AP State Board Syllabus AP SSC 10th Class English Textbook Solutions Chapter 5A Environment Textbook Questions and Answers.
AP State Syllabus SSC 10th Class English Solutions Chapter 5A Environment
10th Class English Chapter 5A Environment Textbook Questions and Answers
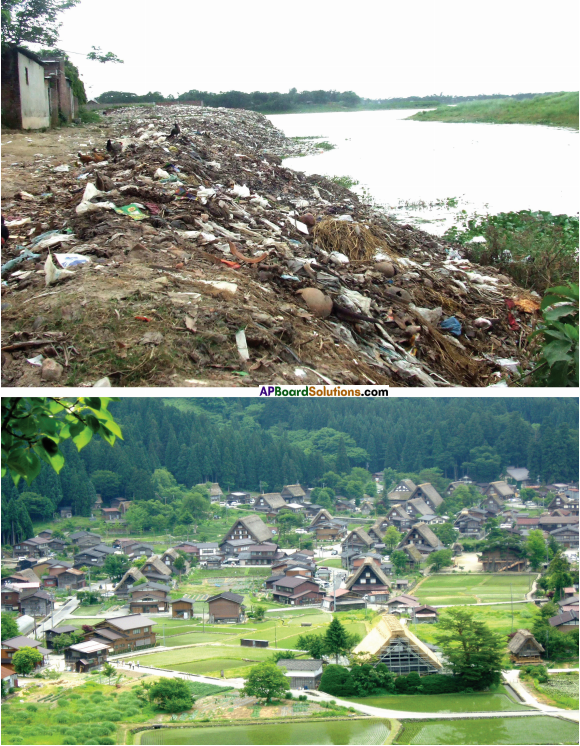
Look at the pictures and answer the questions that follow.

Question 1.
What do you see in the first picture? Do you like it? If not, why?
Answer:
In the first picture we can see a polluted area which is a dumping yard of garbage near a water body. I don’t like it because garbage should not be dumped near a drinking water source. The garbage should be burnt in an open unused area. If we dump garbage near a water source, it will lead to water pollution which in turn spreads diseases.
Question 2.
How is the second picture different from the first? Do you feel good about it? Give reasons for your view.
Answer:
The first picture represents a polluted area whereas the second picture represents a clean and green village which is the best example of perfect, polluted-free environment. It is a beautiful village with full of lush green vegetation.
Yes, I feel good about it because we can see greenery everywhere which feasts our eyes and also we find cleanliness in this picture. As a responsible human being I wish such an environment might be in my surroundings which fills healthiness both in our body and mind.
These two pictures indicate a best example for biodiversity.

Question 3.
What is meant by Biodiversity? Can you explain it?
Answer:
Biodiversity is the degree of variation of life. This can refer to genetic variation, species variation or ecosystem variation.
Comprehension
Answer the following questions.
Question 1.
How are people’s basic needs connected with the environment?
Answer:
The forested mountains are the sources of water and the source of rain. So when we deforest we cause a shortage of water and a change of rainfall patterns and therefore people are not able to get food and water. In such a way people’s basic needs are connected with the environment.
Question 2.
Wangari Maathai has described the environment of her childhood in the interview. Is the environment of her childhood different from the environment you live in? If yes, in what ways?
Answer:
Yes, the childhood environment of Wangari Maathai is entirely different from the environment I live in at present. Her childhood environment was very pristine, very beautiful, and very green whereas my environment includes all the human made things, and the natural things like plants and trees are scarcely found. Her environment is pollution free one with fresh air whereas mine is damaged because of comfortable means of living and indiscriminate destruction of forests.

Question 3.
According to Maathai, how are women responsible for the protection of the environment?
Answer:
As per the view of Maathai, women are responsible for the protection of environment because women are in need of food, clean drinking water, and fodder for their animals. Women work on farms, they plant, they cultivate, they produce food and they manage the environment.
Question 4.
What is the specific message of Wangari Maathai?
Answer:
The specific message of Wangari Maathai is, “When we plant a tree, we plant hope.” Plant a tree that will last, long after we are gone to rehabilitate environment in order to save the environment and to obtain a good environment.
Question 5.
List the transformations that Wangari Maathai was able to bring about over the years. Which one of them is the biggest in your opinion?
Answer:
The transformations that Wangari Maathai was able to bring about over the years are
- The ability of an ordinary illiterate woman to get to understand to be able to plant trees
- Transformation of the landscape
- Willingness of people to fight for their rights
In my opinion all these three transformations are important.

