Students get through AP Inter 1st Year Zoology Important Questions 8th Lesson Ecology and Environment which are most likely to be asked in the exam.
AP Inter 1st Year Zoology Important Questions 8th Lesson Ecology and Environment
Very Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
Define the term ecology and its branches.
Answer:
- Ecology is defined as “the study of the relationship of organisms with their environment”.
- It has two main branches:
- Autecology- Ecology of one species or population in relation to its environment.
- Synecology- It is the study of the structure, development and distribution ecological communities.
Question 2.
What is an Autecology?
Answer:
- Autecology: It is the study of a ‘single species (population)’ in relation to their environment.
- It is also known as ‘species ecology’.

Question 3.
What do you call the study of interactions of organisms of a community?
Answer:
- The study of interactions of organisms of a community is known as synecology.
- It deals with the structure, development and distribution of ecological communities living in a specified area.
Question 4.
What is an ecological population?
Answer:
- Ecological population is the population of a group of organisms of same species living in a specific area at a specific time.
- Ex: Species of catla catla living in a pond at a given time is catla population.
Question 5.
Define a community?
Answer:
- Community is an association of interacting populations of different species in a particular area.
In a community there will be a dominant population and the community is named after it.
- Ex: Himalayan region is called pine-Deodar community.
Question 6.
What is an ecosystem?
Answer:
- Ecosystem is a functional unit of biosphere in which the members of community interact among themselves and also with the surrounding environment, in relation to ‘flow of energy’.
- Ex: Lake, Pond .
Question 7.
Distinguish between ecosystem and biome.
Answer:
- Ecosystem is a functional unit of biological community. It is generally small.
Ex: Aquarium, Pond etc.
- Biome is a large community of plants and animals. It occupies a vast region.
Ex: Desert, rain forest, tundra
Question 8.
What is biome? Name any two biomes you studied.
Answer:
- Biome is a large community of plants and animals. It occupies a vast region.
- Ex 1: Desert, rain forest, tundra
Ex 2: Aquatic biomes which include fresh water biomes and marine biomes.
Question 9.
What is meant by ecosphere?
Answer:
- Ecosphere (or biosphere) includes all the habitable zones of earth. It is the part of earth that supports life.
- It extends upto several kilometers into air and several meters below the earth surface and deep into bottom of the oceans.

Question 10.
Define the term habitat?
Answer:
- Habitat: It is the place in which an organism lives.
- It is just like the address of a person.
- Ex : The habitat of Lion is forest; Habitat of fish is a pond (or) lake (or) Sea.
Question 11.
Explain the difference between the ‘niche’ of an organism and its ‘habitat’.
Answer:
| Niche |
Habitat |
| 1) Niche is the functional role of the organism in the ecosystem.
2) It is just like occupation of a person.
3) Ex: Rose bush is a producer. |
1) Habitat is a place where an organism lives in the ecosystem
2) It is just like address of a person.
3) Ex: Habitat of a fish in a pond or lake. |
Question 12.
A population has more genetically similar organisms than those on biotic community. Justify the statement.
Answer:
- Population is a group of similar organisms belonging to the same species with a similar karyotype (genetic unit). So, in a population there are more genetically similar organisms.
- A community is an association of populations of two or more species with different karyotypes in a particular area. So, in a community there are less genetically similar organisms.
Question 13.
Among the red, green and brown algae that inhabit the sea, which is likely to be found in the deepest waters? why?
Answer:
- Red algae is found in the deepest water.
- Red light has longest wavelength which can penetrate to the deepest waters.
- The pigment called phycoerythrin in red algae absorbs blue colour and reflects red colour.
Question 14.
What is the source of energy for deep sea inhabitants?
Answer:
- The source of energy and food for deep sea inhabitants are the ‘other organisms’.
- Reason: In deep sea regions, producers are absent and only consumers are present.
Question 15.
How do the fish living in Antarctic waters manage to keep their body fluids from freezing?
Answer:
- Fish living in Antarctic water manage their body fluids from freezing
- By staying in deeper zones, where temperature is above freezing point i.e., above 4°C They reduce their oxygen consumption by reducing metabolic rate.
- They produce an antifreezing protein called antifreeze glyco-protein (AFGP). It prevents the growth of ice crystals in their body fluids which prevents their body fluids from freezing.
Question 16.
How docs your body solve the problem of altitude sickness, when you ascend fall mountains?
Answer:
- At high altitudes like tall mountains, the partial pressure of oxygen is low due to the low atmospheric pressure.
- The body compensates the low oxygen availability by increasing the RBC count and increasing the rate of breathing.
Question 17.
Name the structural components of an ecosystem.
Answer:
Structural components of ecosystem: (a) abiotic factors (b) biotic factors.
- Abiotic factors: Light, temperature, water, pressure, O2 etc.
- Biotic factors: Producers, Consumers and decomposers.

Question 18.
What is the effect of light on body pigmentation?
Answer:
- Light influences the colour of the skin. Animals living in low intensity light are pale in colour and animals living in high intensity of light are dark coloured.
- Proteus anguinus is pale coloured when in caves. When it is brought into sunlight, skin colour becomes dark over a period of time.
Question 19.
Distinguish the terms phototaxis and photokinesis. [TS M-19]
Answer:
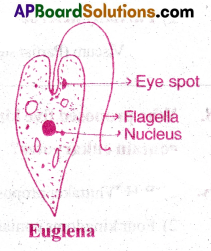
- Phototaxis is the influence of light on directional movement of organism either towards or away from light. Ex: Euglena exhibits positive phototaxis. It moves towards light.
Cockroach exhibits negative phototaxis. It moves away from light.
- Photokinesis is the influence of intensity light on non-directional movement of organism. Ex: Larvae of Pinnotheres maculatus (mussel crab) moves fast with increasing intensity of light in its own direction.
Question 20.
What is the primardial source of energy for all organisms?
Answer:
- ‘Sun light’ is the primardial source of energy for all organisms.
- It is also transferred from one trophic level to another trophic level.
Question 21.
What are biological rhythms?
Answer:
- Biological Rhythms: The behavioural activities which repeat at regular intervals in the bodies of organisms are called Biological rhythms.
- Ex: Circadian rhythms – Like sleep wake cycle which occurs in the interval of 24 hours.
Question 22.
What arc circadian rhythms? |TS M-15,22|
Answer:
- The biological rhythms that occur in a time period of 24 hours are called Circadian rhythms.
- Biological rhythms are behavior activities that are repeated at regular intervals.
Question 23.
What is Photoperiod ism?
Answer:
- Response shown by the organisms for the photoperiod is called Photoperiodism.
- Ex: Migration of birds. During winter, Siberian birds migrate southward to get more sunlight because the day time is short in Siberia for breeding and feeding.
Question 24.
Distinguish between photoperiod and critical photoperiod.
Answer:
- Photoperiod is the duration of light hours in a day.
- Critical Photoperiod is the specific day length that is essential for initiation of seasonal events.
Question 25.
Explain bioiuminescence.
Answer:
- Production of light by certain living organisms is called bioiuminescence.
- It is devoide of infrared rays. So it is called cold-light.
- It is for intra – specific communication like sexual attraction, sending protective warning signals.
- Ex : Firefly, Jelly fishes, Chaetopterus, squids, pyrosoma etc.,
Question 26.
Mention the advantages of some UV rays to us. [TS M-16,20] [IPE-14]
Answer:
- UV rays kill micro organisms on the body surface of animals.
- UV rays convert the sterols in the skin to vitamin D.

Question 27.
Distinguish between the terms heat and temperature.
Answer:
| Heat |
Temperature |
1) Heat is a form of energy
2) Heat flows from hotter object to cooler object.
3) Heat is measured by calorimeter. |
1) Temperature is a measure of the intensity of heat energy.
2) Temperature rises when heated and falls when cooled.
3) Temperature is measured by thermometer. |
Question 28.
Distinguish between minimum effective temperature and maximum effective temperature.
Answer:
| Minimum effective Temperature |
Maximum effective Temperature |
1) It is the ‘lowest temperature’ at which an organisms can live indefinitely.
2) Below this temperature the organism enters into ‘chill coma’. |
1) It is the ‘maximum temperature’ at which a species can live indefinitely in an active state.
2) Above this temperature the organism enters into ‘heat coma’. |
Question 29.
What is optimum temperature?
Answer:
- Optimum temperature: The temperature at which the metabolic activities occur at the ‘greatest level’ is called the optimum temperature.
- The optimum temperature of human body is 98.4F (or) 37°C.
Question 30.
What is cyciomorphosis? Explain its importance in Daphnia. [APM-19,22] [TS May-17]
Answer:
- Cyciomorphosis: The cyclic seasonal morphological changes of organisms is called cyciomorphosis. Ex: Daphnia (water flea).
- Importance: In Daphnia, it is an adaptation for the changing densities of water.
- In winter its head is round. In spring season, a hood starts developing.
- In summer, a prominent hood is formed. In autumn the hood starts receding.
- By the winter, the head becomes round again.These changes are helpful for the Daphnia to keep floating easily.
Question 31.
What are ’regulators’?
Answer:
- Regulators are the animals which maintain constant body temperature and osmotic concentration.
- Thus they maintain homostasis by physiological or behavioral means. Ex: Birds and mammals.
Question 32.
What are ‘conformers’?
Answer:
- Conformers are the animals whose body temperature changes according to the surrounding temperature. Ex: Invertebrates and lower vertebrates.
- In aquatic conformers, their osmotic concentration changes along with surround water.
Question 33.
Define commensalism. Give one example. [AP May-17]
Answer:
- Commensalism is a type of interaction between different species in which one is benefited and the other is neither benefited nor harmed.
- Ex: Barnacles growing on the back of a whale benefit, while the whale derives no noticeable benefit.
Question 34.
Define mutualism. Give one example. [AP M-15][TS M-17]
Answer:
- Mutualism is a type of interaction between different species in which both are benefited.
- Ex: Bees and flowering plant. Bees get nector, pollen and plants get pollinated
Question 35.
Define parasitism. Give one example.
Answer:
- Parasitism: It is the interaction between two organisms of different species, in which one gets benefited and the other gets harmed.
- Ex : Plasmodium vivax (Malarial parasite) in the body of a man.
Question 36.
Define amensalism. Give one example.
Answer:
- Amensalism: It is a type of interaction between different species in which one is harmed and the other is not affected. Ex: Ibex and weevils on the plant.
- Ibex feeds on the leaves of the plant. Weevils are attached to the leaves. So the weevils are also taken along with leaves. The weevils are harmed but Ibex is not affected.
Question 37.
What is predation? Give an example.
Answer:
- Predation is a feeding strategy, between two different species in which predator gets benefited at the cost of the prey.
- Ex : Lion (Predator) & Deer( Prey).
Question 38.
What is meant by interspecific competition? Give one example.
Answer:
- Inter specific competition is the competition between different species for the same resource.
Ex: Flamingoes and fishes. Both of them compete for the same food that is zoo plankton.
- When one species is efficient in collecting food then the other species gets eliminated.

Question 39.
Distinguish between predation and parasitism.
Answer:
| Predation |
Parasitism |
1) It is a feeding strategy, between two different species in which predator gets benefited at the cost of the prey.
2) Usually predator is large in size and low in number.
3) Ex : Lion(Predator) & Deer (Prey). |
1) It is the interaction between two organisms of different species, in which one gets benefited and the other gets harmed.
2) Usually Parasite is small in size and high in number.
3) Ex: Plasmodium vivax (Malarial parasite) in the body of a man. |
Question 40.
Distinguish between the interactions commensalism and amensalism.
Answer:
| Commensalism |
Amensalism |
1) It is an association in which commensal gets benefit and the host is neither benefit nor harmed.
2) Ex:Bamacles growing on the back of a whale. |
1) It is an association in which ammensal gets harmed and the host is neither benefit nor harmed.
2) Ex: Ibex and weevils on a plant. |
Question 41.
In an ecological food chain, what types of interactions exist between trophic levels?
Answer:
Types of interactions that exist between various trophic levels are mutualism, commensalism, parasitism, amensalism and predation.
Question 42.
What is camouflage? Give its significance. [AP M-19]
Answer:
- Camouflage is the phenomenon exhibited by some animals and insects which change colours according to the surrounding. Some are naturally coloured which suit their surroundings.
Ex: Chameleon, leaf insect, stick insect.
- Significance: Then animals exhibiting camouflage can hide from their predators.
Question 43.
What is Gause’s principle? When does it applicable?
Answer:
- Gause’s principle: Two closely related species competing for the same resources cannot co-exist indefinitely and the competitively inferior one will be eliminated in due course of time.
- It is applicable only when the resources are limited.
Question 44.
Name the association that exists in micqrrhiza.
Answer:
- The association that exists in micorrhizae is ‘mutualism’ in which both the organisms mutually benefitted.
- Ex: Fungi and Plants. Fungi help in absorption of essential nutrients from soil. Plants provide the fungi with energy-yielding carbohydrates.
Question 45.
What are lichens?
Answer:
- Lichen: A lichen is not a single organism.
- It is a symbiosis between a fungus and an alga with an intimate mutualistic relation.
- Ex: Parmita, usnea.
Question 46.
Name the major types of ecosystem?
Answer:
Major types of Ecosystem:
- Ecosystems are of two types (i) natural (ii) artificial.
- Natural ecosystems : (i) Aquatic (ii) Terrestrial
- Artificial ecosystems : (i) Agricultural ecosystem (ii) Aquaculture ponds.
Question 47.
Distinguish between natural ecosystem and an artificial ecosystem.
Answer:
| Natural ecosystem |
Artificial ecosystem |
| 1) It is naturally occurring ecosystem, with no role of humans in its formation. |
1) It is a man made ecosystem |
| 2) Ex : Deserts, forests, lakes. |
2) Ex : Aqua ponds, Aquariums etc |
Question 48.
What is an estuary?
Answer:
- Estuary: It is the zone where river water joins the sea water.
- Sea water ascends up into the river, twice a day.
- Estuarine waters show fluctuations in salinities depending upon the seasons.
- During rainy season water is less saline and in summer water is more saline.

