TS Board Telangana SCERT Class 6 Science Solutions 10th Lesson Changes Around Us Textbook Questions and Answers.
TS 6th Class Science 10th Lesson Questions and Answers Telangana – Changes Around Us
Question 1.
Is the change of ice into water a temporary or permanent change? Explain.
Answer:
Explanation: The change of ice into water is a temporary change. It is not a permanent change. It is only a physical change.
Reason : Here, the cause of change is ‘heat. When we remove the cause of change (heat) the process gets reversed. It means, when we cool water (or remove heat from water), it changes again to ice. So it is a temporary change.
![]()
Question 2.
How do you know that rusting of iron ¡s a change?
Answer:
When iron rusts
- its colour changes. The dull greyish iron changes to reddish brown
- the smooth metal surface becomes quite rough
- particles of rusted metal detach from the metal surface.
These are all the physical changes we observe, when iron rusts.
![]()
Question 3.
If a raw egg is boiled in water, what changes do you notice in it?
If you are given two eggs, can you determine which one is boiled and which one is not? Explain.
Answer:
Raw egg possesses more density than boiled egg. When raw egg is boiled, naturally its density decreases. When we shake a raw egg, we Feel the fluid moving inside.
Question 4.
Name five changes you notice in your surroundings. Classify them as natural or man-made changes.
Answer:
| Change | Type of change |
| 1. Fall off leaves from a tree 2. Colour of sky changes 3. Flowers bloom and wither away 4. Colour of leaves changes 5. Curdling of milk |
Natural change Natural change Natural change Natural change Man-made change |
Question 5.
Choose incorrect statements from the following and rewrite them correctly:
Answer:
| Given statement | Corrected statements | |
| a. The coldness in air during winter is a permanent change | The coldness in air during winter is a temporary change. | |
| b. Boiled egg is a temporary change. | Boiled egg is a permanent change | |
| c. There is a cause for every change. | The statement is correct. | |
| d. An electric bulb going ON and OFF is a permanent change. | An electric bulb going on and off is a temporary change. | |
| e. There is a change in state when ice-cream melts. | The statement is correct. It is a temporary change in its physical state. Solid state |
|
Question 6.
Some changes are listed below, classify them as temporary and permanent.
Answer:
| Given change | Type of change |
| a. Souring of curd | Permanent change |
| b. Ripening of oranges | Permanent change |
| c. The sawing of a piece of wood into two | Permanent change |
| d. Cooking of food | Permanent change |
| e. Heating of milk | Permanent change |
![]()
Question 7.
We use clay to make idols. Can we get back clay from the idol ? What type of change is it? Explain.
Answer:
If only clay is used to make idols, we can get back clay from the idol. The idol is soaked in water for sometime. Again we get back the clay. So it is a temporary change. Eg : Ganapathi idol is made from clay.
Question 8.
Carpenter made a chair using wood, what type of change is it?
Answer:
From a raw wood, carpenter makes a chair. The raw wood is often cut, chiselled and polished for the purpose. So from this finished wood, we cannot get back the original raw wood. So the change is a permanent change.
Question 9.
Rafi said that “Flour from Rice I Wheat is a man made change.” He wants to make a list of examples of this kind of change, help him to expand his list.
Answer:
Some man-made changes:
- Flour from rice
- Juice from lemons
- Cream from milk
- Butter milk from curd.
- Tea from tea leaves.
- To peel an orange.
Question 10.
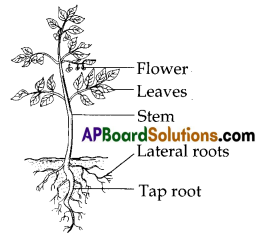
Select a plant in your house I school observe and record changes keeping in view height of plant, number and size of leaves and flowers etc., over a period of 2 months. Display your observations.
Answer:
I have observed the guava plant. It grew in size and height. The number of leaves increased in the period of two months and their size also increased.
![]()
Question 11.
What will happen if a decorative colour paper is dipped in water? Predict the possible changes. Verify your predictions by doing experiments and write down the steps of the process.
Answer:
- The paper is dipped in water.
- The colour fades.
- The paper loses stiffness and turns to a pulp.
- The paper becomes useless.
Question 12.
Write various steps involved in making ghee from milk, what changes do you find, during this process?
Answer:
Production of ghee from milk involves various stages.
Stage 1: Milk changing to curd: (Curdling of milk): Milk is heated gently to boiling temperature and allowed to cool.
To the warm milk, a very small quantity of curd is added and stirred well.
The vessel is kept undisturbed for a few hours.
Then a white semi-solid mass appears in the vessel. It is curd.
Observed change : There is a slight difference in colour from milk to curd. Milk is slightly sweet and curd is slightly sour in taste.