Question 6.
Maathai said, “When we plant a tree we plant hope.” What does she mean by this?
Answer:
She meant that a tree is a wonderful symbol for the environment and when we plant a tree, we plant the future for ourselves, for our children, for the birds. We plant something that will last, long after we are gone.
Question 7.
Wangari Maathai in her interview with NHK Radio often repeats phrases/sentences probably to emphasize her point.
For example : referring to women-groups she says:
They’re the ones who plant.
They’re the ones who cultivate.
They’re the ones who produce food.
Pick out from the text (of her interview) such repetitions and write them down and find out what she is emphasizing in each context.
Answer:
‘What is happening in Somalia’
‘What is happening in the Sudan’
‘What is happening in West Africa’
The above repetitions emphasize Wangari Maathai’s hope in creating a peaceful environment.
‘We plant a tree, we plant a hope.’
‘We plant the future for ourselves, for our children, for the birds.’
’We plant something that will last, long after we are gone.’
The above repetitions emphasize Wangari Maathai’s message to people insisting the importance of rehabilitation of a peaceful environment.
II. Pick out the correct choice in each of the following :
1. We have allowed some people, especially those in power, to acquire a lot at the expense of the majority.
The underlined phrase means :
a) with a loss or damage to the majority
b) by spending money on the majority
Answer:
(a) with a loss or damage to the majority

2. What was the implication of the growth of exotic trees, such as the pines and the eucalyptus for the environment?
a) It increases timber business.
b) Forests were not able to contain water.
Answer:
(b) Forests were not able to contain water.
3. When women started working with Maathai, they learnt _____________.
a) to become very competent foresters.
b) to grow and transplant seedlings.
Answer:
a) to become very competent foresters.

4. Maathai’s efforts will inspire the people _______________ .
a) to stop wasting their resources.
b) to use their resources miserly.
Answer:
(a) to stop wasting their resources.
Vocabulary
I. Replace the underlined words in the following sentences with the words from the box that have the same meaning.

1. The government is trying to bring back normalcy in the riot-hit areas of the city.
2. Wangari Maathai fought for the same privileges for men and women in Africa.
3. I cannot hold my attention on any subject for a long time.
4. The poster is offensive and disrespects women.
5. Some people argue that the wealth in this world should be distributed fairly and reasonably among all.
6. After certain amount of growth the seedlings have to be taken out and shifted elsewhere for further growth.
7. She travels to all kinds of exciting locations all over the world.
8. The Tirumala hills are covered by lush green plants.
9. The judge advised the disputing parties to settle through discussion.
10. The alcohol addict has to be put in a recovery centre for becoming a normal person.
Answer:
- restore
- equal rights
- sustain
- degrades
- equitably
- transplanted
- exotic
- vegetation
- negotiation
- rehabilitation
II. Read the following sentence and notice the underlined words.
Wangari Maathai is an environmentalist and has a lot of interest in ecology.
In the above sentence ‘environmentalist’ stands for ‘a person who is concerned . about the natural environment and wants to improve and protect it’. ‘Ecology’ stands for ‘the study of relation of animals and plants to their surroundings. ‘Both the words stand for many words. So they are called ‘one-word substitutes’.
What are the following persons called?
1. A person who studies the human race, especially of its origins
2. A person who studies the remains of buildings and objects found in the ground
3. A scientist who studies the earth, the origin of the history of rocks
4. A person who studies birds scientifically
5. A scientist who studies Physics
6. A doctor who studies and treats heart diseases
7. A person who believes in solving human problems with the help of reason
8. A scientist who studies animals and their behaviour
9. A scientist who studies the mind of a person
10. A person who solves problems in a practical and sensible way
11. A person whose job is to take care of people’s teeth
12. A person who studies languages
Answer:
- anthropologist
- archaeologist
- geologist
- ornithologist
- physicist
- cardiologist
- rationalist
- zoologist
- psychologist
- pragmatist
- dentist
- linguist
III. Fill in the blanks with the appropriate forms of the underlined words.
1. It is everyone’s duty to keep the environs clean, with the co-operation of the citizens the government can protect the _________ .
2. The government of the day should show its capability by providing good ___________ to people.
3. Wangari Maathai was successful in transforming women of Africa and the ___________ made her happy.
4. We must restore our environment and always try to ensure its ___________ .
5. Natural resources in this world can be sustained if only there is ___________ management of them.
6. Wangari Maathai is an environmental activist. Her ___________ led her to win Nobel Peace Prize.
7. We were trying to respond to the basic needs of the people in the rural areas. Our ___________ was well received by them.
8. In a developed country, the ___________ is balanced.
Answer:
- environment
- governance
- transformation
- restoration
- sustainable
- activities (or) activity
- response
- development
IV. Tick (✓) the meaning of the word underlined as suggested in the context.
1. ‘For me, my greatest activity is to plant a tree,’ said Wangari Maathai.
a) a living thing with stem, roots, branches and leaves
b) put seeds in the ground to grow
Answer:
(b) put seeds in the ground to grow
2. My uncle wants to build a chemical plant in Hyderabad,
a) a product
b) a factory
Answer:
(b) a factory

