Telangana SCERT 8th Class Biology Study Material Telangana Pdf Lesson 3A The World of Microorganisms Part 1 Textbook Questions and Answers.
TS 8th Class Biology Lesson 3A Questions and Answers Telangana – The World of Microorganisms Part 1
Question 1.
Which organisms act as an interlink between living and non-living organisms? Why do you think so?
Answer:
Viruses are the organisms which are interlinked between living and non-living because they behave like non-living things when they are outside of a living cell. But they behave like living organisms by reproducing in host’s living cells like bacteria, plants and animals. Eg: HIV, Tobacco Mosaic virus.
![]()
Question 2.
Write about the diseases caused by micro-organisms.
Answer:
Different types of harmful microbes cause various diseases to the animals, birds and man.
Diseases caused by viruses:
| Animals | Man |
| Chicken – bird flu Cattle – foot and mouth disease, measles, rinder pest Sheep: blue tongue | Small pox, polio, AIDS flu fever, swine flu, chikun gunya, rubella, mumps, conjunctivitis |
Diseases caused by bacteria:
| Animals | Man |
| Cattle: Mastitis, cholera Sheep : Anthrax, hemorrhagic septicemia, enteritis. |
Typhoid, diptheria, whooping cough, T.B, leprosy, tetanus. |
Diseases caused by fungus in man: Allergy, ring worm, candidiasis.
Diseases caused by protozoa in man : Malaria, kala azar, amoebiasis, sleeping sickness etc.
Diseases caused by micro arthropodes: Scabies, Allergy etc.
Question 3.
What type of micro-organisms we can observe in pond water?
Answer:
We can observe the following micro-organisms in pond water.
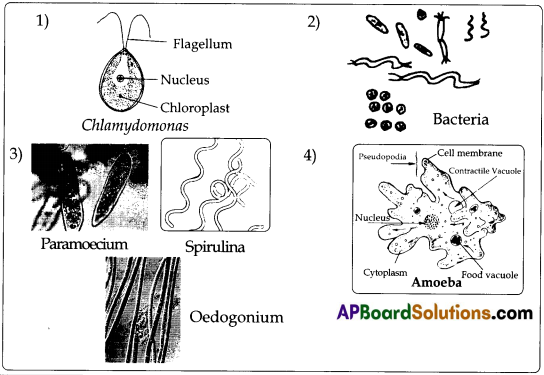
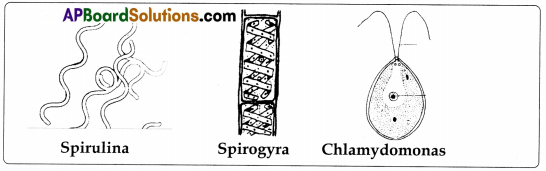
- Algae : Chalamydomonas, Spirogyra, Oedogonium, Spirulina etc.
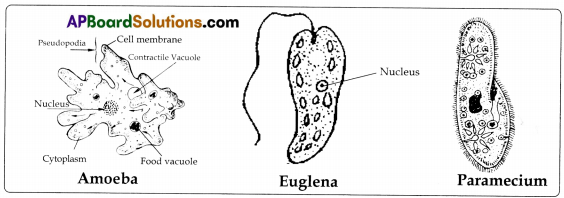
- Protozoa: Amoeba, Euglena, Paranioecium, Vorticella etc.
- Micro Arthropods : Cyclops, Daphnia etc.
![]()
Question 4.
Whether micro-organisms are useful and harmful. How? Explain.
Answer:
1. Some of the micro-organisms are highly helpful to man, animals and plants. By decomposing the dead bodies of plants and animals, they return valuable nutrients to earth and these nutrients are used by other plants and animals for their growth.
2. Some of the micro-organisms are present in the intestines of living animals. For example, animals like termites, cattle, horses, rabbits etc., have several thousands of micro-organisms in their stomach that help them to digest cellulose present in the plants.
3. Some of the micro-organisms are used in preparing food material. For example preparation of curd, buttermilk and cheese require the presence of micro-organisms.
4. In recent years, use of micro-organisms is also increased in industries for the production of alcohol, drugs (such as antibiotics and vitamins) and a wide variety of products.
5. However, all the micro-organisms are not helpful. There are some micro organisms which cause diseases in plants, animals and man. For example, cholera, T.B, typhoid are caused by micro organisms.
