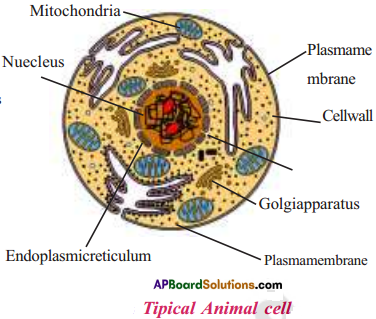
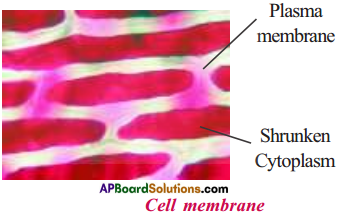
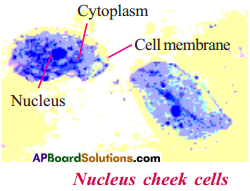
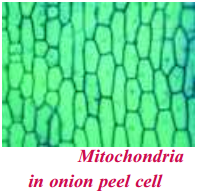
AP State Syllabus AP Board 9th Class Biology Solutions Chapter 8 Challenges in Improving Agricultural Products Textbook Questions and Answers.
AP State Syllabus 9th Class Biology Solutions 8th Lesson Challenges in Improving Agricultural Products
9th Class Biology 8th Lesson Challenges in Improving Agricultural Products Textbook Questions and Answers
Improve Your Learning
Question 1.
Suggest some ways through which our country could increase the production of rice to meet at least global limits. (AS 1)
(OR)
Day by day population is increasing. But the cultivated land is very limited. To produce required quantity of food for the growing population, what are the poible solutions in your view?
Answer:
- Increasing area of cultivated land.
- Increasing production in the existing land.
- Developing high yielding rice varieties.
- Conserving the genetic diversity of rice so it can be used in the development of new varieties suited to different growing conditions.
- Developing rice crop management strategies that improve nutrient use efficiency.
- Management of crop protection and suitable irrigation methods.
- Organic manure to be used for rice crop.
- Alternating crops and mixed crop system to be followed.
![]()
Question 2.
How are biofertilizers more beneficial as compared to chemical fertilizers? (AS 1)
Answer:
- Biofertilizers add natural nutrients to soil.
- They increases soil organic matter and improves soil structures.
- Biofertilizers improves water holding capacity of the soil and reduces soil crusting problems.
- They reduces soil erosion from wind and water.
- Biofertilizers increases crop yield.
- Biofertilizers improves the percentage of humus and remained long time in the soil.
Question 3.
a) Find out the adverse effects of chemical fertilizers need for growing the high yielding varieties of crops. (AS 1)
Answer:
- Chemical fertilizers pollute lakes, rivers and streams.
- They destroy beneficial soil life including earthworms.
- By using chemical fertilizers, we can get high yielding for only 20 to 30 years.
- After that soil becomes reluctant to plant growth.
- Chemical fertilizers damage soil fertility.
- Make certain crops vulnerable to diseases.
- Prevent some plants from absorbing needed minerals.
- Food produced by using chemical fertilizers do not taste as good.
b) Can high yielding varieties be grown without them (Chemical Fertilizers) as well? How? (AS 1)
Answer:
- Yes, high yielding varieties be grown without chemical fertilizers.
- By using biofertilizers, instead of chemical fertilizers and synthetic pyrethroids we get higher yielding.
![]()
Question 4.
What threats to nature do chemical fertilizers, pesticides, insecticides and herbi-cides pose? (AS 6)
Answer:
- When we use insecticides to kill pests or weedicides/herbicides to destroy weeds, a large percentages of herbicides, chemical fertilizers, pesticides, insecticides remain in the soil.
- From the soil, these chemicals find their way into water sources.
- People spray these chemicals in fields are exposed to them and some of the chemi-cals enter their body.
- Insecticides destroy all insects in which some of them are useful in pollination.
- Extensive use of chemical fertilizers, pesticides, herbicides and weedicides makes the soil unsuitable to grow crops after sometime.
