TS Board Telangana SCERT Class 6 Science Solutions 8th Lesson Fibre to Fabric Textbook Questions and Answers.
TS 6th Class Science 8th Lesson Questions and Answers Telangana – Fibre to Fabric
Question 1.
What will happen if a rain coat is made from cotton fabric? Why?
(OR)
Raincoat is made up of polythene sheet. Why is the raincoat not made by cotton threads?
Answer:
Cotton fibres absorb water. Drying of cotton fibres take longer hours. Polythene fibres can resist water and do not absorb water. Therefore rain coat is made up of polythene sheet.
![]()
Question 2.
Make a flow chart showing the process of getting a fabric (clothes) from cotton plant.
Answer:
Flow chart showing various stages from fibre to fabric.
![]()
Question 3.
Coconut is also a fibre. Name somethings made of coconut fibre.
Answer:
Door mats, sofa cushions, chair cushions, bus seats, ropes etc.
Question 4.
Classify the fabric of following items as natural or artificial – Dhothl, Venkatagirl sarees, jeans, umbrella cloth, bed-sheets, your shirt or skirt, rain – coat, gunny – bags.
Answer:
All of them are made from natural (plant or animal) fibres.
![]()
Question 5.
Explain the process of making yarn from cotton wool.
Answer:
- Cleaned cotton wool is drawn out and twisted. This brings the cotton wool fibres together to form yarn.
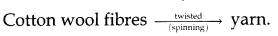
- The process of making yarn from cotton wool is called spinning.
- Spinning is done on a large scale with the help of spinning machines.
- After spinning, yarn is used for making fabric. It is called weaving.

Question 6.
Small strand-like structures are called
a. fabric
b. fibres
c. looms
d. cocoons.
Answer:
b. fibres
Question 7.
Making fabric from cotton yarn is called
Answer:
weaving
![]()
Question 8.
What would you do to remove wrinkles from your shirt or skirt?
Answer:
The shirt or skirt is ironed to remove wrinkles.
(Note : The clothes are pressed with heated iron.)
Question 9.
Prepare a bag using cloth. Collect pieces of fabric and make designs on your bag by using them. Display it on school display day.
Answer:
Students’ activity.
Question 10.
Make a scrap book containing pictures of different types of fabric and name them.
Answer:
Question 11.
With the help of an atlas, discuss with your teacher and prepare an information chart about spinning mills in our state.
Answer:
There are many spinning mills in our state like Guntur, Yedlapadu, Martur,
Mangalagiri, Chirala, Ganguru, Prathipadu, Rarnagiri, Madanapalli etc.
![]()
Question 12.
Collect news items about handloom workers and cotton growers. Analyse one news item in your own way.
Answer:
Handloom workers – the life is miserable
March 16- Pochampalli : Hand loom workers in the state are facing lot of burdens. Since they are accustomed only to handloorn industry, they are not able to find any other suitable livelihood to feed the family. Middlemen make selfish business by cheating the labourers at work places.
Handloom workers spend their whole time at the work. But getting wages is very less. It is not enough to fulfill the family needs. Interestingly, retail business men also see profit as middlemen bring lot of work through unauthorised marketing.
The Umnin of handloom workers urged the government to take necessary action in favour of hiking their daily wages. They also insisted to see transparent business which brings at least sharing in the profit from the handloom industry owners.
Time should help the cotton growers:
April 17 – Gadwal : Cotton growers have had bitter experiences due to unfavourahie weather conditions and lack of support from the government. Middle men and some brokers cheat the farmers by not giving the profitable price for the harvested cotton. Unfair activities to earn the money becomes main motto of raw material buyers.
They huy the harvested crop at low cost, hut they sell it to the price which is two times more than the price paid to farmers. In this way the farmers are cheated. Many times, farmers requested the government to help them.