Question 5.
Why cooked food spoil soon but not uncooked food ? Give your reasons.
Answer:
The biochemical substances such as enzymes and metabolites in the cooked food are prone to the action of microbes. The enzymes and metabolites are inactive in the uncooked or raw food. Microbes cannot show immediate influence on the inactive chemicals in the raw food. Hence cooked food spoils within less time compared to uncooked or raw food material.
Question 6.
What questions would you like to ask your teacher to know about different shapes of Bacteria?
Answer:
- How many shapes of bacteria are here?
- Is there any relationship between the shape of the bacteria and the disease caused by them?
- Does the shape of a bacterium help it to survive in odd conditions?
- Which is the most common shape found?
![]()
Question 7.
What would happen if you add buttermilk to
a) chilled milk
b) hot milk
c) luke warm milk?
Answer:
The lukewarm milk turned into curd, because the atmosphere between 30’3c – 40°c is favourable for the curdling of milk. The lukewarm condition of milk is favourable for the growth of micro organisms called Lactobacillus.
Lactobacillus helps in curdling milk. The temperature below and above lukewarm conditions may lessen the growth of Lactobacillus bacteria which further slows down the curdling of milk.
Question 8.
How are the human actions causing the death of useful bacteria and fungi? What will happen, if it continues?
Answer:
- Human actions such as indiscriminate applying of pesticides on crops, over usage of artificial fertilizers and releasing industrial effluents affect the death of useful bacteria and fungi.
- This indiscriminate applying of pesticides and fertilizers kill useful soil-nitrifying bacteria.
- Indiscriminate releasing of industrial effluents mix in soil and water and kill useful decomposers (bacteria and fungi). If this action continues the earth becomes a garbage of plants and animal wastes.
- If this continues, entire bio-diversity is disturbed threatening the very existence of human beings.
Question 9.
What procedure did you follow to observe lactobacillus bacterium in the Lab?
Answer:
Aim: To observe Lactobacillus bacteria.
Apparatus :
- few drops of butter milk
- glass slide
- lamp
- crystal violet
- microscope.
Procedure : One or two drops of butter milk is taken on slide. They are spread on the slide and heated on a lamp. Then a few drops of crystal violet is added on slide. The slide is left for 30 – 60 seconds and washed it gently with water. The slide is kept under the compound microscope.
Observation : Small stick like structures are seen on the slide.
Result: There is the presence of Lactobacillus bacterium in the butter milk.
Question 10.
Visit any bakery or milk chilling center near your school with the help of your teacher or parents. Learn about some techniques to culture and usage of some Micro organisms and prepare a note on them.
Answer:
Project Work:
Aim of the project: To learn about some techniques of culturing and usage of microbes in the milk chilling station.
- Curdling of Milk: Boiled milk is soured by harmless bacteria called “lactic acid bacteria”.
- Ripening of cheese: By adding micro-organisms to milk, the milk protein (casein) is coagulated. This results in the formation of semi solid substance. It is called cheese.
Question 11.
Observe some permanent slides of micro-organisms in your school lab with the help of Microscope. Draw their pictures.
Answer:
Question 12.
Prepare a model of any micro organism. And write a note on them.
Answer:
Aim : To prepare a model of a micro organism.
![]()
Requirements: A plastic tin or glass bottle (5 to 10 inches), binding wire (few centimetres), stick (7- 12 inches), paper pieces (slipper shape).
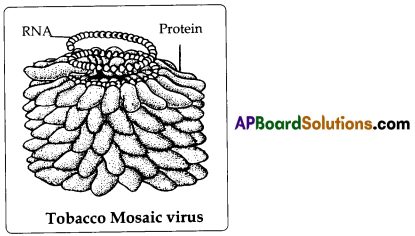
Process : Take a glass or plastic bottle of moderate size. Glue thick slipper shaped paper pieces (1 – 2 cm size) around the bottle from top to bottom as it is shown in the picture. Fix a spring shaped binding wire on the top of the bottle. We should see that the mouth of the bottle removed or covered with paper pieces. Model of Tobacco mosaic virus is ready.
Note on the model – Virus: Viruses are an interesting type of micro organisms. They behave like non living things when they are outside of living cell. They behave like living organisms when they are inside hosts living cells and reproduce Like other organisms
Question 13.
