
B) Western Ghats
C) Bay of Bengal
Answer:
B) Western Ghats
Question 10.
East coastal plains are formed near this sea ( )
A) Arabian Sea
B) Black Sea
C) Bay of Bengal
Answer:
C) Bay of Bengal
Look at the map and answer the questions 11, 12 and 13
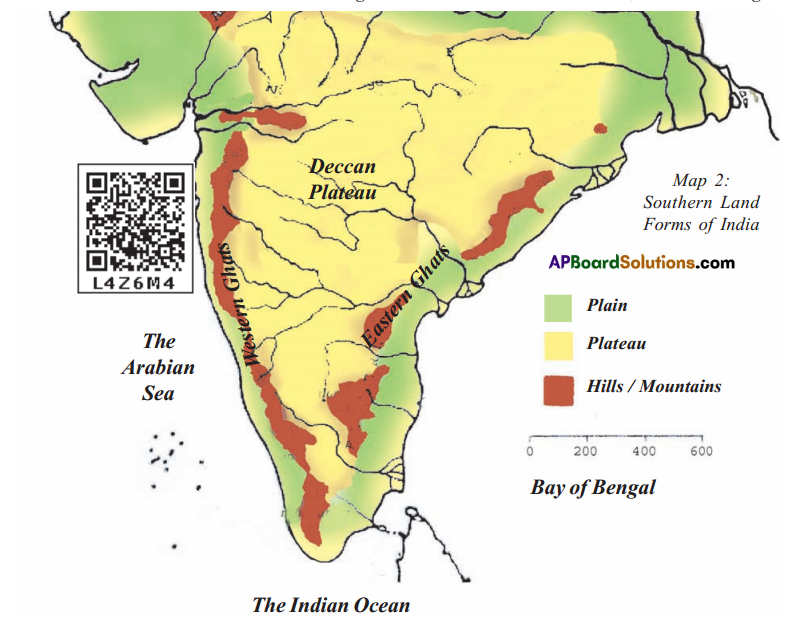
Question 11.
The river Godavari originates in ( )
A) Western ghats
B) Eastern Ghates
C) The Arabian sea
D) Bay of Bengal
Answer:
D) Bay of Bengal
Question 12.
Which grab are in broken and not in continuous stretch ( )
A) Western Ghats
B) Eastern Ghates
C) Both Ghates and western Ghates
D) We can not say
Answer:
B) Eastern Ghates
![]()
Question 13.
What plateau does Telangana exist in ( )
A) Aravali
B) Vindhya
C) Deccan
Answer:
C) Deccan