Students get through AP Inter 1st Year Botany Important Questions 1st Lesson The Living World which are most likely to be asked in the exam.
AP Inter 1st Year Botany Important Questions 1st Lesson The Living World
Very Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
What does ICBN stand for? [TS M-22] [AP May 19]
Answer:
ICBN stands for International Code for Botanical Nomenclature.
Question 2.
What is flora? [ TS M 15]
Answer:
Flora is the actual account of habitat, distribution and systematic listing of plants of a given area.
Question 3.
Define metabolism. What is the difference between anabolism and catabolism?
Answer:
Metabolism is the sum total of all the chemical reactions occurring in the body of an organism.
| Anabolism | Catabolism |
| 1) It is a constructive metabolic process. 2) Here, complex molecules are formed from simpler molecules by Photosynthesis. |
1) It is a destructive metabolic process. 2) Here, complex molecules are broken down into simpler molecules by respiration. |
![]()
Question 4.
Which is the largest botanical garden in the World? Name a few well known botanical gardens in India. [TS M 49]
Answer:
- Royal Botanical Garden(RBG) at Kew(England) is the Largest Botanical garden in the World.
- Well-known botanical gardens in India:
(i) Indian Botanical Garden, Howrah (Kolkata)
(ii) National Botanical Research Institute, Lucknow.
Question 5.
Define the terms ’couplet* and ‘lead* in taxonomic key. [AP & TS M-16, APM-15]
Answer:
- Couplet: The keys based on the contrasting characters in a pair are called couplet.
- Lead; Each statement in the key is called a lead.
Question 6.
What is meant by manuals and monographs? [APM-17]
Answer:
- Manual is a small book designed for ready reference. It provides information for identification of names of species found in an area.
- Monograph is a specialist book written on a single (any one) taxon.
Question 7.
What is systematics?
Answer:
- Systematics is the study of different kinds of organisms, their diversities and also relationship among them.
- The word systematics is derived from the Latin word systema which means systematic arrangement of organisms.
Question 8.
Why are living organisms classified?
Answer:
- There exists vast number of organisms which differ very greatly in their form, structure and mode of life.
- In order to study these vast number of organisms easily, they are classified into various groups.
Question 9.
What is the basic unit of classification? Define it.[TS M-20]jAP M -17,2022]
Answer:
- Species is the basic unit of classification.
- Species is a group of individual organisms with fundamental similarities.
Question 10.
Give the scientific name of Mango. Identify the generic name and specific epithet.
Answer:
- The scientific name of mango is Mangifera indica. [TS Mar-17]
- Its generic name is Mangifera and its specific epithet is indica.
Question 11.
What is growth? What is the difference between the growth in living organisms and growth in non-living objects?
Answer:
- Growth is a permanent and irreversible increase in the size & dry weight of a living organism.
- The growth in living organisms occurs by cell division; where as growth is non-living objects occurs by the accumulation of materials. Ex: Mountains, boulders.
![]()
Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
What is meant by identification and nomenclature? How is a key helpful in the identification and classification of an organism?
Answer:
Identification: The determination of a collected organism whether is entirely new or already known, is called Identification.
Nomenclature: Providing a universal scientific name to an identified organism is called Nomenclature.
- Key is a taxonomical aid used for identification of plants and animals based on the similarities and dissimilarities.
- The keys based on the contrasting characters generally in a pair are called couplets.
- It represents the choice made between two opposite options. This results in acceptance of only one and rejection of the other.
- Each statement in the key is called a lead.
- In plants, identification can be done by directly comparing the characters with an authentic herbarium specimen or indirectly with the help of keys in floras.
- Separate taxonomic keys are required for each taxonomic category such as family, genus and species for identification purposes.
Question 2.
What are taxonomical aids? Give the importance of herbaria and museums.
Answer:
Taxonomical aids are the collection of actual specimens of plant and animal species.
These are used to preserve information regarding various species.
Ex: Herbarium, Botanical gardens, Zoological parks and Museums.