Do you clean your hands with soap before eating? Why?
Answer:
Yes, I do. Our hands have contact with numerous harmful microbes while working. If we eat food without washing hands the microbes on the hands directly enter our body along with food. Those microbes cause harmful diseases. Therefore we should clean our hands with soap before eating.
TS 8th Class Biology Lesson 3A The World of Microorganisms Part 1 Activities
Activity – 1 :
Question 1.
Collect some pond water or water from any tank in your surroundings. Ensure to take some of the greenish scrapings from the side of the tank. Take 1-2 drops of water (from the sample you have collected) on a slide and observe through Microscope. Draw rough sketches in your note book of what you observed.
Answer:
Aim of the project: To observe the pond water and greenish scrapings of the tank under the microscope.
Procedure : Certain amount of pond water and greenish scrapings from the tank were collected. 1-2 drops of collected sample water is taken on the slide. It is kept under the microscope. We found some organisms in the pond water along with greenish scrapings. Our teacher told us their names also. They are given below. We drew rough sketches of those organisms.
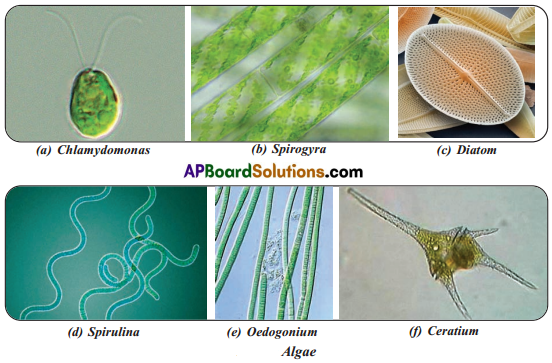
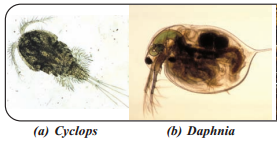
![]()
Activity – 2 :
Question 2.
Write a simple experiment to find out fungi.
Answer:
Aim : To find fungi with simple experiment.
Requirements: Rotten part of vegetable, slide, coverslip and microscope.
Procedure : Some rotten part of vegetables is taken on a slide with the help of a needle. A drop of water is put on the slide, covered with a cover slip and observed through a microscope.
Observation: Filament like structures are seen in the rotten part of vegetables. They are black grevish in colour.
Result: It is decided that the filamental structures are fungi.
Question 3.
When do we see structures of fungi with our naked eye?
Answer:
Usually after the rainy season we may find small umbrella like growths over rotton material of dumped water between the grasses in a field or edges of wet rotten wooden planks. Often we may observe white patches on the bark of trees.
Activity – 3 :
Question 4.
Take one or two drops of butter milk on a slide, spread it. Heat the slide slightly on a lamp (3-4 seconds). Add a few drops of crystal violet on it. Leave it for 30 to 60 seconds and wash the slide gently with water. Observe the slide under the compound Microscope. Draw rough sketches in your note book of what you have observed.
Answer:
Observation : When we put the stained slide of buttermilk under the microscope we had seen specific shaped micro organisms. Then we requested our teacher to give clues for finding the name of the micro organism.
It is declared that the micro organism present in the butter milk is Lactobacillus bacterium. The rough diagram is drawn here.
Question 5.
What are the ways of finding bacteria ?
(or)
Where do you find bacteria in your surroundings ?
Answer:
We can see bacteria in butter milk or curd or early morning scraping of tongue (before washing the mouth) We can also see bacteria in the soil, over bark of tree, over our skin, in our arm pits and in many other places.
Activity – 4 :
Question 6.
Collect a cup of greenish pond water in our surroundings. Put a drop of water on the slide. Keep it under microscope and observe. What would you find out ? Draw rough sketches. What can you name them ?
Answer:
When we observe greenish pond water there are algae and other plants in it. We can see some of algae like Spirulina, Spirogyra, Chlamydomonas etc.
Activity – 5 :
a. How can you observe protozoa with a simple activity ? Draw the sketches of organisms you observe.
Answer:
Hay is soaked in pond water for 3 to 4 days to prepare a decoction of hay. Later a drop of water is put on the slide. It is kept under microscope. Protozoan organisms like Amoeba and Paramoecium are seen in the hay decoction.
b. Do you agree soil contains micro organisms ? Explain.
