Students get through AP Inter 1st Year Botany Important Questions 2nd Lesson Biological Classification which are most likely to be asked in the exam.
AP Inter 1st Year Botany Important Questions 2nd Lesson Biological Classification
Very Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
What is the nature of cell-walls in diatoms? [ TS M-22] [AP M-16, 17]
Answer:
- In diatoms, the cell walls form two thin overlapping shells like soap box.
- The walls are embedded with silica and thus the walls are indestructible.
- The upper shell is called epitheca and the lower one is called hypotheca.
Question 2.
How are ‘Viroids’ different from ‘Viruses’?
Answer:
| Viroids | Viruses |
| 1) Viroids are infectious agents to plants 2) Protein coat is absent. 3) Viroids contain nucleic acid only. 4) Their nucleic acid consists of only RNA. |
1) Viruses are infectious agents to all organisms 2) Protein coat is present. 3) Viruses contain nucleic acid & protein coat. 4) The nucleic acid may be RNA or DNA. |
![]()
Question 3.
What do the terms phycobiont arid mycobiont signify? [APM -17] [IPE Mar- 13]
Answer:
- The algal component of lichen is called phycobiont.
- The fungal component of lichen is called mycobiont.
Question 4.
What do the term algal bloom and red tides signify? [AP May-19]
Answer:
- Algal bloom signifies the excessive growth of algae (members of Cyanophyceae) in the water bodies. This causes eutrophication.
- Red tides signifies the rapid multiplication of red dinoflagellates in the marine environment. The red colour of red sea is due to Trichodesmium erythrium, gonulax.
Question 5.
State two economically important uses of heterotrophic bacteria. [TS M-16,20]
Answer:
Heterotrophic bacteria are useful
- in making curd from milk, (by lactic acid bacteria)
- in the production of alcohol, antibiotics, enzymes and aminoacids.
Question 6.
What is the principle underlying the use of cyanobacteria in agricultural fields for crop improvement ? [ AP M-15,19]
Answer:
- Cyano bacteria (like Nostoc and Anabaena)contain dinitrogenase enzyme.
It can fix atmospheric nitrogen in specialised cells called heterocysts. - They help in improving the soil fertility.
Question 7.
Plants are autotrophic. Name some plants which are partially heterotrophic.
Answer:
- All green plants are autotrophs because they synthesize the food by photosynthesis.
- Partially heterotrophic plants:
Ex: Viscum (Partial stem parasite), Cuscutta(Complete stem parasite), Striga (Partial root parasite)
Question 8.
Who proposed five kingdom classification? How many kingdoms of this classification contain eukaryotes? [TS M-19]
Answer:
- R.H. Whittaker proposed five kingdom classification.
- Four kingdoms contain eukaryotes. They are Protista, Fungi, Plantae and Animalia
Question 9.
Give the main criteria used for classification by Whittaker.[AP M-20, 22] [ TS M-15,20]
Answer:
Main criteria used for classification by Whittaker: Cell structure, thallus organisation, mode of nutrition, reproduction and phylogenetic relations.
![]()
Question 10.
Name two diseases caused by Mycoplasmas. [TS May-17,22]
Answer:
Mycoplasmas cause
- ‘Witches broom’ disease in plants.
- Pleuropneumonia in cattle
- Mycoplasmal urethritis in Flumans.
Question 11.
What are slime moulds? Explain what is meant by piasmodium with reference to slime moulds.
Answer:
- Slime moulds are saprophytic protists.
- Under suitable conditions, they form an aggregation called piasmodium.
- It grows and spreads over several feet and forms fruiting bodies bearing spores at their tips.
Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
What are the characteristic features of Euglenoids? [AF M-16, 20, 22]
Answer:
Characteristic features of Euglenoids: [TS M-17, 20]
- Euglenoids belong to kingdom Protista.
- They are a group of unicellular flagellate eukaryotes.
- They are seen in fresh stagnant water.
- Ex: Euglena.
