Teachers often recommend practicing with AP 10th Class Biology Model Papers Set 1 to enhance exam readiness.
AP SSC Biology Model Paper Set 1 with Solutions
Time : 2.00 hours
Max. Marks : 50
Instructions :
- Question paper consists of 4 sections and 17 questions.
- Internal choice is available only for Q.no.12 in section III and for all the questions in section IV.
- In the duration of 2 hours, 15 minutes of time is allotted to read the question paper.
- All answers shall be written in the answer booklet only.
- Answers shall be written neatly and legibly.
SECTION -1
(6 × 1 = 6 M)
Note :
- Answer all the questions.
- Each question carries 1 mark.
Question 1.
What does the following equation represent ?
C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + Energy
Answer:
Aerobic respiration
Question 2.
What are the valves present at the auriculo-ventricular septum ?
Answer:
- Tricuspid valve
- Bicuspid valve or Mitral valve
Question 3.
Natural resources are decreasing more rapidly. Guess the consequences of future.
Answer:
Water crisis and shortage of food. Air and soil pollution also occur.
Question 4.
Read the information of Kolleru lake given here under and answer the questions.
| Causes of reduction | Area in 1967 (km2) | Area in 2004 (km2) |
| 1. Lake with sparse weed | 0 | 47.45 |
| 2. Aquaculture ponds | 0 | 99.74 |
| 3. Rice fields | 8.40 | 16.62 |
| 4. Encroachments | 0.31 | 1.37 |
a) What are the reasons for decrease in lake area ?
Answer:
Lake with sparce weed, aquaculture ponds, rice fields and encroachments.
b) Which human activity leads to a significant decrease in lake area ?
Answer:
Establishment of aquaculture ponds, rice fields and encroachments.
Question 5.
How do you appreciate the role of hormones in stomach that cause hunger alarming ?
Answer:
Ghrelin produced in the stomach stimulates hunger pangs. This makes it possible for living organisms to become hungry, eat and survive.
Question 6.
Draw the picture of logo for recycling.
Answer:
![]()
![]()
SECTION – II
(4 × 2 = 8 M)
Note :
- Answer all the questions.
- Each question carries 2 marks.
Question 7.
What are the important events that take place in chloroplast during photosynthesis ?
Answer:
In photosynthesis these actions take place in chloroplast.
- Light energy is converted into chemical energy.
- Disintegration of water molecule into H+ and OH– releasing ATP & NADPH.
Question 8.
You want to know more information about harmful effects of using chemical pesticides in agriculture. What questions will you ask to an agronomist ?’
Answer:
- What are the disadvantages of excessive use of chemical fertilizers?
- Do chemical fertilizers cause soil erosion?
- Do chemical fertilizers increase yield?
- What is the difference between organic fertiLizers and chemical fertilizers?
Question 9.
Observe the following table that shows the human evolution chronology and answer the questions given under the data.
| Human species | lived/appeared |
| 1. Homo habilus | 1.6 2.5 million years ago |
| 2. Homo erectus | 1 1.8 million years ago |
| 3. Homo neanderthalensis | 1,00,000 40,000 million years ago |
| 4. Homo sapiens | 15,000 10,000 million years ago |
1) Which human species lived before the present human species ?
Answer:
Homo neanderthalensis
2) Who lived between 1 – 1.8 million years ago ?
Answer:
Homo erectus.
Question 10.
What happens to the rate of photosynthesis, if CO2 concentration is kept increased continuously ?
Answer:
CO2 is a photosynthetic factor.
In the air if the amount of CO2 increases, the rate of photosynthesis also increases naturally.
- This happens till it increases by 1 percent.
- After crossing 1 percent it becomes toxic and harms the plant.
![]()
SECTION – III
(5 × 4 = 20 M)
Note :
- Answer all the questions.
- Each question carries 4 marks.
Question 11.
Write die differences between veins and arteries.
Answer:
| ARTERIES | VEINS |
| 1) The vessels which transport blood from heart to body parts. | 1) The vessels which transport blood from body pars to heart. |
| 2) WaIls are thick. | 2) Walls are thin. |
| 3) No valves. | 3) Valves are present. |
| 4) High pressure in the vessels. | 4) Low pressure in the vessels. |
| 5) Cames oxygenated blood except pulmonary artery. | 5) Carries deoxygenated blood except pulmonary vein. |
Question 12.
Draw the internal structure of kidney and label the parts.
Answer:

OR
Draw a neat labelled diagram of internal structure of leaf. Which mesophyll cells of the leaf consist of chloroplast ?