Answer:
Yes, I agree that soil is highly rich in micro organisms such as bacteria, fungi, protozoa and micro arthropods.
The top 8 inches of soil of one area may contain as many as 5½ tons of fungi and bacteria only.
Activity – 6 :
Question 7.
Write the experiment of observing soil micro organisms ?
Answer:
Soil is collected from the field in a beaker or in a glass. Some water is added to the soil and stirred. Soil particles settle down after sometime. Then a drop of water is taken on a slide and observed under microscope. It is observed that some micro-organisms are present in the soil.
Question 8.
Draw a neat diagram of Tobacco Mosaic virus.
Answer:

TS 8th Class Biology Lesson 3A The World of Microorganisms Part 1 Important Questions
Question 1.
Write a short notes on Anthony Van Leeuwenhoek.
Answer:
Anthony Van Leeuwenhoek was a fabric merchant. Microbiology as a science was born in 1674 when Anthony Van Leeuwenhoek observed a drop of lake water through a glass lens that he had carefully found. He built a single lens powerful microscope, which could magnify the objects 300 times. He is called inventor of the Microscope. He observed many micro organisms under his microscope which led to discovery of other microbes.
![]()
Question 2.
Who invented microscope?
Answer:
Anthony Van Leeuwenhoek invented a powerful single lens microscope.
Question 3.
What are the major groups of micro-organisms?
Answer:
Bacteria, Fungi, Protozoa and Algae are major groups of micro-organisms.
Question 4.
Where do viruses reproduce?
Answer:
Viruses can reproduce only in host’s living cells.
Question 5.
Name some diseases caused by bacteria and protozoa. (CU)
Answer:
Diseases caused by bacteria : Typhoid, tuberculosis (T.B) and septicemia or blood poisoning etc.,
Diseases caused by protozoa: Malaria, Amoehiasis etc.
Question 6.
How can you stain bacteria?
Answer:
Before going to observe bacteria smear bacteria is put on a slide and the slide is slightly heated. Then drops of crystal violet is added on the slide. After 30- 60 seconds the slide is washed gently. Then the slide is ready to be observed under the microscope.
Question 7.
When do viruses behave like living organisms?
Answer:
Viruses behave like living organisms by reproducing in host living cells like bacteria, plants or animals.
Question 8.
Who called bacteria as animalcules?
Answer:
Anthony Van Lecuwenhoek called bacteria as ‘animalcules’.
Question 9.
Name the micro organism present in the butter milk.
Answer:
Lactohacillus or Lactic acid bacteria present in curd and butter milk.
Question 10.
Visit any Microbiology Department of Degree, PG College or Bakery nearby you with the help of your teacher or parents. Know some techniques to culture some micro-organisms from air, water, soil and from rotten vegetables or fruits.
Answer:
I visited T.M.T college along with my teacher. I approached Microbiologist. There he gave me sufficient material about different techniques to culture micro organisms.
Background : To demonstrate the presence of micro organisms by allowing the samples such as soil, water and air to come in contact with the sterile nutrient medium in which they readily grow.
![]()
Princicple : Sterile nutrient medium is exposed to air, soil or water under aseptic conditions for one day. Some of the techniques are given below:
- Chernostat
- Turbostat and hanging drop techniqiw
- Synchronous culture
- Fed – batch culture
- Agar plate culture
- Selective medium culture
- Wet mount preparation
- Dry mount preparation
- Differential staining
Question 11.
Visit a nearby microbiology laboratory or go to internet centre with your teacher. Collect the information about culturing of micro organisms in air, water, soil, rotten vegetables and fruits.
Answer:
Culturing of microbes: Vegetable peels, food wastes, fallen leaves and fruit wastes are collected. All the collected wastes are kept in the pit. Some water is sprinkled on the wastes. Later the pit is covered with soil. Water is sprinkled on the top of the pit regularly for a few days. As a result the wastes in the closed pit re-decayed and decomposed. Bio-fertilizer or compost is formed by the action of micro – organisms. The closed pit facilitates the growth of micro organisms that act on the wastes. Compost contains useful micro organisms which make the soil fertile.
Questions based on Do you know?
Question 1.
Our body is good example for symbiotic relations with microbes. Explain briefly.
Answer:
- There are several bacteria growing on our skin.