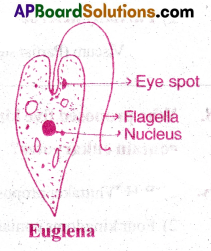
- Their body is covered by a protein layer called pellicle.
- They have two flagellae, one is short and other is long. Euglena
- The anterior part of their body consists of cytostome, cy topharynx and reservoir.
- On eye spot (or stigma) is present on the membrane of the reservoir.
- Reproduction in euglinoids is by longitudinal binary fission.
- They are autotropic, but in the absence of sunlight they exhibit heterotrophic nutrition.
Question 2.
What are the advan tages and disadvantages of two kingdom classification?
Answer:
I) Advantages:
- Two-kingdom classification was the first and most basic classification of living organisms.
- It is very easy to understand.
Disadvantages:
- Certain organisms do not fit either in plants or animals. Ex: Fungi
- No fixed position for organisms which showed both plant & animal characters. Ex: Euglena
- This system doesn’t distinguish between Eukaryotes and Prokaryotes (doesn’t contain nuclear membrane).
- In this classification, both Photosynthetic & Non-photosynthetic were placed together.
Question 3.
Give the salient features and importance of Chrysophytes. [AP M-15] [IPE Mar- 13]
Answer:
Features and importance ofChrysophytes: [TS M-17,22]
- Chrysophytes belong to kingdom Protista.
- They are a group of Algae.
- They are found both in fresh water and marine water
- Ex: Desmides Chrysophyte

- They are small in size, freely floating and photosynthetic.
- They have soap box like structure.
- Chrysophytes include diatoms and golden algae.
- Sillicated walls are seen in diatoms.
- Cell wall of diatoms has 2 shells (i) epitheca and (ii) hypotheca.
- They reproduce asexually by binary fission and sexually by gamete.
Uses:
- Polishing of glasses
- Filtration of oils and syrups.
![]()
Question 4.
Give a brief account of Dinoflagellates. [AP May-19] [APM-17,19] [TSM-15,16,19,22]
Answer:
- Dinoflagellates belong to kingdom Protista.
- They are a large group of flagellate eukaryotes.
- Dinoflagellates are seen mostly in marine water.
- Ex: Red Dino flagellates like Gonyaulax in Mediterranean sea.
- They appear in various colours depending upon their pigments.
- The outer surface of their cell wall has stiff cellulose.
- They have two flagellae, one lies longitudinally and the other transversely.
- The flagellae produces spinning movements, so these are called whirling whips.
- The nucleus has condensed chromosomes.
- Due to absence of histones, nucleus is called mesokaryon.
- Marine dinoflagellates like Noctiluca show bioluminescence.
- Toxins released by dinoflagellates may harm to animal cules.
Question 5.
Write the role of Fungi in our daily life. [IPE Mar-14]
Answer:
Role of Fungi in our daily life:
a) Advantages of Fungi:
- Yeast is the unicellular fungus. It is used in the commercial preparation of bread and beer.
- The Antibiotic ‘penicillin’ is obtained from a fungus called peniciliium.
- Mushrooms (Agaricus), morels and truffles are the common edible fungi.
b) Disadvantages of Fungi:
- Some fungi cause diseases in plants.
- Red rot disease on sugar cane is due to Collectotrichum.
- Rust disease on wheat is due to Puccinia.
Long Answer Questions
Question 1.
Give the salient features and comparative account of different classes of fungi studied by you.
