TS Board 6th Class Science Guide Telangana 9th Lesson Plants: Parts and Functions Textbook Questions and Answers.
TS 6th Class Science 9th Lesson Questions and Answers Telangana – Plants: Parts and Functions
Question 1.
What are the important parts of a plant ?
Answer:
Stem (trunk), branches, leaves, twigs (small branches) and roots are the important parts of a plant.
Question 2.
How will you tell which part of a plant is the stem and which is the root?
Answer:
- We can identify stem and root parts by the following way.
- The part which bears branches, leaves, flowers and flower buds is called stem.
- The stem bears entire aerial part of the plant.
- The part of the plant which helps in anchoring the plant body to the soil is called root.
- Roots absorb water and minerals from the soil.
![]()
Question 3.
Collect any plant from your surroundings. Draw its root structure. What can you say about its root system?
(Or)
Draw a neat labelled diagram of root system of tridax plant.
Answer:

- The root system in the collected plant exhibits tap root system
- In this plant, the main root becomes thick. This main root is called tap root.
- From the main root, small sideward roots are formed. These small roots are called lateral roots.
Question 4.
John has no place in his house but he wants to plant vegetables like tomato in his house. Suggest him different ways to do so.
Answer:
- If John’s house is with reinforced concrete cement roof (slab), there are alternative methods of harvesting vegetable plants like tomato.
- The following methods can be followed by John.
- By introducing the small height wooden pots (or rectangular tubs) along with collected humus or vermicompost.
- By preparing cement tubs is also a possible method of growing tomato plantations. The cement tubs are to be filled with humus or compost.
- If John’s house is not with RCC roof, he has to do the following.
- Hanging the potted tomato plants outside his house to allow them for better aeration. This also helps him to grow the plants.
Question 5.
What will happen if a plant doesn’t have any leaves?
Answer:
- Leaves are the essential food factories of plants. They synthesize food for whole plant by the process of photosynthesis.
- Appearance and development of more leaves lead to synthesis of more food in the plant.
- If number of leaves decrease in the plant, there will be a decrease in food production.
- Except in few plants, leaves are the only prime sources for synthesis of food.
- Therefore, if a plant doesn’t have any leaves it will die soon.
![]()
Question 6.
How does the stem help the plant?
Answer:
Functions of Stem:
- Gives support to branches, leaves and fruits.
- Establishes connection between roots and leaves.
- Supplies water and minerals dissolved in water from roots to leaves, flowers and fruits.
- In young plants, the stem also performs photosynthesis.
- In some plants, stem stores food material.
Question 7.
What type of venation is found in the leaves of plants with fibrous roots?
Answer:
Parallel venation is found in the leaves of plants like grass, coconut, date palm etc. These plants possess fibrous roots.
Question 8.
If the leaves have reticulate venation, what would be the type of root?
Answer:
Naturally, the plants which have tap root system possess reticulate venation.
The veins and veinlets divide into small branches. Eg: Datura (Ummetta), Guava.
![]()
Question 9.
Explain the various parts of a plant with the help of a diagram.
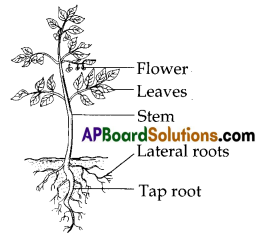
Answer:
The plant diagram that is drawn above shows the following important parts.
- Stem: Stem is the main part of the plant. It supports the entire aerial part of the plant.
- Branches: Stem of the plant divides into so many branches. Branches are the other main parts of the plant. They bear leaves, flowers, buds and fruits.
- Leaves: Leaves are the main sources of the plant. They prepare food for the plant. They are called food factories of the plant.
- Flowers: Flowers are the reproductive parts of the plant. They develop into fruits.
- Stem tp: This is the growing region of the plant.
- Roots: Roots are the anchors which fix the plant firmly to the soil. These provide water and minerals to other parts of the plant.
Question 10.
Explain the parts of a leaf with the help of a diagram.
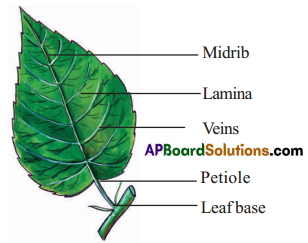
Answer:
There are five important parts in a leaf. They are.
1. Leaf base 2. Petiole 3. Lamina or leaf blade 4. Midrib 5. Veins.
- Leaf base: This is the lower part of the leaf where the leaf attaches to the stem near the node.
- Petiole: The stem – like part of the leaf that joins the leaf blade to the stem is called petiole.
- Lamina or leaf blade : This is the green, expanded portion of the leaf.
- Veins : Many ridged branched structures that spread on the lamina are called veins. They spread as veinlets.
- Midrib : The long vein present in the middle of the lamina is called as Midrib.
Question 11.
How can you show that plants absorb water through their roots?
(Or)
Roots of plant absorb water and minerals that are present in the soil. How can you prove this with experiment?
