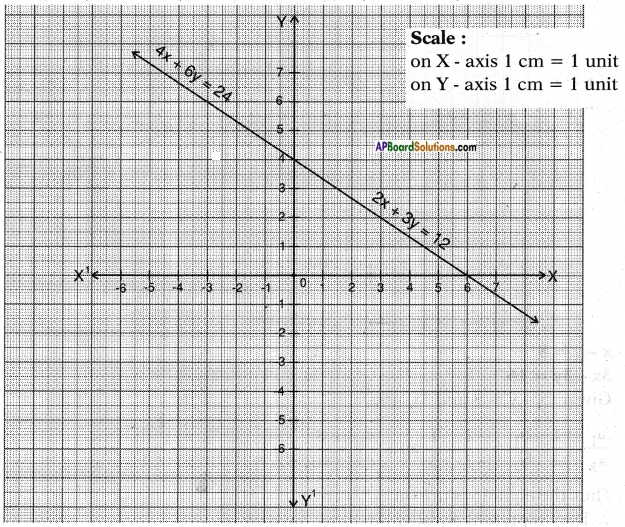
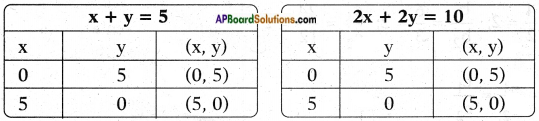
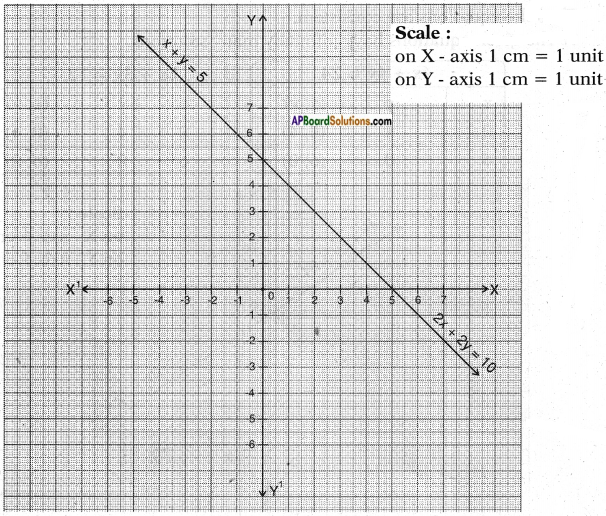
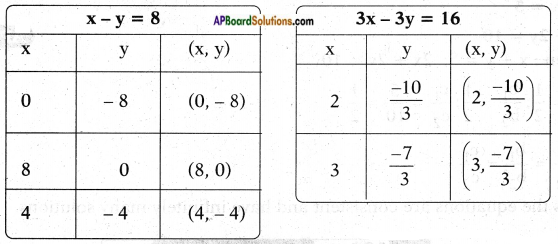
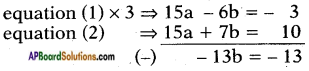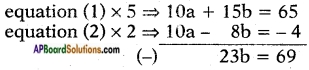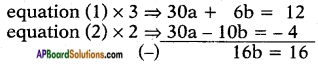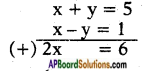AP State Board Syllabus AP SSC 10th Class English Textbook Solutions Chapter 3C What is My Name? Textbook Questions and Answers.
AP State Syllabus SSC 10th Class English Solutions Chapter 3C What is My Name?
10th Class English Chapter 3C What is My Name? Textbook Questions and Answers
Comprehension
Answer the following questions.
Question 1.
What made Mrs. Murthy so restless to know her name?
Answer:
In her scrubbing zeal, Mrs. Murthy had forgotten her name. At once she felt that she had lost her own identity. She had lost her self-respect. That made her so restless to know her name.
Question 2.
How did Mrs. Murthy’s husband look upon her desire to know her name?
Answer:
Mrs. Murthy’s husband laughed at her when she asked him about her name. He did not take it seriously. He wanted her to be called by his name ‘Mrs. Murthy’. He did not give any importance to her feelings.

Question 3.
Do you notice any change in Mrs.Murthy in the first picture and Sarada in the second picture?