Question 49.
How does an estuarine ecosystem differ from fresh water ecosystem?
Answer:
| Estuarine Ecosystem |
Fresh water ecosystem |
1) It is the zone where river water joins the sea water.lt shows fluctuations in salinity depending on the seasons.
2) Estuarine organisms are capable of withstanding the fluctuations in salinity. |
1) It is the smallest aquatic ecosystem which show’s less salinity.
2) Fresh water organisms are not capable of withstanding the fluctuations in salinity. |
Question 50.
Distinguish between lotic and lentic habitats. [AP-18]
Answer:
- Lentic ecosystems: The still water bodies like ponds, lakes and reservoirs are the lentic eco systems.
- Lotic ecosystems: The flowing waterbodies like streams and rivers are the lotic eco systems.
Question 51.
What is limnology?
Answer:
- Limnology: It is the study of fresh water ecosystem.
- Ex: Lake ecosystem, river ecosystem.
Question 52.
What is Euphotic zone?
Answer:
- Euphotic zone: The water zone in a lake, in which good light penetration happens is called Euphotic zone.
- It is the shallow part of the lake, closer to the lake.
- It is an oxygen rich and vegetarian rich zone with higher rate of photosynthesis.
Question 53.
What is zone of compensation in an aquatic ecosystem?
Answer:
- Zone of compensation: The imaginary line that separates the limnetic zone from profundal zone is called zone of compensation. It is the zone of effective light penetration.
- In the zone of compensation, rate of photosynthesis equals to rate of respiration.
Question 54.
Distinguish between phytoplankton and zooplankton.
Answer:
- Floating micro organisms with chlorophyll are called phytoplankton.
Ex: Diatoms, green algae, Euglenoids and dinoflagellates.
- Floating micro organisms without chlorophyll are called zooplankton.
Ex: Water flees, rotifers and ostracoids.
Question 55.
Distinguish between neuston and nekton.
Answer:
- Neustons are animals living at the ‘air-water interface’.
Ex 1: Water striders, beetles and water bugs (they live above water surface)-epineuston
Ex 2: Mosquito larvae (they live below the water surface)- hyponeuston
- Nektons are animals capable of swimming. Ex: Fishes, amphibians, water snakes.
Question 56.
What is periphyton?
Answer:
- The animals that live on or attached to aquatic plants are called periphyton.
- Ex: Bryozoans, turbellarians, hydras, nymphs of insects.
Question 57.
What is benthos?
Answer:
- Benthos: It refers to all the ‘attached, creeping (or) burrowing organisms’ that inhabit the bottom of rivers, lakes and sea.
- Ex: Red annelids, Cray fishes, amphipods etc.
Question 58.
Write three examples for man-made ecosystems.
Answer:
Man-made artificial ecosystems are
- Cropland ecosystem
- Aquaculture ponds
- Aquaria

Question 59.
What is meant by osmotrophic nutrition? [AP M-17]
Answer:
- Osmotrophic Nutrition is the mode of nutrition in which organisms take pre-digested food through their body wall from the surrounding medium.
- Ex: Fungi secrete enzymes and breakdown dead and waste materials and absorb the digested material.
Question 60.
Explain the process of’leaching’.
Answer:
Leaching is the process in which water soluble inorganic nutrients go down into the soil and get precipitated as unavailable salts.
Question 61.
What is catabolism?
Answer:
Catabolism: It is a process in which ‘bacterial and fungal enzymes’ degrade ‘detrites into simpler inorganic substances’.
Question 62.
What is humification? Name the organisms which act on it.
Answer:
- Humification is the development of humas from dead and decaying organic matter.
- Microbes act on humas.
Question 63.
What is PAR?
Answer:
- PAR is Photosynthetically Active Radiation. Plants capture only 2-10% of PAR.
- PAR is less than 50% of incident solar radiation available on earth.
Question 64.
What is the percentage of PAR, in the incident solar radiation.
Answer:
PAR is less than 50% of incident solar radiation available on earth.
Question 65.
Define entropy?
Answer:
- Entropy is the degraded unavailable heat energy for work.
- According to second law of thermodynamics, ‘energy loss’ is inevitable in any energy changing process. Thus some amount of energy is converted into unused heat energy.
Question 66.
What is standing crop?
Answer:
- Standing crop is the mass of living material at a particular time at each trophic level.
- It is measured as the number of organisms per unit area.
Question 67.
If you were to count the number of insects feeding on a big tree, and asked to graphically represent the relation of structure and function between the tree and insects. What kind of pyramid does it form?
Answer:
- It forms ‘inverted pyramid of numbers’.
- It’s pyramid of energy is upright.
Question 68.
Explain the terms GPP, NPP.
Answer:
- GPP is Gross Primary Productivity. It is rate of productivity organic matter during photosynthesis.
- NPP is Net Primary Productivity. It is gross primary productivity minus respiratory loss(R). Thus, N.P.P = G.P.P – R .
Question 69.
Distinguish between GFC and DFC.
Answer:
| Grazing food chain(GFC) |
Detrites food chain(BFC) |
| 1) It begins with green plants. |
1) It begins with dead organic matter |
| 2) It is madeup of herbivores,carnivores. |
2) It is made up of decomposers. (Fungi & bacteria) |
| 3) Ex:Grass → Grasshopper → Frog → Snake → Hawk |
3) Ex:Dead animals → Flies and maggots → frogs → snakes |
Question 70.
Name the trophic level (s) at which ’decomposers’ feed.
Answer:
- Decomposers feed at the first trophic level.
- Decomposers are the heterotrophic organisms, which live on dead & decaying matters.

Question 71.
Distinguish between production and decomposition.
Answer:
| Production |
Decomposition |
1) The process of fixation of energy from food by producers is called production.
2) Example of producers: Green plants. |
1) The process of Break down of ‘complex organic matter’ into ’simple inorganic substances’ is known as ‘Decomposition.’
2) Example of Decomposers: Microbes. |
Question 72.
Distinguish between upright and inverted ecological pyramids.
Answer:
| Upright pyramid |
Inverted pyramid |
1) The ecological pyramid in which the number, biomass, energy decrease from lower to higher trophic levels is called upright pyramid.
2) Ex: Pyramid of energy. |
1) The ecological pyramid in which the number, biomass, energy increase from lower to’ higher trophic levels is called inverted pyramid.
2)Ex: Pyramid of numbers in parasitic food chain. |
Question 73.
Distinguish between food chain and food web?
Answer:
| Food chain |
Food web |
1) A food chain follows only one straight path for the flow of energy. j
2) If one group gets disturbed then the whole chain will be disturbed.
3) Ex:Grass → Grasshopper → Frog → Snake → Hawk |
1) A food web consists of many food chains
2) Food web doesnot get disturbed by the removal of one group of organisms.
3) Ex: Man, Bear, Crow |
Question 74.
Distinguish between litter and detritus.
Answer:
| Litter |
Detritus |
| Litter is simply the scattered fallen leaves and broken twigs. |
Detritus is humus formed of dead animals, leaves and animal excreta. . |
Question 75.
Distinguish between primary and secondary productivity.
Answer:
| Primary productivity |
Secondary productivity |
| Primary productivity is defined as the amount of biomass or organic matter produced per unit area over a period of time by plants during photosynthesis. |
Secondary productivity is defined as the rate of formation of new organic matter by consumers by utilizing primary productivity of the producers. |
Question 76.
What is the effect of carbon monoxide pollution on human beings?
Answer:
- Effects of CO on human beings are headache and blurred vision at lower concentrations and in higher concentrations it leads to coma and death.
- Haemoglobin has greater affinity for CO and carbon monoxide competitively interferes with oxygen transport.
Question 77.
What is Green House effect?
Answer:
- Green House effect is the naturally phenomenon that warms the earth’s surface and atmosphere.
- It is called green house effect because the exchange of incoming and outgoing radiations that warms the planet is very similar way to a green house.
- Green house gases: Carbondioxide and methane.
Question 78.
Which air pollutants are chiefly responsible for acid rains? [AP M-16]
Answer:
- Sulphur dioxide and nitrogen oxides are the major air pollutants of acid rains.
- Acid rains cause acidification of lakes, streams.
- It accelerates corrosion of buildings and monuments.
Question 79.
What is BOD?
Answer:
- BOD is Biological Oxygen Demand. It is an index for measuring pollution load in sewage.
- BOD indicates the amount of dissolved oxygen needed by aerobic biological organisms in water body to breakdown organic material present in a given water sample at certain temperature over a specific time period.
Question 80.
What is biological magnification? [APM-20]
Answer:
- Gradual increase in the concentration of pollutants at successive trophic levels in an aquatic food chain is called Bio-magnification.
- Ex: DDT concentration in a sample water is 0.003 ppb through biomagnification it reaches to 5 ppm in fish eating birds.

Question 81.
Distinguish between ‘Global warming’ and ‘Thermal pollution’ ?
Answer:
| Global warming |
Thermal pollution |
1) Increase in the level of green house gases has led to considerable heating of the earth leading to ‘Global w’arming’
2) It causes climatic changes. |
1) Thermal pollution is caused by the release of hot water from industries and Thermal power plants.
2) It is harmful to aquatic organisms. |
Question 82.
Why are incinerators used in hospitals?
Answer:
Hospitals generate hazardous wastes like disinfectants, chemicals, pathogenic microorganisms. Before they are disposed they must be treated, otherwise they cause heavy pollution in the surroundings. Incinerators are used in hospitals for disposal of hospital waste.
Question 83.
Why are catalytic converters used in automobiles?
Answer:
- Catalytic converters are used to reduce emission of poisonous gases..
- Catalytic converters have expensive metals like platinum, palladium and rhodium.
Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
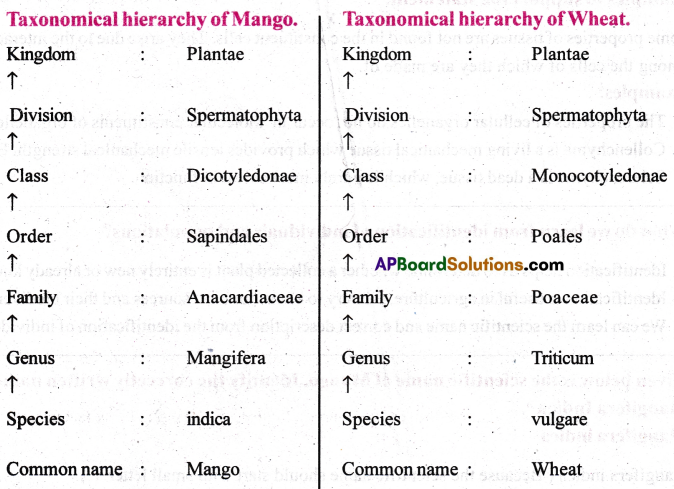
Write about ecological hierarchy.
Answer:
- ‘Hierarchy’means arrangement of things in a’graded series’.
- Ecological hierarchy includes eleven integrative levels, starting from cell to ecosphere. They are (i) cell (ii) tissue (iii) organ, (iv) organ – system, (v) organism, (vi) population, (vii) community, (viii) ecosystem, (ix) landscape, (x) biome and (xi) ecosphere (Biosphere).
- Population: It is a group of organisms of the same species living in a specific area at a special time regulated by a set of factors such as natality, mortality and population density.
- Community: It is an association of the living biotic component of an ecosystem.
- Ecosystem: It is a ‘functional unit of the Biosphere’.
- Landscape:It is the unit of land containing different ecosystems surrounded by natural bound aries.
- Biome: It is a large community of plants and animals that occupies a vast region.
- Ecosphere (Biosphere): All the habitual zones of the earth are called ecosphere. It is the part of the Earth that supports life.
Question 2.
Write a note on habitat and Medium.
Answer:
- Habitat: It is the place in which an organism lives.
It is just like the address of a person.
Ex: The habitat of Lion is forest; Habitat of fish is a pond (or) lake (or) Sea.
- Medium The surroundings of the organism’s body is called medium.
Ex: The medium of fish is water. The medium of lion is air.
Question 3.
Considering the benefits of a constant internal environment to the organism, we tend to ask ourselves why the conformers had not evolved to become regulators?
Answer:
- Only two main groups namely birds and mammals have become regulators. All the other groups remained conformers.
- Originally the animals were completely aquatic. There was no need except osmoregulation, for temperature regulation.
- Temperature regulation has become necessary only in land forms. Amphibians remained partially aquatic.
- Reptiles are distributed in temperate and tropical climatis only. They escape or hide, to tide over extreme temperatures.
- Further thermo regulation is an expensive process especially in small animals.
- Small animals have relatively more surface area and lose body heat very fast.
- They have to spend more energy to maintain constant temperatures.
- If the stressful conditions are localized or only for short duration, the animals either migrate or suspend life activities.
Question 4.
The individuals have fallen through the ice and been submerged under cold water for long periods can sometimes be revived- explain.
Answer:
- When the individuals have fallen through ice they enter into a condition called chill coma and remain in coma while they are in chill water.
- When temperature is gradually raised from minimum effective temperature to optimum temperature the individual regain metabolic activities and survive in some cases.
- The suspension of life activities generally takes place in lower aquatic form but not in air breathing forms.
Question 5.
What is summer stratification? Explain. [AP,TS M-20][TS May-17]
Answer:
Summer Stratification: During summer, in temporate lakes, the formation of three layers of water is called Summer stratification.
During summer the temperature of lakes rises upto 25°C. Hence, periodic circulation of water takes place. Then three types of layers are formed. 1.Epilimnion 2. Thermocline 3. Hypolimnion
- Epilimnion: The upper, warm, oxygen rich layer of water having a temperature range of 21°C-25°C is called epilimnion.
- Thermocline: The below layer of epilimnion is called thermocline or metalimnion.
Here, the temperature decreases at the rate of 1°C per meter.
- Hypolimnion:The bottom layer where the temperature is about 7°C is called Hypolimnion.

