AP State Syllabus AP Board 7th Class Maths Solutions Chapter 13 Area and Perimeter Ex 3 Textbook Questions and Answers.
AP State Syllabus 7th Class Maths Solutions 13th Lesson Area and Perimeter Exercise 3
![]()
Question 1.
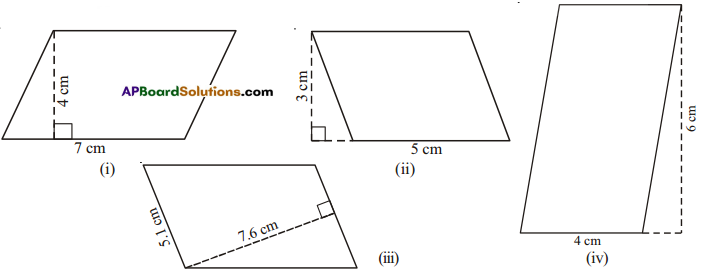
Find the area of each of the following triangles.
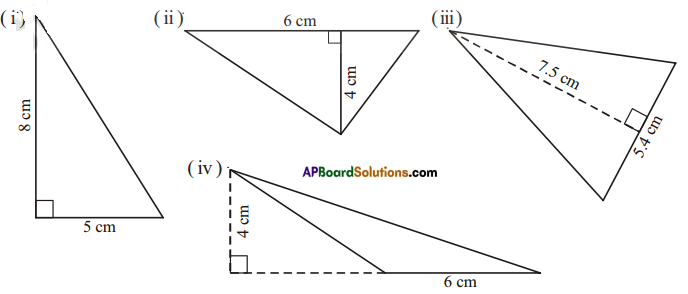
Solution:
î) Area = \(\frac{1}{2}\) = \(\frac{1}{2}\) x 5 x 8 = 20 cm2
ii) Area = \(\frac{1}{2}\) = \(\frac{1}{2}\) x 6 x 4 = 12 cm2
iii) Area = \(\frac{1}{2}\) = \(\frac{1}{2}\) x 5.4 x 7.5 = 20.25 cm2
iv)Area = \(\frac{1}{2}\) = \(\frac{1}{2}\) x 6 x 4 = 12 cm2
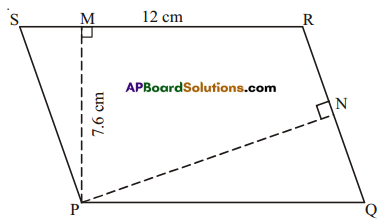
Question 2.
In ΔPQR, PQ = 4 cm, PR =8 cm and RT = 6cm. Find (i) the area of ΔPQR (ii) the length of QS.
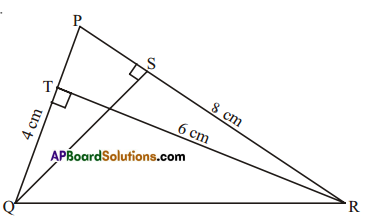
Solution:
Given PQ 4cm, PR = 8cm, RT = 6cm
1) Area of ΔPQR = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) × base × height = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) × PQ × RT
= \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) × 4 × 6 = 12cm2
ii) Also area of ΔPQR = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) × base x height = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) × PR × QS
12 = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) × 8 × QS
QR = \(\frac{12 \times 2}{8}\) = 3cm
![]()
Question 3.
ΔABC is right-angled at A. AD is perpendicular to BC, AB =5 cm, BC = 13 cm and AC = 12 cm. Find the area of ΔABC. Also, find the length of AD.
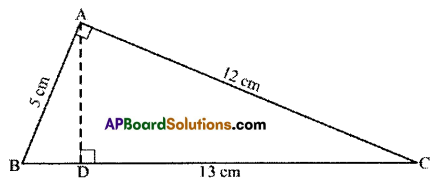
Solution:
Given.
In ΔABC, ∠A = 90°
AB = 5cm; AC = 12cm; AD ⊥ BC; BC = 13cm.
Now area of ΔABC = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) × base × height
= \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) x AB x AC = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) × 5 × 12 = 30cm2
Also area of MBC = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) × BC × AD
30 = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) × 13 × AD
∴ \(\frac{30 \times 2}{13}=\frac{60}{13}=4 \frac{8}{13}\) cm
![]()
Question 4.
ΔPQR is isosceles with PQ = PR = 7.5 cm and QR = 9 cm. The height PS from P to QR, is 6 cm. Find the area of ΔPQR. What will be the height from R to PQ i.e. RT?
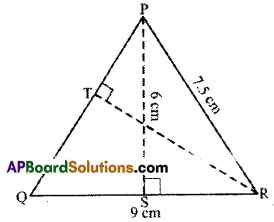
Solution:
Given: PQ = PR = 7.5cm, QR = 9cm PS = 6cm
Area of ΔPQR = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) bh = latex]\frac { 1 }{ 2 }[/latex] x 9 x 6 = 27cm2
Also area of ΔPQR = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) × PQ × RT
27 = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) × 7.5 × RT [PQ = PR]
∴ RT = \(\frac{2 \times 27}{7.5}=\frac{2 \times 27 \times 2}{15}=\frac{36}{5}\) = 7.2 cm
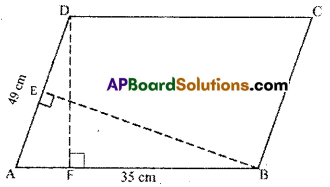
Question 5.
