Students can go through AP Board 6th Class Maths Notes Chapter 6 Basic Arithmetic to understand and remember the concepts easily.
AP State Board Syllabus 6th Class Maths Notes Chapter 6 Basic Arithmetic
→ If a comparison is made by finding the difference between two quantities, it is called comparison by difference.
Eg: Age of Harshita is 11 years and age of Srija is 8 years. Harshita is (11 – 8 = 3) 3 years older than Srija or Srija is 3 years younger than Harshita.
→ If a comparison is made by division it makes more sense than the comparison made by taking the difference.
Eg: If cost a key pad cell phone is Rs. 3000 and another smart phone is Rs. 15000, then the cost of the second phone is five times the cost of the first phone.
![]()
→ Ratio: Comparison of two quantities of the same type by virtue of division is called ratio. Eg: The weight of Ramu is 24 kg and the weight of the Gopi is 36 kg., then the ratio of weights is 24/36. It can also be written as 24:36 and read as 24 is to 36.
The ratio of two numbers ‘a’ and ‘b’ (b ≠ 0) is a ÷ b or a/b or \(\frac{a}{b}\) and is denoted as a : b and is read as a is to b.
In the ratio a : b the quantities a and b are called the terms of the ratio.
In the ratio a : b the quantity a is called the first term or antecedent and b is called the second term or the consequent of the ratio.
The value of a fraction remains the same if the numerator and the denominators are multiplied or divided by the same non-zero number so is the ratio.
That is if the first term and the second term of a ratio are multiplied or divided by . the same non-zero number.
3 : 4 = 3 × 5 : 4 × 5 = 15 : 20
Also 36 : 24 = 36 – 4 : 24 – 4 = 9 : 6.
→ Ratio in the simplest form or in the lowest terms:
A ratio a : b is said to be in its simplest form if its terms have no factors in common other than 1. A ratio in the simplest form is also called the ratio in its lowest terms. Generally ratios are expressed in their lowest terms.
To express a given ratio in its simplest term, we cancel H.C.F. from both its terms. To find the ratio of two terms, we express the both terms in the same units.
Eg: Ratio of 3 hours and 120 minutes is 3 : 2 (as 120 minutes = 2 hours) or 180 : 120 (as 3 hours = 180 minutes)
A ratio has no units or it is independent of units used in the quantities compared. The order of terms in a ratio a : b is important a : b ≠ b : a.
→ Equivalent ratio:
A ratio obtained by multiplying or dividing the antecedent and consequent of a given ratio by the same number is called its equivalent ratio.
Eg: 3 : 4 = 3 × 5 : 4 × 5 = 15 : 20. Here 3 : 4 & 15 : 20 are called equivalent ratios.
Also 36 : 24 = 36 ÷ 4 : 24 ÷ 4 = 9 : 6. Here 36 : 24 & 9 : 6 are called equivalent ratios.
![]()
→ Comparison of ratios: To compare two ratios
a) First express them as fractions
b) Now convert them to like fractions
c) Compare the like fractions
→ Proportion:
If two ratios are equal, then the four terms of these ratios are said to be in proportion. If a : b = c : d, then a, b, c and d are said to be in proportion.
This is represented as a : b :: c : d and read as a is b is as c is d.
The equality of ratios is called proportion.
Conversely in the proportion a : b :: c : d , the terms a and d are called extremes and b and c are called means.
If four quantities are in proportion, then
Product of extremes = Product of means .
If a : b :: c : d, then a × d = b × c
From this we have

→ Unitary method:
The method in which first we find the value of one unit and then the value of required number of units is known as unitary method.
Eg: If the cost of 8 books Rs.96, then find the cost of 15 books.
Cost of one book = 96/8 = 12 Cost of 15 books = 12 × 15 = 180
Distance travelled in a given time = speed × time From this we have
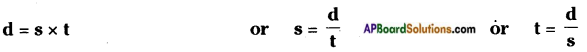
![]()
→ Percentage:
The word per cent means for every hundred or out of hundred. The word percentage is derived from the Latin language. The % symbol is uses to represent percent.
Eg: 5% is read as five percent
5% = \(\frac{5}{100}\) = 0.05
38% = \(\frac{38}{100}\) = 0.38
→ To convert a percentage into a fraction:
a) Drop the % symbol
b) Divide the number by 100
Eg: 25% = \(\frac{25}{100}\) = 0.25 = \(\frac{1}{4}\)
→ To convert a fraction into percentage:
a) Assign the percentage symbol %
b) Multiply the given fraction with 100
Eg: \(\frac{3}{4}\) = \(\frac{3}{4}\) × 100% = 75% = 0.75