- Many of the disease-causing ones live in some symbiotic relations with other bacteria.
- There are different kinds of bacteria in our intestine which are useful in digestion.
- For example some bacteria help in synthesis of vitamins.
Question 2.
Where are bacteria found? Name the biggest bacteria that is discovered?
Answer:
- Bacteria are found everywhere and there are over thousand types of them in soil and water.
- In 1997 Heide N. Schulz discovered a biggest bacteria Thiomargarita antibiosis found in coastal waters of Namibia (0.75 m m).
- This bacteria can be seen with unaided eye.
Question 3.
Write about some of the important soil micro arthropods.
Answer:
- Micro arthropods are also called joint legged micro organisms.
- Some micro arthropods are very important for the soil.
- They help in increasing soil fertility by decomposing the harness through digestion which converts the bigger coompounds into smaller compounds.
Question 4.
Write a short note on soil micro-organisms.
Answer:
- Soil is highly rich in micro organisms such a bacteria, fungi, protozoa, micro arthropods.
- The top eight inches of soil of one-acre area may contain as much as five and half tons of fungi and bacteria.
- This is very much useful for growing crops. But excess use of pestisides kills these micro-organisms.
- We can see them through a microscope or by growing them in different media.
Question 5.
Write a short note on viruses. Write some diseases caused by viruses.
Answer:
- Viruses are an interesting type of microorganism.
- They behave like non living things when they are outside a living cell.
- But they behave like living organisms when they are inside host living cells and reproduce just like bacteria, plants or animals.
- They can only be seen through very powerful electron microscope.
- Diseases like polio, swine flu, conjunctivitis, smallpox, chickenpox and AIDS are caused by viruses.
![]()
Question 6.
Write a short note on how bacterial staining is done.
Answer:
- Bacteria are very small! tiny micro-organisms.
- We must stain before seeing Bacteria under Microscope.
- Smear bacteria on a slide and slightly heat the slide.
- Then put drops of crystal violet on the slide. After 30 to 60 seconds gently wash the slide.
- Dry the slide and now watch the slide under the microscope in 25 X or 40 X.
Question 7.
Classify the following organisms into unicellular and multicellular.
Amoeba, Fish, earthworm, bacteria, camel, paramoecium, snake, human beings.
Answer:
| Unicellular | Multicellular |
| Amoeba, bacteria, paramoecium |
Fish, earthworms, camel, snake, human beings. |
Question 8.
Draw the diagram of Paramoecium and label it. How do you observe unicellular organism ?
Answer:
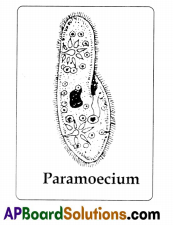
Hay is soaked in pond water for 3 to 4 days to prepare a decoction of hay. Later a drop of water is put on the slide. It is kept under microscope. Protozoan organisms like Amoeba and Pararnoecium are seen in the hay decoction.
Diagram :
Question 1.
Draw any 2 different types of bacteria.
Answer:
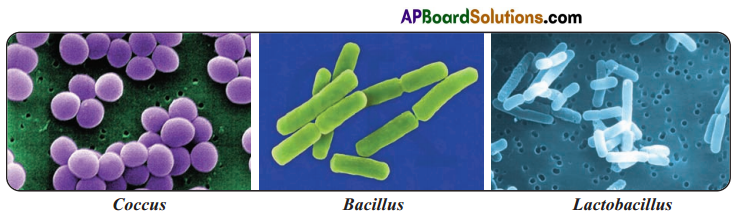
Choose the correct answers :
Question 1.
One of the following is not a viral disease ( )
A) polio
B) typhoid
C) influenza
D) small pox
Answer:
B) typhoid
![]()
Question 2.
The other name of Septicemia ( )
A) tuberculosis
B) micosis
C) tissue decay
D) blood poisoning
Answer:
D) blood poisoning
Question 3.
Parasite means ( )
A) Major organism grows on micro organism
B) Micro organism grows on other organism
C) Both A & B
D) Bacteria alone called parasite
Answer:
B) Micro organism grows on other organism
Question 4.
These stand between living and non living: ( )
A) virus
B) bacteria
C) fungi
D) protozoa
Answer:
A) virus
Question 5.
Malaria is caused by ( )
A) bacterium
B) virus
C) protozoan
D) All
Answer:
C) protozoan
Question 6.
