Access to a variety of TS Inter 1st Year Chemistry Model Papers and TS Inter 1st Year Chemistry Question Paper May 2019 helps students overcome exam anxiety by fostering familiarity.
TS Inter 1st Year Chemistry Question Paper May 2019
Note : Read the following instructions carefully.
- Answer all questions of Section ‘A’. Answer any six questions in Section ‘B’ and any two questions in Section ‘C’.
- In Section ‘A’, questions from Sr. Nos. 1 to 10 are of “Very Short Answer Type”. Each question carries two marks. Every answer may be limited to 2 or 3 sentences. Answer all these questions at one place in the same order.
- In Section ‘B’, questions from Sr. Nos. 11 to 18 are of “Short Answer Type”. Each question carries four marks. Every answer may be limited to 75 words.
- In Section ‘C’, questions from Sr. Nos. 19 to 21 are of “Long Answer Type”. Each question carries eight marks. Every answer may be limited to 300 words.
- Draw labelled diagrams wherever necessary for questions in Sections ‘3’ and ‘C’.
Section – A
Note : Answer all questions.
Question 1.
State Graham’s law of diffusion.
Answer: The rate of diffusion of a given mass of gas at a given pressure and temperature is inversely proportional to the square root of its density. rate of diffusion r ∝ \(\frac{1}{\sqrt{d}}\)
Question 2.
Calculate the weight of 0.1 mole of Sodium Carbonate.
No. of moles = \(\frac{\text { Weight }}{\text { GM Wt }}\)
0.1 = \(\frac{\text { Weight }}{106}\)
No. of moles = 0.1
Weight = 106 × 0.1
= 10.6 gms
G.S Wt of Na2CO3 = 106
Question 3.
What is Lewis acid? Give one example.
Answer:
A substance which can accept an electron pair to from a co-ordinate covalent bond with donor is called Lewis acid, e.g. : H+, BF3, SnCl2 etc.
Question 4.
Describe the important uses of caustic soda.
Answer:
Uses :
- It is used in petrol refining
- It is used in the purification of bauxite.
- It is used in manufacturing of soap, paper.
- It is used in manufacturing of antificial silk.
- It is used in manufacturing of so many chemically.
- It is used in textile industries for mercerising cotton fabrics.
- It is used in preparation of pure fats and oils.
- It is used in as laboratory reagent.
Question 5.
What happens when magnesium metal is burnt in air?
Answer:
Magnesium metal burns with dazzling brilliance in air to give MgO and Mg3N2.
2 Mg + O2 → 2 MgO
3 Mg + N2 → Mg3N2
![]()
Question 6.
Graphite is a good conductor. Explain.
Answer:
In graphite carbon undergoes sp2 hybridisation. Each carbon forms three σ – bonds with three neighbouring carbon atoms. Fourth electron forms π – bond and it is delocalised. Due to the presence of these moving (or) free electrons graphite acts as good conductor.
Question 7.
What is ‘producer gas’?
Answer:
- Producer gas is mixture of CO and N2.
- It is prepared by passing air over hot coke.
Question 8.
What is meant by coal gasification? Explain the relevant, balanced equation.
Answer:
The process of producing synthesis gas (SYNGAS) by using coal at 1270K temperature is called coal gasification.
![]()
Question 9.
Mention any three uses of H202 in modern times.
Answer:
Uses of H2O2 in modern times :
- H2O2 is used in modern times in Green chemistry to control the pollution. Eg —> It is used in the treatment of domestic and industrial effluents and in the oxidation of cyanides.
- H2O2 is used in manufacturing of sodium perborate and sodium per carbonates. These are used in high quality detergents.’
- H2O2 is used in certain food products and in certain pharmaceu-ticals.
- H2O2 is used as bleaching agent to bleach paper pulp, leather etc.
- H2O2 is used as an antiseptic and in hair bleach. .
Question 10.
