Access to a variety of TS Inter 1st Year Chemistry Model Papers and TS Inter 1st Year Chemistry Question Paper May 2018 helps students overcome exam anxiety by fostering familiarity.
TS Inter 1st Year Chemistry Question Paper May 2018
Note : Read the following instructions carefully.
- Answer all questions of Section ‘A’. Answer any six questions in Section ‘B’ and any two questions in Section ‘C’.
- In Section ‘A’, questions from Sr. Nos. 1 to 10 are of “Very Short Answer Type”. Each question carries two marks. Every answer may be limited to 2 or 3 sentences. Answer all these questions at one place in the same order.
- In Section ‘B’, questions from Sr. Nos. 11 to 18 are of “Short Answer Type”. Each question carries four marks. Every answer may be limited to 75 words.
- In Section ‘C’, questions from Sr. Nos. 19 to 21 are of “Long Answer Type”. Each question carries eight marks. Every answer may be limited to 300 words.
- Draw labelled diagrams wherever necessary for questions in Sections ‘3’ and ‘C’.
Section – A
Note : Answer all questions.
Question 1.
Define catenation property.
Answer:
Catenation : The phenomenon of self linkage of atoms among themselves to form long chains (or) rings is called as catenation. Carbon has highest catenation tendency due to its high bond energy (348 KJ/mole).
Question 2.
Define the terms Sink and COD.
Answer:
Sink : The medium which retains and interacts with long lived pollutant is called Sink.
COD : The amount of oxygen required to oxidise organic sub-stances present in polluted water is called Chemical Oxygen Demand (COD).
It is an index for amount of organic substances present in water.
Question 3.
Name two adverse effects caused by acid rains.
Answer:
Effects of acid rains :
- Acid rains are harmful for agriculture, trees and plants because it dissolves and washes away nutrients needed for their ‘growth.
- Acid rains .affects the plants and animal life in aquatic ecosystem.
- Acid rains damages the old buildings and historical monuments like Taj mahal.
- Acid rains corrodes water pipes which lead to decrease the quality of drinking water.
![]()
Question 4.
Write any two used of caustic soda.
Answer:
Uses:
- It is used in petrol refining It is used in the purification of bauxite.
- It is used in manufacturing of soap, paper.
- It is used in manufacturing of antificial silk.
- It is used in manufacturing of so many chemically.
- It is used in textile industries for mercerising cotton fabrics.
- It is used in preparation of pure fats and oils.
- It is used in as laboratory reagent.
Question 5.
Define ionic product of water.
Answer:
At a given temp. The product of the concentrations of H+ and OH– ions in water is called ionic product.
Ionic product Kw = [H+] [OH–]
At 25°C Kw = 1.008 × 10-14 mole2/lit2
Question 6.
Calculate the oxidation number of manganese (Mn) in K2MnO4
Answer:
K2MnO4
2(1) + x + 4(-2) = 0
2 + x – 8 = 0
x = +6
Question 7.
Calculate the ratio of kinetic energies of 3 gm of hydrogen and 4 gm of oxygen at a given temperature.
Answer:

Question 8.
What is synthesis gas?
Answer:
- Water gas is also called as synthesis gas.
- It is a mixture of CO and H2.
- It is prepared by passing steamover hot coke.
- It is used for the synthesis of methanol and a number of hydrocarbons. Hence it is called synthesis gas.
Question 9.
Write the biological importance of Magnesium and Calcium. Biological importance of Mg and Ca :
Answer:
Role of Mg2+ in biology:
- Mg2+ ions are concentrated in animal cells.
- Enzymes like “phosphohydrolases’ and ‘Phospho transferases’ contain Mg2+ ions. These enzymes participate in ATP reactions and release energy in the process. Mg2+ forms a complex with ATP
- Mg2+ is a constituent of chlorophyll, the green component of plants.
Role of Ca+2 :
About 99% of body calcium is present in bones and teeth. It also , plays important roles in neuromuscular function, intemeuronal trans¬mission, cell membrance integrity and blood coaqulation. The calcium concentration in plasma is regulated at about 100 mg/Lit. It is maintained by two hormones, calcitonin and parathyroid hormone. Ca2+ ion are necessary for muscle contraction.
![]()
Question 10.