In this layer, the water is stagnant, relatively cool, nutrient rich, low oxygen content due to absence of Photosynthetic activity.
Summer stratification is followed by autumn overturn:
- During Autumn the temperature of surface water falls to 4°C.
- The water becomes heavy when the temperature is at 4°C. It sinks to the bottom. The bottom water comes to the surface with many nutrients. This circulation is called autumn (fall) over turn.
- Due to autumn overturn uniform temperature and uniform distribution of nutrients and oxygen
in the lakes take place.
Question 6.
What is the significance of stratification in lakes?
Answer:
Significance of Stratification:
- In temperate regions there will be seasonal variations of temperature. These temperature variations cause thermal layers in water. This phenomenon is called thermal stratification.
- Water has maximum density at 4°C. During summer the temperature of surface water increases upto 25°C.
- The upper layer is epilimnion. The middle layer is metalimnion. The bottom layer is hypolimnion.
- During autumn the surface water temperature falls to 4°C. The water becomes heavy and goes down. The bottom water with nutrients comes to surface. This circulation of water is autumn or fall overturn.
- During winter the temperature of surface water falls below 4°C and ice is formed. Below the ice there is water. The animals that live in such water, reduce their oxygen consumption and metabolic activity and survive in winter.
- At the onset of spring the ice becomes water and sinks down bringing nutrient rich water to surface. It is called spring overturn.
- The stratifications and overturns help survival of organisms at all levels as they help in redistribution of oxygen and nutrients.
Question 7.
Explain Van’t Hoff rule. [APM-19]
Answer:
- According to Van’t Hoffs rule, with the increase in every 10°C, the rate of metabolic activities of the animal doubles.
- If stated in reverse, for every decrease of 10°C of temperature the rate of metabolic reactions is halved.
- The temperature effect on the rate of reaction is expressed interms of temperature coefficient Q10
- Q10 is the ratio between the rate of reaction at X°C and rate of reaction at (X-10°C).
- In living organisms, the value of Q10 is about 2.0. That means, the rate of metabolism doubles for every 10°C increasing temperature.
Question 8.
Unlike mammals the reptiles cannot tolerate environmental fluctuations in temperature. How do they adapt to survive in desert conditions?
Answer:
- Reptiles are cold blooded animals. Ex: Crocodiles, Lizards.
- Their body temperature changes in tune with surrounding temperature to certain extent.
- When the temperature is low they bask (staying in the warmth of the sun light).
- When the temperature is high they go to shades or underground burrows.
- The desert lizards bask in the sun when the temperature is low.
- They escape to shades and burrow when the temperature is beyond their optimum temperature.
Question 9.
Write a short note on soil as an ecological abiotic factor?
Answer:
- Abiotic factor is a condition or thing that determines which species of organisms survive in a given environment
- Soil is a major ecological abiotic factor.
- The study of soil is called soil science (or) Pedology.
- Soil is a complex physical biological system providing support, water, nutrient and oxygen for the plants.
- Soil is formed from rocks. So rocks are the parent materials of soil.
- The process of formation of soil from rock is called pedogenesis.
- Soil is abridge between inorganic and organic material
- Soil composition, grain size and aggregation determine the percolation and water holding capacity of soil.
- PH, mineral composition etc determine the vegetation in any area.
Question 10.
How do terrestrial animals protect themselves from the danger of dehydration of bodies? [TS M-22]
Answer:
- Water is very important ingredient of the body.
- So, any reduction in the amount of water leads to dehydration of the body and the animal dies.
- Animals have evolved several adaptations to conserve water.
- Certain desert animals are active during night only to prevent dehydration.
- Reptiles have dry scaly skin which prevents escape of w’ater.
- Birds have dry skin which prevents escape of water.
- Insects (arthropods) have cuticle to prevent escape of water.
- All these groups of animals release dry uric acid as their excretory product.
Question 11.
How do marine animats adapt to hypertonic seawater?
Answer:
- Sea water is high in salt content compared to that of body fluids.
- So the marine animals continuously lose water through their body surface by exosmosis.
- To overcome this problem, marine fishes have
- Aglomerular kidneys with less number of nephrons to minimise water loss through urine.
- The fish drinks water to compensate loss of water. But the salt content is increased due to this.
- To remove the excess salts, salt secreting cells are present in gills.
- In many sea animals, salts enter the body along with the food.
- To remove the salts, sea gulls and penguins have salt secreting cells in nose and release drops of salts.
- Turtles and crocodiles have salt glands near eyes which release salt drops.
- Cartilaginous fishes retain urea and trimethylamine oxide (TMO) in their blood to keep the body fluid isotonic to the sea water.
Question 12.
Discuss the various types of adaptations in fresh water animals.
Answer:
The osmotic pressure of fresh water is very low than that of body fluids of fresh water animals. So water tends to enter the bodies by endosmosis. Fresh water organisms have evolved several adaptations to encounter endosmosis.
Adaptations of Fresh water animals:
- In fresh water protozoans, contractile vacuoles remove the excess water from their body.
- In fresh water fishes, well developed glomerular kidneys remove excess water from the body through urine.
- In summer, most of the ponds dry up. To overcome this protozoans developed encystment .
- Fresh water sponges produce gemmules, to survive in summer.
- African lung fish undergoes aestivation by forming a gelatinous cocoon, to survive in summer.

Question 13.
Compare the adaptations of animals with freshwater and seawater mode of life.
Answer:
Adaptations of Fresh water animals: [TS M-I6]
- Fresh water organisms undergo endosmosis.
- Fresh water fishes developed glomerular kidneys to remove excess water from the body through urine.
- Fresh water sponges produce gemmules, to survive in summer.
- African lung fish undergoes aestivation by forming a gelatinous cocoon, to survive in summer.
Adaptations of Sea water animals:
- Sea water is high in salt content compared to the body fluids. So, marine animals continuously lose water from their bodies by exosmosis.
- Marine forms developed Aglomerular kidneys, with less number of nephrons, salt secreting chloride Cells in gills.
- Marine birds and penguins eliminate salt drops through nostrils.
- Sharks retain urea and limethylamine oxide in fishes to maintain salt balance in body fluids.
Question 14.
Distinguish between euryhaline and stenohaline animals. [TS M-22]
Answer:
Euryhaline animals are adapted to withstand wide fluctuations of salinity.
Ex: Brackish water fishes (Salmon, Hilsa) withstand with fresh water during low tide and saline water during high tide. Migrating fishes migrate from sea to fresh water (anadromous migration) for breeding.
2) Stenohaline animals are unable to tolerate fluctuations in salinity.
Ex: Marine fishes die when placed in fresh water and fresh water fishes die when placed in sea water.
Question 15.
How do the non – migratory animals over come the unfavorable climatic conditions?
Answer:
- Non-migratory animals overcome the unfavourable climatic conditions by escaping in time.
- For example polar bears go into hibernation during winter.
- Some snails and fish go into aestivation to avoid summer-related problems heat and desiccation.
- Freshwater protists undergo encystment.
Question 16.
Many tribes living in high altitude of Himalayas normally have higher red blood cell count (or) total haemoglobin than the people living in the plains. Explain?
Answer:
- When people visit high altitudes such as Rohtang pass near Manali or Manasarovar in Tibet they are subjected to altitude sickness.
- The symptoms are nausea, fatigue and heart palpitations. This is due to less oxygen in atmosphere and low pressure.
- But there are several tribal people who have been living there for thousands of years. They are acclimatized and do not experience altitude sickness.
- Their body compensates low oxygen availability by increasing red blood cell production and increasing the rate of breathing.
Question 17.
An orchid plant is growing on the branch of mango tree. How do you describe this interaction between the orchid and mango tree?
Answer:
- The inter specific relationship between and Mango and Archid is commensalism.
- Archid is an epiphyte by growing on high branches of mango plants it gets sunlight.
- The mango plant is neither benefited nor harmed.
- Archid is a commensal on the mango host.
Question 18.
Do you believe that an ideal parasite should be able to thrive within the host without harming it. Then why did n’t natural selection lead to the evolution of such totally harmless parasites?
Answer:
- Yes. It may be possible that an ideal parasite should be able to thrive with in the host without harming it.
- The success of an ideal parasite may not simply depend upon adaptiveness of the parasite in host.
- The adaptiveness of the host is relatively to that ideal parasite may be not allowing that ideal parasite to continuous generations.
- The changing adaptiveness of hosts is different generations may be an obstacle for the adaptiveness parasite.

Question 19.
The female mosquitp is not considered completely a parasite although it needs our blood for reproduction. Can you explain why?
Answer:
- Female mosquitoes use two different food sources.
- They need sugar for energy, which is taken from sources such as nectar.
- They need blood as a source of protein for egg development
- Once blood is in the stomach, the midgut of the female synthesizes proteolytic enzymes that hydrolyze the blood proteins into free amino acids.
- These are used as building blocks for the synthesis of egg yolk proteins.
Question 20.
Predation is not an association. Support the statement.
Answer:
- In association, a group of organisms live together in a geographical region and constitute a community with a few dominant species.
- Predation is not an association. It is a just feeding strategy.
- It is an interaction between two different species.
- The predator gets benefit at the cost of the prey and the interaction is detrimental to the other species.
- It is a nature’s way of transferring the energy fixed by plants to higher trophic lends.
- By predation we recollect that lion eats deer. But a sparrow eating seeds also a type of predation.
Question 22.
Predation has a significant role in maintaining of species diversity discuss.
Answer:
1) Predators maintain species diversity in a community. It is done by reducing the intensity of competition among competing prey species.
Ex: In the American pacific coast there are intertidal communities.
2) The starfish pisaster is an important predator. In a field experiment the star fish is removed from the intertidal area. After a specific time (one year) it was found that more then 10 species of prey became extinct.
3) In the absence of predator there was severe inter specific competition and more than 10 species could not survive the competition and became extinct.
4) If the predator was present it would have predate on all the types of prey equally, reducing their number. Then all the prey species would have survived.
Question 23.
What is the biological principle behind the biological control method of managing pest insects?
Answer:
Biological control methods adopted in agricultural pest control are based on the ‘ability of the predators’ to regulate prey population.
There are 3 basic types;
- Importation
- Augmentation and
- Conservation.
1) Importation: Introduction pest’s natural enemies to a new area where they do not occur naturally. Ex: Icerya purchase a cottony scale of California was controlled by Rodolia cardinalis from Australia.
2) Augmentation: Supplemental releasing of natural enemy, boosting natural population.
Ex: Encarsia formosa are used to control green house whitefly.
3) Conservation: Conservation of existing natural enemies because they are already adapted to the habitat. They are provided shelters, nectar rich plants etc.
Question 24.
Name important defence mechanisms in plants against herbivory.
Answer:
- Herbivores are the predators of plants.
- Phytophagous condition is the feeding on plant sap and other parts of plants by all insects
- Plants have some morphological and chemical defences against herbivores.
- Some ‘cactus plants’ show thorns for morphological defence.
Ex: Acacia, Bougainvillea
- Many plants produce and store chemicals which make herbivores sick when eaten, inhibit feeding or digestion, disrupt its reproduction (or) even kill it.
- A weed calotropis produces highly poisonous cardiac glycosides. So cattle (or) goats never browns these plants.
- A wide variety of chemical substances like nicotine, caffeine, quinine extracted strychnine, opium etc., are from plants. They exhibit defence against grazing and browsing animals.