Answer:
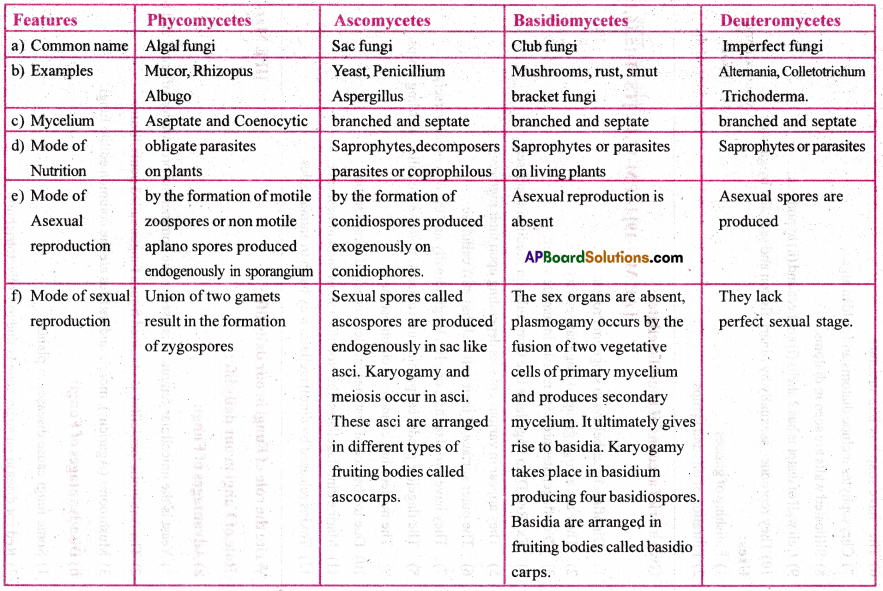
Question 2.
Describe briefly different groups of Monerans you have studied.
Answer:
Kingdom Monera includes all prokaryotes like Archaebacteria, Eubacteria, Mycoplasma and Actinomycetes.
I) Archaebacteria:
- These are special monerans as they live in extreme salty areas, hot springs and marshy areas.
- Cell wall doesnot contain peptidoglycan but contains pseudomurein.
- Cell membrane contain branched chain lipids which enables them to live in extreme condition.
- Methanogens are present in the gut of several animals like cows and buffaloes.
- They are responsible for the production of methane (biogas) from the dung of these animals.
![]()
II) Eubacteria:
- Bacteria are spread almost everywhere.They live in extreme habitats like hot springs, deserts, deep oceans and snow.
- They may live as parasites and symbionts also.
- Based on the shape, bacteria are classified as spherical [coccus], rod shaped [Bacillus], comma shaped [Vibrium] and spiral [Spirillum],
- Rigid cell wall consists of peptidoglycan also called murein or mucopeptide.
- In foldings of cell membrane are called mesosomes. .
- Genetic material is naked, not enveloped by nuclear membrane.
- Cell organellae are the only ribosomes.
- Motile bacteria contain one or more flagella.
- Based on the nutrition bacteria are two types, (a) Autotrophs (b) Heterotrophs
- Autotrophs are of 2 types: (i) Photosynthetic autotrophs (ii) Chemosynthetic autotrophs
- Heterotrophs are of 2 types: (i) Saprophytes or decompsers (ii) Parasites
- Bacteria reproduce mainly by binary fission.
- Sexual reproduction is by the transfer of genetic material from one bacterium to the other.
III) My coplasmas:
- Mycoplasmas completely lack cell wall and are pleomorphic.
- They are smallest living organisms and can survive without oxygen.
- Mycoplasmas are pathogenic in plants and animals.
- In plants, they cause witches broom disease.
- They cause pleuro pneumonia in cattle and mycoplasmal urethritis in humans.
IV) Actinomycetes:
- Actinomycets are branched filamentous bacteria which form radiating colonies in culture.
- The cell wall contains mycolic acid.
- Most of them are saprophytic and decomposers.
- Myco bacterium and corynebacterium are parasites.
- Some bacteria like streptomyces produce antibiotics.
Question 3.
Enumerate the salient features of different groups in protista.
Answer:
Different groups in Protista: Chrysophytes, Dinoflagellates, Euglenoids, Slime moulds, Protozoans.
I) Chrysophytes:
- Chrysophytes include diatoms and golden algae called desmids.
- They are found in fresh water and marine water as plankton.
- They are microscopic and float passively in water currents.
- Most of them are photosynthetic.
- In diatoms the cell walls form two thin over lapping shells, epitheca and hypotheca.
- They fit together as in a soap box.
- The walls are embedded with silica and are indestructible.