3. Applicants must have a clean driving licence.
a) complete
b) never done anything wrong
Answer:
(b) never done anything wrong
4. He thinks that he should either resign or come clean,
a) free from dirt
b) as not corrupt
Answer:
(b) as not corrupt
5. Rest your hand on my shoulder.
a) The remaining part
b) Support
Answer:
(b) Support
6. All our hopes rest on you.
a) support
b) depend
Answer:
(b) depend

7. A publisher’s note says: all rights reserved,
a) authority
b) interests
Answer:
(a) authority
8. I want this parcel to be sent right away.
a) immediately
b) completely
Answer:
(a) immediately
9. He knew this was his last hope of winning,
a) final
b) most recent
Answer:
(a) final

10. The last thing she needed was more and more work.
a) the only remaining part
b) most recent
Answer:
(a) the only remaining part
Grammar
I. Non-finite clauses
In English, we have two types of clauses. They are finite clauses and non-finite clauses. Look at the following examples:
1. Wangari Maathai led the movement. She won the Nobel Prize.
2. Leading the movement, Wangari Maathai won the Nobel Prize.
In.the example (1) there are two sentences. There is a verb in each, sentence and ‘. each verb has. a tense (a tense marker)! We can identify the tense of the verbs by looking at them. Both of them are in the past tense, since they are in the past tense having ‘V2’ forms (‘led’ and ‘won’). These are called ‘finite verbs’ as they have tense. Whereas in example (2), there are two clauses: ‘Leading the movement’ and ‘Wangari Maathai’ won the Nobel Prize’. The verb in the first clause has no tense while the one in the second clause has a tense i.e., the past tense.
The verb with tense is known as ‘finite verb’ and the clause that has a finite verb is known as a ‘finite clause’. In the same way, the verb that has no tense is known as a . ‘non-finite verb’ (leading) and the clause is called a ‘non-finite clause’.
Non-finite clause depends on the finite clause for its tense.

We should note that a non-finite clause has no subject, and we only can decide the
tense of a non-finite clause from the finite clause.
Explanatory Notes:
Finite Clause :
A typical finite clause consists of a verb together with its object and other dependents (i.e. a verb charge or predicate) along with its subject, (although in certain cases the subject is not expressed)
e.g.:
1. Kids play on computers, (independent clause)
2. I know that kids play on computers, (a dependent subordinate clause but still finite).
3. Play on your computer, (an imperative sentence, an example of finite clause lacking a subject.)