Question 5.
What are the adverse effects of using high yielding varieties of seeds? (AS 1)
Answer:
The adverse effect of using high yielding seeds is – they use more nutrients from the soil. Thus the soil can lose its fertility if they are used continuously.
![]()
Question 6.
What are the essential measures that a farmer needs to take before sowing the seeds of a crop? (AS 1)
Answer:
- Preparation of soil is done before sowing the seeds.
- The soil is ploughed to loosen and break the solid pieces of soil.
- The field is watered before sowing.
- Seed treatments against/soil-borne diseases to reduce the incidence of diseases.
Question 7.
Suppose you had a farm in a drought striken area of your state, what crops would you grow and how? (AS 1)
Answer:
- Sorghum, Pearlmillet, Red gram, Green gram, Horse gram can be grown in drought striken area.
- We can grow these crops by rain water harvesting building check dams, drip irrigation methods, watershed management and soil and water conservation methods.
![]()
Question 8.
What measures will you take to save your field from seasonal outburst of insects? (AS 1)
Answer:
Nowadays farmers use insecticides and other chemicals to save their crop field.
- I prefer catching the insects manually and removed from the field.
- I also use predatory insects to remove insects from the field.
- I place lighted bulb (Deepapu Teralu) so that insects could cluster around it.
- Insecticides are sprayed at regular intervals.
Question 9.
What basis would you adopt to explain to a farmer using chemical fertilizers switch over to organic fertilizers? (AS 4)
Answer:
- Organic fertilizers replenish the soil, keeps soil easily broken up into small pieces.
- Organic fertilizers promotes beneficial soil life.
- Organic fertilizers increase crop yield.
- They maintain a natural balance in the soil.
- They protect certain crops from diseases.
- Benefit the environment by recycling agricultural wastes into energy for local community.
Question 10.
A farmer had been using a particular insecticide for a long time. What consequences will it have on – a) insect population b) soil ecosystem? (AS 1)
Answer:
a) Insect population :
- Insect develop immunity to the insecticide used.
- And it has any effect on the insect it targets. Hence the number of insects increases,
b) Soil ecosystem :
- A large percentage of insecticide chemicals remain in the soil.
- These chemicals kill the worms in the soil which are useful to soil.
- Hence soil ecosystem destroys by increasing the concentration of salts in the soil.
![]()
Question 11.
Venkatapuram village is in drought prone area. Somaiah wants to cultivate sugar-cane in his fields. Is it beneficial or not? What questions will you ask him to convey your belief? (AS 7)
Answer:
- It is not beneficial for Somaiah to cultivate sugarcane crop.
- Sugarcane grown in places where rich water resources are present.
- “Where do you get water to cultivate sugarcane crop?” I ask this question to Somaiah.
- I advise him to grow crops which needs less water (Aruthadi Pantalu) in drought prone area.
Question 12.
Draw a block diagram of water resources in your village. (AS 5)
Answer:
Question 13.
Ramaiah has soil testing done in his field. The percentages of nutrients are 34-20-45. Is it suitable for cultivating sugarcane crop ? Which crops can be cultivate without using pesticides in Ramaiah’s field? (AS 2)
Answer:
- Ramaiah’s field is not suitable for cultivating sugarcane crop.
- Because sugarcane needs 90% of nitrogen in the soil but Ramaiah’s field has only 34% of nitrogen.
- Maize and groundnut can be cultivated in Ramaiah’s field.
![]()
Question 14.
Organic manure is helpful to biodiversity. How do you support this statement? (AS 6)
Answer:
- Biological research on soil and soil organisms has proven beneficial to the system of organic farming.
- Varieties of bacteria and fungi breakdown chemicals, plant matter and animal waste into productive soil nutrients.
- In turn the producer benefits by heal their yields and more suitable soil for future crops.
Question 15.