Write the IUPAC names of the following compounds :
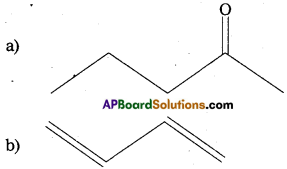
Answer:
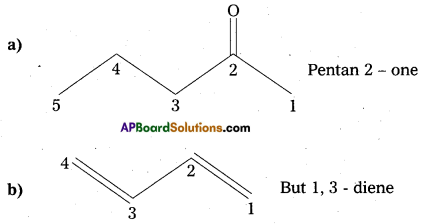
Question 11.
Explain the hybridisation involved in PCl2 molecule.
Answer:
1) In PCl5 the electron configuration of phosphorus is
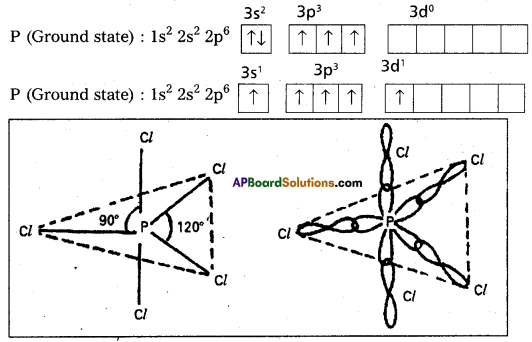
2) Phospho undergoes sp3d – hybridisation by intermixing of one s-orbital[3s] three p – orbital [3px, 3py, 3pz] and one d – orbital.
These five hybrid orbitals overlap. The pz orbitals of chlorine atoms forming five Gsp3d _ s bonds. Out of these five p – Cl bonds three are coplanar and the remaining two are in the axial position. There by PCl5 acquires the trigonal bipyramidal shape. The molecule contains two bond angles 90° and 120°.
Question 12.
What is hydrogen bond? Explain the different types of hy¬drogen bonds with examples.
Answer:
Hydrogen bond is a weak electrostatic bond formed between partially positive charged hydrogen atom and an highly electronegative atom of the same molecule or another molecule. Hydrogen bond is formed when the Hydrogen is bonded to small, highly electronegative atoms like F, 0 and N. A partial positive charge will be on hydrogen atom and partial negative charge on the electro¬negative atom.
The bond dissociation energy of hydrogen bond is 40 KJ/mole. Hydrogen bond is represented with dotted lines (……..). Hydrogen bond is stronger than Vander Waals’ forces and weaker than covalent bond. Hydrogen bonding is of two types. (1) Intermolecular hydrogen bond and (2) Intramolecular hydrogen bond.
1) Intermolecular hydrogen bond :
If the hydrogen bond is, formed between two polar molecules it is called intermolecular hydrogen bond, i.e., the hydrogen bond is formed between hydrogen atom of one molecule and highly electro¬negative atom of another molecule is known as intermolecular hydrogen bond.
Ex.: Water'(H2O) ; HF : NH3; p – nitrophenol, CH3COOH, ethyl alcohol ect.
Water:
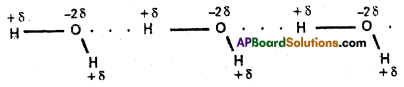
Water molecule forms an associated molecule through inter-molecular hydrogen bond. Due to molecular association water possess high boiling point.
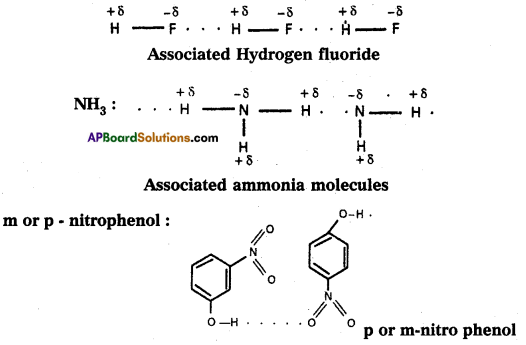
2) Intramolecular hydrogen bond :
If the hydrogen bond is formed within the molecule it is known as intramolecular hydrogen bond.
Ex. : o – nitrophenol; o – hydroxy benzaldehyde.
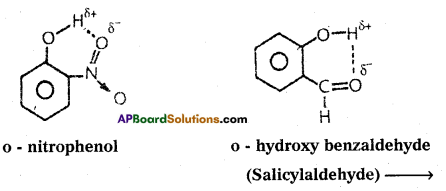
- The physical state of substance may alter. They have high melting and boiling points.