Question 25.
Discuss competitive releases.
Answer:
1) Competitive releases: Competition is present among species can be clearly shown by the phenomenon competitive release. When one of the competing species is removed from the area, the other species have grown in number because the factor that is preventing its growth is released.
2) A species which is occupying only small area when subjected competitive release, dramatically expands its territory. Ex: Balanus dominates the intertidal zone of Scotland.
When this Balanus is experimentally removed the smaller barnacle Chathamalus increased its population.
In general herbivores and plants appear to be more adversely affected by competition than carnivores.
Question 26.
Write a short note on the parasitic adaptations.
Answer:
In order to lead a successful parasite life, parasites evolved special adaptations.
- Loss of sense organs, which are not necessary when they are inside the host.
- Development of suckers and hooks to cling to host’s body parts. Ex: Tape worm, liver fluke.
- Loss of digestive system- Tapeworm.
- Enormous increase of reproductive system Ex: Tapeworm.
- Release of plenty of eggs so that at least few can reach the host. Ex: Round worm, Tapeworm,
- Complex life cycles involving more hosts.
Ex: Malarial parasite has two hosts, man and mosquito.
Question 27.
Explain brood parasitism with a suitable example.
Answer:
1) Brood parasitism: Certain birds like koel do not a build a nest. It lays its egg in the nest of crowr The koel’s egg hatches earlier than the crow’s eggs.
2) The koel hatchling pushes the crow’ eggs out of nest. Because its colour and cooing resembles that of crow hatchling the parent crows believe that its their offspring.
3) The crow parent feed the koel hatchling till it begins cooing like koel. So the hatchling of koel . is parasitic on crow and the phenomenon is called brood parasitism.
4) Similar example is found between cuckoo and sparrows of Europe. In this case the cuckoo hatchling over grows the size of sparrows. Both parents some times find it difficult it to feed cuckoo hatchling.
Question 28.
How do predators act as biological control?
Answer:
1) Predator as biological control: In prey and predator interactions the number of prey and predators show correlation. In early 1920 the pricklypear cactus was introduced in Australia. It spread rapidly into millions of hectares.
2) This cactus was brought under control after a ‘cactus feeding moth’ was introduced.
3) This type of biological control methods adapted in agriculture pest control are based on the ability of predator to control the prey.
Question 29.
Explain the interaction mechanism between fig trees and wasps.
Answer:
- The interaction mechanism between fig trees and wasp is a’Mutualism’.
- Many species of fig trees can be pollinated only by its ‘partner’ wasp, no other species.
- The female wasp uses the fruit not only as a site for egg laying site (oviposition) but also uses developing seeds for nourishing its larvae.
- In fig plants, pollination is occurred by the wasp while searching for suitable egg – laying sites, in return.
- Fig offers developing seeds as food for developing wasp larvae.
Question 30.
Write notes on the structure and functioning of an ecosystem.
Answer:
1) Structure and functioning of an Ecosystem: An ecosystem is a community of living organisms in relation with non living components interacting as a system. The biotic and abiotic components are linked together through nutrient cycles and energy flows. Energy and carbon enter ecosystem through photosynthesis.
2) The energy and carbon are incorporated into living tissue and they are released through respiration as CO2 most mineral nutrients are recycled with in ecosystem. Ecosystems are controlled by external factors like climate, underlying soil material and topography.
3) The internal factors are decomposition, competition and succession of types.

Question 31.
Explain the different types of aquatic ecosystems.
Answer:
Aquatic Ecosystems: Aquatic Ecosystems are classified based on salinity into three types Marine.
Estuarine and Freshwater ecosystems.
1) Marine Ecosystem: It is largest of all aquatic ecosystems. It is the most stable ecosystem.
2) Estuarine Ecosystem: Estuary is the zone where river meets the sea. The salinity depends on season and nature of tides. During the rainy season the estuary is less saline. In summer it is more saline. Estuarine organism can withstand these fluctuations in salinity.
3) Freshwater Ecosystem: It is the smallest ecosystem. It includes rivers, lakes, ponds etc. It is divided into lentic and lotic systems. Lentic systems are still water systems like lakes and ponds. Lotic systems are flowing water systems like rivers and streams. The study of freshwater ecosystems is called Limnology.
Question 32.
Explain the different types of terrestrial ecosystems.
Answer:
The land ecosystems are terrestrial ecosystems. They are forest, grass land and desert ecosystems.
1) Forest ecosystem: Two important types of forests are present in India, a) Tropical rain forest b) Tropical deciduous forest.
2) Grass land ecosystem: They are present in the himalayan region. In western Rajasthan they occupy large areas of sandy and saline soils.
3) Desert ecosystem: The areas having less than 25cm rainfall per year are called deserts. They have characteristic flora and fauna. There are two types of deserts namely hot type and cold type. Desert of Rajasthan is hot type desert. Desert near Ladakh is cold type.
Question 33.
Draw a diagram of the lake ecosystem and its physical (or) Ecological divisions.
Answer:

Question 34.
Write about the producers of the littoral zone with suitable examples.
Answer:
- Littoral zone is the shallow part of the lake, where light penetrates up to the bottom.
- It is ‘Euphotic’ – with good light, rich vegetation and higher rate of photosynthesis with rich O2.
Producers of Littoral Zone:
- Littoral zone is rich with pedonic flora. It is abundant with firmly fixed roots of emergent vegetation called amphibious plants
Ex: Cattails (Typha), bulrushes (Scirpus), arrowheads (Sagittaria)
- Water lilies (Nymphaea), Nelumbo, Trapa etc are slightly deeper rooted plants.
- Submerged plants such as Hydrilla, chara, potamogeton etc., are also present in littoral zone.
- Pistia, Wolffia, lemna (duck weed), Azolla, Eichhomia etc., are the free floating vegetation of these zone.
- Phytoplankton of littoral zone is diatoms (coscinodiscus, Nitzschia, etc.,), green algae (volvox, Spirogyra etc.,) euglenoids (Euglena, phacus etc.,) and dinoflagellates (Gymnodinium, cystodiniumetc.,)
Question 35.
Write a short note on the limnetic zone of a lake ecosystem.
Answer:
- Limnetic Zone: It is the open water zone away from the shore, which extends upto the effective light penetration level.
- Zone of compensation (or) compensation point (or) light compensation level is the imaginary line that separates the limnetic zone and profundal zone.
- There is no contact with bottom of the lake . Rate of photosynthesis and respiration are same
- It is the largest zone of a lake ecosystem.
- Rapid variations occur in the level of water, temperature, oxygen availability etc., from time to time.
- There is more availability of photosynthesis plants (autotrophs) euglenoids, diatoms, cyanobacteria, dinoflagellates and green algae are the chief phytoplankton of this region.
- Zooplanktonic organisms like copepods, fishes, frogs and water snakes etc are nekton of this zone.
Question 36.
Write a short note on the profundal zone of the lake ecosystem.
Answer:
- Profundal zone: It is the deep water zone below the limnetic zone.
- Light is absent. Photosynthesis does not take place. It is poor in oxygen.
- Organisms that live in this zone are decomposers, chironomid larvae, chaoborus (Phantom larva) red annelids, clams etc.,
- This zone releases nutrients to the biotic communities of both littoral and limnetic zone (recycling of minerals).
Question 37.
Give a brief account of a lake ecosystem?
Answer:
Lake Ecosystem: Lakes are large inland water bodies containing still water. They contain water throughout the year. The lake ecosystem performs all functions of ecosystems. They are photosynthesis, heterotrops feeding on autotrops, decomposition, mineralization and recycling of minerals and circulation of nutrients.
Deep water lakes contain three distinct zones. They are
I) Littoral zone II) Limnetic zone III) Profundal zone.
1) Littoral zone: It is the shallow part of the lake and is close to the shore. Light reaches upto its bottom. Hence it is Euphotic(good light zone). It has rich vegetation and high rate of photosynthesis. It is rich in oxygen.

II) Limnetic zone: It is the central largest and open zone away from shore and it does not touch the bottom. It extends vertically upto effective light penetration level. Zone of compensation separates the limnetic zone from the profundal zone. Here, the rate of photosynthesis is equal to the rate of respiration.
III) Profundal zone: It is the deep water zone below the limnetic zone. Light is absent. Photosynthesis does not take place. It is poor in oxygen.
Question 38.
How is a lake ecosystem described as a ’Micro – model’ for the Entire biosphere?
Answer:
- The lake ecosystem performs all the functions of any ecosystem and of the biosphere as whole that is conversion of inorganic substances into organic material.
- With the help of radiant solar energy by the autotrophs.
- Consumption of the autotrophs by the heterotrophs.
- Decomposition and mineralization of the dead matter to release them back of reuse by the autotrophs. Hence lake ecosystem can describe as a ‘Micro-model’ for the entire biosphere.
Question 39.
In GFCs the number of trophic levels is restricted. Give reason.
Answer:
- Grazing Food Chain (GFC) is also called as Predatory food chain.
- It starts with producers (green plants) and ends with secondary carnivores.
- Generally in a grazing chain, at the 1st trophic level green plants perform photosynthesis.
- At the first trophic level only one percent of the solar energy is converted into chemical energy.
- GPP, NPP herbivores at second trophic level are not efficient in using the NPPand converting them into GSP and a lot of energy is wasted .
- So if there are many trophic levels in a grazing food, the subsequent energy transfers will be more, which may not completely fulfill the energy needs of the much more higher trophic levels.
- So the number of trophic levels in GFC’s is restricted.
Question 40.
What are the ecological limitations for ecological pyramids?
Answer:
Limitations for ecological pyramid concept:
- It does not take into account the same species belonging to two (or) more trophic levels.
- It assumes a simple food chain, something that almost never exists in nature.
- It does not accommodate a food web.
- Saprophytes play a vital role in the ecosystem eventhough they are not given any place in ecological pyramids.
Question 41.
How is the second law of thermodynamics applicable to the functional part of an eco¬system.
Answer:
- Second law of thermodynamics states that no process involving energy transformation will spontaneously occur unless there is degradation of energy.
- Energy dispersed in the form of unavailable heat energy which constitutes the entropy.
- The organisms need a constant supply of energy to synthesize the molecules they require.
- The amount of energy available decreases at successive trophic levels.
- When an organism dies, it is converted to detritus or dead biomass that serves as a source of energy for the decomposers.
Question 42.
Discuss the main reason for the low productivity of ocean.
Answer:
1) Production of ocean: Most primary producers of ocean require nitrogen and phosphorus which are abundant. Two principal categories of producers are pelagic phytoplankton and benthic micro and macro algae. Benthic plants grow only on the fringe of oceans.
2) Chaemo autotrophs are producers of deep sea. Primary productivity is determined by measuring the uptake of CO2 and output of O2. Production rates are expressed as grams of organic carbon per unit area per time.
3) The productivity of the entire ocean is estimated to be approximately 16 xlO10 tons of carbon per year which is about eight times that of land. Upwelling and seasonal cycles of production are two important factors. Low productivity is recorded when these two factors fail.
Question 43.
Explain the terms saprotrophs, detritivores and mineralizers.
Answer:
1) Saprotrophs: These are organisms that break down dead and waste materials and meet their energy and nutrient requirements. Ex: Fungi and bacteria.
2) Detritivores: They feed on detritus. They break down the detritus into smaller particles. Ex: Earthworm.
3) Mineralizers: Decomposition of detritus takes place by humification and mineralization. Humus is formed by humification. It is highly resistant microbial action. It serves as reservoir of nutrients. It is further degraded (slowly) by some microbes which release inorganic nutrients. This process is called mineralization.
Question 44.
Discuss the factors that influence the process of decomposition.
Answer:
- Decomposition: It is the process in which complex organic matter breaks down into simple inorganic substances like CO2, water and nutrients.
- It requires large amount of oxygen and it is controlled by (i) chemical composition of the detritus and (ii) climatic factory.
- Decomposition rate is slow, if detritus is rich in lignin and chitin.
- It is fast with nitrogen and water soluble substances like sugars.
- Temperature and soil moisture are most important climatic factors that regulate decomposition.