Answer:
Yes. I have found a lot of difference in her being Mrs. Murthy and her being Sarada. After she got her name back she got her confidence back. After she recollected her name she felt like a real person because she got her identity and self-respect back. When she was a housewife she was different, and after she has remembered her name she has become flamboyant.
Question 4.
Do you find any similarities between Mrs.Murthy and the women in your family? If yes, list them.
Answer:
Yes. There are so many similarities between Sarada and the members of our family. Not only in our family but almost in all families we can find a woman like Sarada because she is a representative of women of any class of Indian society who are always confined to domestic work like cleaning floors, washing clothes, cooking, and looking after her children, her husband, and other family members.

Question 5.
Why do you think the writer decided to focus on the question of married women’s identity?
Answer:
The writer decided to focus on the question of married women’s identity because she wanted them to live with their own identity and self-respect. She did not want them to confine to their homes. She wanted them to be given equal rights, equal respect. She wanted that they should also assume some responsibility in nation building activity.
Question 6.
Do you really think a woman can forget her name? What do you think is the intention of the author here?
Answer:
No. I don’t think any woman can forget her own name. The intention of the author is that the women should be respected and should not be confined to the domestic work. She feels that women should not lose their own identity.
Question 7.
Which part of the story shows that Mrs. Murthy feels her identity restored?
Answer:
In the last part of the story, when she returned to her husband’s house Mrs. Murthy feels her identity restored. It is clear from her words “…. from now onwards don’t call me yemoi, geemoi. My name is Sarada – call me Sarada, understood ?”
Writing
I. Translation
Read the following news item in Telugu and compare it with its translation in English given after that.

The following is the translated version of the above Telugu news item.
Centre’s Nod to Kasturi Rangan Committee Recommendations on Western Ghats
NEW DELHI :
The Ministry of Environment has accepted the report made by the Kasturi Rangan Committee on the conservation of Western Ghats. The committee, in its recommendations, made it clear that no further development activities be undertaken in the Western Ghats spread across the 60 thousand square kilometers in six states. The committee was appointed by the Union Government and headed by Kasturi Rangan to suggest measures to conserve the rarest ecosystem of the Western Ghat forests. The committee submitted its Report on 15th of April. The Ministry of Environ¬ment , after taking opinions of the six state governments and the people of the states, accepted the recommendations. The Western Ghats extend in Gujarat, Maharashtra, Goa, Karnataka, Kerala and Tamil Nadu states.
Let’s think of the following :
Question 1.
Do you think that translation is just translation of language ? Or does it also include translation of ideas?
Answer:
No. I don’t think that translation is just a translation of language. It includes linguistic, pragmatic and cultural elements. A literary translation must reflect the imaginative intellectual and intuitive writing of the author. Literary translation must reflect all the literary features of the source text such as sound effects, selection of words, figures of speech, etc.

Question 2.
Which translation is better, true translation or free translation?
Answer:
True translation is a dynamic equivalent translation which focuses on creating an equivalent effect in the target languagae.
Free translation is a formal equivalent translation in which the form and content of the originaUmessage is to be preserved. Of these two types of translations, true translation is better. Since true translation yields in the equivalent effect and it conveys the message of the original to the receptor audience and are equivalent to the original text in a dynamic way, true translation is better.
Question 3.
Do you find any change in the order of the sentence? For e.g : We have Subject, Verb,Object in English but the order is Subject, Object, Verb in Telugu.
Answer:
Not only the structure of the sentence but the diction and style and the order of arrangement of phrases also changes from Telugu to English.
Languages have different pragmatic linguistic structures and norms transferring the norms of one language may well lead to pragmatic failure.
Question 4.
Do you think sometimes it creates problems in the choice of vocabulary while attempting to translate a text?
Answer:
Translation should implicate accurate meaning. It may be problematic for translators. Wrong choice of words may cause ambiguity. While choosing the apt words for translating a text the translator should consider the situationality, intentionality and acceptability.
Question 5.
Is it possible to translate a poem from one language to the other?
Answer:
No. Poetry is not possible to translate because no poem means just one thing. It is very difficult to translate a poem into another language because we may not be aware of many of the possible meanings of the poem.

Question 6.
Is it necessary to take cultural aspects into consideration?
