Students must rely on TS 10th Class Biology Model Papers Set 4 to gauge their understanding of exam patterns.
TS 10th Class Biology Model Paper Set 4 with Solutions
Time:1:30 hours.
Max. Marks:40
Instructions:
- Read the question paper carefully and understand.
- Answer the questions under Part – A in the answer sheet provided.
- Part- A contains three sections: sections – I, II and III.
- There is an internal choice to the questions under section – III.
- Part-B Answers should be written in the given brackets and attach to the Part – A answer sheet.
- Write the answers following the instructions given in each section.
Part – A (Marks 30)
Section – I (3 x 2 = 6 M)
Instructions:
- This section contains 3 very short answer questions.
- Answer ALL the questions.
- Write answer to each question in 3 to 4 sentences.
- Each question carries 2 marks.
Question 1.
Name the enzymes present in the gastric juice. What are their functions?
Answer:
Pepsin and lipase are. the enzymes present in the gastric juice. Pepsin breaks down proteins into peptones. Lipase converts fats into fatty acids and glycerol.
Question 2.
What are respiratory substrates?
Answer:
Substances which are oxidised in the body during respiration to produce energy are called respiratory substrates.
E.g.: Glucose, fatty acids.
![]()
Question 3.
What is a heartbeat?
Answer:
- The word heartbeat represents one contraction and one relaxation of heart.
- The contraction phase is called systole and relaxation phase is called diastole.
Section – II (3 x 3 = 9 M)
Instructions:
- This section contains 3 short answer questions.
- Answer ALL the questions.
- Write answer to each question in 5 to 6 sentences.
- Each question carries 3 marks.
Question 4.
Write a brief note on the nervous system that regulates pupil of eye.
Answer:
- When we enter a dark room we cannot see anything immediately. Slowly we are able to see the things around us in the room.
- This is because of increase in diameter of pupil, which allows more light in.
- When we come out of the room into broad day light the diameter of the pupil decreases allowing less light to enter into the eye.
- Both these functions occur under the influence of the autonomous nervous system.
Question 5.
Who discovered DNA? Write a short note on it?
Answer:
- Francis Crick and James Watson discovered DNA in 1953.
- DNA molecule looks rather like spiral staircases having a shape known as double helix.
- The framework of the staircase consists of alternate sugar and phosphate groups and the steps which join the framework together are the pairs of chemical compounds called bases.
- They are adenine, guanine, thymine and cytosine.
![]()
Question 6.
What are the effects caused by the consumption of fossil fuels?
Answer:
Effects of overconsumption of fossils fuels.
- Fossil fuels emit CO2 and other volatile gases into the atmosphere.
- Affects acid rains.
- Increase atmospheric pollution.
Section-III (3 x 5 = 15 M)
Instructions:
- This section contains 3 essay-type questions.
- Answer ALL the questions.
- There is an internal choice for each question.
- Write answer to each question in 8 to 10 sentences.
- Each question carries 5 marks.
Question 7.
What is heterotrophic nutrition? Explain the feeding mechanism of heterotrophs.
(OR)
How scientists prove that the food is transported through the phloem?
Answer:
Organisms which cannot prepare their own food but depend on the other organisms to get their food. Such type of organisms are called heterotrophs. This type of nutrition is called heterotrophic nutrition.
Feeding mechanism:
- The size of the food particles varies from microscopic organisms to large animals and plants.
- Each organism is adapted to the particular environment.
- The form of nutrition differs depending on the availability of food materials as well as how it is obtained by the organism. Some animals use pseudopodia. Ex: Amoeba. Some animals use tentacles. Ex: Hydra. Some animals cut the food into small pieces before they take it. Ex: Snails have sharp teeth-like structures on their tongue called radula which helps in making the food materials into pieces.
- In herbivorous animals like deer, cow teeth help for grazing the grass and masticating the food.
- Some animals like lions and tigers are equipped with organs to chase, capture, kill, cut and eat the prey.