Question 45.
Define decomposition and describe the process and products of decomposition.
Answer:
1) Decomposition: The organic material in the soil is detritus. It is subjected to decomposition.
Decomposition is an oxygen requiring process. The rate of decomposition is controlled by
a) Chemical decomposition of detritus b) Climatic factors.
2) Decomposition rate is slower if the detritus is rich in lignin and chitin. Decomposition rate is quicker if the detritus is rich in nitrogen and water soluble substance (sugars).
3) Decomposition is regulated by important climatic factors namely temperature and soil moisture.
Warm and moist environment favours decomposition. Low temperature and anaerobic environment inhibit decomposition. The decomposers are micro consumers(micro-scopic form).
Question 46.
Explain GFC.
Answer:
- GFC means Grazing Food Chain. It is also known as predatory food chain.
- The first trophic level begins with the green plants (producers). Ex: Rose bush
- The second trophic level is occupied by primary consumers like herbivores.Ex: Aphids.
- The third trophic level is occupied by secondary consumers like carnivores. Ex: Spider
- The fourth trophic level is occupied by tertiary consumers like top carnivores. Ex: Small birds.
- In some food chains there is yet another trophic level called climax camivores.Ex: hawk.
- Rose bush→Aphids→Spider→ Small birds →hawk
Question 47.
Write a short notes on the various trophic levels in a typical ecosystem.
Answer:
- Energy flows into biological systems (ecosystems) from the sun.
- The biological systems of environment include several food levels called trophic levels.
- A trophic level is composed of those organisms which have the same source of energy.
Various trophic levels in a typical ecosystem:
- The first trophic level begins with the green plants (producers). Ex: Rose bush
- The second trophic level is occupied by primary consumers like herbivores.Ex: Aphids.
- The third trophic level is occupied by secondary consumers like carnivores. Ex: Spider
- The fourth trophic level is occupied by tertiary consumers like top carnivores. Ex: Small birds.
Question 48.
Give examples for GFCs with three, four and five trophic levels from your locality. Explain the parasitic food chain. How does it differ from GFC.
Answer:
In GFCs 3rd , 4th and 5th tropic levels are occupied by primary, secondary and tertiary carni¬vores respectively.
- 3 trophic levels → Grass → Grasshopper → Garden lizard.
- 4 trophic levels → Grass → Grasshopper → Frog → Hawk
- 5 trophic levels → Phytoplankton → Zooplankton → Water insects → Frog → Snake → Hawk
Parasite food chain (PFC) :
- PFC is a part of the GFC. It starts with producers. Energy passed from large organisms to small organisms.
- 1st trophic level producers provide shelter and food for many birds and insects. These birds host many ecto – parasites and Endoparasites.
- PFC is differ from GFC in the path of the flow of energy. PFC energy flows from lower trophic levels (Large sized organisms) to successive higher trophic levels(small sized organisms)
Question 49.
Write a note on DFC. Give the significance in a terrestrial ecosystem. [AP,TS-18]
Answer:
- DFC is Detritus Food Chain. It is an important food chain in terrestrial ecosystem.
- Detritus is formed from leaf litter, dead bodies, and faeces of animals.
- Detritus has decomposers which are heterotrophic organisms. Ex: Fungi and bacteria.
- They meet their energy and nutrition requirements by degrading detritus.
- These organisms are called saprotrophs.
- Decomposers secrete enzymes that break down detritus into simple absorbable substances.
- Detritus food chains are as follows:
(i) Detritus – Earthworms – Frogs – Snakes.
(ii) Dead animals – Flies and maggots – Frogs – Snakes.

Question 50.
What is primary productivity? Give a brief description of the factors that affect primary productivity.
Answer:
- The rate of production of biomass is called productivity.
- It is divided in primary productivity and secondary productivity.
- Primary productivity is defined as the amount of biomass produced, in an unit area, over a period of time during photosynthesis.
- The primary productivity can be divided into Gross Primary Productivity(GPP) and Net Primary Productivity(NPP).
- Gross primary productivity (GPP) of an ecosystem in the rate of total production of organic matter during photosynthesis. About 20-25% of GPP is used for respiration.
- The net primary productivity is the biomass available for the consumption of herbivores and decomposers. Clouds and pollution affect gross primary productivity.
- Net primary productivity (NPP) is the resultant productivity after the amount used for respiration is deducted from gross primary productivity.
NPP= G.P.P. – Respiration(R)
Question 51.
Define ecological pyramids and describe with examples, pyramids of numbers and biomass. [TSM-19]
Answer:
- Ecological Pyramids: It is a graphic representation of the trophic structure and function of an ecosystem
- The pyramids were first studied by Elton. Hence those are known as Eltonian pyramids.
- Types of Pyramids: (i) Pyramid of number (ii) Pyramid of biomass (iii) Pyramid of energy.
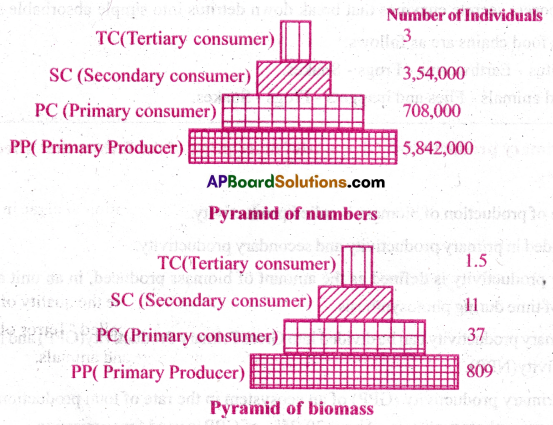
- Pyramid of numbers: A pyramid of numbers is a graphical representation that shows the number of organisms at each trophic level. It is an upright pyramid where the producers are always more in number than other trophic levels.
- Pyramid of Biomass: A pyramid of biomass is a graphical representation of biomass present in a unit area of various trophic levels. It shows the relationship between biomass and trophic level quantifying the biomass available in each trophic level at a given time.
- Pyramid of energy: An energy pyramid is a graphical model of energy flow in a community. The different levels represent different groups of organisms that might compose a food chain.
- The base of each pyramid represents the producers or the first trophic level.
- The top of pyramid represents top order consumer.
- Producers are more in number than herbivores and herbivores are more in number than carnivores.
- Similarly biomass and energy is more at lower levels than at higher levels.
Question 52.
Can you work out the number of trophic levels at which human – beings can function in a food chain?
Answer:
- A vegetarian man who takes only vegetarian food occupies the second trophic level as herbivore.
- A non-vegetarian who also takes chicken and mutton occupies third trophic level as primary carnivore.
- A non vegetarian who also takes fish occupies fourth trophic level as secondary carnivore.
- So total number of trophic levels at which human beings can function in a food chain are two or three levels.
Question 53.
Measurements of biomass interms of dry weight is more accurate justify?
Answer:
- Each trophic level has certain mass of living material at a particular time is called ‘standing crop.
- The standing crop is measured as the “biomass” of living organisms.
- Biomass is the number of organisms per unit area.
- The biomass of a species is expressed in terms of fresh or dry weight which is more accurate because water contains no usable energy.
Question 54.
What are the deleterious effects of depletion of ozone in the stratosphere? [IPE-14]
Answer:
- When ozone layer is depleted marketedly, it leads to ozone hole. [APM-19,20]
- Then ozone layer becomes very thin and it can’t prevent the UV radiation completely.
- Then the UV radiations with shorter wavelengths (UV-B) enter the earth surface.
Deleterious(Harmful) effects of depletion of ozone:
- UV rays damage DNA and may induce mutations.
- They cause aging of skin, damage to skin cells and cause skin cancer.
- High concentrations of UV-B radiation results in inflammation of cornea.
- This leads to snow blindness and cataract. Some times it permanently damages cornea.
Question 55.
Write a note on ’algal blooms’?
Answer:
- Algal blooms: It is a rapid increase (or) accumulation in the population of algae in an aquatic system.
- Algal blooms increases the death rate of the fishes
- Algal booms impart distinct colour to the water bodies and deteriote the quality of water.
- It causes blocks in water ways by its excessive growth. It is also called “Terror of Bengal”
- Algal blooms of some algae members are toxic to human beings and animals.

Question 56.
Describe Green House Effect. [AP M-20] [AP Mar,May-17] [IPE-14]
Answer:
Green bouse effect: ‘Green house effect’ is a naturally occurring phenomenon, that is responsible for heating of the Earth’s surface and atmosphere.
- When sunlight reaches the outer most layer of the atmosphere, it absorbs some radiation.
- About one fourth of solar radiation is reflected back by clouds and gases and only half of the incoming solar radiation reaches the earth surface and earth gets heated.
- Then a small portion of heat is reflected back into the atmosphere. Due to the presence of green house gases CO2 and methane a major part of the radiation again reflects back to the earth surface.
- Due to this, earth surface heats up once again (Global warming). This phenomenon is called Green house effect.
Question 57.
Write notes on the following.
a) Radioactive waste disposal b) E-wastes management.
Answer:
a) Radioactive waste disposal:
- Initially, nuclear energy was hailed as a non-polluting way for generating electricity.
- Later on it was realised that the use of nuclear energy has two serious problems.
(i) Accidental leakages, (ii) Safe disposal
- Radiation, that is released from nuclear waste is extremely dangerous to biological organisms, because it induces mutations.
- Exposure to high doses of nuclear radiation is lethal as it can lead to cancers (Ex: Leukemia).
- So, nuclear waste is an extremely potent pollutant and has to be dealt with utmost caution.
- Storage of nuclear wastes should be done in suitably shielded containers and buried deep in the soil or oceans about 500 meters depth.
b) E – wastes (Electronic wastes) Management:
- E – wastes consist of irreparable computers and electronic goods which are the modem day pollutants.
- E – wastes are buried in landfills (or) incinerated.
- Developing countries like China, India and Pakistan are importing the half of the E – wastes from developed world.
- Metals like Copper, iron, silicon, nickel and gold are recovered during recycling process.
- Eventually recycling is the only solution for the treatment of e-wastes provided it is carried out in an environmental friendly manner.
Question 58.
Discuss the role of women and communities in protection and conservation of forests in India.
Answer:
- In 1974, local women Garhwal Himalayas showed enormous bravery in protecting trees from the axe of contractors by hugging trees.
- People all over the world have acclaimed the Chipko movement.
- Realising the significance of participation by local communities the Government of India in 1980s has introduced the concept of Joint Forest Management (JFM) so as to work closely with the local communities for protecting and managing forest.
- In return for the services to the forest, the communities get benefit of various forest products like fruits, gum, rubber, medicine.
Question 59.
Discuss briefly the following: (a) Green house gases (b) Noise pollution (c) organic farming (d) Municipal solid wastes.
Answer:
(a) Green house gases: Gases like carbondioxide and methane are known as green house gases. Like a green house, these gases allow only the passage of light onto the Earth but not escape of heat from the Earth. Thus they result in the increase of Earth’s temperature.
(b) Noise pollution: Sound is measured in decibels. Human ear is sensible to sounds ranging from 0-180 dB. Any noise above 120dB is considered as noise pollution. Noise also causes, auditory fatigue, anxiety, sleeplessness, increased heart rate and B.P. etc. High sounds may damage ear drums.
(c) Organic Farming: It is an almost zero-waste procedure where, recycling of waste products is efficiently carried out.
- There is maximum utilization of resource and increased production.
- R.C.Dagar managed bee keeping, dairy, water harvesting, composting and agriculture as a chain reaction.
- Crop waste and cattle waste is used as natural fertilizer.
- Biogas is used for energy needs.
(d) Municipal solid wastes:
- Wastes from homes, offices, institutions, shops, hotels and restaurants in towns and cities are the municipal solid wastes.
- They are generally consists of paper, food waste, plastic, rubber, glass, metals, leather, textiles etc.
- The wastes are burnt to reduce the volume. They can be categorised into biodegradable, recyclable and non biodegradable.
Question 60.
Discuss the causes and effects of global warming. What measures need to be taken to control ‘Global Warming’? [TS M-15] [AP M-15,16]
Answer:
1) Global Warming: Rise of temperature above normal level in the atmosphere is called global warming. This happens due to the increase in the emission of green house gases.
2) Causes of Global Warming:
(a) Air pollutant (CO2) is the major responsible factor for global warming.
(b) It is produced by
- incomplete combustion of fossil fuels,
- Automobile exhausts
- Factory fumes
- Emissions from power plants
- Forest fires
3) Effects of Global Warming:
- Climatic changes
- Elnino effect
- Melting of snow caps of mountains resulting in submergence of coastal areas.
4) Control measures:
- Reducing the use of fossil fuels.
- Improving efficiency of energy usage.
- Planting of trees and avoiding deforestation.
- Slowing down the growth of human population.
- Kyoto protocol: To save earth from the dangers of global warming. 191 countries have signed the protocol in Kyoto of Japan to reduce the emission of green house gases to the level of 1990.
Question 61.
Write critical notes on the following: (a) Eutrophication (b) Biological magnification
(c) Ground water depletion and ways for its replenishment
Answer:
(a) Eutrophication:
- Natural aging of lakes by nutrient enrichment of its water is Eutrophication.
- In a young lake the water is cold and clear with little flora and fauna.
- Gradually nitrates and phosphates are carried into lakes via streams.
- Consequently aquatic algae, plants and animals reach the lake. After several thousands of years the lake become shallower due to silt and organic debris.
- The water becomes warm. Marsh plants appear and lake gives way to large masses of floating plants (bog). Gradually water dries up and land emerges. This process may take thousands of years.
- But due to human interference (the pollutants) there is cultural or accelerated eutrophication.
- In the past century many lakes were severely atrophied by sewage, agricultural and industrial wastes.