Answer:
Yes. It is necessary to take cultural aspects into consideration while translating. Because translation is a kind of activity which inevitably involves at least two languages and two cultural traditions. There may be cultural difference between the source text and the target text.
The lesson, “What Is My Name?” is a translated version in English from Telugu.The following is a part of the Telugu version of the lesson. Read the Telugu version and observe how it was translated into English.

Activities :
Question 1.
Is this a good translation? Yes or no? Give reasons.
Answer:
Yes. This is a good translation because this translation is a formal equivalent to the original text in the form and the content. It is a good translation because it reflected the imaginative intellectual and intuitive writing to the author. But we have found some difficulties in the structure of the sentences, in diction and style.
Question 2.
Now translate the Telugu version on this page into English and list the difficulties you face.
Answer:
A young woman, before she became a housewife had been an educated, cultured, intelligent, capable, and quick-witted with a sense of humour and elegance.
A young man, who liked her beauty and intelligence and was attracted by the dowry offered by her father, tied the three sacred knots around her neck and made her a housewife. After making her his housewife he told her, “Look Ammadu. This house is yours”. On hearing his words the housewife at once pulled the edge of her sari and tucked it in at the waist and swabbed the entire house and decorated the floor with rangoli designs. On seeing this that young man praised her promptly by saying “Ammadu ! You are dexterous in swabbing floors and even more adept in drawing the muggulu. Sabash Keep it up.” He said it in English, giving her a pat on the shoulder in appreciation.
Overjoyed with this, the housewife continued to live with swabbing as the chief mission of her life. Always she used to scrub the floor spotlessly and decorate it with beautiful multi-coloured rangoli designs. Thus her life went on with a sumptuous and ceaseless supply of swabbing cloths and muggu baskets.
But one day while scrubbing the floor, the housewife suddenly asked herself, “What is my name?”. The query shook her up. Leaving the mopping cloth and the muggu basket there itself, she stood near the window scratching her head, lost in thoughts.
“What is my name ? What is my name ?”. The house across the street carried a name-board, Mrs. M. Suhasini, M.A., Ph.D., Principal, ‘X’ College. Yes, she too had a name as her neighbour did. “How could I forget like that? In my scrubbing zeal I have forgotten my name — what shall I do now?” The housewife was perturbed. Her mind became totally restless. Somehow she finished her daubing for the day.
Meanwhile, the maidservant came there. Hoping that at least she would remember her name, the housewife asked her, “Look ammayi, do you know my name ?”

Question 3.
Translate the following extract from the story into Telugu and compare it with the original story in Telugu. (Refer to teacher’s handbook for Telugu version.)
‘Sarada! My dear Sarada!’ she shouted and embraced her. The housewife felt like a person — totally parched and dried up, about to die of thirst — getting a drink of cool water from the new earthen kooja poured into her mouth with a spoon and given thus a new life.The friend did indeed give her a new life — ‘You are Sarada. You came first in our school in the tenth class. You came first in the music competition conducted by the college. You used to paint good pictures too. We were ten friends altogether — I meet all of them some time or other. We write letters to each other. Only you have gone out of our reach! Tell me why you are living incognito?’ her friend confronted her.
Answer:
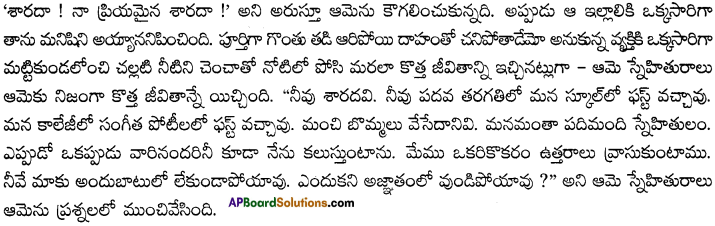
Project Work
I. Influence of technical gadgets on human relations.
Visit five houses in your neighbourhood and collect the information in the given format related to human relations, i.e. spending quality time with the members of the family and friends, sharing and caring. Analyse the information and write a report by adding your opinion on how the modern gadgets are influencing human relations and present it before the class.