- Ammonia has higher boiling point than HCl eventhough nitrogen and chlorine have same electronegativity values (3.0). Ammonia forms an associated molecule through inter- molecular hydrogen bond.
- p – hydroxy benzaldehyde have higher boiling point than o- hydroxy benzaldehyde. This is due to intermolecular hydrogen bonding in para isomer.
- Ethyl alcohol is highly soluble in water due to association and co-association through intermolecular hydrogen bonding.
Question 13.
Derive ideal gas equation.
Answer:
Ideal gas equation : The combination of the gas laws leads to the development of an equation which relates to the four parameters volume, pressure, absolute temperature and number of moles. This equation is known as ideal gas equation. In this Boyle’s law and Charles’ law combined together and an equation obtained is called the gas equation.
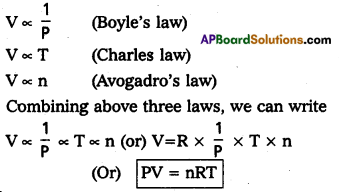
Where V = volume of the gas
p = pressure of the gas
n = no. of moles of gas
T = absolute temperature
R = Universal gas constant.
![]()
Question 14.
State and explain the Hess’s law of constant of heat summation.
Answer:
Hess’s Law:
Hess’s law states that the total amount of heat evolved or absorbed in a chemical reaction is always same whether the reaction is carried out in one step (or) in several steps.
Illustration:
This means that the heat of reaction depends only on the initial and final stages and not on the intermediate stages through which.the reaction is carried out. Let us consider a reaction in which A gives D. The reaction is brought out in one step and let the heat of reaction be ∆H.
A → D; ∆H
Suppose the same reaction is brought out in three stages as follows
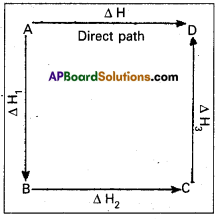
A → B : ∆H1
B → C : ∆H2
C → D : ∆H3
The net heat of reaction is ∆H1 + ∆H2+ ∆H3.
According to Hess law AH = ∆H1 + ∆H2+ ∆H3.
Ex : Consider the formation of CO2. It can be prepared in two ways.
1) Direct method : By heating carbon in excess of O2.
C(s) + O2(g) → CO2(g); ∆H = – 393.5 kJ
2) indirect method : Carbon can be converted into CO2 in the following two steps.
C(s) + \(\frac{1}{2}\) → O2(g); → CO2(g);
∆H1 = – 110.5 kJ
CO (g) + \(\frac{1}{2}\) O2(g) → CO2(g); ∆H2 = – 283.02 kJ
Total ∆H = -393.52 kJ
The two AH values are same.
Question 15.
Explain Lewis acid-base theory with suitable example.
Answer:
Lewis theory of acids and bases : G.N. Lewis proposed a more generalised theory of acids and bases. According to this theory.
Acid : A substance that can accept an electron pair to form a co-ordinate covalent bond is called an acid.
Types of Lewis acids :
Lewis acids are of 5 types.
1) All Cations : Simple cations Ag+ , CO+3, Cu+2, Fe+3, Al+3 can act as Lewis acids.
2) Compounds in which the central atom has an incomplete octet and possessing an empty orbital can act as Lewis acids.
Ex : BF3, BCl3, AIC13, FeCl3.
3) Compounds in which the central atom has vacant d-orbitals and may expand its octet can act as lewis acids.
Ex : SiF4, SF4, TeF4, SnCl4, FeCl3.
The net heat of reaction is ∆H1 + ∆H2 + ∆H3.
According to Hess law ∆H = ∆H1 + ∆H2 + ∆H3.
Ex : Consider the formation of CO2. It can be prepared in two ways.
4) Molecules having multiple bonds between atoms of dissimilar electronegativities can behave like Lewis acids.
Ex : CO2, SO2, SO3, NO2, Cl2O7, P4O10
5) Elements with six electrons in the valence shell or electron sextet can act as Lewis acids.
Ex: O, S
Base : According to Lewis theory a base is a substance which can donate an electron pair to form a co-ordinate covalent bond.
Types of Lewis bases: Lewis bases are divided into three types.
1) All anions
Ex : CP, OHe, CNe, N Hf , Fe, SCNe All simple anions can act as Lewis bases.
2) Molecules with one or two lone pairs on the central atom can act as Lewis bases.