(b) Biological Magnification:
- Gradual accumulation and concentration of pollutants from producers to top consumers is called biological magnification.
- This phenomenon is well known in DDT and mercury pollution.
- In water the DDT concentration was 0.003 ppb. It passed through producers, primary consumer, secondary consumer and reach the fishing eating birds to a concentration of 5 ppm.
- This high concentration of DDT causes
(i) Disturbance of calcium metabolism.
Ex: Thin egg shells and premature breaking of shell.
(ii) Reduction in the population of these birds.
(c) Ground water depletion:
Causes for ground water depletion:
- No seasonal rains
- Prolonged summer
- Excessive usage of water by pumpsets
Effects of ground water depiction:
- Drying up of wells
- Reduction of water in streams and lakes.
- Decrease in water quality
Ways for ground water replenishment:
- Constructing recharge wells for proper storage of rain water.
- Constructing waste water treatment plants in each town and village.
- Growing trees to allow water lagging.
Long Answer Questions
Question 1.
Write an essay on temperature as an ecological factor.
Answer:
Temperature as an ecological factor:
Temperature is a measure of intensity of heat. Temperatures vary greatly on land from equator to poles and sea level to high altitudes. Temperatures in water vary very little.
1) Thermal stratification in temperature and lakes: Temperature variations are more pronounced in temperate lakes.
2) Summer Stratification:
- During summer the temperature of surface water reaches upto 25°C.
- The surface layer is called epilimnion.
- The middlelayer is thermocline or metalimnion.
- The temperature decreases at the rate of 1 °C per meter down the depth.
- The bottom layer is hypolimnion. The water is cool, stagnant with low oxygen.
3) Autumn over turn:
- During autumn (fall)epilimnion cools down to 4°C. Water is more dense at 4°C.
- Surface water becomes heavy and sinks to the bottom. The bottom water comes up.
- This circulation is called autumn or fall over turn.
4) Winter Stratification:
- During winter the surface temperature reaches 0°C and water freezes.
- Below the surface, water is present.
- In this condition organisms survive by reducing their metabolic rate and oxygen consumption.
5) Spring Overturn:
- In the following spring the surface warms upto 4°C. The heavy water goes down bringing up nutrient water. This overturn is spring over turn.
- Thus temperature circulates the water, distributing oxygen and nutrients in a temperate lake. The lakes which show overturns twice a year are called dimictic lake.
6) Biological effects:
- Eury thermal: Some animals can tolerate wide range of temperature. They are Eurythermal animals. Birds & Mammals.
- Stenothermal: Some animals cannot tolerate fluctuations in temperature. They are stenothermal. Fishes & Corals.
7) Metabolism:
- Temperature changes the activity of enzymes.
- Optimum temperature is the temperature at which the activity of animal is at peak.
- Minimum effective temperature, below which animal cannot survive and undergoes Chill coma
- Maximum effective temperature, above which animal undergoes heat coma.
8) Van’t Hoffs rule: For every increase of 10°C the metabolic rate doubles.
- Q10 = X-{X—10°C) Q10= Temperature coefficient.
- It the value of Q10 is 2.0 then it means that the rate of metabolism is doubled.
9) Cyclomorphosis: Temperature through seasonal changes bring about morphological changes
in animals like Daphnia (water flea).
- In winter head of Daphnia is round.
- During spring a helmet begins to grow
- In summer there is a large helmet.
- In autumn the helmet gradually decreases.
- By winter the head becomes round.
- The density of water changes with temperature.
- Cyclomorphosis is an adaptation to changing densities so that the animal can float freely.
10) Adaptations Behaviour: The reptiles bask in sunlight during cold days. They burrow in soil and hide in crevices during summer.
11) Morphological adaptations: Animal living in colder climates and cold water have a thick layer of fat below the skin (blubber).

12) Bergman’s rule: Animals of colder regions have larger bodes than their counter parts in warmer region. It is the Bergman’s rule. Large sized animals have less surface area. Hence heat loss is less.
13) Allen’s rule: Mammals in colder region have small ear lobes (pinnae). Their counterparts in warmer region have large pinnae. It is called Allen’s rule. Ex: Fox. Temperature loss is less in small ear lobes.
14) Physiological adaptations: All the animals try to maintain constant body temperature and constant inner fluid concentration.
15) Regulators: Birds and mammals maintain homeostasis i.e., thermoregulation and osmoregulation. Ex: Sweating in summer. Closure of sweat pore in winter and shivering.
16) Conformers: in many animals the body temperature vary to certain extent according to outside temperature. Ex: Invertebrates, Fishes, Frogs and reptiles. Camel is apartial regulator.
17) Migration: Animals move from one place to another to escape from severe climate in search of food and reproduction. Ex: Birds of Siberia.
18) Suspension of life activity: Thick walled spores are formed to tide over unfavourable conditions. Ex: Bacteria, fungi and lower plants.
Higher forms undergo aestivation in summer and hibernation in winter to escape severe temperature.
19) Diapause: Certain organisms delay their development in unfavourable conditions. Ex: Insect and embryos of fish.
Question 2.
Write an essay on water as an ecological factor.
Answer:
Water as an ecological factor:
1) Water: Water is an important ecological factor that influences the life of organisms.
Salt concentration is high in sea water and very low in fresh water.
2) Eury haline: Some organisms can tolerate wide fluctuations of salinity. They are eury haline Ex: Estuarine animals.
3) Steno halinc: Many organisms cannot tolerate fluctuations in salinity. They are stenohaline. Ex: Fresh water fishes & Marine fishes.
4) Adaptations of fresh Water animals: The salt concentration of body fluids is much higher than surrounding fresh water. So endosmosis takes place to send out excess water.
- Protozoans have contractile vacuoles.
- Fresh water fishes have large glomerular kidneys. Along with water, salts are also lost.
- Fishes have salt absorbing chloride cells in gills which absorb salts from surrounding water,
- Ponds dry up during summer. So, to survive in summer,
a) Protozoans undergo encystment.
b) Sponges produce gemmules.
c) Fishes like protopterus aestivate.
5) Adaptations of Sea water animals: Salt concentration sea of water is more than that of body fluids. So exosmosis takes place and to prevent dehydration.
- Fishes have aglomerular kidneys with few nephrons.
- They drink water. So salts accumulate inside the body.
- Excess salts are sent out through salt secreting chloride cells in gills.
- Sea gulls and penguins secrete salt drops through nose.
- Turtles and crocodiles have salt secreting glands near eyes.
- Sharks maintain salt concentration by having urea and TMO in their blood.
6) Adaptations of Brackish water: Animals of estuaries are euryhaline. Salmon and Hilsa are anadromous & Anguilla is catadromous. They can adjust their kidneys according to changing salinity. The chloride cells either absorb or secrete salt according to situation.
7) Terrestrial adaptations: Deserts have very less amount of water. Kangaroo rat utilizes its metabolic water for its water needs. It releases concentrated urine to prevent water loss.
Question 3.
Give an account of various types of interactions among the animal species of an ecosystem.
Answer:
Types of interactions among the animal species:
I) Inter-specific Interaction: It arises from population of two different species.
It is divided into four types, (i) mutualism, (ii)commensalism, (iii)parasitism & (iv) amensalism.
- Mutualism Both the species get benefited with each other.
- Commensalism : One gets benefited and the other one is neither benefited nor harmed.
- Parasitism : in both of these only one species benefits and the other one is detrimental.
- Amensalism : One species is harmed and the other one is unaffected.
II) Predation Predation is a feeding strategy, between two different species in which predator gets benefited at the cost of the prey.Ex : Lion (Predator) & Deer( Prey).
Important functions of Predation:
- Energy transfer: Predators take the basic role of energy transfer in trophic level.
- Biological Control: The ability of the Predators regulate the population of the prey.
- Species diversity: Predators reduce the intensity of competition among the prey species.
- Predators are prudent: if a predator is too efficient and overexploits its prey, then the prey might become extinct and following it, the predator will also become extinct due to lack of food. This is the reason why predators in nature are prudent.
- Preys develop defensive mechanism to avoid their predators.

III) Competition: inter specific competition is the competition between different species for the same resource.
Ex: Flamingos and fishes. Both of them compete for the same food, zoo plankton.
Darwin convinced that ‘interspecific competition’ is a ‘potent force’ in the process of organic evolution involving natural selection.
Types of Competition:
(i) Competition among unrelated species: It is a process in which the fitness of one species is significantly lower in the presence of another species.
(ii) Competitive exclusion : Gause & other ecologists experiments explained that when sources are limited, superior species will eliminate the other species.
Ex: Greater browsing efficiency of the goats in Galaspagos Islands, eliminates the Abingdon tortoise,
(iii) Competitive release; It occurs when one of the two competing species is removed from an area, thereby releasing the remaining species from one of the factors that limited its population size.
(iv) Coexistence: Gausse’s principal of exclusion states that two closely related species competing for the same resource, could avoide competition by choosing, for instance, different times for feeding (or) food collecting patterns.
IV) Parasitism : It is the interaction between two organisms of different species, in which one gets benefited and the other gets harmed.
Ex: Plasmodium vivax (Malarial parasite) in the body of a man.
Types of Parasites:
- Ectoparasites: They feed outside the body of the host. Ex : Ticks on dogs, lice on humans.
- Endoparasites: They live inside the body of the host. Ex : Malaria parasite.
- Brood parasites: During breeding season cuckoo (koel) lays it eggs in the host (crow) for incubation.
V) Commensalism : It is the interaction in which one species benefits and the other neither harmed nor benefited.
Ex : 1) Bannacles growing on the back of a whale benefit while the whale is not benefited.
2) Orchid growing as an epiphyte on a mango branch gets benefited, while the mango tree does not benefited.
(VI) Mutuaslism : In this interaction both species get benefited.
Ex : 1) Plants need the help of animals for pollination & seed dispersals where as animals get nectar & juicy and nutrients from fruits.
2) Lichens are the association of fungus and algae members. Fungi gives essential nutrients and water to the algae where as fungi gets shelter and carbohydrates from algae.
Question 4.
Describe lake as an ecosystem by giving examples for the various zones and the biotic components in it. [AP M-19][TS M-15,17]
Answer:
(A) Lake Ecosystem: Lakes are large inland water bodies containing still water. They contain water throughout the year. The lake ecosystem performs all functions of ecosystems. They are photosynthesis, heterotrops feeding on autotrops, decomposition, mineralization and recycling of minerals and circulation of nutrients.
Deep water lakes contain three distinct zones. They are I) Littoral zone II) Limnetic zone III) Prbfundal zone.
I) Littoral zone: It is the shallow part of the lake and is close to the shore. Light reaches upto its bottom. Hence it is Euphotic(good light zone). It has rich vegetation and high rate of photosynthesis. It is rich in oxygen.
II) Limnetic zone: It is the central largest and open zone away from shore and it does not touch the bottom. It extends vertically upto effective light penetration level. Zone of compensation separates the limnetic zone from the profundal zone. Here, the rate of photosynthesis is equal to the rate of respiration.
III) Profundal zone: It is the deep water zone below the limnetic zone. Light is absent. Photosynthesis does not take place. It is poor in oxygen.
(B) Biotic components of Lake:
1) Biota of Littoral zone :
(a) Flora- Plants – Examples
- Free floating hydrophytes – Pistia, Lemna, Salvinia
- Rooted hydrophytes with floating leaves – Nymphaea, Victoria regia
- Submerged suspended hydrophytes – Hydrilla, utricularia
- Submerged rooted hydrophytes – Vallisneria
- Amphibious plants(roots below water & upper plant above water) – Sagittaria, Typha
- Phytoplankton – Diatoms, Green algae