- The diatoms have left behind large amount of cell wall deposits in their habitat over billions of years to form diatomaceous earth (or) Kieselghur.
- Diatoms are two types – Centrale diatoms and pennales.
- They reproduce asexually by binary fission and sexually by the formation of gametes.
II) DinoflageIlates:
- Dinoflagellates are mostly marine and photosynthetic organisms.
- They appear yellow, green, brown, blue or red depending upon the pigments present in the cells.
- The cell wall has stiff cellulose on the outer surface.
- They have two flagellae, one lies longitudinally and the other transversely in a furrow between the wall plates.
- The flagellae produce spinning movements, so these dinoflagellates are called whirling whips.
- The nucleus has condensed chromosomes and do not have histones.
- This nucleus is called mesokaryon.
- Marine dinoflagellates like Noctiluca show bioluminescence.
- Red Dino flagellates like Gonyaulax under go rapid multiplication in the Medeterranian sea and cause red tides.
- Toxins released by dinoflagellates may even kill the marine animals like fishes.
III) Euglenoids:
- Euglenoids are fresh water organisms found in stagnant water.
- They are unicellular and flagellate.
- Covered by a protein rich layer called pellicle, which gives flexibility to the body.
- They have two flagellae, a short and a long one.
- The anterior part of the body consists of cytostome, cytopharynx and reservoir.
- On the membrane of the reservoir an eye spot or stigma is present.
- In the presence of sunlight they perform photosynthesis.
- In the absence of sunlight they predate on smaller organisms and behave as heterotrophs.
- The reproduction is by longitudinal binary fission.
- Palmella stage is found. Ex: Euglena.
![]()
IV) Slime Moulds:
- Slime moulds are saprophytic protists.
- Under suitable conditions, they form an aggregation called plasmodium.
- It grows and spreads over several feet and forms fruiting bodies bearing spores at their tips.
V) Protozoans:
- All protozoans are heterotrophs and live as predators or parasites.
- They are believed to be the primitive relatives of animals,
- They do not contain cell wall. The protoplasm is surrounded by plasma membrane.
- There are four major groups in protozoa.
a) Amoeboid Protozoans:
- These organisms live in freshwater, sea water and moist soil.
- They move and capture the prey with the help of pseudopodia as in Amoeba.
- Marine forms have silica shells on their surface.
- Entamoeba like forms are parasites.
b) Flagellated Protozoans:
- The members are either free living or parasites, contain flagellae.
- Parasite forms cause diseases like sleeping sickness. Ex: Trypanosoma.
c) Ciliated Protozoans:
- Aquatic, actively moving organisms because of thousands of cilia on them.
- They have a gullet that opens to the out side of cell surface. Ex: Paramecium
d) Sporozoans:
- This includes diverse organisms that have an infectious spore like stage in their life cycle.
- Ex: Plasmodium which causes malaria fever in man.
Exercise
Question 1.
State two economically important uses of:
(a) Heterotrophic bacteria (b) Archaebacteria
Answer:
a) Heterotrophic bacteria is useful
- In making of curd from milk, (by lactic acid bacteria)
- in the production of alcohol, antibiotics, enzymes and aminoacids.
b) Archaebacteria is useful in
- Production of methane (biogas) from the dung of ruminants
- Biotechnology
Question 2.
Give a comparative account of the classes of Kingdom Fungi on the basis of the following:
(i) mode of nutrition
(ii) mode of reproduction
Answer:
(i) Mode of nutrition:
- Phycomycetes: Obligate parasites
- Ascomycetes: Saprophytic, decomposers
- Basidiomycetes: Parasites
- Deuteromycetes: Saprophytes, decomposers.
(ii) Mode of reproduction:
- Phycomycetes: Asexually by zoospores or aplanospores, sexually by gametes.
- Ascomycetes: Asexually by conidia, sexually by ascospores.
- Basidiomycetes: Asexually by fragmentation, sexually by fusion of two somatic cells.
- Deuteromycetes: Asexually by conidia.
![]()
Question 3.
