Students must rely on TS 10th Class Biology Model Papers TS 10th Class Biology Model Paper April 2023 to gauge their understanding of exam patterns.
TS 10th Class Biology Model Paper April 2023
Time: 1:30 hours
Max. Marks:40
Instructions:
- Read the question paper carefully and understand it.
- Answer the questions under Part – A in the answer sheet provided.
- Part – A contains three sections: sections – i, ii, and iii.
- Part-B Answers should be written in the given brackets and attached to the Part-A answer sheet.
- Write the answers by following the instructions given in the each section.
Part – A (Marks 30)
Section – I (3 x 2 = 6M)
Question 1.
Write two materials required to conduct an experiment to prove Sunlight is essential for Photosynthesis.
Answer:
Two materials required to conduct an experiment to prove Sunlight is essential for Photosynthesis a potted plant and iodine solution.
Question 2.
Name two fossil fuels that are used in daily life.
Answer:
Two fossil fuels that are used in daily life Petroleum and Natural gas.
![]()
Question 3.
What will happen if there is no mucus in the Oesophagus?
Answer:
If there is no mucus in the Oesophagus, it will be difficult for food to slide down into the stomach. The mucus also protects the lining of the esophagus from stomach acids during digestion.
Section – II (3 × 4 = 12 M)
Instructions:
- This section contains 3 short answer questions.
- Answer ALL the questions.
- Write the answers in 5 – 6 sentences.
- Each question carries 4 marks.
Question 4.
Write four differences between arteries and veins.
Answer:
- Arteries carry blood away from the heart, while veins carry blood towards the heart.
- The blood in arteries is oxygenated, except for the pulmonary artery. The blood in veins is deoxygenated, except for the pulmonary veins.
- Arteries have thick, muscular walls to withstand pressure, while veins have thinner walls.
- Veins have valves to prevent backflow of blood, while arteries do not.
Question 5.
Name any four secondary metabolites that are used in daily life and write their uses.
Answer:
- Caffeine (used as a stimulant in coffee and tea)
- Nicotine (used in tobacco products)
- Morphine (used as a painkiller)
- Quinine (used to treat malaria)
Question 6.
Observe the following table.
| Vitamin | Deficiency disease | Symptoms |
| Thiamin | Beri Beri | vomitings, difficulty in breathing. |
| Retinol | Eye and skin diseases | Night blindness, Cornea failure, Xerophthalmia. |
| Tocopherol | Fertility-related disorders | Sterility in males, abortions in females. |
| Niacin | Pellagra | Dermatitis, diarrhea, loss of memory. |
Answer the following questions based on the given table.
i) Name two water-soluble vitamins from the table.
ii) Write two fat-soluble vitamins from the table.
iii) Which vitamin from the given table is called vitamin ‘E’?
iv) Write any one deficiency disease caused due to deficiency of vitamin ‘A’.
Answer:
i) Two water-soluble vitamins from the table: Thiamin (Vitamin B1) and Niacin (Vitamin B3).
ii) Two fat-soluble vitamins from the table: Retinol (Vitamin A) and Tocopherol (Vitamin E).
iii) The vitamin from the given table that is called Vitamin E’ is Tocopherol.
iv) A deficiency disease caused due Lo deficiency of Vitamin A’ (Retinol) is Night blindness.
Section-III (2 x 6 = 12 M)
Instructions:
- This section contains 3 essay-type questions.
- Answer ANY TWO questions.
- Write the answer in 8 to 10 sentences.
- Each question carries 6 marks.
Question 7.
Explain the various stages of Mitosis.
Answer:
Mitosis is the process of cell division that ensures the equal distribution of replicated chromosomes to two daughter cells. It consists of several distinct stages, each crucial for the accurate separation of genetic material. The stages of mitosis are as follows:
1. Prophase: Prophase marks the beginning of mitosis. During this stage, the chromatin (a complex of DNA ami proteins) condenses and becomes visible as individual chromosomes. Each chromosome consists of two sister chromatids, connected by a structure called the centromere. The nuclear envelope starts to break down, and the mitotic spindle, composed of microtubule les, begins to form.