Herbarium is a store house of collected plant specimens that are dried, pressed and preserved on sheets.
- These sheets are arranged according to a universally accepted system of classification.
- These specimens, along with their descriptions become a store house for future use.
- The herbarium sheets carry a label providing information about the date and place of collection, local and botanical names, family, collector’s name etc.
- Herbaria also serve as quick referral systems in taxonomical studies.
Museum:
- Museums have collection of preserved plant and animal specimens for study and research.
- These are established in educational institutes such as schools and colleges.
- Specimens are preserved in the containers or jars in preservative solutions.
- Plant and animal specimens may also be preserved as dry specimens.
Question 3.
Define a taxon. Give some examples of taxa at different hierarchial levels.
Answer:
- Taxon is a unit or category in a taxonomic system.
- Classification involves hierarchy of steps in which each step represents a rank or category.
- All categories together constitute the taxonomic hierarchy.
Taxon Examples Kingdom
↑Plantae, Animalia Division
↑Spermatophyta, Bryophyta, Thallophyta Class
↑Dicotyledonae, Monocotyledonae Order
↑Sapindales, Poales Family
↑Anacardiaceae, Poaceae Genus
↑Mangifera, Triticum Species indica, vulgare
![]()
Question 4.
How are botanical gardens useful in conserving biodiversity? Define the terms Flora, manuals, monographs and catalogues.
Answer:
- Botanical gardens are the specialised gardens having collection of plants for scientific study, public education and recreation.
- Each plant is labelled with its common, botanical names and its family.
- They are provided with suitable soil and environmental conditions for growing the rate, endangered and endemic plant species. Hence, they are useful in conserving biodiversity.
- Flora is a book containing the actual account of habitat, distribution and systematic listing of plants of a given area.
- Manual is a small book specially designed for ready reference for identification of names of plant species of an area.
- Monograph is a specialist book written on a single (any one) taxon.
- Catalogue is a book useful for correct identification of plants.
Question 5.
Explain binomial nomenclature. [TS M 22]
Answer:
1) Binomial nomenclature: The system which provides a correct scientific name for a plant with two components is called binomial nomenclature.
2) The first one is generic name and second one is specific name (epithet).
3) Universal rules:
- The scientific name should be in Latin and must be underlined or printed in Italics.
- The generic name starts with a capital letter.
- The specific name starts with a small letter.
- Ex: The scientific name of ‘Brinjal’ is Solanum melongena.
- In this, Solanum is the name of the genus and melongena is the name of its species.
- Name of the author (the scientist who gave that name) may be written at the end.
Long Answer Questions
Question 1.
What is meant by ‘living’? Give a detailed account of any four defining features of life forms.
Answer:
The meaning of ‘living’ refers to the distinctive characters exhibited by living organisms like growth, reproduction, metabolism, ability to sense environment (consciousness), ability to self- replicate, interaction and emergence.
Defining features of life forms:
1) Metabolism:
- All living organisms are made of chemicals of different sizes and functions. They are constantly being made and changed into some other biomolecules. These conversions are called metabolic reactions.
- Thus, the ‘sum total’ of all chemical reactions occurring in the body is called metabolism.
- All plants, animals, fungi and microbes exhibit metabolism.
2) Consciousness:
- All living organisms are able to sense their surroundings.
- They respond to the environmental stimuli which may be physical, chemical or biological.
- Plants respond to external factors like light, water, temperature etc.
- Human being is the only one who is aware of himself i.e., has self consciousness.
3) Interactions:
- All living phenomena arise due to underlying interactions.
- Properties of tissues are due to the result of interactions among the cells.
- Properties of cellular organelles are not present in the molecular components comprising the organelle. Such under lying molecular interactions are also apparent in macro molecules such as starch.
- These interactions result in emergent properties of a higher level of organisation.
4) Reproduction:
- Reproduction refers to the production of progeny, possessing features more or less similar to those of parents.
- It is a characteristic feature of living organisms which is not found in non-living things.
- Organisms generally reproduce by sexual and asexual means.