Write the IUPAC names of the following,
a) CH3 – CH2 – CH2– CH2– CH = CH2
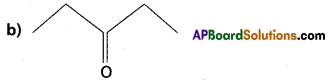
Answer:
Question 11.
Derive idea! gas equation.
Answer:
Ideal gas equation : The,combination of the gas laws leads to the development of an equation which relates to the four parameters volume, pressure, absolute temperature and number of moles. This equation is known as ideal gas equation. In this Boyle’s law and Charles’ law combined together and an equa-tion obtained is called the gas equation.
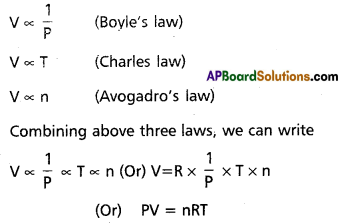
V = volume of the gas
P = pressure of the gas
n = no. of moles of gas
T = absolute temperature
R = Universal gas constant.
![]()
Question 12.
State and explain Hess’s law of constant heat summative. Give example.
Answer:
Hess’s law states that the total amount of heat evolved or absorbed in a chemical reaction is always same whether the reaction is carried out in one step (or) in several steps.
Illustration : This means that the heat of reaction depends only on the initial and final stages and not on the intermediate stages through which the reaction is carried out. Let us consider a reaction in which A gives D. The reaction is brought out in one step and let the heat of reaction be ∆H.
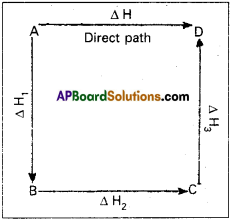
A → D; ∆H
Suppose the same reaction is brought out in three stages as follows
A → B : ∆H1
B → C : ∆H2
C → D : ∆H3
The net heat of reaction is ∆H1 + ∆H2 + ∆H3.
According to Hess law AH = ∆H1 + ∆H2+ ∆H3.
Ex : Consider the formation of CO2. It can be prepared in two ways.
1) Direct method : By heating carbon in excess of O2.
C(s) + O2(g) → CO2(g); ∆H1 = – 393.5 kJ
2) Indirect method : Carbon can be converted into CO2 in the following two steps.
C(s) + \(\frac{1}{2}\) O2(g) → CO2(g); ∆H1 = -110.5 kj
CO(g) + \(\frac{1}{2}\) O2(g) → CO2(g); ∆H2 = -283.02 kj
Total ∆H = -393.52 kJ (∆H1 + ∆H2)
The two ∆H values are same.
Question 13.
Balance the following redox reactions by ion – electron method :
Cr2O72- SO2 → Cr3+(aq) + SO42-(aq) (in acidic solution)
Answer:
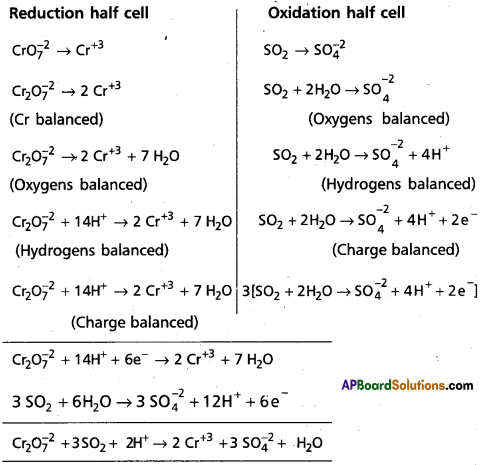
Question 14.
Explain the structure of diborane.
Answer:
Diborane is an electron deficient compound. It has ’12’ valency elec¬trons for bonding purpose instead of ’14’ electrons. In diborane each boron atom undergoes sp3 hybridization out of the four hybrid orbitals one is vacant. Each boron forms two, σ – bonds (2 centred – 2 electron bonds) bonds with two hydrogen atoms by overlapping with their ‘1s’ orbital. The remaining hybrid orbitals of boran used for the formation of B- H-B bridge bonds.
