Students can go through AP Board 7th Class Maths Notes Chapter 12 Quadrilaterals to understand and remember the concepts easily.
AP State Board Syllabus 7th Class Maths Notes Chapter 12 Quadrilaterals
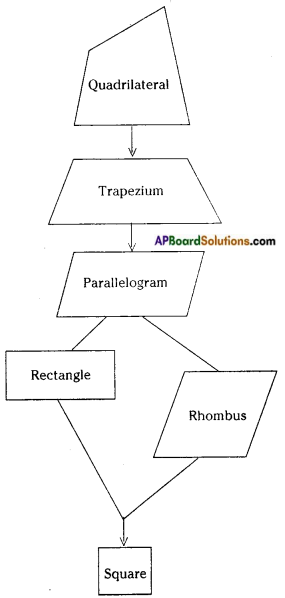
→ Quadrilateral: A closed figure bounded by four line segments is called a quadrilateral.
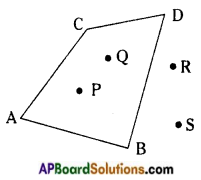
In the figure, ABCD is a quadrilateral.
→ A quadrilateral divides a plane into three parts.
i) Interior of the quadrilateral
ii) Exterior of the quadrilateral
iii) Boundary of the quadrilateral
→ In the figure the points P, Q are in the interior of the quadrilateral. i3r In the figure the points R, S are in the exterior of the quadrilateral.

→ In the figure the points A, B, C, D are on the boundary of the quadrilateral.
→ A quadrilateral is said to be a convex quadrilateral if all line segments joining points in the interior of it also lie in its interior completely.
□ BELT is a convex quadrilateral.
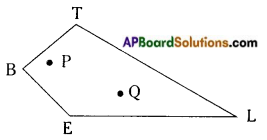
→ A quadrilateral is said to be a concave quadrilateral if all line segments joining points in the interior of it do not necessarily lie in its interior completely.
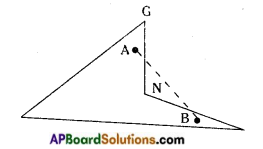
In □ RING, the line segment \(\overline{\mathrm{AB}}\) does not lie completely in its interior, as such the quadrilateral RING is a concave quadrilateral.
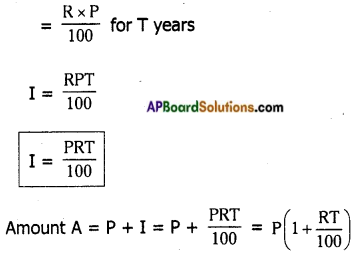
→ Sum of the interior angles of a quadrilateral is 360°.
∠A + ∠B + ∠C + ∠D = 360°
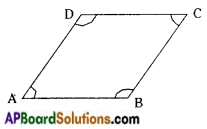
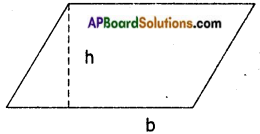
→ A quadrilateral in which one pair of opposite sides are parallel is called a trapezium.
In □ ABCD ; AB // CD


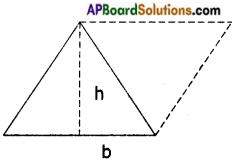
→ A kite has four sides. There are exactly two distinct pairs of equal length.
In quadrilateral KITE,
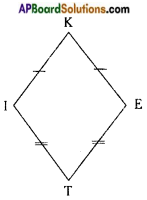
KI = KE and IT = ET
→ A quadrilateral in which both pairs of opposite sides are parallel is called a parallelogram. In quadrilateral ABCD,
AB // CD and AD // BC. Hence □ ABCD is a parallelogram.
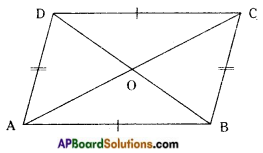
→ In a parallelogram,
- Opposite sides are parallel and equal [AB = CD and AD = BC]
- Diagonals bisect each other (AO = OC and BO = OD)
- Opposite angles are equal (∠A = ∠C and ∠B = ∠D)
- Adjacent angles are supplementary (∠A + ∠B = ∠B + ∠C = ∠C + ∠D = ∠D + ∠A = 180°)

→ A parallelogram in which adjaœnt sides are equal is called a Rhombus.
In quadrilateral ABCD,
AB = BC = CD = DA and hence □ ABCD is a Rhombus.
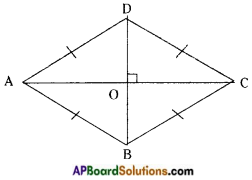
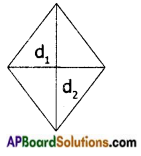
In a rhombus diagonals bisect each other at right angles,
(i.e.) AC ⊥ BD and AO = OC, BO = OD
→ A rectangle is a parallelogram with equal angles (OR)
A parallelogram in which one angle is a right angle is called a rectangle.

In fig. ∠A = ∠B = ∠C = ∠D = 90° and □ ABCD is a rectangle.
In a rectangle the diagonals are equal.
In a rectangle the diagonals bisect each other.
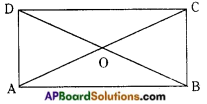
(AC = BD and AO = OC; BO = OD)
→ A square is a rectangle with equal adjacent sides.
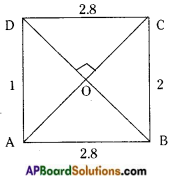
In the figure AB = BC = CD = DA
∠A = ∠B = ∠C = ∠D = 90°
In a square the diagonals are equal and bisect at right angles. Also they are equal.
[(AO = OC ; BO = OD), (AC ⊥ BD) and (AC = BD)]

Flow chart of family of quadrilaterals