Non-finite Clauses:
A non-finite clause is similar, except that the verb must be in a non-finite form (such as infinitive, participle, gerund or gerundive) and it is consequently much more likely that there.
e.g.:
1. Kids like to play on computers, (an infinitive clause using the English to +infinitive)
2. It’s easy for kids to play on computers, (an infinitive clause contains periphrastic expression of the subject)
3. Playing on computers, they whiled the day away.
4. The kids playing on their computers, we were able to enjoy some time along, (a participial clause with a subject)
5. Having played on computers all day they were pale and hungry, (a participlial clause using a past participle)
6. Playing on computers is fun. (a gerund clause)
Some types of non-finite clauses have zero in one of the object or complement posi-tions. The gap is usually understood to be filled by a noun from the larger Glause in which the non-zero clause appears, (as is the subject gap in most non-finite clauses)
e.g.:
1) He is the man to beat.
(infinitive clause with zero object, the man is understood as the object)
2) The car wants looking at straight wav.
(gerund clause with zero preposition complement after’at’)
3) The building was given a new lease of life.
( past participle clause with zero indirect object)
A. Underline the non-finite clauses in the following sentences.
1. Born in London, he became the citizen of the U.K.
2. Having done his homework, he went out to play.
3. Recognized by his boss, he got an appreciation letter.
4. Encouraged by his father, Ravi got distinction in his final examination.
5. With the tree grown tall, we get more shade. .
6. We left the room and went home to search for the books.
7. Do we have the money to buy that car?
8. We were not able to get away until now.
9. Having read the book, I returned it to the library.
10. Jumping on his horse, the farmer rode to the market.
Answer:
- Born in London, he became the citizen of the U.K.
- Having done his homework, he went out to play.
- Recognized by his boss, he got an appreciation letter.
- Encouraged by his father. Ravi got distinction in his final examination.
- With the tree grown tall, we get more shade.
- We left the room and went home to search for the books.
- Do we have the money to buy that car?
- We were not able to get away until now.
- Having read the book. I returned it to the library.
- Jumping on his horse, the farmer rode to the market.
B. Look at how the following sentences have been rewritten to include non-finite clauses.
1. Vincent Van Gogh, who was born in Holland in 1853, is one of the world’s most famous painters.
Born in Holland in 1853, Vincent Van Gogh is one of the world’s famous painters.
2. Although his talent was unrecognized throughout his life, it was much appreciated after his death.
Despite.being unrecognized throughout his life, his talent was much appreciated after his death.
3. After he had failed in every career he had attempted. Van Gogh first turned to art to express his strong religious feelings.
Having failed in every career he had attempted, Van Gogh first turned to art to express his strong feelings.
Rewrite the following sentences to include non-finite clauses.
1. After he had decided to become a painter, in about 1880, he started to paint studies of peasants and miners.
2. During the next few years, which are known as his ‘Dutch period’, he produced paintings with rather dark greenish-brown colours.
3. In 1886, when he went to Paris to visit his brother Theo, he was immediately attracted to the Impressionist work he saw there. He decided to stay in Paris and continued his painting there.
4. He was encouraged by Pissaro to use more colour in his pictures and his subsequent paintings were bright and immensely colourful.
5. After Van Gogh had moved to Arles in the south of France, in 1888, he worked frantically.
6. This frenzied activity, which was interrupted by bouts of deep depression and despair, produced the majority of his most famous paintings.
7. One of these, which is called Self Portrait with Bandaged Ear, shows Van Gogh. He was wearing a bandage after he had cut off his ear. A year later, in 1890, he committed suicide.
8. A lot is known about Van Gogh’s life and his feelings because of the hundreds of letters,which were written by him to his brother Theo and others.
9. His brother always encouraged him in his work because he believed in Van Gogh’s genius. He was the person closest to Van Gogh.
Answer:
- Having decided to become a painter, in about 1880, he started to paint studies of peas-ants and miners.
- During the next few years known as his Dutch Period’, he produced paintings with rather dark greenish-brown colours.
- In 1886, after going to Paris to visit his brother Theo, after seeing and immediately getting attracted to the Impressionist work there, he decided to stay in Paris and continued his painting there.
- Encouraged by Pissaro to use more colour in his pictures, his subsequent paintings were bright and immensely colourful.
- Having moved to Arles in the South France, in 1888, Van Gogh had worked frantically.
- This frenzied activity, interrupted by bouts of deep depression and despair, produced the majority of his most famous paintings.
- One of these, called Self Portrait with Bandaged Ear, showing Van Gogh, wearing a bandage after cutting off his ear, committed suicide a year later in 1890.
- A lot is known about Van Gogh’s life and his feelings because of the hundreds of letters, written by him to his brother Theo and others.
- Believing (believed) in Van Gogh’s genius, his brother, the closest person to Van Gogh always encouraged him in his work.
(or)
Being the closest person to Van Gogh and believing (believed) in his genius, his brother always encouraged Van Gogh.
II. Reported speech
Apart from the ground rules that are laid down for reporting in traditional grammar books, there are certain other principles that are to be followed to make the speech appealing.
Suppose you want to tell somebody what Ram said. There are two ways of doing this :
You can repeat Ram’s words (direct speech).
Ram said, I am feeling ill.’
Or you can use reported speech :
Ram said that he was feeling ill.
It is not always necessary to change the verb in reported speech. If you report something and the situation hasn’t changed, you need not change the verb to the past:
Direct : Neelima said, My new job is very interesting.’
Reported : Neelima said that her new job is very interesting.
(The situation hasn ‘t changed. Her job is still interesting.)
Direct : Ravi said, I want to go to New York next year.’
Reported : Ravi told me that he wants to go to New York next year.
(Ravi still wants to go to New York next year.)
You can also change the verb to the past:
Neelima said that her new job was very interesting.
Ravi told me that he wanted to go to New York the following year.
The past simple (did/saw/knew etc.) can usually remain the same in reported speech, or you can change into past perfect (had done/had seen/had known, etc.).
Direct : Ravi said : 1 woke up feeling ill, so I didn’t go to work.”
Reported : Ravi said (that) he woke up feeling ill, so he didn’t go to work, (or)
Ravi said (that) he had woken up feeling ill, so he hadn’t gone to work.