Give a brief account of viruses with respect to their structure and nature of genetic material. Also name four common viral diseases.
Answer:
Viruses:
- Structurally Virus consists of two parts. The outer protein coat is called capsid and the central core consists of genetic material.
- Genetic material in virus is either DNA or RNA it may be ds or ss.
- Four Common Viral diseases: (i) Polio (ii) AIDS (iii) Hepatitis (iv) Influenza
Question 4.
Organise a discussion in your class on the topic – Are viruses living or non-living?
Answer:
I) Living characters of Viruses:
- Presence of genetic material DNA or RNAnswer:
- The ability of multiplication.
- Can infect the host.
- Host specificity.
- Occurrence of mutations.
II) Non-living characters of Viruses:
- Behave like particles only out side the host.
- Ability to get crystallisation.
- Protoplasm is absent.
- High specific gravity as in non-living objects.
- Metabolic aspects like growth respiration, nutrition are absent.
Conclusion: Viruses are not truly ‘living’. They exist in crystal form outside the host. They are called obligate parasites.
Question 5.
Suppose you accidentally find an old preserved permanent slide without a label and in your effort to identify it, you place the slide under the microscope and observe the following features;
a) unicellular body
b) well-defined nucleus
c) biflagellate condition – one flagellum lying longitudinally and the other transversely
What would you identify it as? Can you name the kingdom it belongs to?
Answer:
a) The permanent slide is identified as a Dinoflagellate.
b) Dinoflagellate belongs to kingdom Protista.
Question 6.
Polluted water bodies have usually high abundance of plants like Nostoc and Oscillatoria. Give reasons.
Answer:
When the nutrients are excess in the polluted water containing an abundance of nostoc and oscillatory, the plants utilise the nutrients, perform growth and reproduction and multiply their number enormously resulting in algal blooms.
Question 7.
Cyanobacteria and heterotrophic bacteria have been clubbed together in Eubacteria of kingdom Monera as per the five kingdom classification, even though the two are vastly different from each other. Is this grouping of the two types of taxa in the same kingdom justified? If so why?
Answer:
Yes, because both are unicellular prokaryotes.
Question 8.
What observable features in Trypanosoma would make you classify it under kingdom Protista?
Answer:
- Trypanosoma gambiense is a flagellate parasite.
- It causes African sleeping sickness or gambia fever in African people.
- It lives in the blood and cerebrospinal fluid of man.
- Reason for the inclusion of Trypanosoma under protista are – the cell contain well defined nucleus, membrane bound organelles, flagellum and reproduce asexually by longitudinal binary fission.
![]()
Question 9.
At a stage of their life cycle, ascomycetous fungi produce the fruiting bodies like cleistothecium, perithecium or apothecium. How are these three types of fruiting bodies differ from each other?
Answer:
- In members of ascomycetous, sexual spores called ascospores are produced in sac like structures called asci.
- The asci are arranged in different types of Suiting bodies called ascocarps.
- The globose ascocarp without opening is called cleistothecium
- The flask shaped ascocarp with an apical opening is called perithecium.
- The cup or saucer shaped ascocarp is called apothecium.
Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
Five Kingdom classification was proposed by
1. R.H.Whittaker
2. Linnaeus
3. Theophrastus
4. Hutchinson
Answer:
1. R.H.Whittaker
Question 2.
Two kingdoms that are common to all biological classifications are
1. Monera and Plantae
2. Plantae and Animalia
3. Protista and Monera
4. Animals and Fungi
Answer:
2. Plantae and Animalia
Question 3.
Five kingdom classification is not based on
1) Complexity of body organisation
2) Presence or absence of a well-defined nucleus
3) Mode of reproduction
4) Types of pigments
Answer:
1) Complexity of body organisation
Question 4.
Among 5-Kingdom classification, eukaryotes are placed in how many kingdoms?
1) 1
2) 2
3) 3
4) 4
Answer:
4) 4
Question 5.
Cell walls of fungi are made up of
1. Cellulose
2. Lignin
3. Chitin
4. Suberin
Answer:
3. Chitin
![]()
Question 6.