Ex: H2O, NH3, ROH,RNH2, ROR, C5H5N
a) Hydrenyl ion is a lewis base as it can donate an electron lone pair (:OH–).
b) Flouride ion acts as a Lewis base as it can donate any one of its four electron lone pairs.
c) A Proton is a lewis acid as it can accept a lane pair of elec trons from bases like hydrenyl ion and flowride ion.
d) BCl3 acts as a lewis acid as it can accept a lane pair electrons from species like ammonia or amine molecules.
![]()
Question 16.
Explain the following with suitable examples :
a) Electron deficient hydrides
b) Electron rich hydrides.
Answer:
a) Electron – deficient hydrides :
These are the molecular hydrides in which the available no.of valency electrons is less than the number required for normal covalent bond formation.
(or)
These are the molecular hydrides in which the available va¬lency electrons are lessthan the required for writting the Lewis structure of the molecule.
Eg : (AlH3)n, B2H6 etc.
These hydrides acts as Lewis acids i.e. electron pair acceptors. These forms dative bond with donors.
b) Electron – rich hydrides :
These are the molecular hydrides in which the valency elec¬trons on the central atom are more than that are required for bond formation.
(or)
These are the molecular hydrides in which the available va¬lency electrons are more than the required for writting the Lewis structure of the molecule. These hydrides contains lone pairs on central atoms.
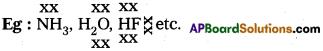
These hydrides have high boiling points than those of the hydrides of the subsequent members of group because of hydrogen bond formation.
Question 17.
Explain the structure of Diborane.
Answer:
Diborane is an electron deficient compound. It has ’12’ valency electrons for bonding purpose instead of ’14’ electrons.
In diborane each borane atom undergoes sp3 hybridization out of the four hybrid orbitals one is vacant.
Each borane forms two, a – bonds (2 centred – 2 electron bonds) with two hydrogen atoms by overlapping with their ‘Is’ orbital. The remaining hybrid orbitals of borane used for the formation of B-H-B bridge bonds.
In the formation of B-H-B bridge, half filled sp3 hybrid orbital of one borane atom and vacant sp3 hybrid orbital of second borane atom overlap with Is orbital of H-atom.
These three centred two electron bonds are also called as ba-nana bonds. These bonds are present above and below the plane of BH2 units.
Diborane contains two coplanar BH2 groups. The four hydrogen atoms are called terminal hydrogen atoms and the remaining two hydrogens are called bridge hydrogen atoms.
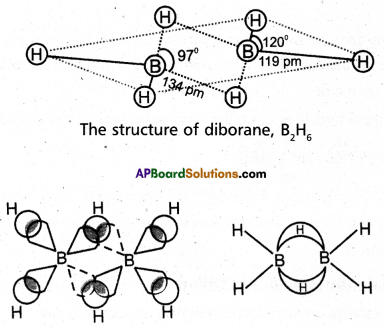
Bonding in diborane, Each B atom uses sp3 hybrids for bonding. Out of the four sp3 hybrids on each B atom, one is without an electron shown in broken lines. The terminal B-H bonds are normal 2-centre-2- electron bonds but the two bridge bonds are 3-centre- 2-electron bonds. The 3-centre-2-electron bridge bonds are also referred to as banana bonds.
Question 18.
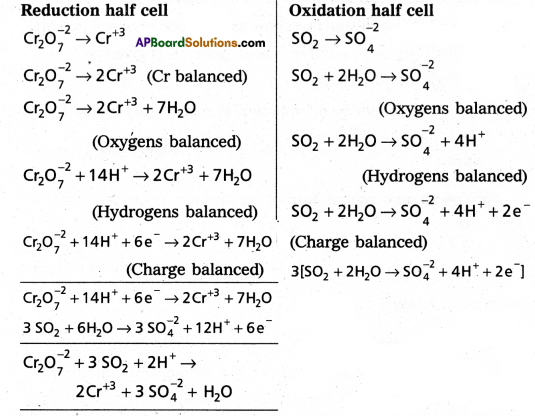
Balance the following redox reaction by ion-electron method:
Cr2 O72-(aq) + SO2(g) → Cr+3(aq) + SO4-2(aq)
Answer:
Cr2 O72- → Cr+3 + SO4+2
Question 19.
a) What are the postulates of Bohr’s model of hydrogen atom?
b) Explain the significance of n and l quantum nos.