Explanatory Notes:
We may report the words of a speaker in two ways.
1. Direct Speech
We may quote the actual words of the speaker. This method is called Direct Speech.
2. Indirect Speech
We may report what he said without quoting his exact words. This method is called . Indirect Speech or Reported Speech.
Example:
• Direct : Clinton said, “I am very busy now.”
• Indirect : Clinton said that he was very busy then.
• Direct : He said, “ My mother is writing a letter.”
• Indirect : He said that his mother was writing a letter.
How to change Direct to Indirect Speech?
It will be noticed that in Direct Speech, we use inverted commas to mark off the exact words of the speaker. In Indirect Speech we do not use the inverted commas.
It will be further noticed that in changing the above Direct Speech into Indirect speech, certain changes have been made.
Thus:
i) We have used the conjunction ‘that’ before the Indirect Statement.
ii) The pronoun “I” is changed to “HE”. (The Pronoun is changed in Person)
iii) The verb “am” is changed to “was”.
iv) The adverb “now” is changed to “then”.

Rules for changing Direct into Indirect Speech :
A. When the reporting or principal verb is in the Past Tense, all the Present Tenses in the Direct Speech are changed into Past Tense.
a. A simple present tense becomes simple past tense.
Example :
Direct : He said, “I am unwell.”
Indirect : He said that he was unwell.
b. A present continuous tense becomes a past continuous.
Example :
Direct : He said, “ My mother is writing a letter.”
Indirect : He said that his mother was writing a letter.
c. A present perfect becomes a past perfect.
Example:
Direct : He said, “I have passed the examination.”
Indirect : He said that he had passed the examination.
d. As a rule the simple past tense in the Direct Speech becomes the past perfect tense in Indirect Speech.
Example :
Direct : He said, “His horse died in the night.”
Indirect : He said that his horse had died in the night.
NOTE:
The ‘shall’ of the future is changed into ‘should’.
The ‘will’ of the future is changed into ‘would’.
The ‘can’ and ‘may’ of the future are changed into ‘could’ and ‘might’ respectively.

B. The tenses will not change if the statement is still relevant or if it is a universal truth. We can often choose whether to keep the original tenses or change them.
Examples:
Direct : “I know her address,” said John.
Indirect : John said that he knows/knew her address.
In this Indirect Speech, both the past tense and the present tense make the sentence a correct one.
Direct : The teacher said, “The earth goes round the sun.”
Indirect : The teacher said that the earth goes round the sun.
Direct : She said, “German is easy to learn.”
Indirect : She said that German was/is easy to learn.
The past tense is often used when it is uncertain if the statement is true or when we are reporting objectively.
C. If the reporting verb is in present tense, the tenses of the Direct Speech do not change. For example, we may rewrite the above examples, putting the reporting verb in the present tense.
Examples :
Direct : He says, “I am unwell.”
Indirect : He says that he is unwell.
Direct : He says, “ My mother is writing a letter.”
Indirect : He says that his mother is writing a letter.
Direct : He says, “I have passed the examination.”
Indirect : He says that he has passed the examination.
Direct : He says, “His horse died in the night.”
Indirect : He says that his horse died in the night.