In the formation of B-H-B bridge, half filled sp3 hybrid ofbital of one boron atom and vacant sp3hybrid orbital of second boron atom overlap with 1s orbital of H-atom. These three centred two electron bonds are also called as banana bonds. These bonds are present above and below the plane of BH2 units. Diborane contains two coplanar BH2 groups. The four hydrogen atoms are called terminal hydrogen atoms and the remaining two hydrogens are called bridge hydrogen atoms.
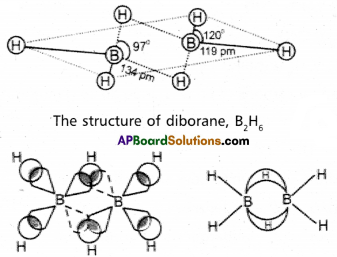
Bonding in diborane, Each B atom uses sp3 hybrids for bonding. Out of the four sp3 hybrids on each B atom, one is without an electron shown in broken lines. The terminal B-H bonds are normal 2-centre-2-electron bonds but the two bridge bonds are 3-centre-2-electron bonds. The 3-centre-2- electron bridge bonds are also referred to as banana bonds.
Question 15.
What is Chemical Oxygen Demand (COD) and Bio Chemical Oxygen Demand (BOD)?
Answer:
Chemical Oxygen Demand (COD): The amount of oxygen required to oxidise organic substances present in polluted water is called Chemical Oxygen Demand (COD). It is an index for amount of organic substances present in water.
Bio Chemical Oxygen Demand : The amount of oxygen used by the suitable micro organisms present in water during five days at 20° C is called as Bio Chemical Oxygen Demand (BOD).
![]()
Question 16.
Which hybrid orbital are used by carbon atoms in the following molecules?
a) CH3 – CH3
b) CH3 – CH – CH2
c) CH3 – CH2 – OH
d) CH3 – CHO
Answer:
a) CH3 – CH3 (ethane) .
The two carbons of ethane undergo sp3 hybridisation.
b) CH3 – CH = CH2 (1 – propene)
Carbon – (1) – undergoes sp2 hyrbidisation
Carbon – (2) – undergoes sp3 hyrbidisation
Carbon – (3) – undergoes sp3 hyrbidisation
c) CH3 – CH2 – OH (ethyi alcohol)
Carbon (1) and (2) both undergo ‘sp3’ hybridisation.
d) CH3 – CHO : (acetaldehyde)

Question 17.
Discuss the application of Le-Chatlier’s principle for the industrial synthesis of Ammonia and Sulphur Trioxide.
Answer:
Applications of Le Chatelier’s principle to synthesis of Ammonia by Haber’s process :
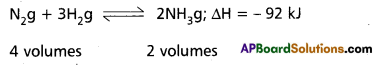
Nitrogen and Hydrogen combine to form ammonia. The forma- tion of ammonia is reversible and exothermic reaction. It is accompanied by decrease in volume.
Effect of Pressure :
1 volume of N2 combines with 3 volumes of H2 to form 2 volumes of NH3. There is decrease in volume in the forward reaction (4 volumes to 2 volumes). According to Le Chatelier’s principle increase of pressure favours the reaction where there is decrease in volume. So higher the pressure, greater the yield of ammonia. In practice 200 atmospheres are used in the manufacture of ammonia by Haber’s process. Low pressures favour the reverse reaction i.e., decomposition of NH3 already formed.
2) Effect of Temperature :
The formation of ammonia (forward reaction) is exothermic reaction
N2 + 3 H2 → 2 NH3; ∆H = – 92 kJ.
Low temperatures favour the forward reaction. But at low temperatures the reaction is too slow. Therefore an optimum temperature (725 K – 775 K) is chosen in Haber’s process. To speed up the reaction, a catalyst, finely divided iron is used. To increase the activity of the catalyst molybdenum or a mixture of oxides of K and Al is used as promoter.