Make a list of major weeds in your area (You have already conducted the project) Find out the different weeds that grow along with different crops in your area. (AS 4)
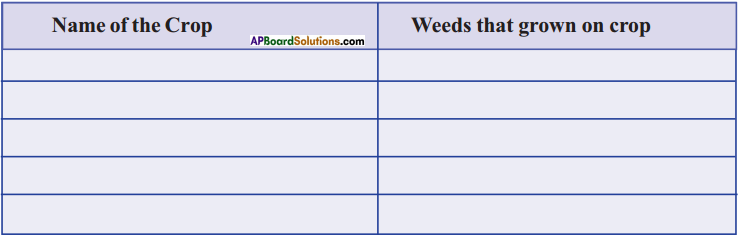
Answer:
Cynodondacylon, Digitaria longifolia, Dacty loctenium colonum, Setaria glauca, Cyperus rotundus, Cyperus difformis, Eichornia crassipes, Salvinia mollusta, Alternathera sps. Celosia argentea, Leucas aspera, Portulaca oleracea, cleome sps. Solanum nigum, Argemone mexicana, Abutilon indicum, Euphorbia sps. Vernonia Cinnera, Eichnochloa colonum, Commelina bengalensis, Avenafatua, Eichnochloa Crusgalli, Eleusine indica, Euphorbia hirta, Achyranthus, despera, Eclipta prostrata.
| Name of the Crop | Weeds that grown on crop |
| Paddy | Cynodon dactylon, Digitaria longi folia, Cyperus rotundus, Eichornia. |
| Groundnut | Leucas aspera, portulaca oleracea, Cleome sps, Abutilon indicum, Euphorbia cynodon dactylon, Commelina bengalensis, Cyperus roturdus. |
| Black gram | Cynodon dactylon, Cyperus rotundus, Abutilon indicum, Commalina bengalensis, Euphorbia hirta. |
| Maize | Euphorbia hirta, solanum nigrum, cyperus rofundus, cynodon dactylon. |
| Green gram | Eichnochloa colonum, cyperus rotundus cynodon dactylon, Argemone mexicana, Portulaca oleracea. |
Question 16.
Spraying high dose of pesticides is hazardous to biodiversity and crop yielding. How can you support this statement?
Answer:
- When we use pesticides large percentage of it will remain in the soil. These kill the germs in the soil.
- From the soil pesticides find their way into water bodies affecting the aquatic animals.
- People who spray these pesticides in the fields are exposed to them and some of the chemicals enter their bodies causing health problems or some times the person dies.
- Pesticides destroy all the insects which are useful to the plants causing hazardous to biodiversity.
Question 17.
Natural pest controlling methods are useful to biodiversity. Comment it.
Answer:
- Some insects control the harmful insects and they are called friendly insects.
E.g.: Spiders, Dragonfly, Krisopa etc. - Trachoderma bacterium lives in the eggs of stemborer, tobacco caterpillar destroy the pests at the egg stage.
- Some bacteria like Bacillus Turengenisis destroy some pests.
- Mixed crops also control some pests and diseases.
- Hence natural pest control methods are useful to biodiversity because these methods destroys only the selected pests.
![]()
Question 18.
Observe the fields in your surroundings and collect the information from farmers about the process to remove weeds.
Answer:
Farmers use different methods to remove weeds. Some of them are
1) Manual method:
Many farmers still remove weeds by manually pulling them out of the field, making sure to include the roots that would otherwise allow them to resprout.
2) Stale seed bed method :
This method involves cultivating the soil, then leaving it follow for a week or so when the initial weeds sprout, the farmer lightly hoes them away before planting the desired crop.
3) Using Herbicides :
Selective herbicides kill certain targets while leaving the de¬sired crop relatively unharmed.
4) Biological control:
Vinegar kills the visible part of the weed. They will wrinkle and die next day.
5) Ploughing & Tilling :
Ploughing includes filling of soil, inter-cultural ploughing and summer ploughing. Ploughing up roots weeds causing them to die. Mechanical tilling can remove weeds around crop plants at various points in the growing process.
Crop rotation method also helps in controlling weeds.