D. The pronouns of the Direct Speech are changed where necessary, so that their relations with the reporter and his hearer, rather than with the original speaker are indicated.
Examples:
Direct : He said to me, “I do not believe you.”
Indirect : He said that he did not believe me.
Direct : She said to him, “I do not believe you.”
Indirect : She said to him that she did not believe him.
Direct : I said to him, “I did not believe you.”
Indirect : I said to him that I did not believe him.
Direct : I said to you, “I do not believe you.”
Indirect : I said to you that I do not believe you.
E. Words expressing nearness in time or places are generally changed into words expressing distance.
Examples:
Direct : He said, “I am glad to be here this evening.”
Indirect : He said that he was glad to be there that evening.
Direct : He said, “I was here yesterday.”
Indirect : He said that he was there the day before.
Now, let us see the words which get changed when the Direct Speech is changed into Indirect Speech.
- Now becomes then
- Here becomes there
- Ago becomes before
- Thus becomes so
- Today becomes that day
- Tomorrow becomes the next day
- Yesterday becomes the day before
- Last night becomes the night before
- This becomes that
- These becomes those

F. How the questions used in the Direct Speech are changed into Indirect Speech? In reporting questions, the Indirect Speech is introduced by such verbs as asked, inquired, etc…
Examples:
Direct : He said to me, “What are you doing?”
Indirect : He asked me what I was doing.
Direct : A stranger asked me, “Where do you live?”
Indirect : A stranger enquired where I lived.
Direct : The Policemen said to us, “Where are you going?”
Indirect : The Policemen asked us where we were going.
Direct : He said, “Will you listen to such a man?”
Indirect : He asked them whether they would listen to such a man.
Indirect : Would they, he asked, listen to such a man.
Direct : His angry mother jeered, “Do you suppose you know better than your father?”
Indirect : His angry mother jeered and asked whether he supposed that he knew better than his father.

G. How the Commands and the Requests in the Direct Speeches are changed when the Direct Speeches are changed into Indirect Speeches?
In reporting commands and requests, the Indirect Speech is introduced by some verb expressing commands and requests, and the Imperative Mood is changed into Infinitive Mood.
Examples:
Direct : Raja said to John, “Go away.”
Indirect : Raja ordered John to go away.
Direct : He said to Mary, “Please wait here till I return.”
Indirect : He requested Mary to wait there till he returned.
Direct : “Call the first witness,” said the Judge.
Indirect : The Judge commanded them to call the first witness.
Direct : He shouted, “Let me go.”
Indirect : He shouted to them to let him go.
Direct : He said, “Be quite and listen to my words.”
Indirect : He urged them to be quite and listen to his words.
H. How the Exclamation and the Wishes in the Direct Speeches are changed when the Direct Speeches are changed into Indirect Speeches?
In reporting exclamation and wishes, the Indirect Speech is introduced by some verb expressing Exclamation and Wishes.
Examples:
Direct : He said, “Alas! I am undone”.
Indirect : He exclaimed sadly that he was undone.
Direct : Alice said, “How clever I am!”
Indirect : Alice exclaimed that he was very clever.
Direct : He said, “Bravo! You have done well.”
Indirect : He applauded him, saying that he had done well.
Direct : “So help me, Heaven!” he cried, “I will never steal again.”
Indirect : He called upon Heaven to witness his resolve never to steal.
Look at the following conversation and notice how it is reported.
NHK Radio : How is peace connected to a good environment?
Wangari
Maathai : Many wars that are fought in the world are fought over natural resources. Some wars are fought because the environment is so degraded that it is not able to support communities and so they fight over the little that is left. Others are fought because some people want to take a lot of the resources, to control them, and to keep many other people out.