The cell wall of fungi contains a
1. Homopolymer
2. Monosaccharide
3. Heteropolymer
4. Cellulos
Answer:
3. Heteropolymer
Question 7.
Atmospheric nitrogen in Nostoc is fixed in
1. Heterocysts
2. Holdfast
3. Hormogonia
4. Akinetes
Answer:
1. Heterocysts
Question 8.
Nitrogen fixing cyanobaterium is
1. Rhizobium
2. Nostoc
3. Chlorella
4. Methanogen
Answer:
2. Nostoc
Question 9.
Chief producers in the oceans are
1. Diatoms
2. Green algae
3. Blue-green algae
4. Bryophytes
Answer:
1. Diatoms
Question 10.
Capsid is found in
1. Viroids
2. Prions
3. Viruses
4. Lichens
Answer:
3. Viruses
Question 11.
Red colour of red sea is due to
1. Porphyra
2. Trichodesmium
3. Polysiphonia
4. Anabaena
Answer:
2. Trichodesmium
Question 12.
Red tides in Medeterranian sea are because of
1. Gonyaulax
2. Trichodesmium
3. Fungi
4. Actinomycetes
Answer:
1. Gonyaulax
![]()
Question 13.
The smallest living cells which can survive without oxygen are
1. Bacteria
2. Viruses
3. Mycoplasmas
4. Cyanobacteria
Answer:
3. Mycoplasmas
Question 14.
Whirling whips are
1. Chrysophytes
2. Dinoflagellates
3. Euglenoids
4. Slime moulds
Answer:
2. Dinoflagellates
Question 15.
Photosynthetic stigma or eye spot is found in
1. Trypanosoma
2. Amoeba
3. Gonyaulax
4. Euglena
Answer:
4. Euglena
Question 16.
Sleeping sickness disease is caused by
1. Trypanosoma
2. Paramoecium
3. Entamoeba
4. Plasmodium
Answer:
1. Trypanosoma
Question 17.
The DNA of Bacteria (E.coli) is
1) Double stranded & linear
2) double stranded & circular
3) Single stranded & linear
4) Single stranded & circular
Answer:
2) double stranded & circular
Question 18.
Identify the wrong combination
1. Polyporus -Bracket fungus
2. Lycoperdon – Puffball
3. Rhizopus – Bread mould
4. Cuscuta – Autotroph
Answer:
4. Cuscuta – Autotroph
Question 19.
Cell wall of archebacteria is made up of chemicals
1) Peptidoglycans
2) Pseudomurein
3) lip polysaccharide
4) Cellulose
Answer:
2) Pseudomurein
![]()
Question 20.
Rejuvenatory spores in diatoms are
1. Auxospores
2. Parthenospores
3. Akinetes
4. Conidia
Answer:
1. Auxospores
Question 21.
Identify the mis-match of the following
1. Coccus – Spherical
2. Spirillum – Spiral
3. Bacillus – Rodshaped
4. Vibrio-Filament like
Answer:
4. Vibrio-Filament like
Question 22.
Sexual spores are exogenously produced in
1. Penicillium
2. Albugo
3. Agaricus
4. Colletotrichum
Answer:
3. Agaricus
Question 23.
Asexual spores are generally not formed in
1. Mucor
2. Claviceps
3. Puccinia
4. Altemaria
Answer:
4. Altemaria
Question 24.
A primitive animal is
1. Noctiluca
2. Euglena
3. Gonyaulax
4. Trypanosoma
Answer:
4. Trypanosoma
Question 25.
Nutritionally most of fungi are
1. Saprophytes only
2. Parasites only
3. Symbionts only
4. Saprophytes or parasites
Answer:
4. Saprophytes or parasites
Question 26.
All Protozoans have
1. Pseudopodia
2. Contractile vacuole
3. Cilia
4. Eukaryotic organisation
Answer:
4. Eukaryotic organisation
Question 27.