Family-1 (House-1) (Raja Rao’s Family)
Family-2 (House-2) (Rama Rao’s Family)
Family-3 (House-3) (Venkat’s Family)
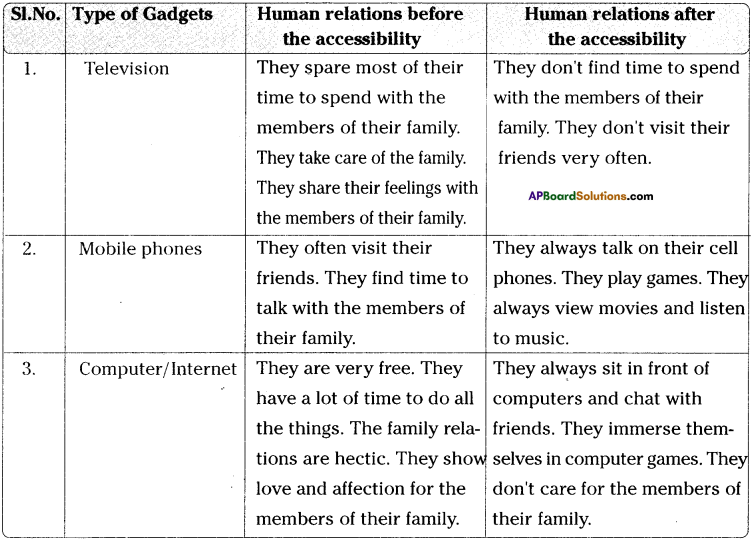
Family-4 (House-4) (Nageswara Rao’s Family)
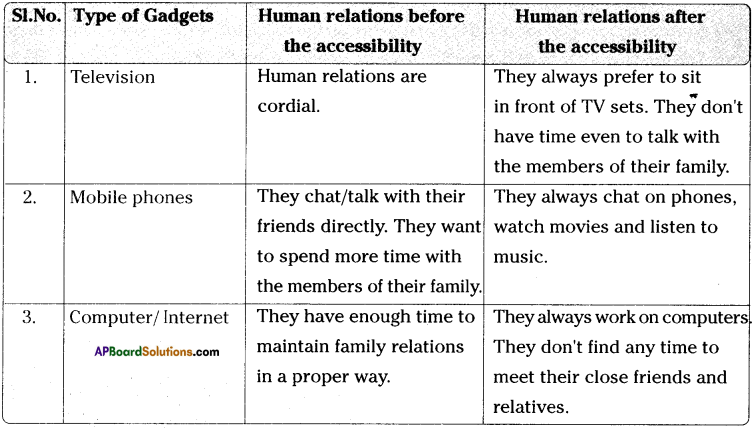
Family-5 (House-5) (Bhaskar’s Family)
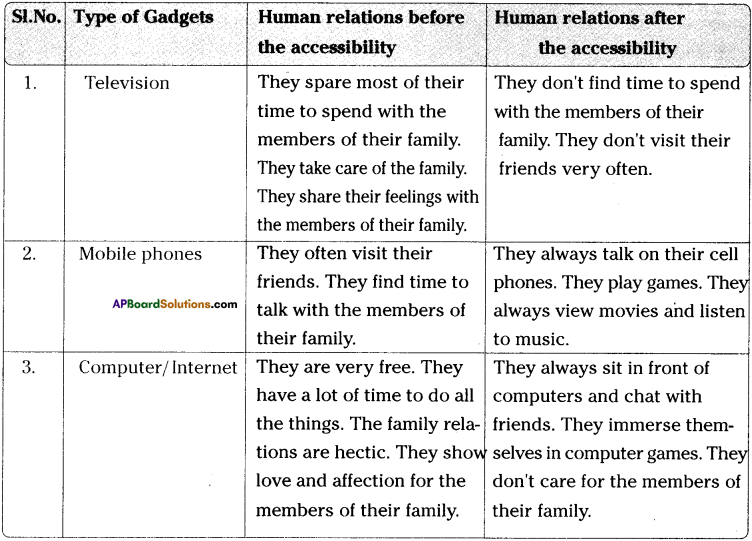
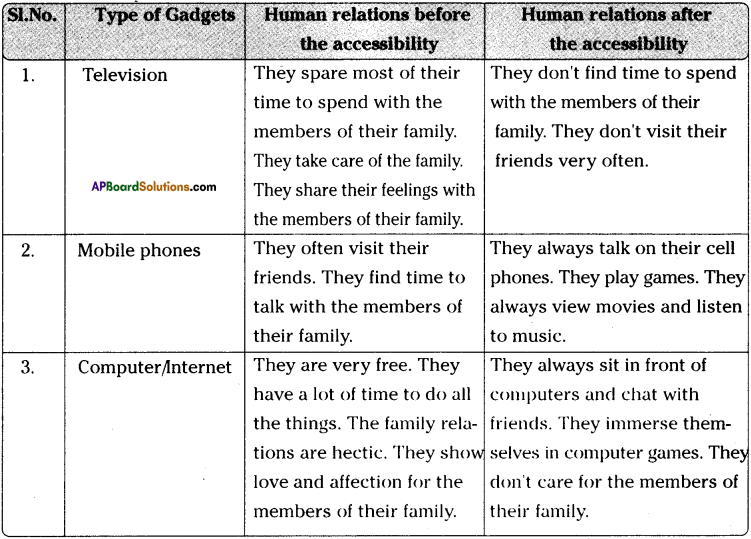
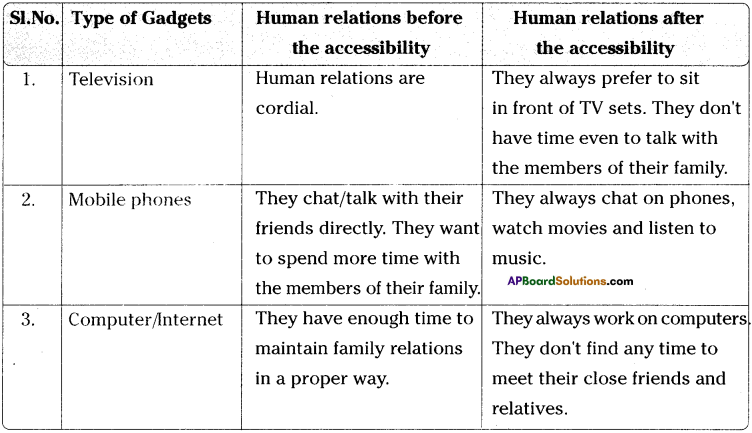
We all know very well that electronic gadgets such as TVs, Mobile phones, Computers occupy a major place in our day-to-day lives. Though these gadgets have their own advantages, they also have a negative influence on the human relationships. They play a vital role in our lives today. Most of us are addicted to them. There are hundreds of channels which are viewed on TV by us. We start watching TV programmes from a very early time in the morning till midnight. Thus we don’t have any time to talk to our near and dear. In the same way, mobile phones too have advantages as well as disadvantages. Most of the children and youth are spending all their time in using their mobile phones. They talk, watch movies, listen to music, play games on their mobile phones. When they engage in using their mobile phones, how can they find time to spend with their family members? Today, computers have become indispensable to each one of us.
In most of the families, we find a complete different situation in managing human relationships before and after the accessibility of the electronic gadgets. Before the accessibility of these modern gadgets, people share most of their time to spend with their family members. They take care of all the family members. They try to share their feelings with their famiy members. They often visit their friends. Their relationships with their family members and friends are very cordial. They find a lot of time to do all the things leisurely. Thus family relations are hectic. They show love and affection for their family members. They find time to play with their friends. They help their family members in all the matters.
After the accessibility of the modern gadgets, they try to spend all their time in using them only. They spend with them hours together. They don’t find time to spend with their family members. They don’t visit their friends very often. They don’t care for their family members. They give importance to the gadgets only. They become mechanical. They don’t have any affection for their family members. They don’t understand the warmth of relationship. They don’t know how much they are missing the joyous family interaction. They should understand that no artificial media can substitute their family’s warmth and interaction. They should give importance to human relationships.
II. Nowadays, we can easily find children even as young as two years old playing with electronic devices and gadgets anywhere. It is not only the video games that make children stay, it also includes television, mobile phones, computers, tablet computers, PSP (Play Station Portable) games, etc. Parents may find it easier to make their children stay in one place by giving them a gadget to play with.