- Fungi multiply and spread easily due to the production of a millions of asexual spores.
- In lower organisms like Yeast and Hydra, budding is observed.
- In unicellular forms like bacteria, amoeba and some unicellular algae, reproduction is synonymous with growth i.e., both refer to increase in the number of individuals.
- Certain organisms like mules, worker honeybees, infertile human couples do not reproduce.
Question 2.
Define the following terms with examples
(i) Class (ii) Family (iii) Order (iv) Genus (v) Division
Answer:
i) Class: A group of related orders constitutes class.
Ex: The class Dicotyledonae consists of oders like Mavales, Rosales, Polemoniales etc.
ii) Family: A group of related Genera is called family. Families are characterised on the basis both vegetative and reproductive features.
Ex: The family Soalnaceae consists of three different genera; Solanum, Nicotiana and Datura
iii) Order: Order is the assemblage of families which exhibit a few similar characters. The similar characters are less in number as compared to different genera included in a family. Ex:The order polemoniales based on the floral characters consists of Plant families like Cortvolvulaceae, Solanaceae.
iv) Genus: Genus is an aggregate of closely related species.
Ex: Genus Solanum consists of potato and brinjal.
v) Division (or) Phylum: A group of related classes is called Division.
Ex: The division spermatophyta consists of Dicotyledonae and Monocotyledonae with a few similar characters.
![]()
Exercise
Question 1.
Some of the properties of tissues are not constituents of their cells. Give two examples to support the statement.
Answer:
Some properties of tissues are not found in the constituent cells. They arise due to the interaction among the cells of which they are made of.
Examples:
- The properties of cellular organelles do not occur in molecular constituents of organelles.
- Collenchyma is a living mechanical tissue which provides tensile mechanical strength. But Sclerenchyma is a dead tissue, which is purely mechanical in function.
Question 2.
What do we learn from identification of individuals and populations?
Answer:
- Identification helps us to determine whether a collected plant is entirely new or already known.
- Identification is useful in agriculture, forestry to know our bioresources and their biodiversity.
- We can learn the scientific name and correct description from the identification of individuals.
Question 3.
Given below is the scientific name of Mango. Identify the correctly written name.
Mangifera Indica
Mangifera indica
Answer:
Mangifera indica (Because the scientific name should start with small letter ‘i’.)
Question 4.
Can you identify the correct sequence of taxonomicai categories?
a) Species, Order, Division, Kingdom
b) Genus, Species, Order, Kingdom
c) Species, Genus, Order, Phylum
Answer:
(c) Species, Genus, Order, Phylum
Question 5.
Define the following terms:
(i) Species (ii) Class (iii) Family (iv) Order (v) Genus
Answer:
i) Species: The species is a group ofindividual organisms with fundamental similarities.
ii) Class : A group of related orders constitutes class.
iii) Genus: It is an aggregate of closely related species. Among plants, potato and brinjal are two different species, but belong to the genus Solanum.
iv) Family: A group of related Genera is called family.
v) Order: Order is the assemblage of families which exhibit a few similar characters. vfiGenus: Genus is an aggregate of closely related species.
![]()
Question 6.
Illustrate the taxonomicai hierarchy with suitable examples of a plant.
Answer:
Taxonomicai hierarchy is the arrangement of organisms in a definite sequence of categories. In descending order, organisms are arranged from kingdom to species, where as in ascending order from species to kingdom.
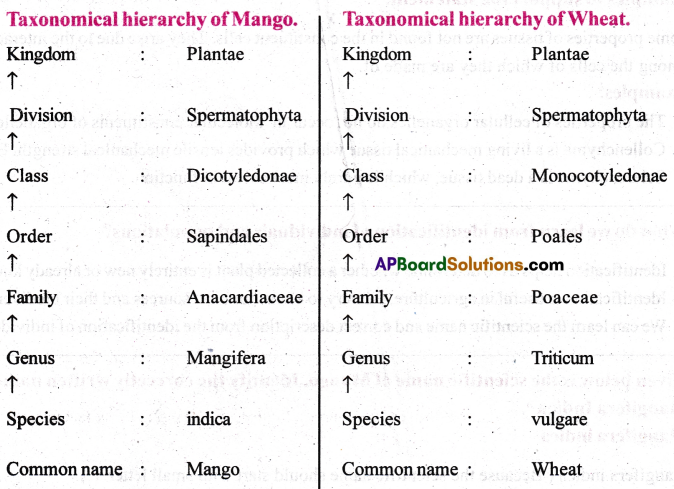
Question 7.