2. Metaphase: In this stage, the chromosomes align at the cell’s equator, forming a single plane known as the metaphase plate. The spindle fibers attach to the centromeres of each chromosome, ensuring they are correctly positioned for the subsequent separation.
3. Anaphase: During anaphase, the centromere holding the sister chromatids together splits, and the spindle fibers shorten. As a result, the sister chromatids are pulled apart towards opposite poles of the cell. Once separated, each chromatid is considered an individual chromosome.
4. Telophase: Telophase is the final stage of mitosis. In this stage, the chromosomes reach opposite ends of the cell and start to decondense back into chromatin. The nuclear envelope reforms around each set of chromosomes, creating two distinct nuclei. Meanwhile, the mitotic spindle breaks down, and the cell prepares for cytokinesis.
![]()
Question 8.
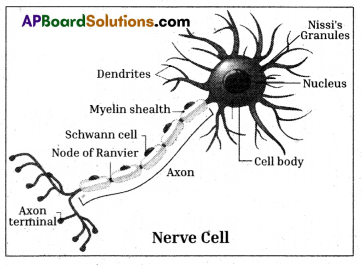
Draw a labelled diagram of a Nerve cell and explain the structure.
Answer:
A nerve cell, or neuron, is the fundamental unit of the nervous system. It is responsible for transmitting electrical signals (nerve impulses) between different parts of the body. Below is a labelled diagram of a typical neuron, followed by an explanation of its key structures.
Structure of a Neuron:
- Cell Body (Soma): The main part of the neuron containing the nucleus and most of the cellular organelles.
- Dendrites: Branch-like extensions that receive signals from other neurons or sensory receptors.
They function to transmit these signals toward the dendrite cell body. - Axon: A long, slender extension that carries nerve impulses away from the cell body and towards other neurons, muscles, or glands.
- Axon Hillock: The region where the axon originates from the cell body. It plays a crucial Axon role in initiating the nerve impulse.
- Myelin Sheath: A fatty, insulating layer that surrounds some axons. It helps to increase the speed of nerve impulse conduction.
- Nodes of Ranvier: Gaps in the myelin sheath along the axon. They are essential for the rapid transmission of nerve impulses. ,
- Axon Terminals (Synaptic Terminals): Small branches at the end of the axon that communicate with the next neuron or target cell through synaptic connections.
Question 9.
Explain the procedure and results of the experiment that proves “Heat is released during Respiration”.
Answer:
The experiment to demonstrate that heat is released during respiration can be conducted using a simple setup involving germinating seeds. here’s a step-by-step procedure, along with an explanation of the expected results.
Materials:
- Germinating seeds (e.g.: mung beans),
- Non-germinating seeds (e.g.: dry mung beans)
- Thermometer,
- Two identical insulated containers with lids (e.g.: Styrofoam cups),
- Water,
- Adhesive tape
Procedure:
- Take two identical insulated containers and label them as Container A and Container B.
- Place a thermometer through the lid of Container A and secure it in place using adhesive tape. Make sure the thermometer’s bulb is positioned at the center of the container.
- Fill Container A with a known quantity of germinating seeds (e.g.: mung beans) that have been soaked in water overnight.
- Fill Container B with the same quantity of non-germinating seeds (e.g.: dry mung beans).
- Close the lids of both containers tightly.
- Allow both containers to stand for an equal amount of time, such as 24 hours, in a room at a constant temperature.
- After the specified time, record the temperature inside both containers using the thermometer.
Results: During the 24-hour period, the germinating seeds in Container A undergo cellular respiration, which involves the breakdown of glucose to produce energy in the form of ATP (adenosine triphosphate). This process releases heat as a byproduct. On the other hand, the non-germinating seeds in Container B do not respire actively and therefore do not release heat to the same extent.
As a result, you would expect to see that the temperature inside Container A, containing the germinating seeds, is higher than the temperature inside Container B which has non-germinating seeds. This difference in temperature demonstrates that heat is indeed released during respiration, confirming the exothermic nature of this cellular process.