- Some animals feed on only liquid food. For example, scorpions and spiders kill the prey and inject digestive enzymes into the body of dead and convert it into liquid form, which the animal feed.
- Honeybees have tube-like proboscis to suck nectar from flowers. Mosquitoes have special organs to pierce through skin and suck the blood. Animals like earthworms feed on soil containing decomposed organic material.
(OR)
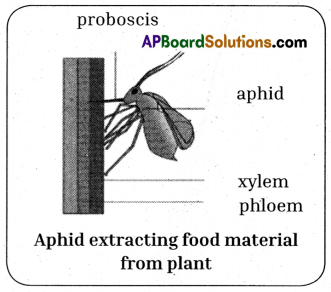
- Food such as sugar is synthesized in the green parts of plants, mainly in the leaves, but this food has to be transported to all living cells, especially to actively growing cells and the cells which stores food.
- Phloem sieve tubes are extremely small and the analysis of their contents is not easy.
- Biologists studied about food transportation in plants with the help of aphids.
- When you see aphids clustering round the young stems of plants as they feed on the plant juices.
- To obtain this juice an aphid pierces the plant tissues with its long needle-like organ “Proboscis”.
- It can be shown when a feeding aphid is killed and the stem carefully sectioned.
- The proboscis only penetrates up to a phloem sieve tube.
- An aphid is killed while in the act of feeding and the body is then carefully cut away, leaving the hollow proboscis still inserted into the phloem.
- It is found that because the contents of the phloem sieve tubes are under slight pressure.
- The fluid slowly excludes from the cut end of the proboscis in the form of drops.
- These drops are then collected and analyzed.
- The fluid is found to contain sugars and amino acids.
Question 8.
Describe male reproductive system of human.
(OR)
Write a short note on structure of the ovule.
Answer:
- In human males, the two testes are located in pocket-like structure outside the body wall called ‘scrotum.
- Each testes has several lobules and Seminal vesicle each lobule contain several seminiferous Prostate gland tubules.
- They are small, highly coiled tubes and 80 cm in length.
- Vasefferentia, collect from epididymis. Here Urethra sperms are stored temporarily and moved – Epididymis into vas deference then to urethra of penis and expel out of the body.
- One prostate, two Cowper glands which Scrotum are accessory glands in male reproductive system secretes a fluid called ‘semen’.
- They provide nutriènts for sperm to keep alive and helps as a medium for the movement of sperms.
- The sperm is a flagellated structure with long tail. This helps them to move towards the ovum.
8. The development of the male reproductive organs is regulated by the male sex hormone called ‘testosterone’.
9. Men produce sperm, from the age of about 13 or 14 years and can go on doing so most of their lives, although their power to do so decreases as they grow older.
(OR)
- An ovule is an egg-shaped structure attached by a stalk to the inner side of the ovary.
- An ovary may have one, two, several or even hundreds of ovules.
- At the centre of each ovule is a microscopic embryo sac filled with food and water.
- The embryo sac is composed of gametophyte cells.
- The majority of flowering plants have an embryo sac consisting of seven cells and eight nuclei.
- The structure which receives pollen is called stigma and the long tube-like structure which helps in the passage of compatible male sex cells is called ‘style.
![]()
Question 9.
What is peristaltic movement? Explain the food movement in alimentary canal comparing with the experiment of moving potatoes in cycle tube.
(OR)
What determines the terrestrial ecosystems on the Earth?
Answer:
Peristaltic movement is the contraction and relaxation of the muscles of the digestive system.
The movement of food through food pipe is known as peristaltic movement.
Food movement in alimentary canal:
- The walls of the food pipe secrete a slippery substance called mucus. Mucus lubricates and protects the oesophageal walls from damage.
- This helps the food bolus to slide down easily just as the oiled potatoes that move in the tube. Oil acted as lubricant to push the potatoes easily in the forward direction.