ABCD rectangle with AB =8 cm, BC = 16 cm and AE = 4 cm. Find the area of ABCE. Is the area of ΔBEC equal to the sum of the area of ΔBAE and ΔCDE. Why?
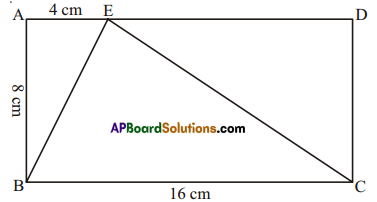
Solution:
Given : In rectangle ABCD,
AB = 8cm, BC = 16 cm, AE = 4cm
Now Area of ΔBAE = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) x base x height
= \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) × \(\overline{\mathrm{BC}} \times \overline{\mathrm{AB}}\)
= \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) × 16 x 8 = 64cm2
Area of ΔCDE = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) x base x height
= \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) × \(\overline{\mathrm{ED}} \times \overline{\mathrm{DC}}\)
= \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) × 12 × 8 = 48cm2
(∵ \(\overline{\mathrm{ED}}\) = AD – AE = 16 – 4 = 12cm and \(\overline{\mathrm{DC}}=\overline{\mathrm{AB}}\))
Now ΔBAE + ΔCDE = 16 + 48 = 64 = ΔBCE.
Question 6.
Ramu says that the area of ΔPQR is, A = \(\frac{1}{2}\) × 7 × 5 cm2.
Gopi says that it is, A = \(\frac{1}{2}\) × 8 × 5 cm2. Who is correct’? Why?
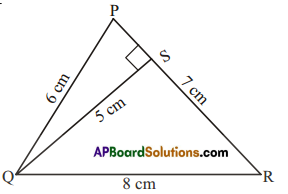
Solution:
Ramu is correct.
Since area of a triangle = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) × base × corresponding height
= \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) × 7 × 5cm2
But height 5cm is not corresponding to side &m.
∴ Gopi is not correct.
![]()
Question 7.
Find the base of a triangle whose area is 220 cm2 and height is 11cm.
Solution:
Given Area = 220 cm2, h = 11 cm
Area of a triangle = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\)b.h
= \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) × b × 11 = 220cm2 (given)
b × 11 = 220 × 2
b = \(\frac{220 \times 2}{11}\) = 40
∴ base of the triangle = 40 cm.
Question 8.
In a triangle the height is double the base and the area is 400 cm2. Find the length of the base and height.
Solution:
Area = 400 cm2
Let the base of the triangle be x.
height = 2x
Area of the triangle = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\)b.h
\(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) × x × 2x = 400 (given)
x2 = 400
x = \(\sqrt{400}\) = 20
∴ base of the triangle = 20 cm
height = 2(base)= 2(20) = 40 cm.
![]()
Question 9.
The area of triangle is equal to the area of a rectangle whose length and breadth are 20 cm and 15 cm respectively. Calculate the height of the triangle if its base measures 30 cm.
Solution:
Given :Length of the rectangle = 20 cm
Breadth of the rectangle = 15 cm
Base of the triangle = 30 cm
Area of the rectangle = Area of the triangle
Length x breadth = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) × base × height
20 × 15 = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) × 30 × height
∴ height = \(\frac{20 \times 15}{15}\) = 20cm
![]()
Question 10.
In Figure ABCD find the area of the shaded region.
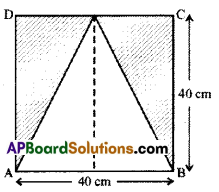
Solution:
Given : Side of the square ABCD = 40cm
Area of the shaded rgion = (Area of the square) — (Area of the unshaded region)
= (side × side) – \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) × base × height
= 40 × 40 – \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) × 40 × 40
= 1600 – 800 = 800cm2
Question 11.
In Figure ABCD, find the area of the shaded region.

Solution:
Given: Side of the square = 20 cm
Area of the shade region
= (Area of the square) – (Area of unshaded region)
= (Square ABCD) – (ΔEAF + ΔFBC + ΔEDC)
= side × side – (\(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\)AF × AE + \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) FB × BC + \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) DE × DC)
= 20 × 20 – (\(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) × 10 × 12 + \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) × 10 × 20 + \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) × 8 × 20)
= 400 – [60 + 100 + 80] = 400 – 240 = 160cm2
![]()
Question 12.
Find the area of a parallelogram PQRS, if PR =24 cm and QU = ST =8 cm.
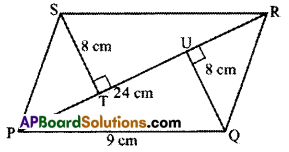
Solution:
Given : In PQRS, PR = 24cm, ST = 8cm, QU =8cm
Area of ![]() PQRS = ΔPQR + ΔPRS
PQRS = ΔPQR + ΔPRS
= \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) × \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\)base x height + x base x height
= \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) × 24 x 8 + \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) × 24 × 8 = 96 + 96 = 192 cm2
![]()
Question 13.
The base and height of the triangle are in the ratio 3:2 and its area is 108 cm2. Find its base
and height.
Solution:
Given : Area = 108 cm2
Let the base of the triangle be 3x and height of the triangle be 2x.
Area of the triangle = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) × base × height = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) x (3x) (2x) = 108 cm2 (given)
3x2 = 108
x2 = 108/3 = 36
x = \(\sqrt{36}\) = 6
∴ base 3x = 3(6) = 18 cm
height = 2x = 2(6) = 12cm