Timed practice with TS 10th Class Physical Science Model Papers and TS 10th Class Physical Science Question Paper April 2023 is crucial for improving speed and efficiency during exams.
TS 10th Class Physical Science Question Paper April 2023
Time: 1 Hour 30 minutes
Maximum Marks: 40
General Instructions:
- Read the question paper and understand every question thoroughly and write answers in given 1.30 min. time.
- 3 very short answer questions are there in section – I. Each question carries 2 marks. Answer all the questions. Write answer to each question in 3 to 4 sentences.
- 3 short answer questions are-there in section – II. Each question carries 4 marks. Answer all the questions. Write answer to each question in 5 to 6 sentences.
- 3 essay type answer questions are there in section – III. Each question carries 6 marks. Answer any two questions. Write answer to each question in 8 to 10 sentences.
Part – A (30 Marks)
Section – I (3 × 2 = 6 Marks)
Instructions :
- 3 Very short answer questions are there in this section – I.
- Answer ALL the questions. Each question carries 2 marks.
- Write answer to each question in 3 to 4 sentences.
Question 1.
Mention uses of Nanotubes which is an allotrophy form of Carbon in day to day life.
Answer:
Carbon nanotubes have several uses, such as in electronics for making transistors, in materials to make them stronger and lighter, in batteries to enhance their capacity, and in medicine for drug delivery.
Question 2.
List out the material required in the experiment “Reaction of acids with metals”.
Answer:
The materials required for the “Reaction of acids with metals” experiment would typically include a suitable acid (like hydrochloric acid or sulfuric acid), a metal (like zinc or magnesium), a test tube, and safety equipment.
Question 3.
What will happen if household electric appliances are connected in series connection ?
Answer:
If household electric appliances are connected in series, they would share the total voltage supply, which could cause them to operate improperly or not operate at all. Also, if one device fails, it would break the circuit and all devices would stop working.
Section – II (3 × 4 = 12 Marks)
Instructions :
- 3 Short answer questions are there in section – II.
- Answer ALL the questions. Each question carries 4 marks.
- Write answer to each question in 5 to 6 sentences.
Question 4.
Write the uses of Washing Soda in day life.
Answer:
Washing soda, also known as sodium carbonate, is used for various purposes in day-to-day life. Here are some of its uses :
- Laundry Detergent : Washing soda is commonly used as a laundry detergent, it helps to remove tough stains and grime from clothes.
- Cleaning Agent : It is used as a general household cleaner. It’s particularly effective on tough stains in sinks, tiles, and grout.
- Water Softener : Washing soda can be added to hard water to ‘soften’ it. It does this by combining with the calcium and magnesium ions present in the hard water and precipitating them out.
- Dishwasher Soap : It can also be used in dishwashers as a detergent, or as a rinse aid to prevent spots and film from forming on dishes and glasses in the rinse cycle.
- Garden Use : Washing soda can alter the pH of soil when gardening, making it less acidic, which is beneficial for certain types of plants.
- Unclog Drains : Washing soda can be used to unclog drains. When combined with vinegar, it creates a reaction that can help to break up the clog.
![]()
Question 5.
Observe the given table and answer the following questions.

i) Which period does the elements belongs ?
ii) Mention the non-metals in the above.
iii) Which elements has more atomic radius in the above ?
iv) From left to right how is the metallic character changes ?
v) From left to right how is the metallic character changes ?
Answer:
i) The elements belong to the third period of the Periodic Table.
ii) The non-metals in the given list are Phosphorus (P), Sulfur (S), and Chlorine (Cl).
iii) As a general trend, atomic radius decreases across a period from left to fight in the periodic table. So in this list, Sodium (Na) would have the largest atomic radius.
iv) As we move from left to right across a period in the periodic table, the metallic character decreases. This is because the number of valence electrons increases, which increases the ability to attract electrons (electronegativity), leading to a decrease in metallic character. So in the given elements, Na is the most metallic, and as we move to the right, the metallic character decreases, with Cl being the least metallic.