- The wall of the oesophagus is made up of two kinds of smooth muscles. The inner layer consists of circular muscles and the outer layer of longitudinal muscles.
- Contraction of the circular muscles results in narrowing of the oesophagus just behind the bolus.
- So the food is squeezed downwards.
- Contraction of the longitudinal muscles in front of the bolus widens the tube, this results in shortening of that particular part of the oesophagus.
- Contraction and relaxation of these muscles bring in wave-like motion that propels the food bolus into the stomach by the action called as peristalsis.
- This is involuntary and under the control of autonomous nervous system.
(OR)
- The terrestrial ecosystems on the Earth are being determined largely by the variations in climatic conditions between the poles and equator.
- The main climatic influences which determine these ecosystems are rainfall, temperature and availability of light from the Sun.
- For instance, forests are usually associated with high rainfall, but the type is influenced by temperature and light.
- The same applies to deserts which occur in regions where rainfall is extremely low.
- Thus, the climatic conditions along the horizontal climatic regions determine the terrestrial ecosystems on the Earth.
- If we move from the equatorial region to the polar region, we can come across tropical rain forests, savannah, deciduous forests, coniferous forests and then tundras respectively.
- Similarly, the altitude of the place is also a determining factor.
- Let’s climb a mountain such as Kilimanjaro in equatorial Africa. We can go through a comparable system of ecosystems, starting with tropical rainforest at the base and ending with perpetual snow and ice.
Part-B (Marks 10)
Instructions:
- Write the answers to the questions under Part – B on the question paper itself and attach It to the answer book of Part – A.
- Each question carries 1 mark. ,
- Marks will not be awarded in any case of overwriting, rewritten or erased answers.
- Write the capital letter (A / B / C / D) showing the correct answer for the following questions in the brackets provided against them.
Question 1.
In which part of the alimentary canal digested food is absorbed? ( ).
A) Stomach
B) Mouth
C) Large intestine
D) Small intestine
Answer:
B) Mouth
Question 2.
Oil is applied on the lower side of the leaf. The result is ( )
A) Photosynthesis does not take place.
B) Respiration does not take place.
C) Transpiration does not take place.
D) All the above.
Answer:
D) All the above.
Question 3.
From nasal cavity, the air goes into pharynx. After pharynx, the track is divided into passages. Those are ……………, …………….. ( )
1) Stomach, duodenum
2) Trachea, digestive canal
3) Larynx, epiglottis
A) 1 only
B) 1 and 2
C) 2 only
D) 1 and 3
Answer:
B) 1 and 2
![]()
Question 4.
B.P. means ( )
A) Atria Pressure
B) Lymph Pressure
C) Ventricular Pressure
D) Blood Pressure
Answer:
D) Blood Pressure
Question 5.
This organ also involved in urea formation. ( )
A) Lungs
B) liver
C) Stomach
D) Colon
Answer:
B) liver
Question 6.
Taking of ……………… rich diet results in more urea in urine. ( )
A) Carbohydrates
B) Proteins
C) Fats
D) Vitamins
Answer:
B) Proteins
Question 7.
Animal that excretes by diffusion ( )
A) Earthworm
B) Scorpion
C) Amoeba
D) Leech
Answer:
C) Amoeba
Question 8.
The correct answer is ( )
1) Abscisic acid (a) a) Ripening of fruit
2) Cytokinins (b) b) Closing of stomata
3) Gibberellins (e) c) Elongation of stem
A) 1 is correct
B) 3 is correct
C) 2 is correct
D) 1, 2, 3 are correct
Answer:
B) 3 is correct
Question 9.
ASHA stands for ( )
A) Accredited Social Health Association
B) Accredited Social Health Activist
C) AIDS Social Health Activist
D) AIDS Sexual Health Activist
Answer:
B) Accredited Social Health Activist
Question 10.
img. What will be in the box? ( )
A) Ovary
B) Graffian follicle
C) Cavity of ovule
D) Canal
Answer:
B) Graffian follicle