Answer:
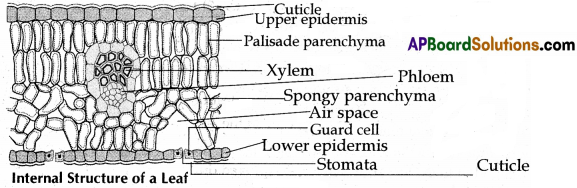
![]()
Question 13.
Explain the process of sex determination in human beings.
Answer:
- There are two types of sex chromosomes – one is ‘X’ and the other is ‘Y’ in the human beings. These two chromosomes determine the sex of an individual.
- Females have two ‘X’ chromosomes in the cells (XX). Males have one ‘X’ and one ‘Y’ chromosome in their ceIls-(XY).
- All the gametes (ovum) produced by women will be with only ‘X’ chromosomes. The gametes (sperm) produced by man will be of two types one with ‘X’ chromosome and other with ‘Y’ chromosome.
- If the sperm carrying ‘X’ chromsome fertilizes with the ovum (X-chromosome), the resultant baby will have ‘XX’ condition. So the baby will be a girl.
- If the sperm carrying ‘Y’ chromosome fertilizes with the ovum (X-chromosome)the resultant baby will have ‘XY’ condition. So the baby will be a boy.
- From the above discussion we can conclude that male is responsible for sex-determination of baby.
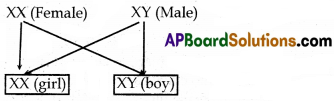
Question 14.
Observe the following data :
| Type of respiration | Respiratory organs | Organisms performing respiration |
| 1. Cutaneous respiration | Skin | Round worms, Earth worm, Frog |
| 2. Tracheal respiration | Tracheae | Cockroach, Grass hopper |
| 3. Branchial respiration | Gills | Fish |
| 4. Pulmonary respiration | Lungs | Reptiles, Birds, Mammals |
Answer:
- Pulmonary Respiration
- Gills
- Cockroach, grass hopper
- Skin
Question 15.
Plant hormones cooperate/differ with one another to attain the plant growth. How do you use this knowledge in your daily life?
Answer:
The phyto hormones act as growth stimulators and reductants
| Hormones | Uses |
| Auxins | Cell elongation, differentiation of shoots and roots. |
| Cytokinins | Promote cell division, delaying the ageing in leaves, opening of stomata. |
| Gibberellins | Germination of seeds, sprouting of buds; elongation of stem; stimulation of flowering; development of seedless fruits, breaking the dormancy in seeds and buds. |
| Abscisic acid | Closing of stomata ; seed dormancy, promoting ageing of leaves. |
| Ethylene | Ripening of fruit. |
In the above table Auxins, Cytokinins, Gibberellins, and Ethylene are growth stimulators. Abscisic acid is a reductant. Control and growth are coordinating activities. We can use this coordinating nature in our daily life activities.
![]()
SECTION – IV
(2 × 8 = 16 M)
Note :
- Answer all the questions.
- Each question carries 8 marks.
- Each question has internal choice.
Question 16.
A) What are the different modes of asexual reproduction in plants. Cite them with examples.
Answer:
Different modes of asexual reproduction:
1. Fission :
Single celled organisms split into two daughter cells that are identical to the parent cell. This method of reproduction is called “binary fission.”
Eg: Bacteria, Euglena, Amoeba etc.
Sometimes they split into more than two and it is called multiple fission.
Eg: Plasmodium.
2. Budding:
A growth on the body is called a bud. It grows nearly identical to the parent. When it is matured it gets separated from the parent and becomes independent.
Eg: Yeast, Hydra.
3. Fragmentation:
1) A detached fragment (piece) of the matured organism gives rise to a new individual under suitable conditions.
Eg: 1) Some flatworms, moulds, lichens, spirogvra etc.
2) These organisms perform sexual reproduction also.
4. Parthenogenesis :
The process of developing eggs without meiosis and without fertilization is called parthenogenesis.
Eg: Bees, ants and wasps
5. Regeneration:
1. Many fully differentiated organisms have the ability to give rise to new individual organisms from their body parts.
2. 1f the individual is somehow cut or broken up into many pieces, each of these pieces grows into separate individuals.
Eg: Planaria
6. Vegetative propagation:
The method in which a vegetative part like stem, root and leaf can produce a new organism, is called vegetative propagation.