9th Class Biology 8th Lesson Challenges in Improving Agricultural Products InText Questions and Answers
9th Class Biology Textbook Page No. 110
Question 1.
Rate of growth of population and food grain production.
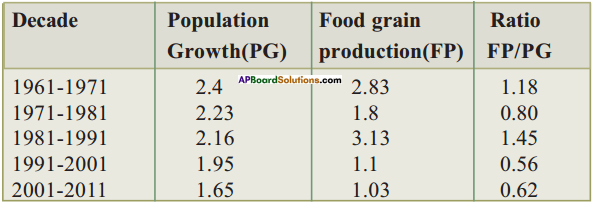
1. In which decade population growth is higher?
Answer:
Population growth is higher in 1961-1971.
2. In which decade food grain production is higher?
Answer:
Food grain production is higher in 1981-1991.
3. What major differences did you find in the table?
Answer:
The major differences find in the table are :
i) Foodgrain production is not increasing according to population growth.
ii) Ratio of FP/PG is in irregular order.
4. Is food grain production increasing according to population growth?
Answer:
No, last two decades food grain production is not increasing according to population growth.
5. In which decades production of food grains didn’t satisfy the needs of population? What will happen if the production is not sufficient?
Answer:
In 1991-2001 production of food grains didn’t satisfy the needs of population. If the food production is not sufficient then it leads to food crisis.
6. The decade 1991-2001 shows that rate of food production was nearly half as compared to population. What can you infer from the decade when population growth was highest?
Answer:
The reasons for the highest population growth :
i) Wide spread diseases are controlled.
ii) Health care programmes were made available in rural areas.
iii) So death rate declined.
iv) Therefore population growth become inevitable.
Question 2.
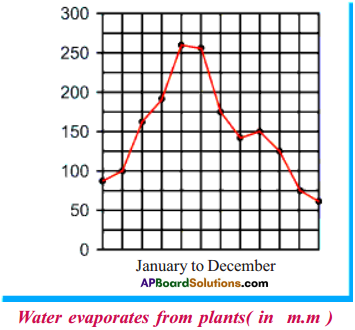
1. Find out from the graph the months in which the most water evaporates from plants.
Answer:
The months in which the most water evaporates from plants are May and June.
2. Are these the same months in monsoon season when the rainfall is heavy?
Answer:
No, these are not same.
3. So how does the availability of more water effect the plant?
Answer:
The availability of more water effects the plant with more evaporation.
9th Class Biology Textbook Page No. 110
Question 3.
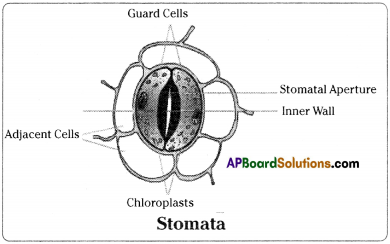
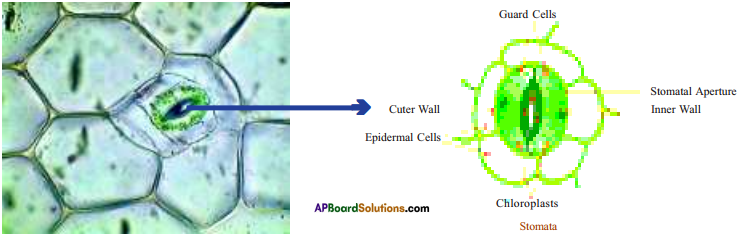
When the weather is hot and the stomata dose, what effect would this have on the absorption of carbon dioxide by the plant?
Answer:
If the stomata closed, then the absorption of carbon dioxide by the plant is less.
Question 4.
What effect would a change in the amount of carbon dioxide absorbed have on the growth of the plant?
Answer:
If the absorption of carbon dioxide by the plant is less then the growth of the plant decreases.
Question 5.
If the plant does not get water at this time, what effect would this have on its growth? Discuss in your class and find out reasons.
Answer:
If the plant does not get water at this time then the growth of the plant will stopped.
![]()
Question 6.
What are the main water sources in your village for agriculture? How farmers utilise them?