The reverse reaction (i.e.,) decomposition of NH3 is an endothermic reactiori. High temperatures favour the decomposition of NH3. Therefore high temperatures are avoided in Haber’s process. Thus the optimum conditions are
Pressure : 200 atm
Temperature : 725- 775 K
Catalyst : Fe (Powered)
Promoter : Mo (or) (K2O + Al2O3)
Application of Le Chatelier’s principle to the synthesis of SO3:
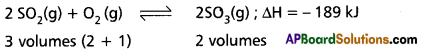
The formation of SO3 is reversible and exothermic reaction. It is accompanied by decrease in volume.
1) Effett of Pressure : 2 volumes of SO2 and one volume of O2 combine to give 2 volumes of SO3. According to Le Chatelier’s Principle increase of pressure favours the reaction where there is decrease in volume. The formation of SO3 is accompanied by decrease in volume (3 volumes to 2 volumes). Higher the pressure greater is the yield of SO3. But in contact process high pressures are not used because towers used in the manufacture are corroded by the acid at these high pressures.
Low pressures favour the decomposition of SO3 as there is increase in the volume of (2 volumes to 3 volumes). Therefore optimum pressures are used (1.5 to 1.7 atmosphere).
2) Effect of Temperature :
The formation of S03 is exothermic. 189 kJ of heat is evolved. High temperatures favour the reverse reaction which is endothermic and do not favour the forward reaction which is exothermic. Low temperatures are favourable for the formation of SO3. At low temperature the reaction is too slow. Therefore an optimum temperature 673 K is used. To speed up the reaction V2O5 is used as catalyst. Thus the optimum conditions are
![]()
Question 18.
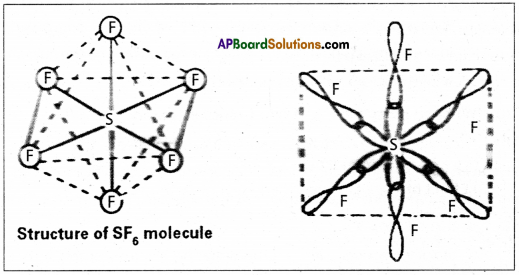
Explain the hybridization involved in SF6 molecule.
Answer:
In this hybridisation one ‘s’ orbital, three ‘p’ orbitals and two’d’ orbitals of the excited atom combine to form six equivalent sp3d2 hybrid orbitals, e.g. : SF6
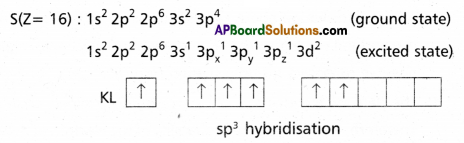
These six sp3 d2 hybrid orbitals overlap six σsp3d2 orbitals ofd fluorine atoms to form six σsp3d2 bonds. The directions of the bonds give an octahedral shape to the molecule. The bond angle is 90° or 180° & 90°.
Question 19.
Explain the salient features of quantum mechanical model of an atom.
Answer:
Important features of quantum mechanical model of atom :
1) The energy of electrons in an atom is quantized (it can only have certain specific values).
2) The existence of quantized electronic energy levels is a direct result of the wave like properties at electrons and are allowed solution at schrodinger wave equations.
3) All the information about the electron in an atom is contained in its orbital wave function Ψ and quantum mechanics makes it possible to extract this information from Ψ.
4) The path of the electron can never be determined accurately. Therefore, we find only the probability of the electron at different pints in space, around an atom.
5) The probability of finding an electron at a point within an atom is proportional to the square of the orbital wave function i.e., |Ψ|1 at that point. |Ψ|2 is known as probability density and is always positive. From the value of |Ψ|2 at different points with in the atom, it is possible to predict the region around the nucleus where electron will most probably be found.
Question 20.
Write an essay on s, p, d and f-block elements.
Answer:
According to the electronic configuration of elements, the elements have been classified into four blocks. The basis for this classification is the entry of the differentiating electron into the subshell. They are classified into s, p, d and f blocks.
‘s’ block elements:
If the differentiating electron enters into ‘s’ orbital, the elements belongs to ‘s’ block.