Natural methods :
- Stem : Potato
- Root : Carrot
- Leaf : Bryophyllum
Artificial methods :
- Cutting : Rose
- Grafting: Mango
- Layering : Pomogranate
OR
B) Write the differences between the following :
i) bolus – chyme
ii) small intestine – large intestine.
Answer:
i) bolus – chyme
| Bolus | Chyme |
| 1) As a result of chewing, the food mixes with saliva and forms slum mass called bolus. | 1) juices secreted in the stomach break down the food into a smooth mixture called chyme. |
| 2) Bolus comprises the salivary enzyme only. | 2) Chyme comprises gastric juices, hydrochloric acid, and pepsin. |
| 3) The carbohydrates in the food only are converted into maltose sugars. There is no change in the I remaining nutrients, | 3) The proteins in chyme are converted into peptones with the help of pepsin. The bacteria present in food are destroyed by HCl. |
| 4) Food goes from mouth to stomach | 4) Food goes from stomach to small intestine. |
ii) Small Intestine – Large Intestine:
| Small Intestine | Large Intestine |
| 1. The long tube like structure of 9 meters length. | 1. Length is short. But the diameter is more than that of small intestine. |
| 2. Small intestine digests the partially digested food completely. | 2. Any type of digestion does not occur. |
| 3. The products which are formed due to the process of digestion are absorbed through villi into blood. | 3. Large intestine absorbs the water and mtheral salts present in waste material. |
| 4. The villi present in the walls of small intestine increases the surface area for absorption. | 4. The colon acts as storage tank for faeces. |
| 5. The undigested food enters into the large intestine. | 5. It expels out the remained waste materials in the form of stool through anus. |
![]()
Question 17.
A) Write the procedure to determine the presence of starch in the leaves.
Answer:
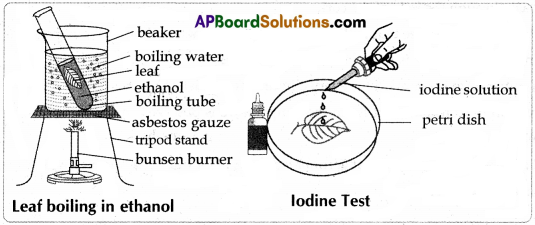
Aim : To prove the presence of starch in leaves.
Required materials : Beaker, water, ethanol, test tube / boiling tube, tripod stand, bunsen burner, petridish and healthy green leaf.
Chemical reagents : Methylated spirit, iodine solution.
Procedure:
- A leaf is taken from the potted plant.
- The leaf is put into a test tube containing methylated spirit (ethanol).
- The leaf is boiled in methylated spirit over a water bath till it becomes pale-white due to the removal of chlorophyll.
- The leaf is taken out of the boiling tube and placed in a petri dish.
- A few drops of tincture iodine / betadine solution are added. Observe the leaf.
Observation :
When we poured iodine solution on the leaf, the leaf turned into blue-black colour showing the presence of starch in it.
Inference :
Basing on the above experiment, it is proved that starch is produced in photosynthesis.
Precautions:
- Take thin leaf well exposed to sunlight.
- Don’t remove the leaf with hand, use brush.
- Use dropper while pouring iodine.
![]()
OR
B) What experiment do you suggest to prove that heat is evolved during respiration ?
Answer:
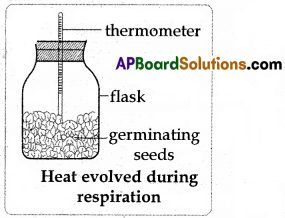
Aim :
To prove that heat is liberated during respiration.
Apparatus :
Thermos flasks, two thermometers, rubber corks dry seeds, germinating seeds.
Procedure :
- Let us take a handful of moong or bajra seeds.
- The seeds are soaked in water a day before experiment.
- Let us keep these soaked seeds in a cloth pouch and tie it with a string tightly.
- The cloth pouch is kept in a corner of class room.
- The sprouts / germinated seeds are collected from the pouch into a thermos flask. Dry seeds are taken into another thermos flask.
- Mouths of the both the flasks are closed with one-holed corks. Thermometers are fixed in each flask through the hole of the cork.
- It is important to see that both the bulbs of thermometers should dip in the seeds in each flask.
- Initial temperature is recorded in both the flasks.
- Temperature is recorded for every 2 hours for at least 24 hours.
Observation :
Constant increase in the temperature is observed in the thermometer placed in the germinated seeds.
Result :
Therefore it is proved that germinated seeds respire and liberate heat which is responsible for the increase in temperature.