Reported speech of the above conversation :
NHK Radio asked Wangari Maathai how peace was connected to a good environ-ment.
She answered that many wars that were fought in the world were fought over natural resources. Some wars were fought because the environment was so degraded that it was not able to support communities and so they fought over the little that was left. Others were fought because some people wanted to fake a lot of the resources, to control them, and to keep many other people out.
A. Write the following in Reported Speech :
NHK Radio : What is the one thing we can do?
Wangari
Maathai : For me, my greatest activity is to plant a tree. I think that a tree is a wonderful symbol for the environment and when we plant a tree we plant hope. We plant the future for ourselves, for our children, for the birds. We plant something that will last, long after we are gone.
Answer:
NHK Radio asked Wangari Maathai what was the one thing that they could do.
She answered that the greatest activity was to plant a tree for her. She thought that tree was a wonderful symbol for the environment and when they planted a tree they planted hope. They planted the future for themselves, for their children, for the birds. They planted something that would last, long after they were gone.
B. Report the following dialogue :
Man : I’m doing a survey on shopping habits.
Woman : OK. As long as it doesn’t take long.
Man : How often do you eat hamburgers?
Woman : Never. I’m a vegetarian. I don’t eat any animal products.
Man : Right! Can I just ask you a personal question? Are you wearing leather shoes?
Woman : Yes, I am.
Man : Don’t you think that’s rather hypocritical?
Woman : No, not really.
Man : Oh, that’s amusing.
Answer:
The man says that he is doing a survey on shopping habits. The woman acknowl-edging that says she will answer the questions if they don’t take much time. The man asks her how often she eats hamburgers. The woman replies that she never eats that as she is a vegetarian and she doesn’t eat any animal products. Then, the man seeks her to permit to ask personal question and enquires if she is wearing leather shoes. The woman says that she is. The man asks her if she doesn’t think that is rather hypocritical. The woman says she really doesn’t. Finally the man says that is only amusing.
(Or)
The man said that he was doing a survey on shopping habits. The woman acknowledging that said she would answer the questions if they didn’t take much time.. The man asked her how often she ate hamburgers. The woman replied that she never ate that as she was a vegetarian and she didn’t eat any animal products. Then, the man sought her to permit to ask personal question and enquires if she is wearing leather shoes. The woman said that she was. The man asked her if she didn’t think that was rather hypocritical. The woman said she really didn’t. Finally the man said that was only amusing.
Writing
I. You have read the interview with Wangari Maathai. You know how and what type of questions have been asked by the interviewer. Imagine that you have decided to interview someone concerned with environment. You may include the following :
1. issues relating to the environment
2. the causes
3. actions that could be taken to save the environment Write down this imaginary interview.
Answer:
Miss Y. Jyothi Reddy is one of the most respected names in environment. She is also a passionate photographer and a well renowned environmentalist. Her photographs, posters and his noble thoughts have inspired me a lot. I decided to further sit with her and take a glance on her efforts for bringing environment awareness and journey of life till now. Below is our conversation with respected Miss Y. Jyothi Reddy.
I : Please tell us something about yourself and your family?
Jyothi Reddy : I was born in Nandyala and did my schooling over there. I pursued my B.Tech from V.R. Siddhartha College, Vijayawada.
I : How were you inspired to be an environmentalist ?
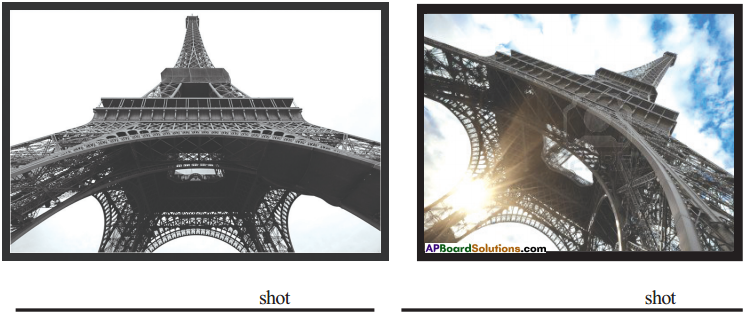
Jyothi Reddy : It was a small incident which changed my life. When my younger sister was in school she participated in poster competition and wanted to make a poster in water pollution. She asked my help. I thought that this time I will do something unique. So 1 took some shots of big drains emptying in our lakes in my camera. I made a collage of all pictures I had taken and gave it to her. She was appreciated in school but that day 1 realised the threat and started working in its direction.
I : According to you, what are the other issues relating to the environment?
Jyothi Reddy : Global warming, deforestation, pollution and all these lead to degradation of environment.
I : According to you, what are the major causes for the pollution in our city?
Jyothi Reddy : Ignorance on the part of local self-government bodies and the citizens plus poverty and illiteracy are main causes. Secondly, we, the citizens and the authorities have started taking lakes for granted, we consider them dumping grounds, sewers of city and many hotels situated near water bodies are opened in them itself.