What are the distinctive characteristics exhibited by living organisms? Describe them in brief.
Answer:
The distinctive characters exhibited by living organisms are growth, reproduction, consciousness, metabolism, interaction and emergence.
1) Growth: In plants growth is by cell division. It occurs continuously throughout their life span. In animals, growth is seen only upto a certain age. Unicellular organisms also grow in size until they divide by cell division. Cell division occurs in certain tissues to replace lost cells.
2) Reproduction: Production of progeny possessing similar features to those of parents is called reproduction. It may be by vegetative, asexual and sexual methods.
3) Consciousness: All living organisms have the ability to sense their surroundings. This response is called irritability. Plants respond to external factors like light, temperature, water, pollutants etc. All living organisms are aware of their surroundings and this is called consciousness.
4) Metabolism: The sum total of all the chemical reactions occurring in the body of a living organism is called metabolism.
Question 8.
Life forms exhibit ‘unity in diversity’ – Discuss with your teacher.
Answer:
1) We see a large variety of living organisms around us such as potted plants, insects, birds, pets or other animals and plants. There are also several organisms that we cannot see with our naked eye.
2) If we were to increase the area that we make observations, the range and variety of organ¬isms would also increase. If we were to visit a dense forest, we would probably see a much greater number and kinds of living organisms in it.
3) Each different kind of plant, animal or any organism represents a species. The number of species that are known and described ranges between 1.7-1.8 million.
4) This refers to biodiversity or the number and types of organisms present on earth.
Question 9.
List out the principles followed to provide scientific names for newly found organism?
Answer:
Universal rules to provide scientific names for newly found organism:
- For a newly found organism there should be one specific scientific name.
- The scientific name should be in Latin and must be underlined or printed in Italics.
- The generic name starts with a capital letter.
- The specific name starts with a small letter.
- Name of the author( the scientist who gave that name) may be written at the end.
- Ex: The scientific name of ‘Brinjal’ is Solanum melongena.
- In this, Solanum is the name of the genus and melongena is the name of its species.
![]()
Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
Father of Botany is
1) Aristotle
2) Leeuwenhoek
3) Theophrastus
4) Linnaeus
Answer:
3) Theophrastus
Question 2.
A defining characteristic of living organisms is
1) Growth
2) Reproduction
3) Fragmentation
4) Response to external stimuli
Answer:
4) Response to external stimuli
Question 3.
The response to ‘environmental stimuli’ is called
1) Metabolism
2) Irritability
3) Chemical reaction
4) Consciousness
Answer:
2) Irritability
Question 4.
Which feature(s) cannot be taken as defining properties of living organisms
1) Metabolism
2) Growth
3) Reproduction
4) 2&3
Answer:
4) 2&3
Question 5.
All plants, animals, fungi and microbes exhibit
1) Self-consciousness
2) Metabolism
3) Sexual reproduction
4) Asexual reproduction
Answer:
2) Metabolism
Question 6.
Metabolic reaction involves
1) Synthesis ofbiomolecules only
2) Breakdown of some biomolecules only
3) All physical changes which occur in objects around us
4) All chemical reactions which occur inside an organism
Answer:
4) All chemical reactions which occur inside an organism
Question 7.
Which of the following is incorrect regarding reproduction
1) Unicellular organisms reproduce by cell division
2) Reproduction is a characteristic of all living organisms
3) In unicellular organisms, reproduction and growth are linked together
4) Non – living objects are incapable of reproducing
Answer:
2) Reproduction is a characteristic of all living organisms
Question 8.