Work in groups and discuss the following:
Ways of managing children’s electronic devices consumption and preventing
Answer:
Group 1 :
The parents should make their children know the bad effects of spending more time with electronic devices.
Group 2:
The parents should monitor their children’s media consumption – television, mobile phones, computers, tablet computers, PSP games, etc.
Group 3 :
The parents should make their children aware about the advantages of playing games, doing exercises and yoga instead of their spending more time with electronic devices.
Group 4 :
The parents should stop themselves from using the electronic gadgets for longer times. Thus they can set an example for their children.
Group 5 :
The parents should make their children aware about the health problems that would arise with spending longer times with electronic gadgets.
Group 6 :
The parents should share thier feelings with their children. They should discuss with them the ill effects of the games they play. They should try to move closer to their children.

Sum up:
Today most of the children are addicted to the modern gadgets such as television, mobile phones, computers, tablet computers, PSP games, etc. These all become an integral part of children’s lives. Today children are heavily exposed to media. Parents may find it easier to make their children stay in one place by giving them a gadget to play with. The parents should watch carefully what their children are doing with the gadgets and how they are using it. They should prevent their children’s addiction to games. They should find ways to manage their children’s electronic device consumption.
They should make their children know the bad effects of spending more time with electronic devices. They should monitor their children’s media consumption. They should make them play games and do exercise and yoga. The parents should stop themselves from using the electronic gadgets and stand as an example to their children. They should share their feelings with their children. They should try to move closer to their children.
Thus, parents can manage their children’s electronic device consumption and prevent their addiction to games.
What is My Name? Summary in English
Sarada, before she got married, was a well-educated and cultured young woman. She was intelligent, capable, quick-witted and she had a sense of humour and elegance. She used to stand first in her class. She was good at music and dance. She used to paint good pictures.
Falling to her beauty, and intelligence and attracted by the dowry her father offered, a young man married her. Later he showed his house and told her that it was her house. Immediately she began to swab the floors and decorated the floor with rangoli designs. On seeing this, her husband praised that she was dexterous at swabbing the floor. Overjoyed by his applause, Sarada began living with swabbing as a mission of her life. Thus, her life went on scrubbing the house spotlessly and decorating the house with multi-coloured designs. In her scrubbing zeal she had forgotten her name. One day she tried to recollect what her name was. But she could not. She became restless. She asked her maid servant, her neighbours, her husband, and her children about her name. But they all told the name by which they used to call her by using their relation. Her husband laughed and did not take it seriously.
Finally the housewife decided to go to her parents’ house and look for her name in her certificates. But her certificates were kept on the attic. Meanwhile she met her classmate. She called the housewife by her name ‘Sarada’. At once Sarada felt like a person. Because our name gives us our personal identity and self-respect. Our name is our own- unique to us.
Here the author wants to tell that every woman has her own responsibility in nation-building. Women should be given equal rights with men. Women should not be confined to the four walls of the house. She should be let free. She can reach to the heights of sky. She can ascend to the pinnacles of any success and thus she can make any nation greater and stronger.
What is My Name? Glossary
quick-witted (adj) : intelligent; able to think quickly
elegance (n) : a satisfying or admirable neatness; ingenious simplicity or precision in something
dowry (n) : money and property paid by a bride’s family to the bridegroom at the time of marriage
swab (v) : clean
dexterous (adj) : skilful
appreciation (n) : recognizing and enjoying the good qualities of somebody or something
sumptuous (adj) : luxurious, splendid
cease (v) : stop
ceaseless (adj) : continuous
zeal (n) : great energy and enthusiasm
mopping (v) : cleaning/washing
perturb (v) : bother/disturb/trouble
daubing (n) : the act of spreading a substance such as mud thickly
take somebody aback : to shock or surprise somebody very much
immerse (v) : absorb oneself in something
urge (v) : to try hard to persuade
giggling (v) : laughing nervously
anguish (n) : severe pain, unhappiness
frantically (adv) : worriedly/anxiously
chore (n) : a task that you do regularly
attic (n) : a room or space just below the roof of a house often used for storing things ; loft
wail (v) : to make a long loud cry
maternity home (n) : hospital for deliveries
parch (v) : dehydrate
incognito (adv) : having a concealed identity
fish (v) : search
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()