(b) Fauna -Animals – Examples
- Zooplankton (have water fleas) – Daphnia, Rotifers, Ostracods
- Neuston -Epineuston (live on water surface) – Water bugs, beetles
- Neuston- Hyponeuston(hang from airwater interphase) – Mosquito larvae
- Nekton(ffee swimming forms) – Fishes, snakes
- Periphyton(attached on plants) – Hydras, Nymphs
- Benthos(live in the bottom) – Red annelids, Cray fishes
II) Biota of Limnetic zone:
- It has phytoplankton, zooplankton and nekton.
- Phytoplankton examples are Euglenoids, diatoms, cyanobacteria, dinoflagellates, green algae.
- Zooplankton examples are copepods.
- Nekton examples are fishes, frogs, water snakes.
III) Biota of Profundal zone: It has decomposers, detritus feeders, chironomid larvae, phantom larva (chaoborus) clams etc. All these are capable of living in low oxygen levels. Recycling of minerals takes place in this zone.
Question 5.
Give an account of the various types of ecosystem on the earth.
Answer:
Ecosystem: An ‘ecosystem’ is a functional unit of nature, where living organisms interact among themselves and also with the surroundings physical environment. Ex: Pond, Forest, Sea.
Types of Ecosystem:
I) Natural Ecosystem: It is a naturally occuring ecosystem, with no role of humans in its formation. Ex : Deserts, forests, lakes.
II) Artificical Ecosystem: It is a man made ecosystem. Ex : Aqua ponds, Aquariums etc Types of Natural Ecosystems:
A) Aquatic ecosystem (water) B) Terrestrial ecosystems (Land)
A) Aquatic Ecosystem: Aquatic ecosystem is based on salinity of water. It is of three types,
(i) Marine (ii) Freshwater (iii) Estuarine
- Marine Ecosystem: It is the largest ecosystem and it is the most stable one.
- Fresh water ecosystem: It is the smallest ecosystem, it is of two types Lentic and Lotic
(a) Lentic: It is the still water bodies ecosystem. Ex : Ponds, lakes reserviors etc.
(b) Lotic: It is the flowing water body ecosystem Ex : Streams, rivers, canals etc.,
- Estuarine Ecosystem: It is the zone of joining of sea & river. It shows ‘fluctuations’ in salinity and the organisms are capable of withstand that ‘fluctuations’
(A) Lake Ecosystem: Lakes are large inland water bodies containing still water. They contain water throughout the year. The lake ecosystem performs all functions of ecosystems. They are photosynthesis, heterotrops feeding on autotrops, decomposition, mineralization and recycling of minerals and circulation of nutrients.
Deep water lakes contain three distinct zones. They are I) Littoral zone II) Limnetic zone III) Profundal zone.
I) Littoral zone: It is the shallow part of the lake and is close to the shore. Light reaches upto its bottom. Hence it is Euphotic(good light zone). It has rich vegetation and high rate of photosynthesis. It is rich in oxygen.
II) Limnetic zone: It is the central largest and open zone away from shore and it does not touch
the bottom. It extends vertically upto effective light penetration level. Zone of compensation separates the limnetic zone from the profundal zone. Here, the rate of photosynthesis is equal to the rate of respiration.
III) Profundal /one: It is the deep water zone below the limnetic zone. Light is absent.
Photosynthesis does not take place. It is poor in oxygen.
B) Terrestrial ecosystem: It is the land ecosystem. Ex: Forest, grassland and desert.
(i) Forest Ecosystem: In India two important types are present.
(a) Tropical rain forest (b) tropical deciduous forests.
(ii) Grass land ecosystems: They are present in Himalayan regions of India.
They occupy large areas of sandy & saline soils in westren rajasthan.
(iii) Desert ecosystem: Lands with less than 25 cm rainfall per year are considered deserts. They have characteristic flora and fauna. These are two types hot & cold.
Ex : Cold desert – Ladakh; Hot desert – Rajasthan.
(iv) Artifictal ecosystems: These are man-made ecosystems such as agricultural or agro¬ecosystems. They include cropland ecosystems, aquaculture ponds and aquaria.
Question 6.
Describe different types of food chains that exist in an ecosystem.
Answer:
- Sun is the main source of energy to ecosystem.
- The biological systems of environment have several food levels called trophic levels.
- A trophic level is composed of organisms which have same source of energy and same number of transfering steps.There are generally 3 to 5 trophic levels.
- Sometimes, a given species may occupy more than one trophic level. Ex: Sparrow The food energy always passes from lower trophic level to higher trophic levels.
- When the food path is linear, the components resemble the links of a chain. Hence, it is called food chain.
- The food chain generally ends in decomposers.
Types of Food Chains:
- Grazing food chain
- Parasite food chain
- Detritus food chain.
1) Grazing food chain: It is also called predator food chain. The first trophic level is occupied by green plants(producers). Second trophic level is occupied by Herbivores. The third, fourth and fifth trophic levels are occupied by primary, secondary and tertiary carnivores respectively.
Ex:
- Rose bush → aphids → spiders → small birds → hawks.
- Grass → Grass hopper → Frog → Snake → Hawk
- Grass → Goat → Man
- Plants → Caterpillar → Lizard → Snake
- Grass → Deer → Tiger.

2) Parasitic Food chain: In this, the food energy passes from large organisms to small organisms. The first trophilc level is occupied by large trees. They provide shelter and food to a variety of birds, reptiles and mammals. These animals form the second trophic level. Each of these animals host many ecto and endo parasites.
Ex: Tree → Birds, lizards, mammals → parasites.
3) Detritus Food chain: This food chain begins with detritus. Detritus is dead organic matter of leaves, dead bodies and faeces of animals. Detritus has decomposers which secrete enzymes, that break down detritus into simple absorbable substance. Detritus feeders are earthworms, flies and maggots which form the second trophic level.
Ex: Detritus → Earthworms → Frogs → Snakes → Hawks.
Food web: The food chains are not isolated chains. They are interconnected. They form a web called food web. The feeding relationships are not simple. There are omnivores which complicate the chains. Ex: Man, Bear, Crow.
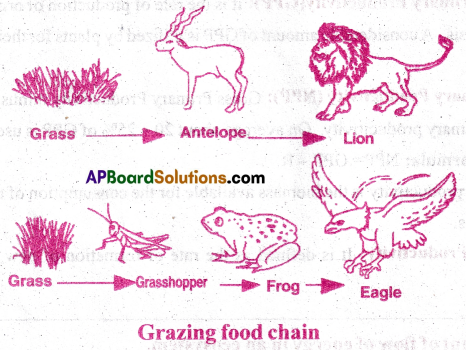
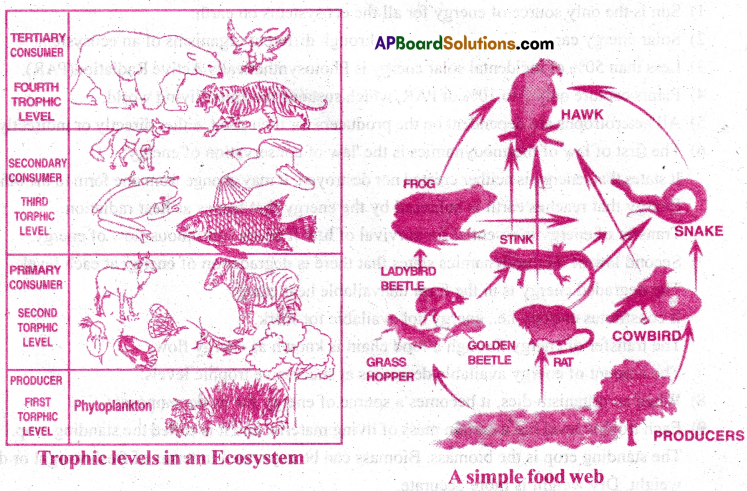
Question 7.
Write an essay on productivity of an ecosystem.
Answer:
Productivity of ecosystem:
Productivity: The rate of production of biomass is called productivity of the ecosystem.
It is of two types (i) Primary Productivity (ii) Secondary Productivity.
(i) Primary productivity : The amount of biomass (or) organic matter produced perunit area over a period of time by plants, during photosynthesis is called primary productivity.
It is of two types (a) Gross Primary Productivity (GPP) (b) Net Primary Productivity (NPP).
(a) Gross Primary Productivity(GPP): It is the rate of production of organic matter during photosynthesis. A considerable amount of GPP is utilized by plants for their catabolic process
(respiration)
(b) Net Primary Productivity (NPP): Gross Primary Productivity minus respirator loss (R) is the net primary productivity. On average about 20 – 25% of GPP is used for the catabolic acitivity. Formula: NPP= GPP – R
Net primary productivity is the biomass available for the consumption of the herbivores and decomposers.
(ii) Secondary Productivity: It is defined as the rate of formation of new organic matter by consumers.
Question 8.
Give an account of flow of energy in an ecosystem. [AP M-15]
Answer:
Flow of energy in an ecosystem:
1) Sun is the only source of energy for all the ecosystems on earth.
2) Solar energy captured by plants passes through different organisms of an ecosystem.
3) Less than 50% of incidental solar energy is Photosynthetically Active Radiation(PAR).
4) Plants capture only 2 to 10% of PAR, which sustains the entire living world.
5) All heterotrophs are dependent on the producers for their food, either directly or indirectly.
6) The first of law of thermodynamics is the ‘law of conservation of energy’.
- It states that, energy is neither created nor destroyed. It may change from one form to the other. Energy that reaches earth is balanced by the energy that leaves as heat radiation.
- Transfer of energy is essential for survival of life. It needs continuous flow of energy.
7) Second law of thermodynamics states that there is degradation of energy at each level.
- The degraded energy is in the form unavailable heat energy.
- It constitutes entropy i.e., energy not available for work.
- The transfer of energy through a food chain is known as energy flow.
- The amount of energy available decreases at successive trophic levels.
8) When an organism dies, it becomes a source of energy for its decomposers.
9) Each trophic level has a certain mass of living material and it is called the standing crop.
The standing crop is the biomass. Biomass can be expressed in terms of fresh weight or dry weight. Dry weight is more accurate.
10) The 10% law: It was introduced by Linderman.(the Founder of the modem Ecosystem Ecology).
It says that, during transfer of energy, only 10% of energy is stored to the trophic level and remaining energy is used for metabolic activities like respiration.
Linderman’s 10% rale is most widely used measure of ecological efficiency.
Ex: If the net primary production of plant is lOOkJ, the biomass available for herbivores is 10kJ.
Next carnivores gets only 1kJ.

Question 9.
List out the major air pollutants and describe their effects on human beings. [TS M-l 8,20] ]AP M-l 7,18] (TS May-17]
Answer:
Air pollution: Any deviation from the natural composition of air in the environment, causing
adverse effects to humans and plants is called air pollution. The agents which carry air pollution are called ‘air pollutants’.
Major air pollutants:
- Carbonmonoxide
- Carbondioxide
- Sulphurdioxide
- Nitrogen oxides
- Aerosols
- Noise pollution.
1) Carbon monoxide (CO): It is produced by incomplete combustion of fossil fuels.
Sources: Automobile exhausts, Factory fumes, Emissions from power plants, Forest fires, Burning of fire wood.
Harmful effects:
- In the presence of carbon monoxide, oxygen carrying capacity of haemoglobin is reduced.
- It causes headache and blurred vision, at lower concentrations.
- It leads to coma and some times death also, at higher concentrations.
2. Carbon dioxide(CO2): It is produced by respiration of living beings. But plants utilise C’O2 for photosynthesis.
Sources: Burning of fossil fuels (gasoline), automobiles, aeroplanes, power plants etc. Harmful effects:
- When its concentration level rises above normal it results in global warming.
- Global warming results so many adverse effects on mankind.
3. Sulphurdioxide(SO2): It is mainly produced by burning of fossil fuels, melting of sulphur ores and metal smelting.
Harmful effects:
- Breathing problems like asthma.
- Aggravation of cardiovascular problems.
- Corrosion of buildings and monuments.
4) Nitrogen oxides (NO, NjO, NO2): They are produced by automobile exhaust.
Harmful Effects:
(i) Oxides of nitrogen and SO2 together produce acid rains.
(ii) Acid rains acidify water bodies, spoil crops, buildings and monuments (Tajmahal).
- Nitrogen dioxide along with hydrocarbons & sunlight in foggy condition produce photochemical smog, (i) Spots are formed on leaves, (ii) Photosynthesis is reduced, (iii) Crop yield is reduced.
- Nitrogen oxides combine with secondary pollutants to form PAN (Peroxy Acetyl Nitrate).
It irritates eyes and respiratory tracts.
5) Aerosols (particulate matter): Aerosols are colloidal particles, dispersed in gas. They are produced from combustion of fossil fuels, flyash thermal plants, cement factories, asbestos plants etc.
Harmful effects: They decrease lung function. They cause Asthma aggravation, Premature death of patients of heart and lung diseases, Chronic bronchitis, irregular heart beat.
6) Noise Pollution: Undesirable high sounds (above 120dB) cause noise pollution.
Harmful effects: Extremely high sounds (more than 150 dB) damage ear drums and causes permanent hearing impairment. Noise also causes auditory fatigue, anxiety, sleeplessness (insomia) and stress.
Question 10.
What are the causes of water pollution and suggest measures for control of water pollution?
Answer:
I) Causes of Water pollution: (1) Domestic sewage (2) Industrial effluents (3) Thermal pollution.
I) Domestic sewage:
- Domestic sewage consists of human and animal excreta, detergents, waste foods etc.
- It is released into fresh water bodies like rivers lakes and canals and seas.
- As per regulation sewage must be treated before release.
- In the treatment the solids are easily removed. Domestic sewage primary contains biodegradable organic matter which will be decomposed by bacteria and micro organisms.
- Nitrates, phosphates, toxic metals and organic compounds are not easily removed.
(i) B.O.D: BOD means Biological oxygen demand. It is a measure of biodegradable substances in sewage. It is measured in terms of O2 consumed over a period of 5 days (BOD5) or seven days (BOD7). It is an index of measuring pollution load in sewage. The micro organisms consume most of the oxygen for biodegradation of organic matter. The fishes and other aquatic organisms die due to the lack of oxygen.
(ii) Algal blooms: Large amount of nutrients cause excessive growth of planktonic algae. Then the water looks green. This condition is called algal blooms. These blooms use more oxygen and reduce the quality of water so fishes and other aquatic animals die. Sewage also contains bacteria causing dysentery, typhoid, Jaundice, cholera etc.
2) Industrial effluents: It contains both inorganic and organic pollutants such as oils, greases, metal wastes, suspended solids. Most of them are not biodegradable. Organic effluents increase BOD and COD.
(i) Biomagnification: It is the progressive concentration of toxicants in successive trophic levels. Ex: DDT in water sample is 0.03 ppb. It is absorbed by autotrophs then passed on to consumer. The top level consumer has 5 ppb (fish eating bird). The DDT causes thinning of egg shells. So egg shells break killing the embryos. So the population of birds decline.