Cell wall is found in somatic body of
1. Euglena
2. Entamoeba
3. Slime moulds
4. Chlamydomonas
Answer:
4. Chlamydomonas
Question 28.
Characteristic spores of diatoms are
1. Zoospores
2. Ascospores
3. Auxospores
4. Basidiospores
Answer:
3. Auxospores
Question 29.
Diatoms are indestructible because of the presence of
1) CaCO3 in cell wall
2) Siliceous cell wall
3) Mucilagenous cell wall
4) A11 of the above
Answer:
2) Siliceous cell wall
Question 30.
Witches broom in plants is caused by
1. Trichoderma
2. Actinomycetes
3. Mycoplasmas
4. Bacteria
Answer:
3. Mycoplasmas
![]()
Question 31.
The most primitive organisms showing oxygenic photosynthesis are
1. Green algae
2. Chrysophytes
3. Green and purplesuiphur bacteria
4. Cyanobacteria
Answer:
4. Cyanobacteria
Question 32.
Smut and rust fungi are respectively
1. Puccinia, Ustilago
2. Ustilago, puccinia
3. Polyporus, Lycoperdon
4. Alternaria, Trichoderma
Answer:
2. Ustilago, puccinia
Question 33.
Monera includes
1) All prokaryotic-only unicellular
2) All eukaryotic — only unicellular
3) All prokaryotic-both unicellular & multicellular
4) All the above
Answer:
3) All prokaryotic-both unicellular & multicellular
Question 34.
Vlroids have
1. Nucleic acid & protein
2. DNA only
3. RNA only
4. DNA&RNA
Answer:
3. RNA only
Question 35.
Puccinia is
1. a fungus that produces antibiotic
2. a fungus of class phycomycetes
3. a fungus that causes rust disease
4. an imperfect fungus
Answer:
3. a fungus that causes rust disease
Question 36.
The protein coat of virus is called
1. Capsule
2. Capsomere
3. Capsid
4. Cypsela
Answer:
3. Capsid
Question 37.
The Viruses which infect bacteria are known as
1. Zoophages
2. Bacteriophages
3. Cyanophages
4. Phytophages
Answer:
2. Bacteriophages
Question 38.
Viroids differ from viruses in the
1. absence of RNA
2. presence or DNA
3. absence of a protein coat
4. absence of nucleic acid and protein
Answer:
3. absence of a protein coat
![]()
Question 39.
Agaricus belongs to the clašs
1. Ascomycetes
2. Phycomycetes
3. Basidiomycetes
4. Deuteromycetes
Answer:
3. Basidiomycetes
Question 40.
Lichens are
1. Parasites
2. Saprophytes
3. Symbionts
4. Chemotrophs
Answer:
3. Symbionts
Question 41.
Viroids have
1. Single – stranded RNA not enclosed by protein còat
2. Single – stranded DNA not enclosed by protein coat
3. Double strande DNA enclosed by protein coat
4. Double – stranded RNA enclosed by protein coat
Answer:
1. Single – stranded RNA not enclosed by protein còat
Question 42.
Lichens are very good’ air pollution indicators because
1) Their population is high at highly polluted area
2) They are very sensitive to SO2, and die at higher level of SO2
3) They play an important role in soil formation
4) Their population is high at the location with high level of SO2
Answer:
2) They are very sensitive to SO2, and die at higher level of SO2
Question 43.
Zoospores are present In
1. Riccia
2. Anabaena
3. Albugo
4. Nostoc
Answer:
3. Albugo
Question 44.
RNA Is not found in one of the following organisms
1. TMV
2. HIV
3. Viroids
4. Prions
Answer:
4. Prions
Question 45.
Asexual spores are generally not found in
1. Ustilago
2. Neurospora
3. Albugo
4. Trichoderma
Answer:
1. Ustilago
![]()
Question 46.
Dikaryotic phase is not found in
1. Aspergillus
2. Agaricus
3. Puccinia
4. Mucor
Answer:
4. Mucor
Question 47.