Scabies mite is ( )
A) annelid
C) micro arthropod
C) virus
D) fungus
Answer:
C) micro arthropod
Question 7.
The size of amoeba ( )
A) 500 microns
B) 0.25 mm.
C) 25 mm.
D) 500 mm.
Answer:
A) 500 microns
Question 8.
The size of paramoecium ( )
A) 500 m.m.
B) 2.5 m.m.
C) 25 nm.
D) 0.25 m.m.
Answer:
D) 0.25 m.m.
![]()
Question 9.
T.B. means ( )
A) paralysis
B) allergy
C) fever
D) tuberculosis
Answer:
D) tuberculosis
Question 10.
Find out the micro arthropod ( )
A) Ceratium
B) Spirulina
C) Paramoecium
D) Eyelash mite
Answer:
D) Eyelash mite
Question 11.
Which organism is not fungus? ( )
A) Lactobacillus
B) Aspergillus
C) Penicillium
D) Rhizopus
Answer:
A) Lactobacillus
Question 12.
Find out the harmful micro-organism ( )
A) Aspergillus
B) Chlamydomonas
C) Amoeba
D) All
Answer:
A) Aspergillus
Question 13.
Which organism does not belong to micro algae: ( )
A) Charndornonas
B) Spirogyra
C) Daphnia
D) Oedogonia
Answer:
C) Daphnia
Question 14.
One of the organisms is not a protozoan: ( )
A) Amoeba
B) Cyclops
C) Vorticella
D) Paramecium
Answer:
B) Cyclops
Question 15.
Identify non-microscopic algae in the following: ( )
A) Chara
B) Spirogyra
C) Chlamydomonas
D) A & B
Answer:
D) A & B
Question 16.
Nithya visited pond. He observed greenish water in it. What could be the reason for this? ( )
A) Bacteria
B) Viruses
C) Fungi
D) Algae
Answer:
D) Algae
Question 17.
Choose the correct matching.
List – I —- List – II
1. Spirogyra ( ) a. Algae
2. Plasmodium ( ) b. Protozoa
3. Rhizopus ( ) c. Fungi
A) 1 – a, 2 – b, 3 – c
B) 1 – b, 2 – a, 3 – c
C) 1 – c, 2 – a, 3 – c
D) 3 – a, 2 – b, 1 – c
Answer:
A) 1 – a, 2 – b, 3 – c
![]()
Question 18.
List-I —- List-Il
1. Malaria ( ) a. Viruses
2. Typhoid ( ) b. Bacteria
3. AIDS ( ) c. Protozoa
A)1 – a, 2 – b, 3 – c
B) 1 – b, 2 – a, 3 – c
C) 1 – c, 2 – a, 3 – c
D) 3 – a, 2 – b,1 – c
Answer:
D) 3 – a, 2 – b,1 – c
Question 19.
Bacteria present in the intestine are useful for ( )
A) Absorption
B) Digestion
C) Excretion
D) Respiration
Answer:
B) Digestion
Question 20.
Find out the materials ised to prove yeast for preparation of alcohol from sugar: ( )
1) Sugar
2) Yeast
3) Alcohol
4) Bowls
A) 1
B) 2
C) 1,2,3
D) 1,2,4
Answer:
D) 1,2,4
Question 21.
Neelu observed white patches on the bark of trees. The reason for this ( )
A) Protozoa
B) Viruses
C) Fungi
D) Insects
Answer:
C) Fungi
Question 22.
Name the fungi you observe on the bread ( )
A) Aspergillus
B) Rhizopus
C) Peziza
D) Puccmia
Answer:
B) Rhizopus
Question 23.
The growing place of the given micro orgranism ( )

A) Vacuum
B) Hot areas
C) Rotten vegetables
D) None of these
Answer:
C) Rotten vegetables
![]()
Question 24.
Identify the correct sentence
1. Viruses are non living things when they are outside
2. They behave like living when they are in the host cells ( )
A) 1, 2 correct
B) 1, 2 are not correct
C) 1 is correct 2 is not
D) 1 is not 2 is correct
Answer:
A) 1, 2 correct
Question 25.
The slipper shaped unicellular organism is ( )
A) Amoeba
B) Paramoecium
C) Spirogyra
D) Penicillium
Answer:
B) Paramoecium