Stage 2 : Butter from curd : Sufficient water is added to the curd. It is well churned.
Butter forms and floats over the liquid. The butter is hand-picked.
Observed change: Butter is a semi-solid mass. It separates from the butter milk.
Stage 3 : Butter to ghee : The butter is heated on a low flame for sometime. When we notice the smell of ghee we stop further heating. Ghee is formed.
Change observed : Semi solid butter is changed into ghee in liquid state which has a characteristic fragrance on heating.
Stage 4 : Separation of ghee from the residue : The mass is allowed to cool. Then it is filtered using a clean cloth. Residue is left over in the cloth. Ghee is collected in the vessel.
All the changes involved in making ghee from milk are permanent changes. They are all irreversible
Question 13.
Observe the following table and answer the questions given below.
Answer:
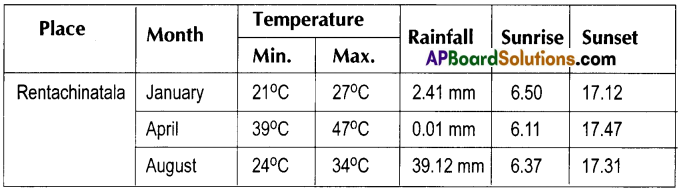
i. Which month had maximum rainfall?
Answer:
August.
ii. Which season occurs in the month of August? How can you support your answer?
Answer:
Rainy season. The rainfall is heavy (39.12 mm) in the month of August.
iii. In which month is the duration of day minimum ? What could be the reason for this?
Answer:
In the month of January, the duration of day is minimum (17.12 – 6.50 = 10.22 hrs.)
It is winter season. The sun rises late and sets earlier.
iv. Do you find any relation between sunrise and seasons?
Answer:
Summer (April) : Sun rises quite early.
Rainy season (August) : Sun rises early.
Winter season (January) : Sun rises quite late
![]()
v. What changes can you identify from January to August?
Answer:
The following changes are identified from January to August.
- Day temperature: Minimum in January, maximum in April and again fall in August to a lower value.
- Rainfall : Very very poor in January, almost nil in April and maximum in August.
- Length of the day : Increases from January to April and then decreases in August. It is minimum in January and maximum in April.
- Change of seasons:
January – Winter season
April – Summer season
August – Rainy season
Thus the seasons change from January to August.
Question 14.
Farha wondered “How could it be possible for the nature to bring changes in seasons periodically”. Can you add some changes like this. How will you explain them?
Answer:
It is wonderful to see so many periodic changes in nature. A few of them are:
- A day returns periodically after 24 hours.
- The week returns periodically after 7 days.
- A month returns periodically after 30 days.
- A year returns periodically after 365 days and so on.
- Trees getting new leaves, shedding off ripen leaves, flowering, fruiting is another seasonal change.
Question 15.
Sita wondered and felt very happy to see the beauty of the fields and insects like twinkling beetles (Arudra) during rainy season in their village. Can you list some such changes which make you wonder and feel happy?
Answer:
In rainy season, the lakes and ponds overflow with water. There is plenty of water every where. The fields are green and trees are loaded with fruits. Everywhere there is plenty of food available. The buffaloes, oxes, goats find enough grass to fill their bellies. Every living being feels satisfied. There is no dearth of food.
![]()
TS 6th Class Science 10th Lesson Notes Changes Around Us
- Some changes take place naturally and some changes are initiated by human beings.
- Some of the naturally occurring changes are : change of seasons, sunrise and sunset, ripening of fruits, blooming of flowers, sprouting of seeds, withering of trees etc.
- Many natural changes take place in our body. Nails grow, hair grows, body – weight changes, etc.
- Classfication of changes is also made based on various indicators of change like the change in state, change in colour, change in size, change in taste etc.
- Changes : In our daily life we notice many changes around us.
- Change in state : A change that occurs physically is called change in state.
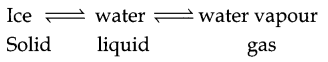
- Duration of day : Duration of day changes from season to season.
Eg: In winter duration of the days shorter and in summer duration of days are longer. - Indicators of change : There will be many indicators of changes to show that a change takes place.
- Slow/fast change : Changes can be classified in many ways. Slow change. Eg: Rusting of iron Fast change: Electric bulb ON and OFF
- Temporary/Permanent Change: A change that can easily be reversed is a temporary change. Eg : water
 ice,
ice, - A change which can not be reversed is a permanent change. Eg: milk → curd
- Natural / man – made change : A change that takes place naturally is called natural change. Eg : change of seasons, growth of plant. A change which is initiated by human beings is called man-made change. Eg: rice to cooked rice.