Answer:
a) Postulates :
- The electron in the hydrogen atom can revolve around the nucleus in a circular path of fixed radius and energy. These paths are called orbits (or) stationary states. These circular orbits are concentric (having same center) around the nucleus.
- The energy of an electron in the orbit does not change with time.
- When an electron moves from lower stationary state to higher stationary state absorption of energy takes place.
- When an electron moves from higher stationary state to lower stationary state emission of energy takes place.
- When an electronic transition takes place between two sta-tionary states that differ in energy by ∆E is given by ∆E = E2 – E1 = hν
- The frequency of radiation absorbed (or) emitted u = \(\frac{E_2-E_1}{h}\) E1 and E2 are energies of lower, higher energy states respectively.
- The angular momentum of an electron is given by mvr = \(\frac{\mathrm{nh}}{2 \pi}\)
An electron revolve only in the orbits for which it’s angular hmomentum is integral multiple of \(\frac{h}{2 \pi}\)
b) n and l quantum no
1) Principal quantum number : The principal quantum number was introduced by Neils Bohr. It reveals the size of the atom (main energy levels). With increase in the value of ‘ri the distance between the nucleus and the orbit also increases.
It is denoted by the letter ‘n\ It can have any simple integer value 1, 2, 3, …….but not zero. These are also termed as K, L, M, N etc. The radius and energy of an orbit can be determined basing on “n” value.
The radius of nth orbit is rn = \(\frac{n^2 h^2}{4 \pi^2 m^2}\)
The energy of nth orbit is En = \(\frac{-2 \pi^2 m e^4}{n^2 h^2}\)
2) Azimuthal quantum number : It was proposed by Sommer- feld. It is also known as angular momentum quantum number or subsidiary quantum number.
It indicates the shapes of orbitals. It is denoted by 7′. The values of 7′ depend on the values of ‘n’, 7′ has values ranging from ‘O’ to (n – 1) i.e., I = 0, 1, 2, (n – 1). The maximum number of electrons present
in the subshells s, p, d, f are 2, 6, 10, 14 respectively.
| Subshell | l – value | Shape |
| s | 1 = 0 | spherically symmetric |
| P | l = 1 | dumb – bell |
| d | l = 2 | double dumb-bell |
| f | l = 3 | four fold dumb-bell |
Energy levels and subshells
| Principal quantum number (n) | Azimuthal quantum number | Symbol | Number of subshells |
| 1 | 0 | s | 1 (Is) |
| 2 | 0 | s | 2 (2s, 2p) |
| 1 | P | ||
| 3 | 0 | s | 3 (3s, 3p, 3d) |
| 1 | p | ||
| 2 | d | ||
| 4 | 0 | s | 4 (4s, 4p, 4d, 4f) |
| 1 | P | ||
| 2 | d | ||
| 3 | f |
Question 20.
Define electron gain enthalpy and electronegativity. How these two periodic properties varies in groups and periods?
Answer:
Electron gain Enthalpy (Elctron affinity) :
The amount of energy released when an electron is added to outer most shall of isolated neutral gaseous atom is called electron gain enthalpy.
Variation in a group :
In a group from top to botton electron affinity decreases. This is due to the increase of atomic size.
Variation in a period :
In a period from left to right electron effinity increases. This is due to the decrease atomic size.
Electro negativity:
The tendency of an atom to attract the shared pair of electrons towards it self in a molecule is called electro negativity.
Variation in a group:
In a group from top to bottom electro negativity decreases. This is due to the increases of atomic size.
Variation in a period:
In a period from left to right electro negativity increases. This is due to the decrease of atomic size.
![]()
Question 21.
Give two methods of preparaton of acetylene. How does it react with hydrogen and water?
Answer:
Preparations of acetylene (CH = CH) :
1. From CaC2 : CaC2 under go hydrolysis to form acetylene.
CaC2 + 2H2O → Ca(OH)2 + CH = CH
2. From Iodo form : Iodoform reacts with silver powder to form acetylene.
CHI3 + 6Ag + CHI3 → CH = CH + 6Agcl
Properties :
1. Reactions with hydrogen : Acetylene reacts with hydrogen to form ethane findly.
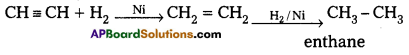
2. Reactions with water : Acetylene reacts with water inpresence of Hg+2, H2SO4 to form vinylalcohol and acetoldehyde