Identify the organism which do not show the reproduction
1) Yeast
2) Sterile worker bee
3) Amoeba
4) Fertile human couple
Answer:
2) Sterile worker bee
Question 9.
In plants, cell growth occurs……whereas in animals, it occurs
1) only upto a certain age, continuously
2) continuously, only upto a certain age
3) continuously in both
4) only upto a certain age in both
Answer:
2) continuously, only upto a certain age
![]()
Question 10.
Number of species that are known and described lie between
1) 1.2 —1.3 million
2) 1.7 -1.8 billion
3) 1.2-1.3 billion
4) 1.7-1.8 million
Answer:
4) 1.7-1.8 million
Question 11.
The first step in taxonomy is
1) Nomenclature
2) Identification
3) Description
4) Classification
Answer:
2) Identification
Question 12.
ICBN stands for
1) International code of Botanical Nomenclature
2) International Congress of Biological Names.
3) Indian code of Botanical Nomenclature
4) Indian Congress of Biological Names
Answer:
1) International code of Botanical Nomenclature
Question 13.
Phylogenetic system of classification is based on
1) morphological features
2) chemical constituents
3) floral characters
4) evolutionary relationships
Answer:
4) evolutionary relationships
Question 14.
Which one of the following is not universal rule of nomenclature?
1) Biological names are printed in italics, irrespective of their origin
2) First word represents genus while the second component denotes specific epithet
3) Both the words when handwritten, are separately underlined
4) The first word and specific epithet starts with a capital letter
Answer:
4) The first word and specific epithet starts with a capital letter
Question 15.
The term ‘Systematics’ refers to
1) Identification and study of organ systems
2) Identification and preservation of plants and animals
3) Diversity of kinds of organisms and their relation ship
4) Study of habitats of organisms and their classification
Answer:
3) Diversity of kinds of organisms and their relation ship
Question 16.
A taxonomic category refers to
1) The basic unit of classification
2) A rank or level in a taxonomic hierarchy
3) Group of related organisms able to interbreed
4) A group of related organisms but unable to interbreed
Answer:
2) A rank or level in a taxonomic hierarchy
Question 17.
Each category found in taxonomic hierarchy is known as
1) Genus
2) Family
3) Species
4) Taxon
Answer:
4) Taxon
Question 18.
The fundamental taxonomic category or basic unit of classification is
1) Genus
2) Species
3) Sub-species
4) Variety
Answer:
2) Species
![]()
Question 19.
The highest taxon in taxonomic hierarchy is
1) Species
2) Genus
3) Order
4) Kingdom
Answer:
4) Kingdom
Question 20.
Genus represents
1) An individual plant or animal
2) A collection of plants or animals
3) Group of related species of plants or animals
4) A group of plants in a given area
Answer:
3) Group of related species of plants or animals
Question 21.
In a taxonomic hierarchy, family is interpolated between
1) kingdom and class
2) class and order
3) order and genus
4) class and genus
Answer:
3) order and genus
Question 22.
The taxon which includes related families is
1) class
2) phylum
3) order
4) genus
Answer:
3) order
Question 23.
Identify the correct sequence of taxonomic categories.
1) Species → phylum → order → kingdom
2) Genus → Species → Order → kingdom
3) Species → Genus → Order → Class
4) Division → Family → Order → Genus
Answer:
3) Species → Genus → Order → Class
Question 24.
Select the correct matching related to man
1) Genus-Homonidae
2) Order-Primata
3) Family-Mammalia
4) Division-Chordata
Answer:
2) Order-Primata
Question 25.
Identify the correct matching
1) Tiger-tigris, species
2) Cuttlefish-mollusca, elass
3) Humans-primata, family
4) Housefly-Musca, order
Answer:
1) Tiger-tigris, species
Question 26.
Collection of plants that are dried, pressed and preserved on sheets is called
1) Herbarium
2) Botanical gardens
3) Museums
4) Zoological parks
Answer:
1) Herbarium
Question 27.