I : As an environmentalist which area you are more concerned about?
Jyothi Reddy : I believe we should not allow the conservation of environment on cost of human life. It is completely senseless to save water for fishes when people in city are dying of thirst. Rather we should teach them the ways which can have a mutual balancing coexistence.
I : According to you, how can we make people aware or step that can be helpful in environment conservation?
Jyothi Reddy : Poster and photo exhibition. We need to make laws prohibiting dumping of religious or solid waste in lakes, and appropriate fine should be imposed upon.
I : How does your family react upon your passion on environment?
Jyothi Reddy : I am fortunate enough to have full support of them.
Environment Summary in English
This is an interview with Wangari Maathai, Environmental Activist and Nobel Prize winner. Wangari Maathai started the Green Belt Movement and also fought for equal rights for women in Africa. She is the first African woman to win the Nobel Peace Prize.
From the very beginning Wangari Maathai understood that she has to rehabilitate the environment as the rural people are asking for clean drinking water, for food, for energy, for building material, for fodder for the animals. She thought peace is connected to a good environment because there won’t be any conflicts if natural resources are abundant. She insists that conflicts over natural sources are even at the global level. When she was a child, which was almost more than fifty years ago, the environment was very pristine, very beautiful and very green but as she grew the people destroyed all the local biological diversity. All the flora and fauna disappeared. One thing she noted is that not only did the rain pattern change, became less, but also the rivers started drying up. So she started campaign to restore the vegetation and to restore the land and to rehabilitate the forests.
When she started working with the women she taught them how to plant trees. In the beginning it was difficult, but they soon gained confidence and they became very competent foresters. She called them “Foresters without Diplomas.”
Wangari Maathai thinks that the women responded well to her message because it is a need for them. She has seen three transformations. One of the biggest was that ability of an ordinary illiterate woman to get to understand and to be able to plant trees. The other two transformations are the transformation of the landscape, the willingness of people to fight for their rights.
Wangari Maathai also influenced the rest of Africa by her efforts. She finally concluded that the greatest activity is to plant a tree which is a wonderful symbol for the environment.
Environment Glossary
Green Belt Movement (n) : a movement to protect environment
excerpts (n) : a short piece of writing taken from a larger whole
building material (n) : material used for building houses
fodder (n) : food for farm animals
degraded : became less in quality
rehabilitate (v) : help something to become normal
sustain (v) : provide something in enough quantity to continue for long
livelihoods (n) : means and ways of earning money in order to live
concerned (adj) : have a feeling of worry or belonging
regional (adj) : of a region
discontent (n) : a feeling of dissatisfaction
conflict (n) : clash
equitable (adj) : treating everyone in an equal way
dignity (n) :respect
governance (n) : controlling or governing an organization
sustainable (adj) : that can continue or be continued for a long time
go about (phr. v) : tackle
forested (adj) : covered with forests
pristine (adj) : fresh or clean
indigenous (adj) : native
plantations (n) : crops such as coffee, banana, etc.
exotic (adj) : unusual and exciting
species (n) : a similar group of plants or animals (for the purpose of reproduction)
exotic species (n) : unusual plants
hemisphere (n) : one half of the earth
destroy (v) : annihilate
diversity (n) : a range of people or things that are very different
flora (n) : plants
fauna (n) : animals
downstream (adv) : in the direction of river flow
reservoir (n) : a natural or artificial pool
biological diversity (n) : the variety of plants and animals in a particular place
campaign (n) : movement
vegetation (n) : greenery
illiterate (n) : a person who doesn’t know how to read and write
seedlings (n) : young plants grown out of seeds
nurture (v) : care for or protect when growing
transplant (v) : take a thing and arrange in another place (transplantation of skin)
competent (adj) : skilful
tropics (n) : warmer places
civic education (n) : public education
govern (v) : control
transformations (n) : complete changes
dignity (n) : a manner that deserves respect
empowering (n) : giving authority or power
corrupt (adj) : spoil
influence (n) : the effect or impact
resources (n) : supplies (natural or artificial)
engage (v) : become or make involved
dialogue (n) : conversation
negotiations : formal discussions
fight over (jphr. v.) : argue about something
grazing land (n) : land meant for cattle to graze

![]()

![]()

![]()


![]()


![]()
![]()