(ii) Eutrophication: Enrichment of water by nutrients is called Eutrophication.
- Due to nutrients organisms grow in lakes.
- During natural course of time debris and organic matter accumulates at the bottom.
- Lakes become shallow. Rooted plants appear. Finally lakes are converted to land.
- Due to human interference, accelerated eutrophication, many lakes have disappeared.
3) Thermal pollution: Thermal power plants and industries use water to cool the boilers and release hot water into rivers and other waterbodies. Stenothermal animal cannot tolerate the raise in temperature and die.
II) iVieasures for control of water pollution:
- Sewage has to be treated through ‘treatment plants’ before it is released into water sources.
- Effluents should be treated properly before being released into the water resources.
- Use of’less stable chemicals’, biodegradable chemicals and biopesticides should be encouraged to prevent organic pesticide pollution.
- Hot water should be directed to cooling towers before being released into the water bodies.
- Ecosan toilets (dry composting toilets) are to be popularised. Because human excreta can be recycled into resources which reduce the need for chemical fertilizers and water usage.
Question 11.
Write an essay on soil pollution and measures to Control soil pollution?
Answer:
Soil Pollution: Higher level concentrations of toxic chemicals in soil is called soil pollution.
Types of Soil pollutants:
- Municipal solid wastes
- Hospital Wastes
- Electronic wastes
- Agrochemicals
- Radio active wastes
(i) Municipal solid wastes:
- Wastes from homes, offices, institutions, shops, hotels and restaurants in towns and cities are the municipal solid wastes.
- They are generally consists of paper, food waste, plastic, rubber, glass, metals, leather, textiles etc.
Controlling measures:
- The wastes are burnt to reduce the volume.
- They can be treated by categorising into biodegradable, recyclable and non- biodegradable.
- Biodegradable materials can be put into deep pits in the ground and be left for natural breakdown.
- Recyclabe materials are to be separated and utilised again.
- Non-biodegradable waste left over is to be disposed off properly.
- To reduce the usage of plastic packets we have to use eco friendly packaging, cloth carrybags.
- Hospital Wastes: Hosipital wastes contian disinfectants, harmful chemicals and also pathogenic microorganisms.
Controlling measures: Hospital wastes can be treated by using incinerators.
Controlling Measures:
- E – wastes are buried in landfills (or) incinerated.
- Recycling is the only solution for the treatment of e-wastes provided it is carried out in an environmental friendly manner.
- E-wastes: it consist of irreparable computers and electronic goods which are the modem day pollutants.
- Agrochemicals: After Green revolution, improper use of inorganic fertilizers and pesticides cause threat to human health, and eco friendly organism.
It leads to increased drain of nutreints from Ecosystems causing eutrophication Controlling Measures:
- Practice of organic farming which is a zero waste procedure.
- R.C.Dagar managed bee keeping, dairy, water harvesting, composting and agriculture as a chain reaction that support one another and allow an extremely economical and sustainable venture.
- Radio active wastes: Radiation, that is released from nuclear waste is extremely dangerous to biological organisms, because it induces mutations.
Exposure to high doses of nuclear radiation is lethal as it can lead to cancers (Ex: Leukemia). Controlling Measures: Storage of nuclear wastes should be done in suitably shielded con¬tainers and buried deep in the soil or oceans about 500 meters depth.
Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
Plants depend on sunlight to meet their photoperiod requirement for
1. Fruiting
2. Flowering
3. Foliage
4. Formation of annual rights
Answer:
2. Flowering
Question 2.
Bending of plants towards sunlight is due to
1. Phototaxis
2. Phototropism
3. Photokinesis
4. Photoperiodism
Answer:
2. Phototropism
Question 3.
Circadian rhythms occur at an interval of
1. 24 Hrs
2. One year
3. One month
4. 15 days
Answer:
1. 24 Hrs

Question 4.
Water shows the maximum density at
1. 1°C
2. 4°C
3. 100°C
4. 21-25°C
Answer:
2. 4°C
Question 5.
Rise and fall of temperature above or below 4°C water will
1. decrease its density
2. increase its density
3. not change in its density
4. increase or decrease
Answer:
1. decrease its density
Question 6.
Organisms that can tolerate wide range of temperatures are called
1. Eurythermal
2. Stenothermal
3. Poikilotherms
4. Thermoconformers
Answer:
1. Eurythermal
Question 7.
The salt concentration in land waters is
1. Less than 5%
2. 30-35%
3. 0%
4. 10.15%
Answer:
1. Less than 5%
Question 8.
The type of interaction in which both the species get benefit is
1. Competition
2. Predation
3. Mutualism
4. Amensalism
Answer:
3. Mutualism
Question 9.
The type of interaction in which both the species lose
1. Competition
2. Predation
3. Mutualism
4. Amensalism
Answer:
1. Competition
Question 10.
Seed predator is known as
1. Herbivore
2. Germivore
3. Granivore
4. Frugivore
Answer:
3. Granivore
Question 11.
Gause’s principle in competition is about
1. Competitive exclusion
2. Competitive release
3. Co-existence
4. Intraspecific competition
Answer:
1. Competitive exclusion
Question 12.
Vector for malarial parasite is
1. Inoculation
2. Mosquito
3. Monkey
4. Pig
Answer:
2. Mosquito
Question 13.
Lice on humans and ticks on dogs are examples for
1. Ectoparasites
2. Endoparasites
3. Brood parasites
4. Hyperparasites
Answer:
1. Ectoparasites

Question 14.
Parasites that live inside the host’s body are known as
1. Ectoparasites
2. Endoparasites
3. Brood parasites
4. Superparasites
Answer:
2. Endoparasites
Question 15.
The interaction between sea anemone and clown fish is
1. Prediction
2. Parasitism
3. Commensalism
4. Mutualism
Answer:
3. Commensalism
Question 16.
Pollination and dispersal of seeds of plants by animals is an example of
1. Mutualism
2. Commensalism
3. Ectoparasition
4. Predation
Answer:
1. Mutualism
Question 17.
Flowers of fig plant are pollinated by
1. Honeybee
2. Hummingbird
3. Wasp
4. Cricket
Answer:
3. Wasp
Question 8.
Pollinators of orchid flowers are
1. Bees and Bumblebees
2. Butterflies and wasps
3. Wasps
4. Honey bee and cricket
Answer:
1. Bees and Bumblebees
Question 19.
The functional unit of nature is
1. Ecosystem
2. Autecology
3. Synecology
4. Biosphere
Answer:
1. Ecosystem

Question 20.
The basis for the identification of three aquatic ecosystems is
1. Salinity
2. Temperature
3. Pressure
4. dissolved oxygen
Answer:
1. Salinity
Question 21.
The largest ecosystem is
1. Estuarine
2. Marine
3. Fresh water
4. Lake ecosystem
Answer:
2. Marine
Question 22.
When river joins the sea, the area is called
1. Marine
2. Fresh water
3. Estuary
4. Lake
Answer:
3. Estuary
Question 23.
The smallest aquatic ecosystem is
1. Fresh water ecosystem
2. Estuarine ecosystem
3. Marine ecosystem
4. Brackish water ecosystem
Answer:
1. Fresh water ecosystem
Question 24.
In deep lakes light, cannot penetrate beyond
1. 100 meters
2. 200 meters
3. 50 meters
4. 10 meters
Answer:
2. 200 meters
Question 25.
The structural components of an ecosystem are
1. Biotic and abiotic factors
2. Energy flow
3. Cycling of nutrients
4. Food chains
Answer:
1. Biotic and abiotic factors
Question 26.
The functional components of an ecosystem are
1. Abiotic factors
2. Decomposers
3. Biotic factors
4. Energy flow
Answer:
4. Energy flow
Question 27.
Animals eat other animals, which can eat plants or plant products are
1. Primary consumers
2. Secondary consumers
3. Herbivores
4. Tertiary consumers
Answer:
2. Secondary consumers
Question 28.
Which of the following Is a predatory food chain?
1. Parasitic food chain
2. Grazing food chain
3. Detritus food chain
4. Linear food chain
Answer:
2. Grazing food chain
Question 29.
In a predatory feed’chain, tiger represent
1. Primary carnivores
2. Tertiary consumers
3. Secondary consumers
4. Primary consumers
Answer:
2. Tertiary consumers
Question 30.
A food web is made up of
1. Three food chains with un-interconnected net-work
2. Many food chains and with interconnection net-work
3. A single food chain
4. Two food chains belong to grazing and detritus food chains
Answer:
2. Many food chains and with interconnection net-work
Question 31.
The sun Is not the source of energy for
1. Agriculture ecosystem
2. Tundra ecosystem
3. Terrestrial ecosystem
4. Hydrothermal ecosystem
Answer:
4. Hydrothermal ecosystem

Question 32.
Energy may transform from one form to the other obeys
1. Solar energy
2. Second law of thermodynamics
3. First law of themodynamics
4. Energy flow
Answer:
3. First law of themodynamics
Question 33.
The energy which is lost or not available for work in an ecosystem is called
1. Entropy
2. Canopy
3. Atrophy
4. Isolated energy
Answer:
1. Entropy
Question 34.
The rate of production of biomass is called
1. Productivity
2. Body mass
3. Standing crop
4. Primary productivity
Answer:
1. Productivity
Question 35.
The inverted pyramid is not seen in
1, All ecosystems
2. Pyramid of biomass in sea
3. Pyramid of numbers in parasitic food chain
4. Pyramid of energy in all ecosystems
Answer:
4. Pyramid of energy in all ecosystems
Question 36.
Denitrification involves the conversion of
1. Nitrites into nitrates
2. Nitrates into nitrogen
3. Organic nitrogen into ammonia
4. Nitrogen to nitrogen oxides
Answer:
2. Nitrates into nitrogen
Question 37.
Many animals need large quantities of phosphorus to make
1. Muscles
2. Skin
3. Teeth
4. Hormones
Answer:
3. Teeth
Question 38.
One of the following is an example for population is
1. Bacteria on a culture plate
2. Teakwood tree in a forest
3. Frog living in a lake
4. Rat in a abandoned dwelling
Answer:
1. Bacteria on a culture plate
Question 39.
The organism that breeds once in its life time is
1. Salamander
2. Vulture
3. Penguin
4. Pacific Salmon fish
Answer:
4. Pacific Salmon fish
Question 40.
Life cannot exist on the earth without
1. Carbon dioxide
2. Oxygen
3. Sunlight
4. Water
Answer:
2. Oxygen
Question 41.
Acid rains are caused by
1. Nitrogen oxides only
2. SO2 and Nitrogen oxides
3. Ammonia&Sulphur dioxide
4. SO2
Answer:
2. SO2 and Nitrogen oxides
Question 42.
Corrosion of buildings and monuments is due to the harmful effects of
1. Acidification of soils
2. SO2
3. Acid rains
4. Alkalinity of water
Answer:
3. Acid rains
Question 43.
The air pollutant that has greater affinity for haemoglobin is
1. Carbon dioxide
2. Sulphur dioxide
3. Carbon monoxide
4. Oxygen
Answer:
3. Carbon monoxide

Question 44.
The colloidal particles dispersed in a gas are called
1. Gasoline
2. Admixture of aero particles
3. Aerosols
4. Charged particles
Answer:
3. Aerosols
Question 45.
Undesirable high sound constitutes Noise pollution, if it crosses the limit of
1. Above 130 dB
2. Above 150 dB
3. Above 120 dB
4. In between 90 dB to 100 dB
Answer:
3. Above 120 dB
Question 46.
One of the heavy common metals discharged from industrial effluents is
1. Carbon
2. Cobalt
3. Chromium
4. Iron
Answer:
3. Chromium
Question 47.
The most harmful pollutant is
1. Nuclear waste
2. Hospital wastes
3. Electronic wastes
4. Nitrogen oxide
Answer:
1. Nuclear waste
Question 48.
The term ’ecology’ was first used by
1. Huxley
2. Haeckel
3. Odum
4. Lancaster
Answer:
2. Haeckel
Question 49.
Synecology is the study of
1. single species
2. abiotic environment
3. group of species
4. ecological reaction
Answer:
3. group of species
Question 50.
A community is defined as
1. interacting populations
2. a group of birds
3. an interactive ecosystem
4. a collection of species
Answer:
1. interacting populations
Question 51.
Movement of organisms towards or away from source of light is called
1. Photoperiodism
2. Phototropism
3. Phototaxis
4. Phota kinesis
Answer:
3. Phototaxis
Question 52.
The formation of layers in water of temperate lakes due to temperature is
1. Summer Stratification
2. Winter Stratification
3. Spring Stratification
4. Thermal Stratification
Answer:
4. Thermal Stratification
Question 53.
Which of the following exhibits catadromous migration
1. Hilsa
2. Anguilla
3. Salmon
4. Protopterus
Answer:
2. Anguilla

Question 54.
The interaction in nature, where one gets benefit on the expense of other is
1. predation
2. mutualism
3. amensalism
4. commensalism
Answer:
1. predation
Question 55.
Competition of species leads to
1. extinction
2. mutation
3. ammensalism
4. symbiosis
Answer:
1. extinction
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()