Answer:
- Canals, Bore wells, ponds are the main water sources in our villages.
- Farmers utilise water from these sources to cultivate crops.
Question 7.
Make a list of crops which require less amount of water.
Answer:
Cotton, Jute, Bajra, Maize, Coconut, Black gram, Green gram etc.
9th Class Biology Textbook Page No. 111
Question 8.
If a field is cultivated for many years, what would happen to the nutrient content of the soil?
Answer:
If a field is cultivated for many years, then the nutrient content of the soil is decreased.
Question 9.
How does the soil get back or replenish these nutrients?
Answer:
The soil get back or replenish of these nurients by adding organic manure or chemical fertilizers.
9th Class Biology Textbook Page No. 112
Question 10.
A farmer cultivated sugar cane in his land for the last five years. Another farmer culti¬vated sugarcane in the first year and soya bean in the second year and sugarcane in third year.
– In which case do you think has the land lost most of its nutrients?
Answer:
The land lost most of its nutrients in the case of first farmer.
Question 11.
Have you ever seen two types of crops in the same field?
Answer:
Yes, I have seen two types of crops in the same field.
![]()
Question 12.
Which crops are grown in this way?
Answer:
In the fruit growing fields like Lemon, Pomegranate, Papaya, etc. pulses like Red gram, Black gram, Green gram, etc. are grown in this way.
Question 13.
What are the uses of cultivating mixed crops?
Answer:
The uses of cultivating mixed crops are :
1) The soil becomes fertile.
2) The nutrients which are used by one crop will be regained by cultivating another crop.
9th Class Biology Textbook Page No. 113
Question 14.
Is betel (Tamalapaku) a mixed crop? How can you justify your answer?
Answer:
Yes. Betel is mixed crop. Sorghum grown along with betel.
9th Class Biology Textbook Page No. 121
Question 15.
If we don’t use these chemicals, how can we get a good crop? How can we increase production? Is there an answer to this question? What coidd it be?
Answer:
Suppose we can use some other methods that do not give rise to these problems. For example, they say we can make use of the natural food chains to control pests. There are many insects that eat other insects. They are called predatory insects. We can make use of these insects. There are also birds that eat insects. We can use these birds to get rid of insects.
![]()
Question 16.
If insects that pollinate crops are killed, what effect will this have on crop production?
Answer:
If insects that pollinate crops are killed, the crop production will decrease.
Question 17.
In recent times, why farmers touch the flowers with handkerchiefs in sunflower fields?
Answer:
Farmers touch the flowers with handkerchiefs in sunflower fields to control the insects.
9th Class Biology Textbook Page No. 122
Question 18.
Do you know why Jatropa in cotton fields and marigold in mirchi fields are cultivated?
Answer:
Some mixed crops controls some diseases and pests. That’s why Jatropa in cotton field, marigold in mirchi fields are cultivated.
9th Class Biology Textbook Page No. 110
Question 19.
In what way this kind of water supply is useful to the crop as well as the farmer?
Answer:
To prevent water wastage and economically helpful to the farmer.
![]()
Question 20.
Water Shed is a process to improve ground water level. In what way it is related to irrigation? Support with your answer.
Answer:
If ground water level will be increased then it will help to irrigation.
9th Class Biology Textbook Page No. 117
Question 21.
In what way vermi compost is better than chemical fertilisers?
Answer:
After using vermi compost, investment on chemical fertilizers and other pesticides became reduced and the quantity of their agricultural products increased.
9th Class Biology 8th Lesson Challenges in Improving Agricultural Products Activities
Activity -1
Question 1.
Observe the Transpiration :
- Take a polythene bag. Cover the bag on leaves and tie it.
- Do this experiment during day time and night time separately.
- Note the difference in your notebook.

Observations :
- If we tie a plastic bag over a leaf, we will be able to see how much water a plant releases in the air.
- It is estimated that a plant use only 0.1 percent of the water it absorbs to form carbohydrate.
- The rate of transpiration is high during day time when compared to night time.