In every group there are two ‘s’ block elements. As an ‘s’ orbital can have a maximum of two electrons, ‘s’ block has two groups IA and IIA.
‘p’ block elements:
If the differentiating electron enters into ‘p’ orbital, the elements belongs to ‘p’ block. ‘p’ block contains six elements in each period. They are IIIA to VII A and zero group elements. The electronic configuration of ‘p’ block elements varies from ns2np1 to ns2np6.
‘d’ block elements :
It the differentiating electron enters into (n – 1) d – orbitals the elements belongs to ‘d’ block. These elements are in between ‘s’ and ‘p’ blocks. These elements are also known as transition elements.
In these elements n and (n – 1) shells are incompletely filled. The general electronic configuration of ‘d’ block elements is (n – 1) d1-10 ns1-2 This block consists of IIIB to VIIB, VIII, IB and IIB groups.
‘f’ block elements :
If the differentiating electron enters into ‘f’ orbitals of antipenultimate shell (n – 2) of atoms of the elements belongs to ‘f’ block. They are in sixth and seventh periods in the form of two series with 14 elements each. They are known as lanthanides and actinides and are arranged at the bottom of the periodic table. The general electronic configuration is (n – 2) f1-14 (n -1) d0-1 ns2
In these shells the last three shells (ultimate, penultimate and anti penultimate) are incompletely filled. Lanthanides belongs to 4f series. It contains Ce to Lu. Actinides belong to 5f series. It contains Th to Lr.
Advantages of this kind of classification :
As a result of this classification of elements were placed in correct positions in the periodic table. It shows a gradual gradation in physical and chemical properties of elements. The metallic nature gradually decreases and non – metallic nature gradually increases from’s” block to ‘p’ block. This classification gave a special place for radioactive elements.
![]()
Question 21.
How do we get Benzene from acetylene? Give the corresponding equation. Explain the halogenation, alkylation and acylation of benzene with equations.
Answer:
Preparation of Benzene from acetylene : On passing acetylene gas through red hot iron tubes, it trimerises to give benzene.
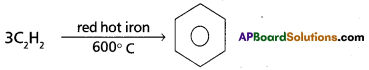
Chemical Properties:
(l)Halogenation: Benzene reacts with chlorine in the presence of FeCl3 or AlC3 to give chloro-benzene.
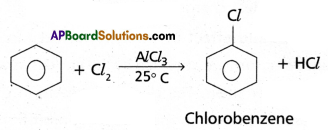
(2) ‘Friedel’- Craft’s Alkylation: Benzene reacts with alkyl halides in the presence of AlCl3 to give alkyl benzene.
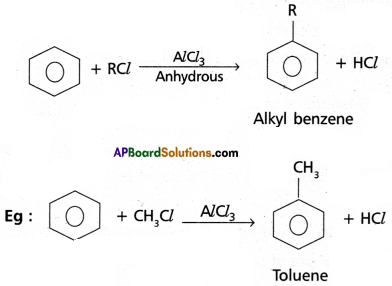
(3) Friedel – Craft’s Acylation: Benzene reacts with acetyl ‘chloride in the presence of AIC13 to give acetophenone.
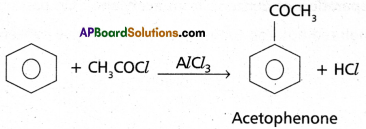
(4) Nitration : Benzene when heated with a mixture of cone. H2SO4 and cone. HNO3 below 60°C to give Nitrobenzene.
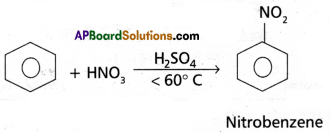
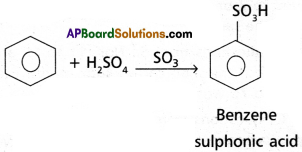
(5) Sulphonation : With fuming H2SO4, benzene, reacts to form benzene sulphonic acid