![]()
Analysis on the report: If handloom department encourages the workers they will renew their life. Middle men dealing should he abolished which will bring the profit up in favour of labourers. Government should help the workers by providing facilities such as free education to the children, free health insurance scheme etc.
Government should take authentic steps to do business by the workers through which they rejuvenate their livelihood. The handloom weaving is an old tradition. The tradition and techniques used by weavers produce finest quality textiles which machine made textiles can not give. Yet, the handloom sector is facing a lot of problems. The government efforts to restructure handlooms are to be appreciated.
Question 13.
While purchasing your dress what doubts would you want to clarify from the shopkeeper?
Answer:
The doubts to be clarified are:
- Type of cloth …………. cotton or synthetic
- Durability of cloth.
- Method of washing : ordinar or dry-wash.
- Guarantee of colour and brightness.
- Whether suitable to wear in all seasons or not.
- Shrinking of the cloth.
Question 14.
What do you do to know when artificial fibres give pungent smell while burning? Write the steps of your experiment.
Answer:
Expt :
- Pull out six to eight yarns from the fabric.
- Hold one end of the yarn with a tongs and bring the other end over the flame of a candle. Observe carefully.
Result : The artificial yarns shrink and burn. They also melt and give out an odour similar to burning plastics (a pungent smell).
![]()
Question 15.
The clothes that we wear have a great background. Track the stages (from seed to dress) and write your feelings about the people working at different levels of the track.
Answer:
Cotton seeds → treatment of seeds → Sowing → cultivation → plants grow protection from natural calamities, insects and pests → cotton boils → hand picking → ginning spinning weaving fabric cloth stores → stitching → final dress.
People working at different levels have one common wish: A good return for their input and hard work.
Question 16.
Observe these logos.

What does this mean ? Collect information from your school library.
Answer:
1. A logo is a symbol that represents an organisation. Tsco is the abbreviation of Telangana State Hand loom Weavers Cooperative Society Limited.
2. Flower: It represents naturality, beauty, freshness, smoothness, attracting colours and other such desirable virtues. The “Tsco” logo means, that the fabric sold by this organisation has all such desirable qualities represented by the flower in their logo.
![]()
3. Butterfly: It represents dynamism, variety of colours, beauty, smoothness, freshness, naturality and other such desirable qualities. The “Co-optex” logo means that the fabric they sell carries all such virtues. cloth stores → stitching → final dress.
TS 6th Class Science 8th Lesson Notes Fibre to Fabric
- The fibres are obtained from natural as well as artificial (synthetic) sources.
- Natural fibres are obtained from cotton, jute, wool and silk.
- Fibres made up of chemicals are called artificial or synthetic fibres.
- Polyester, terylene, nylon, acrylic etc. are made up of art facial fibres.
- Tiny strands-like structures are called fibres.
- Fibres are converted into yarn.
- Yarns are woven together to make a fabric.
- cotton is obtained from cotton fruits or cotton boils. (Note: Cotton balls wrong,)
- lute fibre (‘also called, golden fibre) is obtained from the stem of jute plant (called sun hemp)
- The process of arranging two sets of yarns together horizontally and vertically to make a fabric is called weaving.
- Fabrics : It is a cloth or other material produced by weaving together cotton, nylon, silk or other threads.
- Fibres : Tiny strands like structures are called fibres.
- Yarn : Fibres are converted into yarn. Yarns are woven together to make a fabric.
Fibre → yarn → fabric - Natural Fibres : The fibres which are derived from plants and animals are called natural fibres.
Eg: cotton, wool, silk, jute etc. - Artificial fibres : Fibres made up of chemicals are called artificial or synthetic fibres.Eg: nylon, polyester etc.
![]()
- Ginning : The process of separating cotton wool from seeds is called ginning.
- Spinning : The process of making yarn from fibres is called spinning.
- Weaving : Two sets of yarns arranged together to make a fabric called weaving.
- Looms : Weaving is done on looms. The looms that are worked by man power are called handlooms, run by machines are called powerlooms.