Answer:
Aim : To show that the plants absorb water through their roots.
Apparatus : Two glass tumblers, two plants having soft stems, ink bottle, water or ink filler.
Procedure : Two glass tumblers are taken and filled with water. Two plants having soft stems, along with their roots are placed in the tumblers. Few drops of red ink are added in one of the tumblers. Then the water is changed into red colour. Both the tumblers are undisturbed for 2- 3 hours.
Observation : Red spots are seen in the stem which is in red coloured water. No spots are seen in other plant which is in colourless water.
Inference: It is concluded that roots help in taking up of water. The coloured water enters the stem through roots. Roots have the capacity of absorbing minerals and water from the soil.
Result : Plants absorb water through their roots.
Question 12.
Rajani said “Respiration takes place in leaves”. Is she correct? How can you support this statement?
Answer:
Plants respire as animals perform with special organs. But we cannot recognize external respiration (exhalation and inhalation). Respiring of gases is done through stomata which appear on the leaf surface and lenticels present on the bark of the stem and root surfaces. The mechanism of cellular respiration or internal respiration is very recognisable as it is seen in the animals.
Question 13.
Collect the leaves of various plants. Prepare a herbarium. Write a brief report on their shapes, size and venation.
Answer:
Aim of the project: To collect various plant leaves to find out their shapes, sizes and venation.
There are two types of leaves based on their shape and venation. Based on the shapes, they are two types.
- Simple type
- Compound type.
There are two types of venation
- Reticulate venation
- Parallel venation.
Tabulation of information:
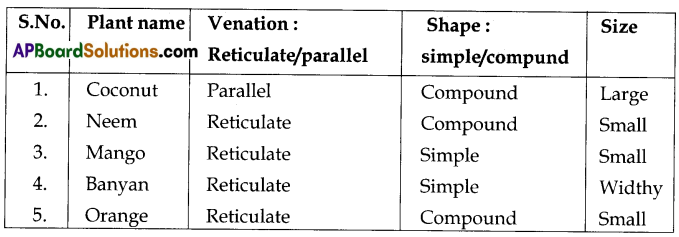
Question 14.
Prepare a greeting card with dry leaves.
Answer:
Aim : To prepare a greeting card with dry leaves.
Requirement: Banyan tree leaf, chart with accurate length and width (6 x 4 inches)
Procedure:
- The collected banyan leaf is soaked in the lime water for one or two days.
- As a result, all the green part disappears.
- Only veins and veinlets are left in the leaf. It looks like a skeleton structure of the leaf.
- Then, gently a picture is drawn on that leaf.
- Painted leaf is pasted on the chart piece with specific length and width.
- Finally, the beautiful greeting card is ready.
Question 15.
Your teacher suggested not to harm other plants when you collect plants for observation. Why did she suggest so?
Answer:
Her suggestion is reasonable. Because,
- to observe the plant parts, it is not needed to pluck the parts from the plant.
- if we continue to pick up the plants, removing from the soil, their population will gradually decrease.
- decreasing plant population is dangerous to the earth and other organisms.
- plants give us oxygen and take carbondioxide from us.
- they provide plenty of food to the man.
- plants stop the clouds and help in giving rains. Due to all the above reasons our teacher suggested us to think of destructing plants for research work.
Question 16.
Observe a plant which has healthy green leaves and beautiful flowers. Write your feeling about the plant in your notebook.
Answer:
- When we see a plant with lush green coloured leaves and beautiful flowers, we wonder at the glance of such plant.
- Naturally, we like to protect beautiful plantations.
- Our feelings make a plan to conserve the living organisms, to sustain the better nature inhalance.
- The beauty of the flowers makes us relax and its fragrance gives us aroma.
- The green colour of the leaves gives us good scenery and good visible colour. Green colour is quite healthy for eyes.
- We also feel to grow the plants having green colour and beautiful flowers in our surroundings.
TS 6th Class Science 9th Lesson Notes Plants: Parts and Functions
- The important parts of a plant are roots, stems and leaves.
- Tap root system and fibrous root system are two types of root systems seen in plants.
- Roots absorb water and minerals from the soil and also help in anchoring the plant body to the soil.
- The stem carries the water absorbed by the roots to different parts of the plant.
- Leaf base, petiole and lamina are all parts of a leaf.
- Tap root : In some plants, the main root becomes thick and has thin rootlets. This main root is known as ‘tap root’ and the rootlets are called lateral roots.
- Fibrous root : Hair like roots of the plants are called fibrous root.
- Leaf : Leaves are involved in preparing food. They also help in exchange of gases and transpiration.
- Petiole : The stalk of the leaf attached to stem.
- Lamina : The green expanded portion of leaf.
- Stomata : The bean shaped part that you see in the leaf acts like our nose. These are called ‘stomata’.
- Reticulate venation : Branched appearence of veins on the leaf.
- Parallel venation : Parallel appearence of veins on the leaf.