Question 6.
During the. Sunset and Sunrise, Sun appears red. Why?
Answer:
The Sun appears red during sunrise and subset due to a phenomenon called Rayleigh scattering. This scattering affects short-wavelength light (like blue and violet) more than long-wavelength light (like red and orange). Therefore, when the Sun is near the horizon, its light has to pass through more of Earth’s atmosphere, causing the blue and violet light to be scattered out, leaving the red and orange light visible.
Section – III (2 × 6 = 12 Marks)
Instructions :
- 3 Essay type questions are there in this section.
- Answer any two questions. Each question carries 6 marks.
- Write answer to each question in 8 to 10 sentences.
Question 7.
List out the material required to observe the types of images and measuring the object distance and image distance from Concave mirror. Explain the experimental procedure.
Answer:
Materials needed : A concave mirror, an object (like an arrow), a white screen or paper, and a ruler.
Procedure:
- Set up the concave mirror on a stand.
- Place the white screen or paper a bit far away from the mirror.
- Take the object (arrow) and hold it in front of the mirror at a certain distance.
- Look through the mirror and find the image of the object on the screen.
- Measure the distance from the object to the mirror (object distance – u) and the distance from the mirror to the image on the screen (image distance – v).
Explanation: A concave mirror is curved inward like a bowl. When light from the object reflects off the mirror, it comes together to form an image. The distance from the object to the mirror is called the object distance (u), and the distance from the mirror to the image is the image distance (v).
By changing the object distance and observing the image, we can learn about how the mirror works. If the object is closer to the mirror than a certain point (the focal point), the image will be bigger and seem closer to the mirror. If the object is farther away, the image will be smaller and appear beyond the focal point.
This experiment helps us understand how concave mirrors create images and lets us measure distances to calculate the focal length of the mirror.
Question 8.
Draw the ray diagram to form the image when the object is placed between F and C on the principle axis of a Convex lens. Write the characteristics of the image formed.
Answer:
Ray Diagram:
- Draw the principal axis of the lens, which is a straight line passing through the center of the lens (O) and perpendicular to the lens surfaces.
- Mark the focal point (F) on both sides of the lens. The focal point on the side where the object is located is called “F'”. The other side’s focal point is called “F”.
- Place the object (arrow or an upright image) between F and C on the principal axis. The object should be positioned closer to F but on the same side as F’.
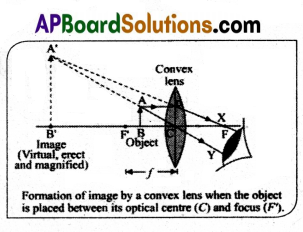
Draw three principal rays:
a) A ray parallel to the principal axis that passes through F (refracts and travels through F’).
b) A ray that passes through the center of the lens (O) – it continues in the same direction.
c) A ray that passes through F’ (refracts and travels through F).
The point where the refracted rays intersect will be the position of the image formed by the convex lens.
Characteristics of the Image:
Position : The image will be formed on the same side as the object, between the focal point (F’) and the lens (closer to F’).
Orientation : The image will be inverted (upside down).
Size : The size of the image will be smaller than the size of the object.
Nature : The image will be real, as it is formed by the actual intersection of refracted rays.
Type : The image will be a diminished and inverted real image.
For a convex lens, when the object is placed between F and C, the image will always be real, inverted, and smaller than the object.
Question 9.
Explain the formation of N2 molecule by using Valence bond theory.
Answer:
The formation of the nitrogen (N2) molecule can be explained using the Valence Bond Theory, which describes the chemical bonding in terms of overlapping atomic orbitals. Nitrogen is a diatomic molecule, and the N2 bond arises from the combination of two nitrogen atoms.