Part – B (Marks 10)
Instructions:
- Write the answers to the questions under Part – B on the question paper itself and attach it to the answer book of Part – A.
- Each question carries 1 mark.
- Marks will not be awarded in any case of overwriting. rewritten or erased answers.
- Write the capital letter (A, B, C, D) showing the correct answer for the following questions in the brackets provided against them.
Question 1.
Identify the material used to conduct the acid and leaf experiment to explain the mucus role in the stomach. ( )
A) Vaseline
B) Oil
C) Glucose
D) Yeast
Answer:
A) Vaseline
![]()
Question 2.
The artificial propagation method used to produce the plants with desirable characters. ( )
A) Cutting
B) Layering
C) Grafting
D) Stolons
Answer:
Question 3.
Identify the theory proposed by Charles Darwin form the following. ( )
A) Law of Dominance.
B) Inheritance of Acquired characteristics.
C) Origin of Species.
D) Natural Selection.
Answer:
D) Natural Selection.
Question 4.
Which of the following is NOT related to transportation of water in plants? ( )
A) Root Pressure
B) Phloem
C) Osmosis
D) Transpiration
Answer:
B) Phloem
Question 5.
Identify the INCORRECT sentence form the following. ( )
A) Medulla oblongata coordinates reflexes like swallowing, coughing and vomiting.
B) Cerebellum is centre for water balance, blood pressure and body temperature.
C) Midbrain shows reflexes for sight and hearing.
D) Cerebrum is a seat of thinking, memory and perception.
Answer:
B) Cerebellum is centre for water balance, blood pressure and body temperature.
Question 6.
Match the following and identify the correct answer. ( )
i) Joseph Priestley (a) Plants release Oxygen in the presence of light.
ii) Jan Ingenhousz (b) Chiorophy II – green coloured substance.
iii)Engelman (c) Plants release a gas which is essential for the survival of living organisms. ,
iv) Pelletier, Caventou (d) Detected the point of maximum rate of Photosynthesis.
A) i – c, ii – d, iii – a, iv – b
B) i – c, ii – a, iii – b, iv – d ,
C) i – a, ii – c, iii – d, iv – b
D) i – c, ii – a, iii – d, iv – b
Answer:
D) i – c, ii – a, iii – d, iv – b
Question 7.
Identify the Monohybridisation genotypic ratio of F2 generation. ( )
A) 3: 1
B) 1: 2: 1
C) 1 : 3
D) 2: 1: 1
Answer:
B) 1: 2: 1
Question 8.
The tendency of pollutants to concentrate as they move from one trophic level to the next is known as …………….. . ( )
A) Bioremediation
B) Biomagnification
C) Bioaccumulation
D) Phyto remediation
Answer:
B) Biomagnification
Question 9.
Identify the parts from the following that should be in the empty boxes regarding blood circulation in the mammalian heart. ( )
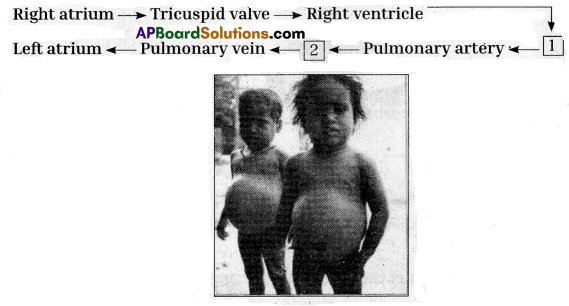
A) 1. Pulmonary Valve 2. Lungs
B) 1. Lungs 2. Pulmonary Valve
C) 1. Systemic Valve 2. Aorta
D) 1. Mitral Valve 2. Inferior vena cava
Answer:
A) 1. Pulmonary Valve 2. Lungs
![]()
Question 10.
Identify the type of malnutritional disease the child is suffering in the given picture. ( )
A) Marasmus
B) Kwashiorkor
C) Pellagra
D) Obesity
Answer:
B) Kwashiorkor