Quick referral system in taxonomic studies is
1) Botanical garden
2) Herbarium
3) Monograph
4) Manual
Answer:
1) Botanical garden
![]()
Question 28.
The largest Herbarium of the world is
1) Royal Botanical Gardens
2) Museum of Natural history
3) Indian Botanical Garden
4) National Botanical Gardens
Answer:
1) Royal Botanical Gardens
Question 29.
The label of a Herbarium sheet does not carry information on
1) date of collection
2) name of collector
3) local names
4) height of the plant
Answer:
4) height of the plant
Question 30.
The famous international Botanical garden is at
1) England
2) USA
3) Holland
4) India
Answer:
1) England
Question 31.
Botanical gardens have
1) Living plants and animals for reference
2) Collection of living plants for reference
3) Preserved plant specimens
4) Living and preserved plants
Answer:
2) Collection of living plants for reference
Question 32.
Botanical gardens mainly serve the purpose of providing
1) Beautiful area of reaction
2) Reservoir for tropical plants
3) Ex situ conservation of germplasm
4) Natural habitat for wild life
Answer:
4) Natural habitat for wild life
Question 33.
Museums have
1) Preserved specimens of plants and animals
2) Collections of living plants and mammals only
3) Skeletons of animals only
4) Collected and dried plant specimens only
Answer:
1) Preserved specimens of plants and animals
Question 34.
Algae are preserved in
1) Flora
2) Museum
3) Zoo
4) Pune
Answer:
2) Museum
![]()
Question 35.
Taxonomic keys are. based on the
1) Morphological characters
2) Reproductive characters
3) Anatomical characters
4) Contrasting characters
Answer:
4) Contrasting characters
Question 36.
Each statement in the key is called
1) Set
2) Lead
3) Cement
4) Statement
Answer:
2) Lead
Question 37.
A pair of contrasting characters in keys are called
1) Doublet
2) Duplet
3) Couplet
4) Triplet
Answer:
3) Couplet
Question 38.
Lead is a (an)
1) statement in the key
2) information given in floras
3) contrasting character in the key
4) description of a single taxon
Answer:
1) statement in the key
Question 39.
Taxonomic key is one of the taxonomic tools in the identification and classification of plants and animals. It is used in the preparation of
1) Museums
2) Flora
3) Both 1&2
4) Neither (1) nor (2)
Answer:
2) Flora
Question 40.
Biological organisation starts with
1) Cellular level
2) Organismic level
3) atomic level
4) submicroscopic molecular level
Answer:
4) submicroscopic molecular level
Question 41.
……….group of organisms multiply by fragmentation
1) Amoeba, fungi
2) Fungi, bacteria .
3) Fungi,filamentous algae, protonema of mosses
4) Amoeba, Hydra, bacteria
Answer:
3) Fungi,filamentous algae, protonema of mosses
Question 42.
The organisms which do not reproduce are
i) Mules ii) Sterile worker bees iii) Infertile human couples
1) i and ii only
2) i and iii only
3) ii and iii only
4) i, ii and iii
Answer:
4) i, ii and iii
![]()
Question 43.
When organisms are in the same class but not in same family, the taxonomic term is called as
1) Order
2) Genus
3) Family
4) Species
Answer:
1) Order
Question 44.
Potato, tomato, brinjal differ in… …taxon
1) Species
2) Genus
3) Family
4) Order
Answer:
1) Species
Question 45.
As we go from species to kingdom in a taxonomic hierarchy, the number of common characteristics
1) will decrease
2) will increase
3) remain same
4) may increase (or) decrease
Answer:
1) will decrease
Question 46.
The taxonomic aid, key is
1) Useful in classification of plants and animals
2) Based on similarities and dissimilarities
3) Common for identification of taxonomic categories like family, genus
4) An index to flora of particular area
Answer:
3) Common for identification of taxonomic categories like family, genus
![]()
Question 47.
Collections of preserved plant and animal specimens for study and reference are kept in
1) Museum
2) Botanical Garden
3) Zoological Park
4) Herbarium
Answer:
1) Museum