The unique character that unified the kingdom plantae of Linnaeus is
1) all organisms have green pigment
2) All organisms are autotrophic
3) All organisms have well developed nucleus
4) All organisms bear cell wall in their cells
Answer:
4) All organisms bear cell wall in their cells
Question 48.
The bacteria forming blooms in polluted water bodies are nutritionally
1) Photosynthetic autotrophs
2) chemosynthetic autotrophs
3) Heterotrophs
4) Saprophytic
Answer:
1) Photosynthetic autotrophs
Question 49.
Maximum modes of nutrition occur in
1) Monera
2) Fungi
3) Protista
4) Plantae
Answer:
1) Monera
Question 50.
Naked cytoplasm, multi nuculeated and saprophytic nature is the characteristic of
1) Mycoplasma
2) BGA
3) Archaebacteria
4) Slime moulds
Answer:
4) Slime moulds
Question 51.
Mark the mis-matched pair
1) Noctiluca -Bioluminescence
2) Whirling whips-soap box like body structure
3) Diatomite-Kiesulgur
4) Blue green algae -zygotic meiosis
Answer:
4) Blue green algae -zygotic meiosis
Question 52.
Select the incorrect statement w.r.t to virus
1) Connecting link between living and nonliving
2) An inert virus is called virion
3) Viruses are obligatory intracellular parasites
4) They do not have the ability to get crystallized eg TMV.
Answer:
4) They do not have the ability to get crystallized eg TMV.
![]()
Question 53.
Coenocytic vegetative mycelium Is found in .
1) Neurospora
2) Rhizopus
3) Pencillium
4) Ustilago
Answer:
2) Rhizopus
Question 54.
Infectious proteins are present in
1) Prions
2) Viroids
3) Both 1 &2
4) Satellite Viruses
Answer:
1) Prions
Question 55.
Select the correct match
1) Phycomycctes-claviceps
2) Ascomycetes- Alternaria
3) Deuteromycetes- Trichoderma
4) Basidiomycetes-colletotrichum
Answer:
4) Basidiomycetes-colletotrichum
Question 56.
Aplanospores, non motile spores are present in
1) Rhizopus
2) Mucor
3) Both 1 & 2
4) Cyanobacteria
Answer:
3) Both 1 & 2
Question 57.
Mark the odd one recording fungi
1) Mycorrhizal association is symbiotic relation ship
2) Septate, Multicellular mycelium is present in Ascomycetes
3) Palmella stage is found in slime moulds
4) Pellicle is present in Euglena
Answer:
2) Septate, Multicellular mycelium is present in Ascomycetes
Question 58.
Dikaryophase in Ascomycetes and Basidiomycetes is
1) Diploid and dikaryotic
2) Haploid and dikaryotic
3) Diploid and monokaryotic
4) Haploid and monokaryotic
Answer:
2) Haploid and dikaryotic
![]()
Question 59.
Choose the correct one from the following
1) True nucleus is absent in Anabaena
2) A virus has both DNA and RNA
3) TMV is a tadpole shaped phytophage
4) Cercospora is considered as Drosophila of plant kingdom
Answer:
1) True nucleus is absent in Anabaena
Question 60.
Archaébacteria differ from other bacteria in having a different
1) Cell organelles structure
2) Cell wall composition
3) Nuclear structure
4) Ribosomal structure.
Answer:
2) Cell wall composition
Question 61.
Virus envelope is known as –
1) capsid
2) virion
3) nuclJtein
4) core
Answer:
1) capsid
Question 62.
With respect to fungal sexual cycle , choose the correct sequence of events.
1) Karyogamy, plasmogamy and meiosis
2) Meiosis, plasmogamy and karyogamy
3) Plasmogamy, karyogamy and meisosis
4) Meiosis, karyogamy and plasmoganiy
Answer:
3) Plasmogamy, karyogamy and meisosis
![]()
Question 63.
Which pair is odd?
1) Phycomycetes — Aquatic fungi
2) Basidiomycetes — Sac fungi
3) Ascomycetes — Penicillum
4) Basidiomycetes — Puffballs
Answer:
2) Basidiomycetes — Sac fungi