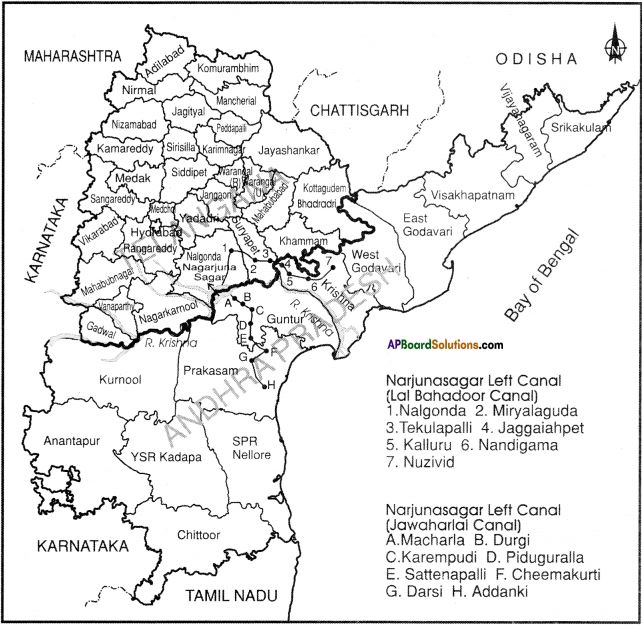
Question 2.
b) Draw the route map of Jawahar and Lai Bahadoor canals of Nagarjuna sagar in Andhra Pradesh & Telangana map.
Answer:
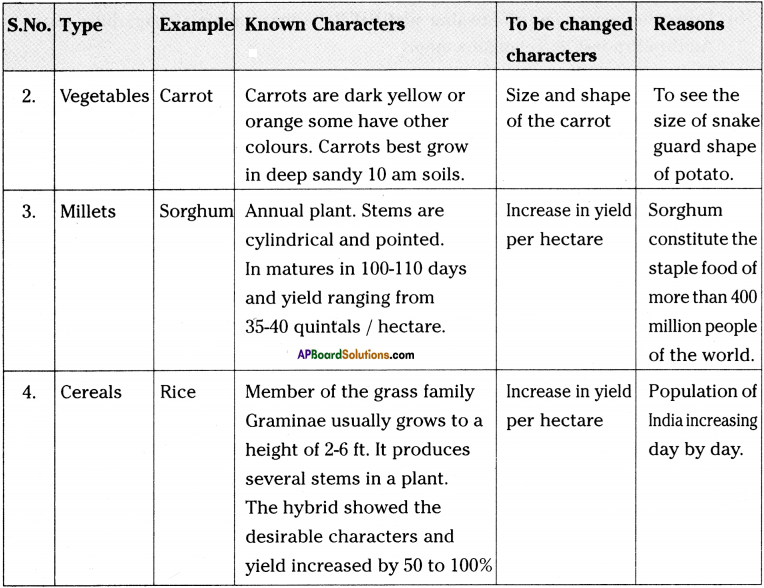
I. 1) Take one example from each of millets, cereals, vegetables, and fruits.
2) First you have to list out the known characters of the above and then list out the characters that you want to change or modify in them.
3) But you need to give your own reasons – why do you want to make such changes in them?

II. Red and yellow equal to rellow.
1) If you want to make your own hybrid flower you need to do the following. But it is time consuming process and patience job too.
2) For this you need red and yellow colour chandrakantha plants.
3) Select 5 or 6 red flowers on a plant.
4) Remove all the other flowers of that plant.
5) Take each flower, remove stamens carefully.
6) Take yellow flower and rub with that flower gently on the stigma of selected red flower for pollination. Do this process in the evening only.
7) Tie a tag with a thread loosely to the pollinated flower to avoid confusion in iden¬tifying these flowers for seeds in the next few days.
8) Within a week days you will get black seeds.
9) Keep them another two weeks to dry and sow them in a pot.
10) Take care to grow the plants until they flower.
Observations:
1) The colour of the flowers will be orange.