In the Valence Bond Theory, each nitrogen atom has three half-filled p-orbitals in addition to its three filled sp2 hybrid orbitals. The N2 molecule is formed by the overlap of the two unhybridized p-orbitals from each nitrogen atom. The formation of the nitrogen molecule can be explained as follows:
1. Promotion of electrons : In the ground state of a nitrogen atom, the electronic configuration is 1s2 2s2 2p3. To form a sigma (σ) bond, one of the electrons from the 2s orbital is promoted to the 2p orbital. The electronic configuration becomes 1s2 2s1 2p4, where there are three unpaired electrons available for bonding.
2. Orbital overlap : When two nitrogen atoms approach each other to form a molecule, their 2p orbitals align parallel to each other. The unpaired electrons in these orbitals then overlap sideways, resulting in the formation of a sigma (σ) bond between the two nitrogen atoms.
3. Electron pairing : Due to the overlap, the two unpaired electrons from each nitrogen atom pair up, forming a stable a bond. This bond consists of two electrons shared between the two nitrogen atoms.
4. Triple bond formation : The N2 molecule contains a triple bond because, in addition to the
sigma bond, there is also a pi (π) bond formed by the sideways overlap of the remaining two p orbitals that are perpendicular to the internuclear axis.
The molecular orbital diagram for N2 is as follows :
σ* (antibonding)____π*(antibonding) ↑↑σ (bonding)____ π(bonding)
The formation of the nitrogen molecule (N2) is accomplished through the overlap of two unhybridized p orbitals from each nitrogen atom, resulting in the formation of a sigma (σ) bond and a pi (π) bond between the two atoms. The triple bond between the nitrogen atoms contributes to the stability and strength of the N2 molecule.
![]()
Part – B (10 × 1 = 10 Marks)
Instructions :
- Answer ALL the questions.
- Each question carries 1 mark.
- In this section there are 4 options (A / B / C / D) to each question, choose the appropriate answer and write the answer in the brackets given against the question.
- Part – B must be attached to the.answer booklet of Part – A.
Question 1.
Which of the following orbitals represents n = 3, l = 0 quantum numbers ?

Answer:
C
Question 2.
The number of Oxygen atoms took part in the following chemical reaction
2Cu2S + 3O2 → 2Cu2O + 2SO2
A) 4
B) 5
C) 6
D) 12
Answer:
C) 6
Question 3.
The resultant resistance of a parallel connection of two resistors of resistance 2Ω and 3Ω is ……………
A) 1.2 Ω
B) 1.5 Ω
C) 0.66 Ω
D) 0.33 Ω
Answer:
A) 1.2 Ω
Question 4.
Modem Periodic Table is constructed based on the properties of the elements is ……………..
A) atomic weight
B) atomic number
C) atomic mass number
D) number of neutrons
Answer:
B) atomic number
Question 5.
If you place a bar magnet inside the Copper coil steadily, then which of the following statement is true ?
A) Current induced in the coil.
B) Current does not induced in the coil.
C) Magnetic field produced by the coil.
D) Current and Magnetic field both produced in the coil.
Answer:
B) Current does not induced in the coil.
Question 6.
IUPAC name of the following Carbon compound is …………….
CH3 – CH = CH – CHCl – CH2OH
A) 2 – chloro – pent – 3 – ene – 1 – ol
B) 4 – chloro – pent – 2 – ene – 5 – ol
C) 2 – chloro – pent – 2 – ene – 1 – ol
D) 4 – chloro – pent – 3 – ene – 1 – ol
Answer:
A) 2 – chloro – pent – 3 – ene – 1 – ol
![]()
Question 7.
Which of the following is not a Concentration method of Ore ?
A) Hand picking
B) Froth floatation
C) Magnetic separation method
D) Polling
Answer:
D) Polling
Question 8.
Maximum focal length of a human eye lens is …………….
A) 0.27 cm
B) 25 cm
C) 2.27 cm
D) 2.50 cm
Answer:
D) 2.50 cm
Question 9.
The quantum number represents the size and energy of the main shell is …………….
A) m1
B) ms
C) n
D) l
Answer:
C) n
Question 10.
The device which converts electric energy into mechanical energy is …………….
A) Electric motor
B) Generator
C) Ammeter
D) Galvanometer
Answer:
A) Electric motor